Visual Fields and Eye Diagnostics
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
retina, optic, chiasm, opposite, tracts, geniculate, radiation, cortex
Visual field pathway
Light rays striking the ______ generate potentials in the photoreceptors which are sent to the _____ nerve
Impulses pass through the optic nerve and go to the optic ______
Inner nasal halves cross to the ________ side where they join fibers from the outer temporal halves
Optic chiasm then progresses to the Optic ______
Fibers of the optic tracts synapse in the dorsal lateral _________ nucleus of the thalamus
Optic tracts progress to the Optic ________
Optic radiation progresses to the primary visual ______ in the occipital lobe
Hemianopia
Defect in half of a visual field
Homonymous
Defect is on the same side of visual field
Heteronymous
Defect is on the opposite sides of visual field
blindness
1 - Complete lesion of Optic nerve will cause _________
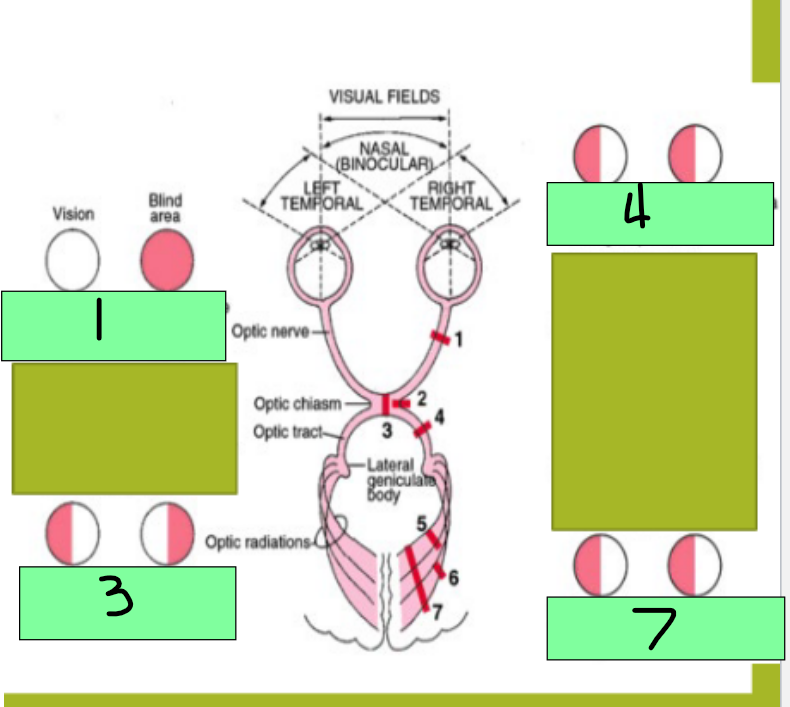
Bitemporal heteronymous hemianopia
3 - lesion of the optic chiasm will cause what visual pathway dysfunction?
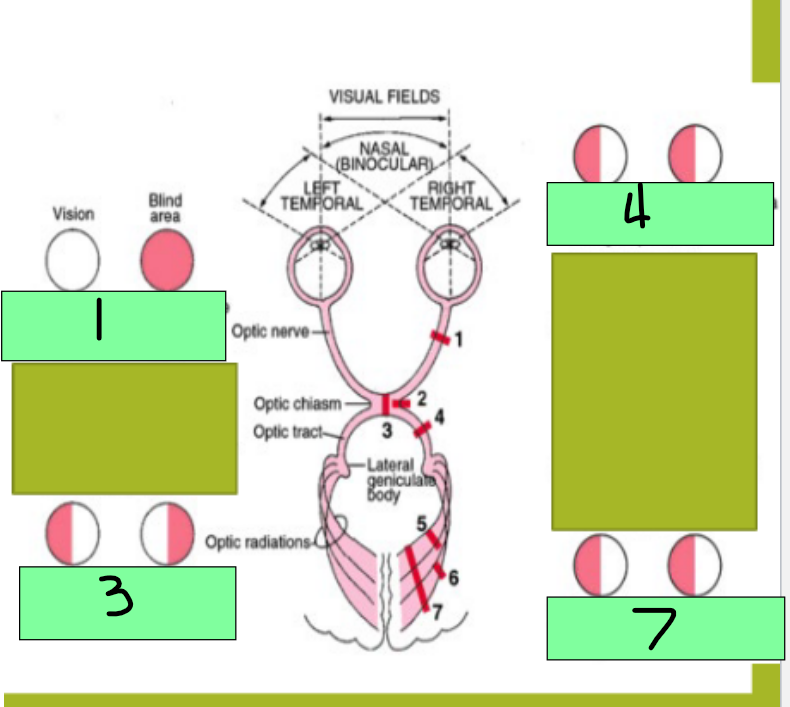
Homonymous hemianopia
4 - Destruction of one optic tract causes which visual pathway dysfunction?
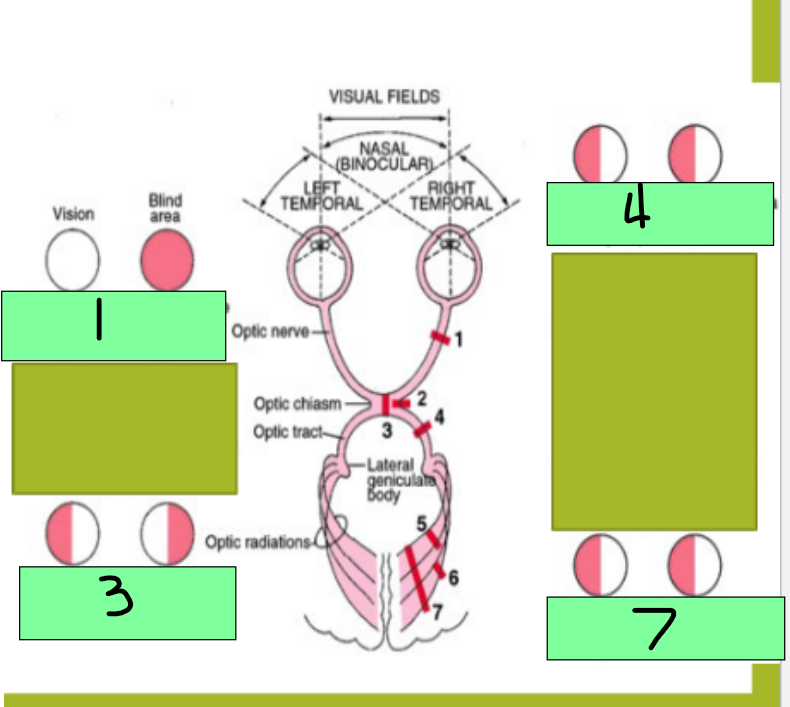
homonymous defect
7 - Optic radiation gets damaged; this is an ocular pathway in the internal capsule, temporal lobe, or occipital lobe and destruction causes this
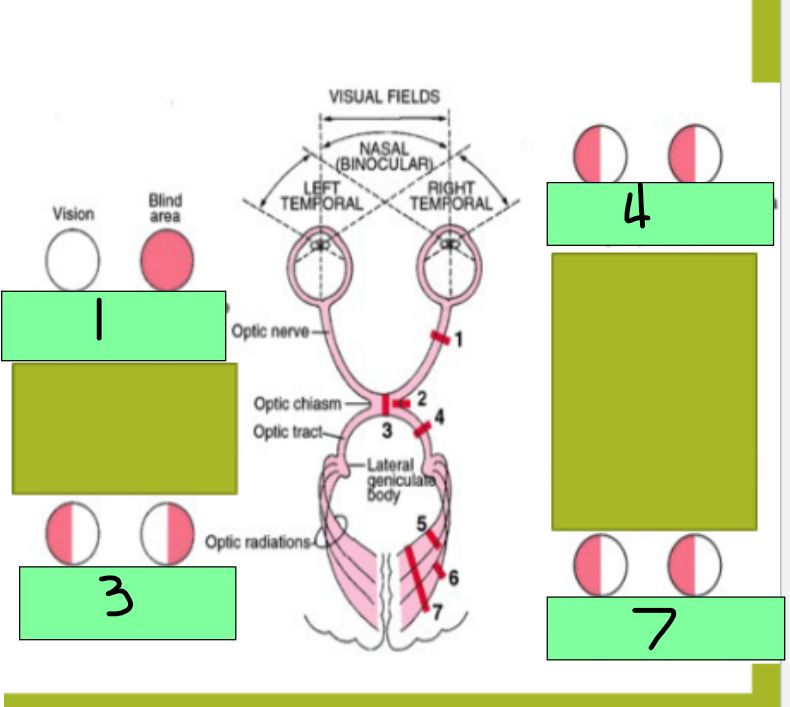
Monocular blindness
Site of lesion: optic nerve
Description of visual field defect: blindness in the affected eye
Bitemporal heteronymous hemianopia
Site of lesion - Optic chiasm
Description of visual field defect: loss of fibers crossing the midline from the nasal half of each retina causes loss of temporal visual field on both sides
homonymous hemianopia
Site of lesion: optic tract
Description of visual field defect: loss of fibers for the visual field on the opposite side to the lesion
Homonymous hemianopia
Site of lesion: optic radiation
Description of visual field defect: loss of fibers for the visual field on the opposite side to the lesion
Homonymous hemianopia with macular sparing
site of lesion: visual cortex (one side)
Description of visual field defect: loss of visual processing for the visual filed on the opposite side of the lesion
Refractory, focal, accommodation, convergence
Vision
Structures in the eye bends light rays (_________ media)
Lens, cornea, and humors
Light rays converge on the retina at a single _____ point
_____________
Curvature of the lens is adjustable
allows for focusing on nearby objects
___________
Active process of turning the eyes inward to maintain alignment of the visual axes with an object
Myopia
Nearsightedness
Globe is too long
Near vision is clear, Distant vision is blurry
Corrected by concave lens
Hyperopia
Farsightedness
Globe is too short
Near vision is blurry, distant vision is clear
Corrected by convex lens
Presbyopia
Lens is unable to increase its refractive power
Can’t accommodate on near objects
Age-related vision problems, why older people need reading glasses
Astigmatism
Unequal curvature of the cornea
images are distorted
Legal Blindness
Best corrected acuity of 20/200 or less in the better eye
Binocular visual field of 20 degrees or less
Flame hemorrhages
represent bleeding from the inner capillary network of the retina
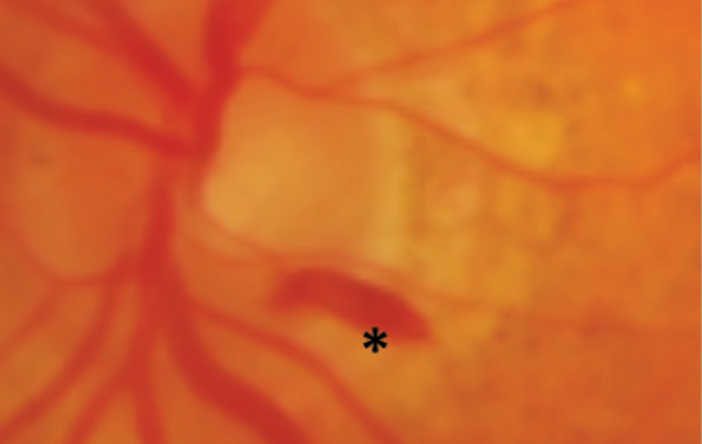
Dot hemorrhages
small, round, superficial hemorrhages that originate from the superficial capillary network of the retina
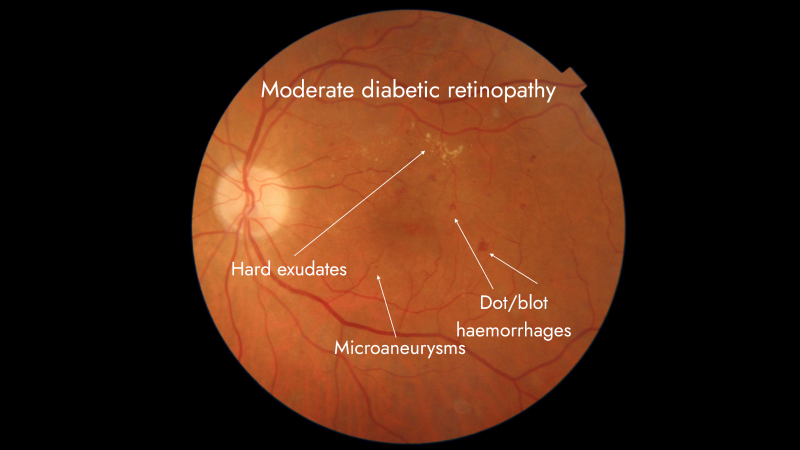
Hard exudates
Well circumscribed, shiny, yellow deposits located within the retina
Arise at areas of retinal edema and indicate increased capillary permeability
Contain lipoproteins and lipid laden macrophages
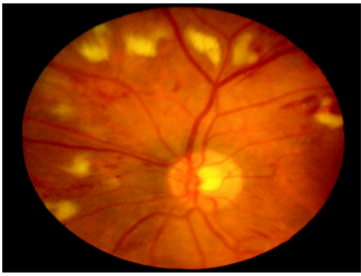
Cotton wool spots
Yellow/white superficial retinal lesions with indistinct feathery borders
Represent areas of edema within the retinal nerve fiber layer due to focal ischemia
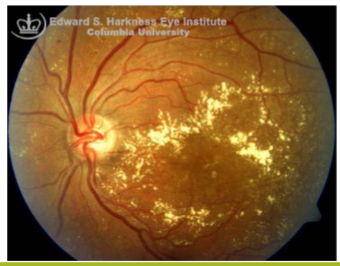
Retinal neovascularization
Irregular meshwork of fine blood vessels that grow in response to severe retinal ischemia or chronic inflammation
very fragile

Cherry red spot
At the macula
Associated with central retinal artery occlusion
surrounded by pallor
conjunctival, corneal, fluorescein, saline, conjunctiva, irregularity, blue, irregularity, altered, green
Fluorescein stain
Instillation of fluorescein into the ___________ sac to outline any irregularities of the _______ surface
Equipment
___________ papers or sterile individual dropper units
Technique
Wet fluorescein paper with sterile ______ > touch ___________ > fluorescein spreads over the corneal surface
Any ___________ in the cornea is stained by the fluorescein and is more easily visualized using a light with a ____ filter
Interpretation
If no superficial corneal __________, a uniform film of dye covers the cornea
If corneal surface has been _______, the affected area absorbs more of the dye and will stain a deeper _____
Slit lamp exam
Table mounted binocular microscope with adjustable illumination source
Linear beam of light is projected onto the globe, illuminating an optical cross section of the eye
The angle, width, length, intensity of the light beam, and magnification (10x-16x) can be adjusted
Three-dimensional view
anterior, conjunctival, tear, dilated, cells, turbidity, inflammation
Slip Lamp Exam
________ half of the globe can be visualized
Details of the lid margins and lashes, the palpebral and bulbar ____________ surfaces, the _____ film and cornea, the iris, and the aqueous can be seen
Through a _______ pupil, the lens and anterior vitreous can be seen
Highest magnification setting can show the abnormal presence of _____ within the aqueous (red or white blood cells, pigment granules)
Aqueous _________, called “flare” (increased protein concentration) due to ____________ can be detected
Ishihara, Hardy-Rand-Rittler, macula, red-green, color, hues
Ishihara/Hardy-Rand-Rittler plates
________ - detects red-green color deficiency
_____-____-_______ - detects red-green and blue-yellow color deficiency
Normal color vision requires healthy function of the ______ and optic nerve
Most common congenital abnormality is ___-_____ color deficiency
Acquired optic nerve and macular conditions can cause impaired _____ vision
Depict colored numbers or figures that stand out from a background of colored dots
____ make it difficult for a color deficient patient to distinguish
Tonometry
Determines Intraocular pressure
8-20 mm Hg
Normal IOP
glaucoma
If the IOP is greater than 20 mm Hg, further investigation is indicated for which disease?
Normal monocular visual field
160 degrees of horizontal plane and 135 degrees in the vertical plane
Normal binocular visual fields
exceeds 180 degrees in horizontal plane
Physiologic blind spot
5 degree blind spot in each eye, corresponding to the optic disc and located 15 degrees temporal in a fixed eye
Perimetry
patient fixates on a central target and test objects are randomly presented at different locations throughout the visual field. If objects seen, patient will respond
Visual field mapping
Reason
Assesses the combined function of the retina, the optic nerve, and the intracranial visual pathway
Used to detect or monitor field loss due to disease at any of these locations
separately, macular, straight, distortion, missing
Amsler Grid
Viewed by each eye __________ at normal reading distance and with reading glasses (if used)
Most commonly used to test _______ function
While fixating on the central dot, the patient checks to see that the lines are all _______, without __________, and that no spots or portions of the grid are _______
scotoma
blank area; either central or paracentral; can indicate disease of the macula or optic nerve
Metamorphopsia
Wavy distortion of the lines while looking at an amsler grid
can indicate macular edema or submacular fluid