Quiz 10: Love
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
You are awarded an NSF grant to conduct a PET study on love. You want to design your study to be as comparable to the fMRI research on romantic love (e.g., Aron et al., 2005) as possible, so you ask the participants to provide photos of their romantic partner and have them complete the … Scale.
a. compatibility b. positive and negative affect c. passionate love d. romantic partner
You image activity in the reward pathway while participants view photos of the romantic partner and unknown individuals. Which neurotransmitter are you most likely to track?
a. acetylcholine b. GABA c. dopamine d. norepinephrine
Which brain area is associated with the production of that neurotransmitter you are tracking in your PET study on romantic love and is activated in individuals when they see a photo of their beloved in all those fMRI studies?
a. FFA b. VTA c. PFC d. OFC
fMRI studies have found another subcortical region consistently activated for romantic love, so you also predict to see greater activity in the … in your PET data.
a. tectum b. cingulate c. thalamus d. caudate
In addition to the PET data, you decide to measure heart rate, skin conductance, and EMG. Which of the following hypotheses makes the most sense based on past research?
a. all physiological measures will be elevated when viewing photos of the beloved.
b. heart rate will be increased when viewing photos of loved ones, but others will not differ.
c. heart rate and skin conductance are increased when viewing loved ones, but no change in EMG.
d. all physiological measures will be decreased when viewing photos of their beloved.
You’ve still got grant money left! You decide to do a second study in which mothers view photos of their beloved (adult), their own child, and strangers (adults and children) during a PET scan. Which of the following predictions makes the most sense based on past research?
a. romantic and maternal love will be associated with similar neural regions.
b. romantic and maternal love will be associated with different neural regions.
c. romantic, but not maternal, love will be associated with reward.
d. maternal, but not romantic, love will be associated with reward.
Aliens come to Earth, and they want to know what love is. Explain to our new overlords whether you think love is an emotion, a goal-directed state, or both, and use a specific piece of evidence or reasoning from any of this week’s readings to support your position.
Love is a proposed emotional state involving chemical, hormonal, reward, and goal-directed components. I think this could suggest that it is more of a goal-directed state. Aron and Bartel’s studies discuss how love can be associated with negative emotions and feelings of comfort towards those you love which could support the idea that love is goal-directed because we tend to seek comfort and emotional relief through others to make ourselves feel better.
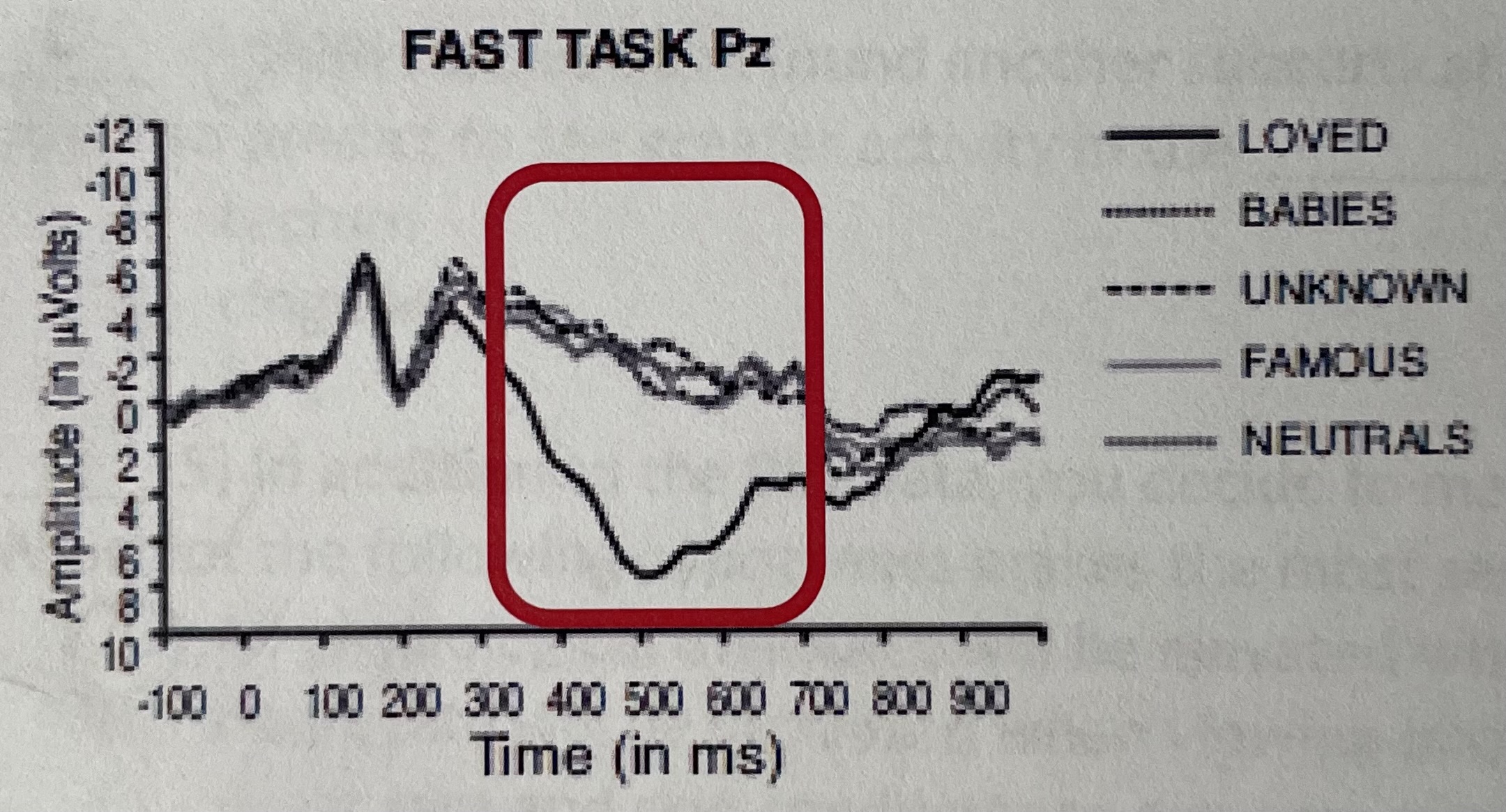
Identify the ERP component inside the red box.
P300
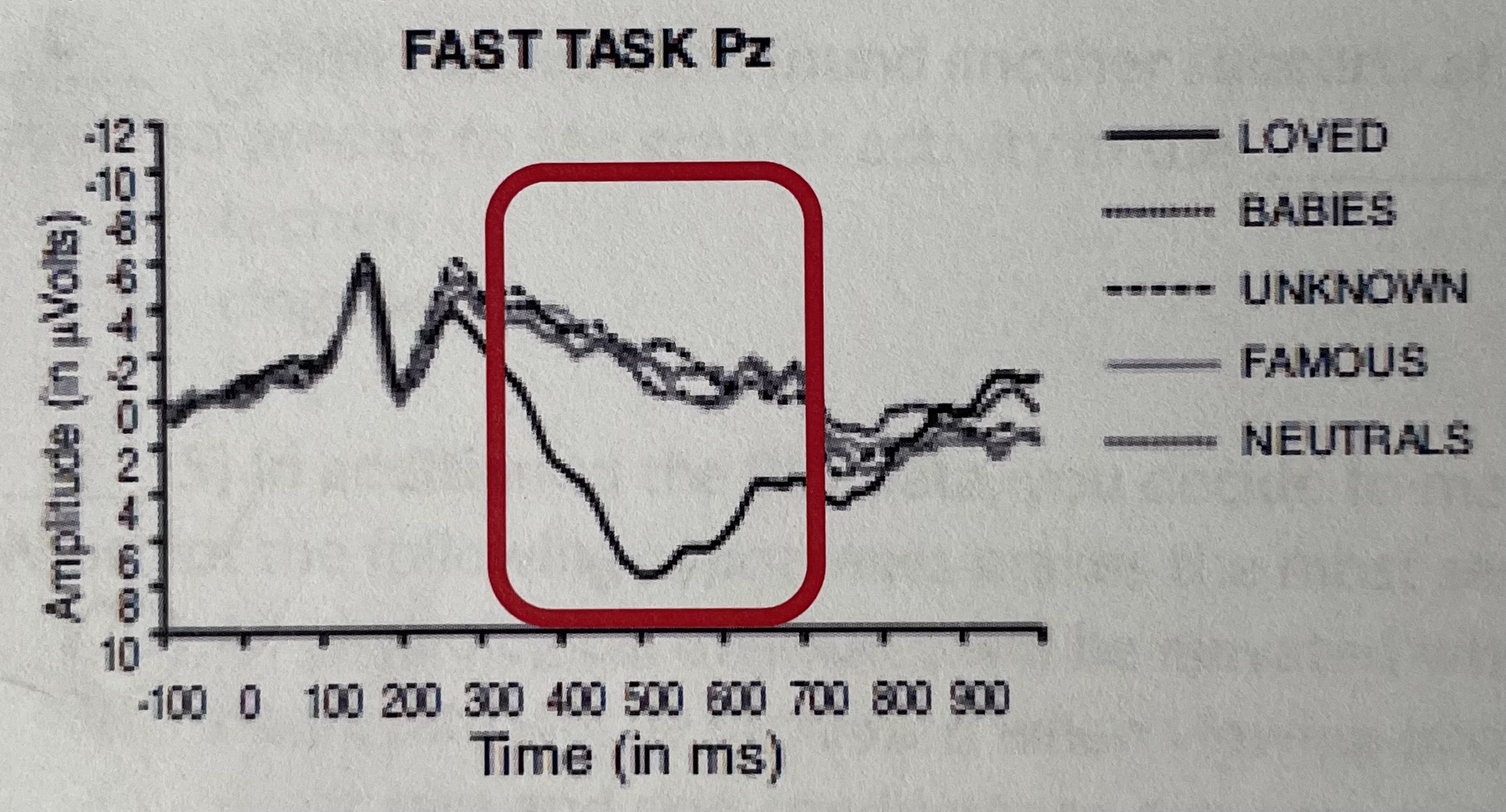
Which type of stimulus elicits the largest amplitude in this component?
Loved ones
In Bartels and Zeki (2004), the posterior cingulate cortex and prefrontal cortex were deactivated for maternal and romantic love, while the globus pallidus and ventral tegmental area were active for both types of love. What is their interpretation of this pattern of data?
They interpreted this pattern by saying that there are similar regions of the brain that are involved in both romantic and maternal love. They also thought that these similarities could be attributed to the fact that both types of love are involved in the survival of the species. Lastly, they interpreted this as a push-pull mechanism.