L19 - 22 Cerebrum External Configuration and Functional Localizations
1/231
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
232 Terms
What are sulci?
Grooves or shallow fissures on the cerebral surface.
What are gyri?
The raised ridges between sulci.
What is the purpose of sulci and gyri?
To increase cortical surface area for more neurons and higher processing capacity.
What does the lateral sulcus separate?
The temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes.
What is another name for the lateral sulcus?
Sylvian fissure.
What artery runs within the lateral sulcus?
The middle cerebral artery (MCA).
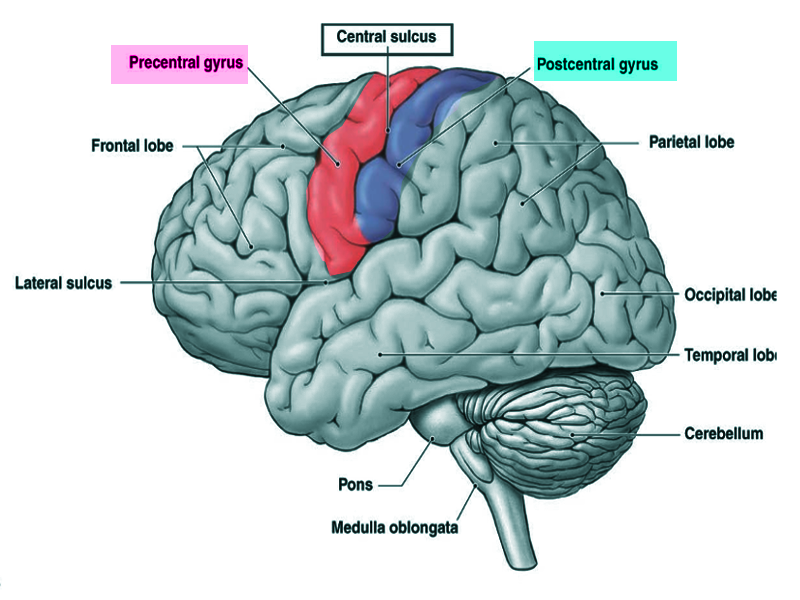
What does the central sulcus divide?
The frontal lobe from the parietal lobe.
What is located just anterior to the central sulcus?
The precentral gyrus (primary motor cortex).

What is located just posterior to the central sulcus?
The postcentral gyrus (primary sensory cortex).
What is the preoccipital notch?

A small indentation marking the anterior border of the occipital lobe.
What does the parieto-occipital sulcus separate and where is it best seen?
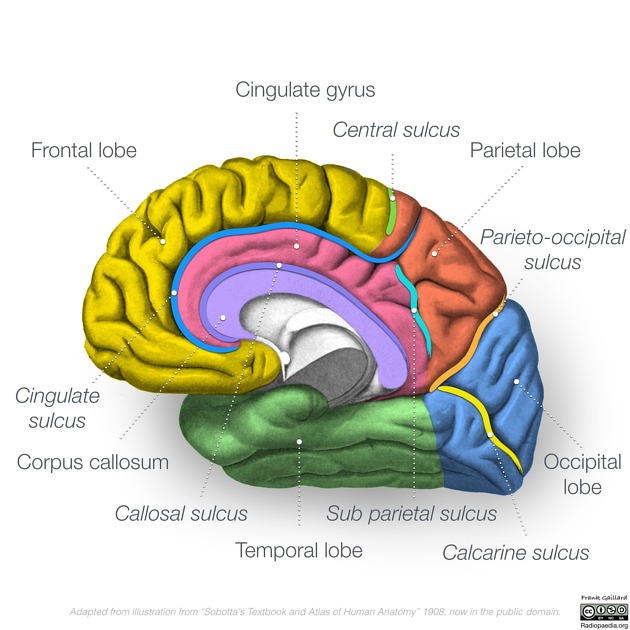
The parietal and occipital lobes. best seen on the medial surface of the hemisphere.
What is the preoccipital notch?
A small indentation marking the anterior border of the occipital lobe.

What is the precentral gyrus? what is the function?
The ridge containing the primary motor cortex.Controls voluntary movement.

Which areas are large in the motor homunculus?
Hands and face (fine motor control).
What is the postcentral gyrus? what is the function?
The ridge containing the primary somatosensory cortex. Processes touch, temperature, pain, and proprioception.

Which body regions have the largest sensory representation?
The hands and face.
What are the three main frontal gyri? what is the function?
Superior, middle, and inferior frontal gyri. Working memory and attention.

What is the superior frontal gyrus responsible for?
Working memory and attention.

What is the middle frontal gyrus responsible for?
Eye movements and decision-making.

What is the inferior frontal gyrus responsible for?
Speech production (Broca’s area).

What are the temporal gyri called?
Superior, middle, and inferior temporal gyri.

What is the superior temporal gyrus function?
Hearing and auditory processing.

What does the middle temporal gyrus do?
Memory and object recognition

What does the inferior temporal gyrus do?
Language comprehension.

What are the occipital gyri used for?
Visual processing.
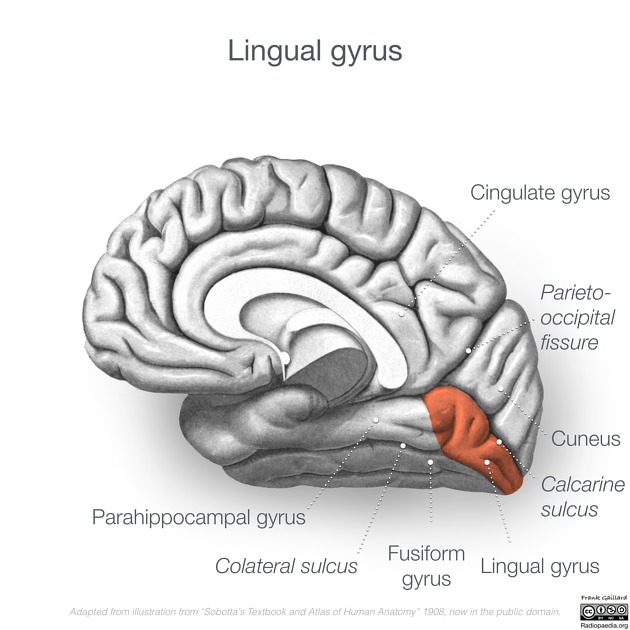
What does the lingual gyrus process?
Words and letters during reading.
Where is the insula located? What is the main function of the insula?
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10153/DMIAPl1Cx4EOfXKpNduhw_Insula_02.png)
Processes emotion, taste, and visceral sensations.
What is the hidden fifth lobe called?
The insula.
What does the frontal lobe control?
Motor control, speech, and executive functions.

What does the parietal lobe control?
Somatosensory input and spatial awareness.

What does the temporal lobe control?
Hearing, language, and memory.

What does the occipital lobe control?
Vision.

What does the insula control?
Emotion, taste, and internal body awareness.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10153/DMIAPl1Cx4EOfXKpNduhw_Insula_02.png)
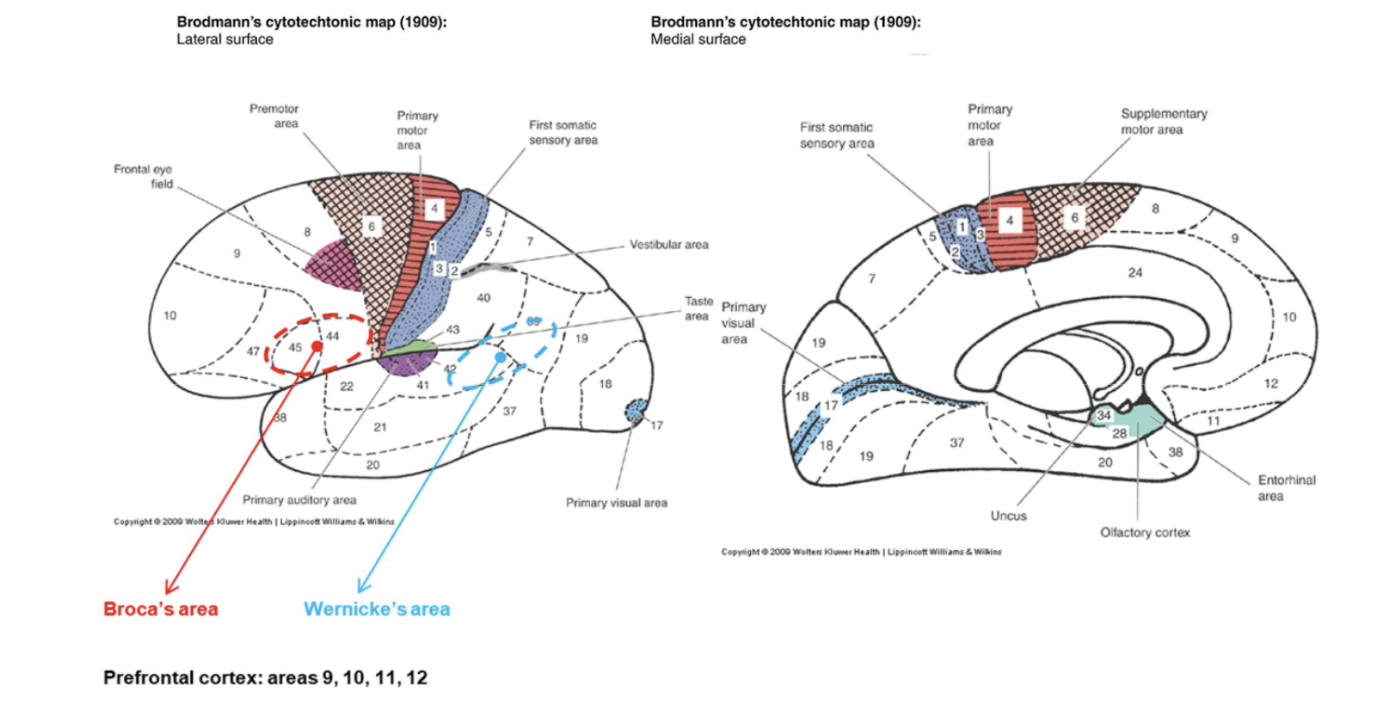
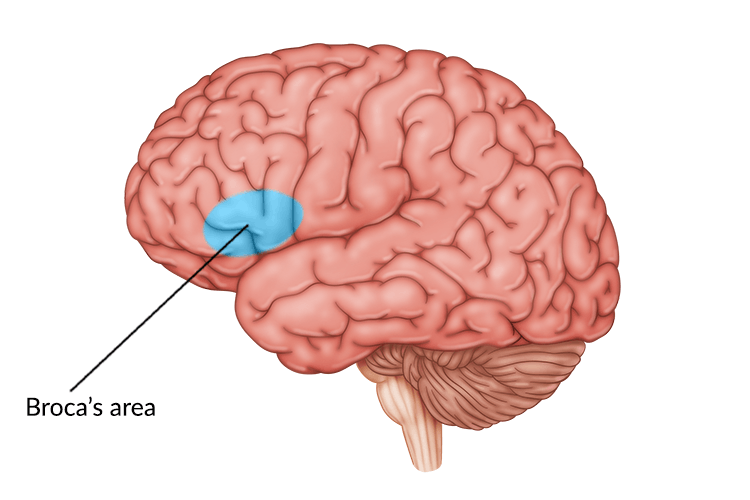
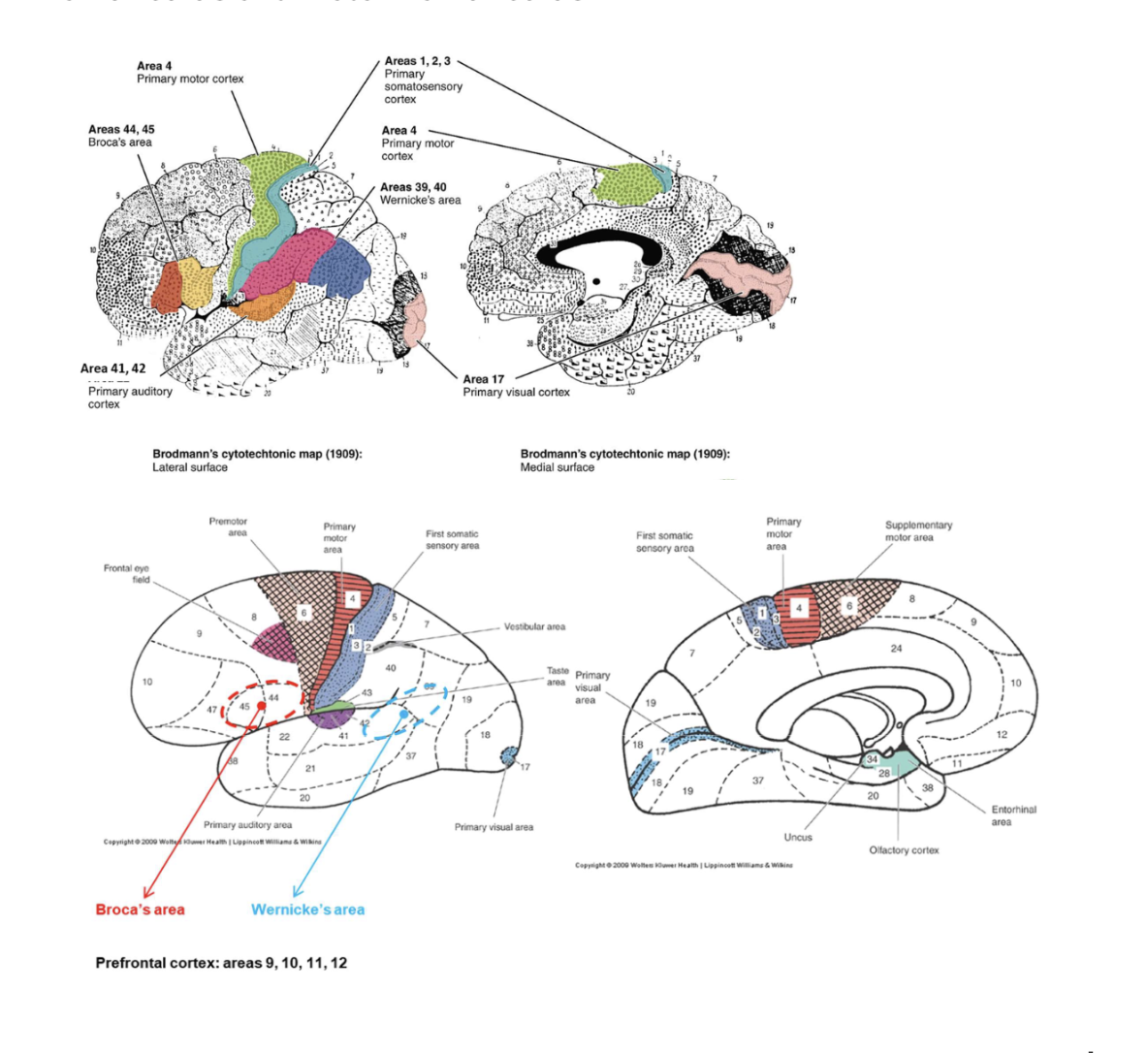
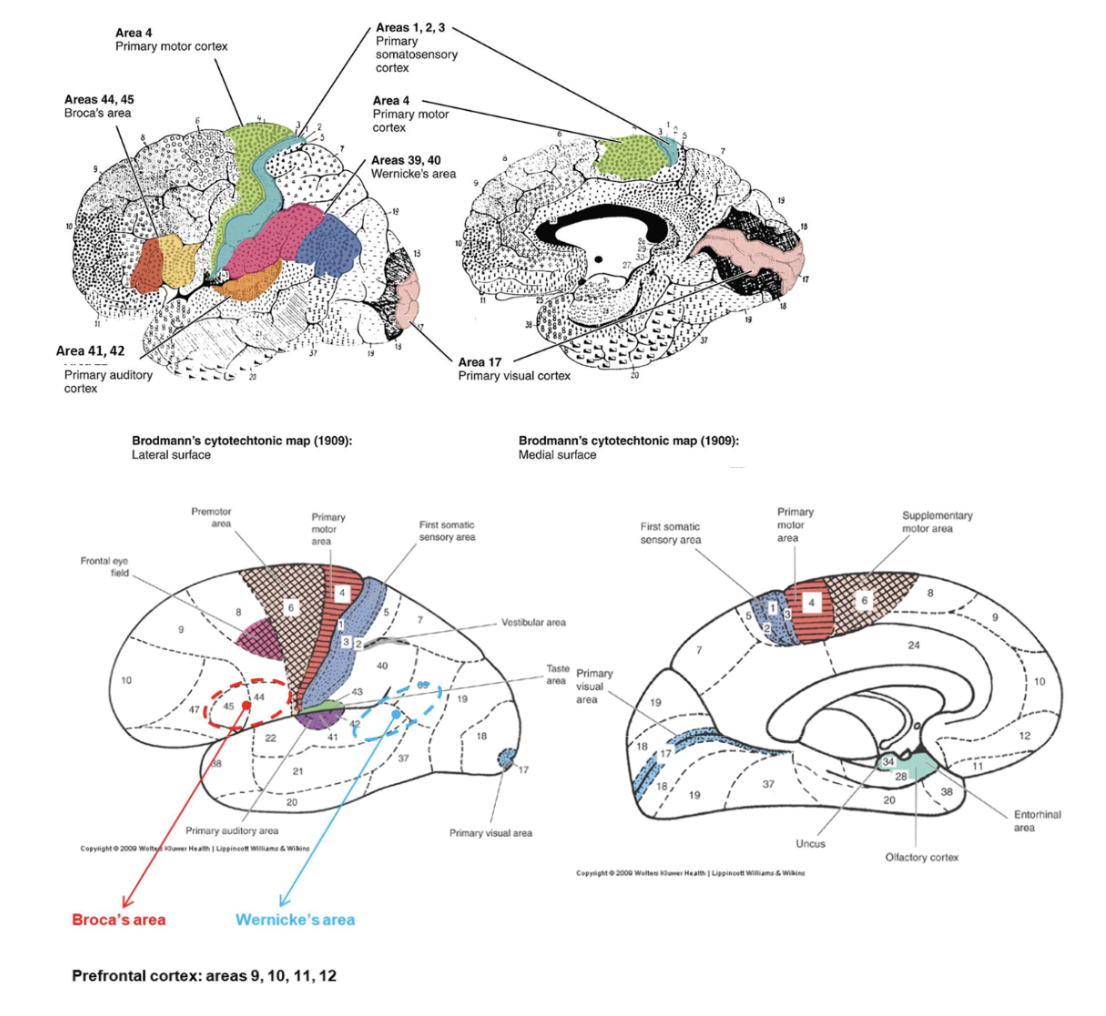
What is Broca’s area responsible for?
Speech production and articulation.
Where is Broca’s area located?
In the inferior frontal gyrus of the dominant hemisphere (usually left).
What is the frontal eye field? where isit found?
A region controlling voluntary eye movements. In the middle frontal gyrus.
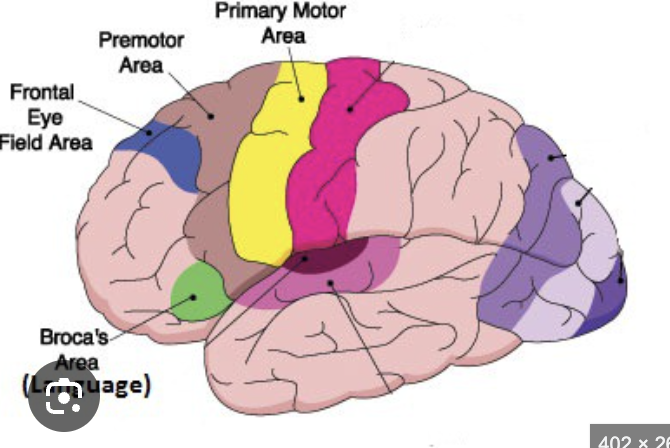
What does the prefrontal cortex do?
Handles planning, reasoning, judgment, and emotion

What is found in the postcentral gyrus?
The primary somatosensory cortex.

What does the primary somatosensory cortex do?
Receives sensory input from the contralateral side of the body.
What are the supramarginal and angular gyri for?
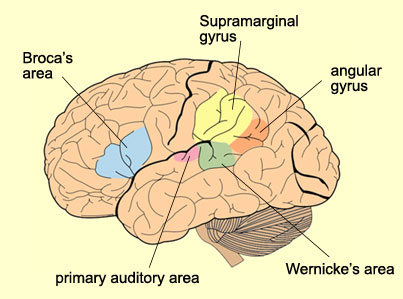
Language comprehension and spatial attention.
What are the superior and inferior parietal lobules for?
Sensory integration and body orientation.
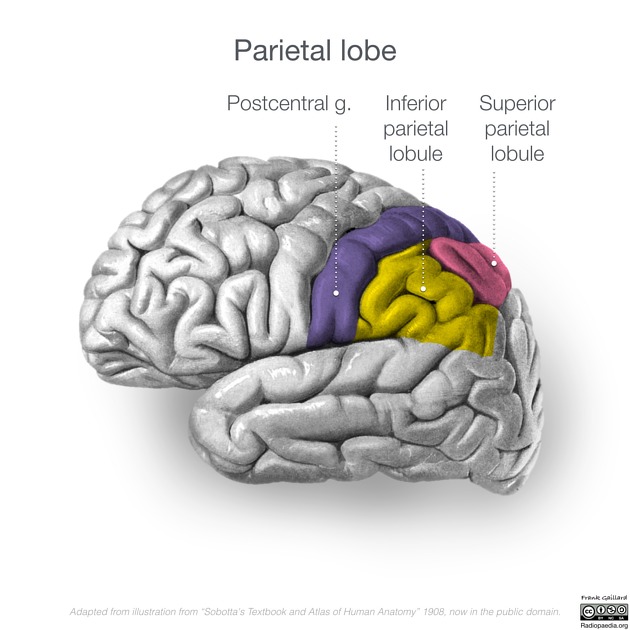
What is located in the superior temporal gyrus? what is the function?
The primary auditory cortex processes sound information from both ears

What is Wernicke’s area? Where is Wernicke’s area located?
The language comprehension center. In the posterior superior temporal gyrus of the dominant hemisphere.

What does the hippocampus do? Where is it?
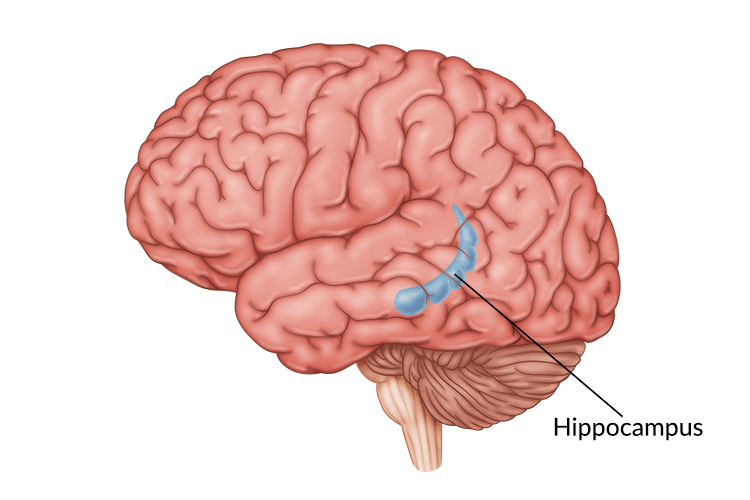
Forms and retrieves long-term memories. found deep inside the temporal lobe shaped like a seahorse
What is the primary visual cortex?
The area that receives and processes visual input. found around the calarine sulcus
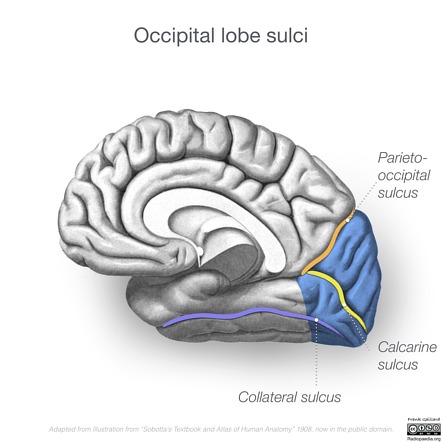
What does the lingual gyrus specialize in?
Reading and recognition of written words.
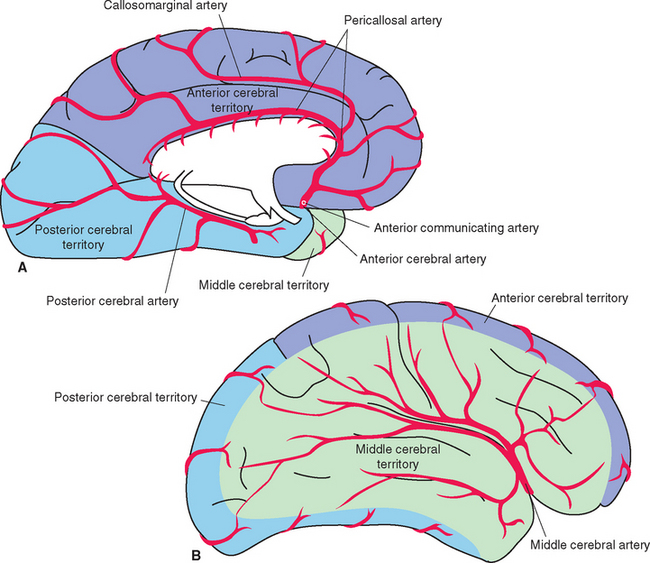
What are the three main arteries that supply the cerebrum?
Middle cerebral artery (MCA), anterior cerebral artery (ACA), and posterior cerebral artery (PCA).
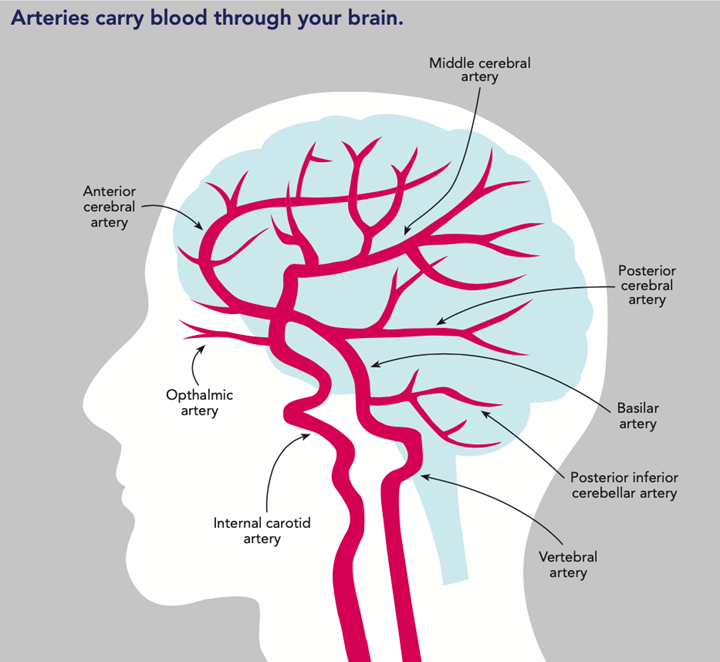
ACA and MCA are from internal carotid
PCA is from basilar artery
What area does the MCA supply?
The lateral surface of the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes.
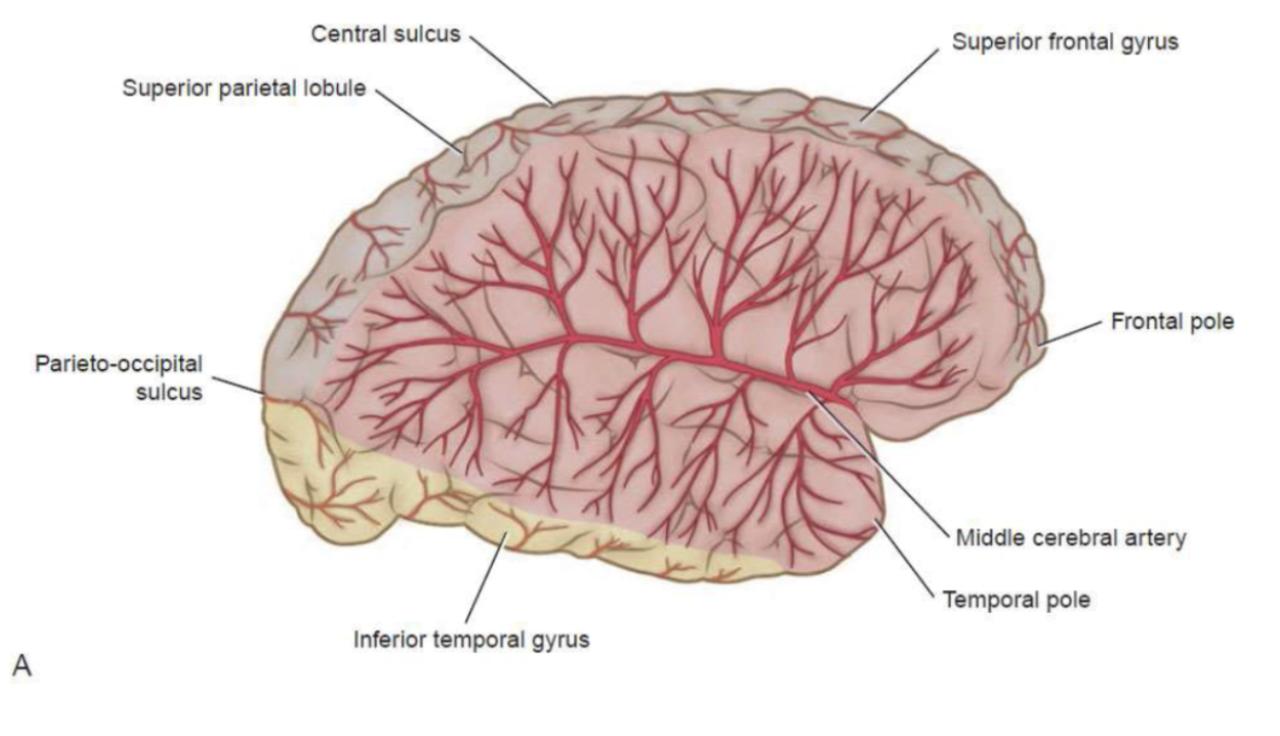
What functions depend on MCA circulation?
Motor and sensory control of the face and arm, and language areas.
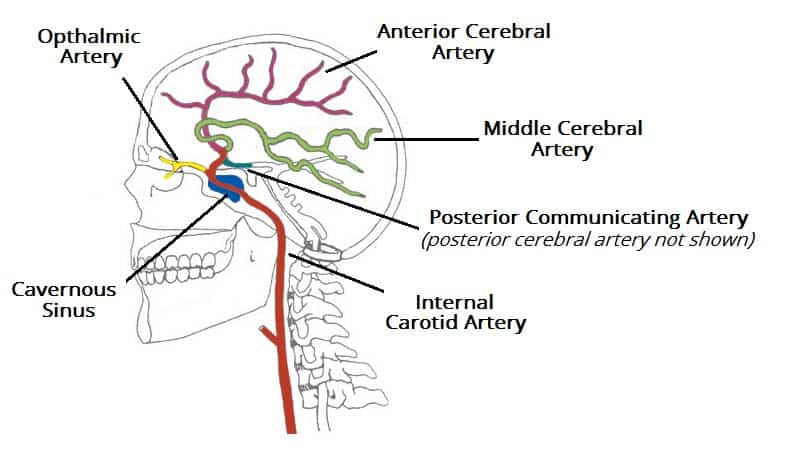
What area does the ACA supply?
The medial surface of the frontal and parietal lobes.

What function depends on ACA supply?
Motor and sensory control of the lower limb.

What area does the PCA supply?
The occipital lobe and inferior temporal lobe.

What function depends on PCA supply?
Vision.
What do the superior cerebral veins drain?
The lateral cerebral surface.
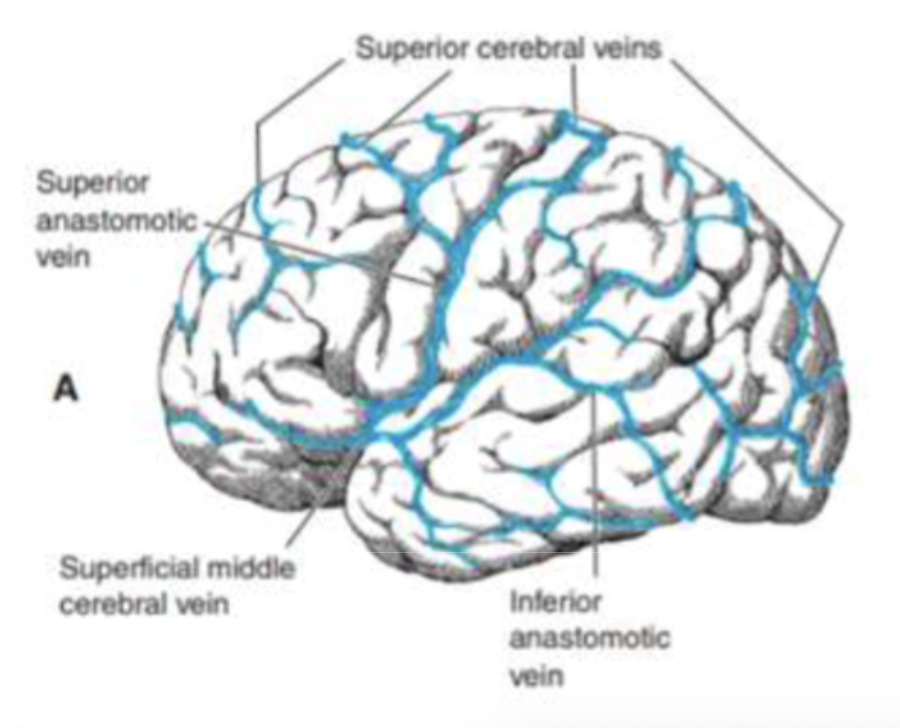
Where do the superior cerebral veins empty?
Into the superior sagittal sinus.
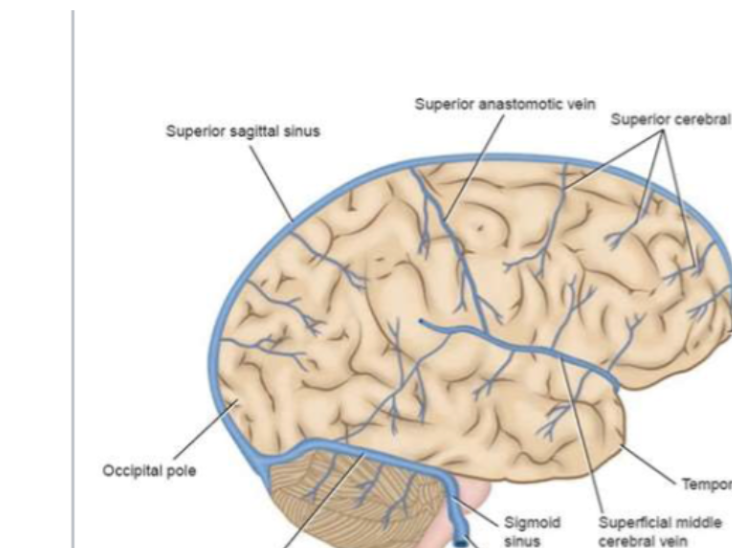
What does the middle cerebral vein drain?
The lateral aspect of the cerebrum.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/vena-media-superficialis-cerebri/0AbO55IEyCtoA3DvS2qiJA_Superficial_middle_cerebral_vein_01.png)
Where does the middle cerebral vein empty?
Into the cavernous sinus.
What does the deep middle cerebral vein drain?
Deep brain structures like the basal ganglia and internal capsule.
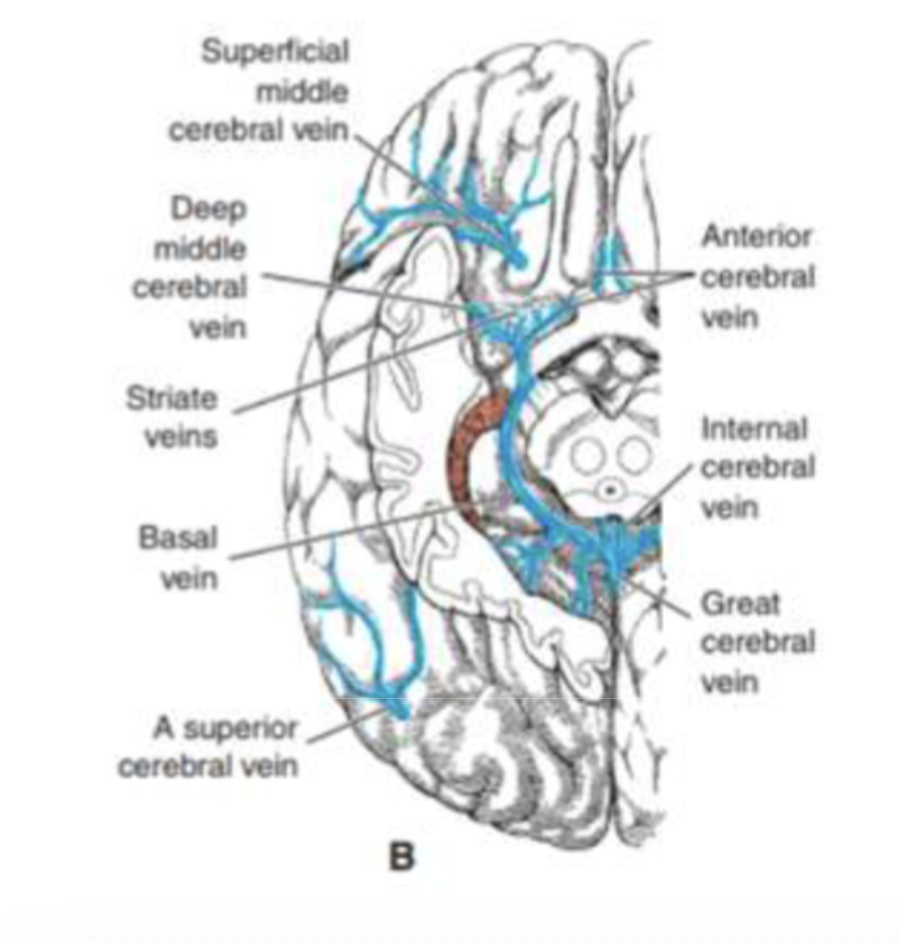
What does the anterior cerebral vein drain?
The medial surface of the cerebrum.
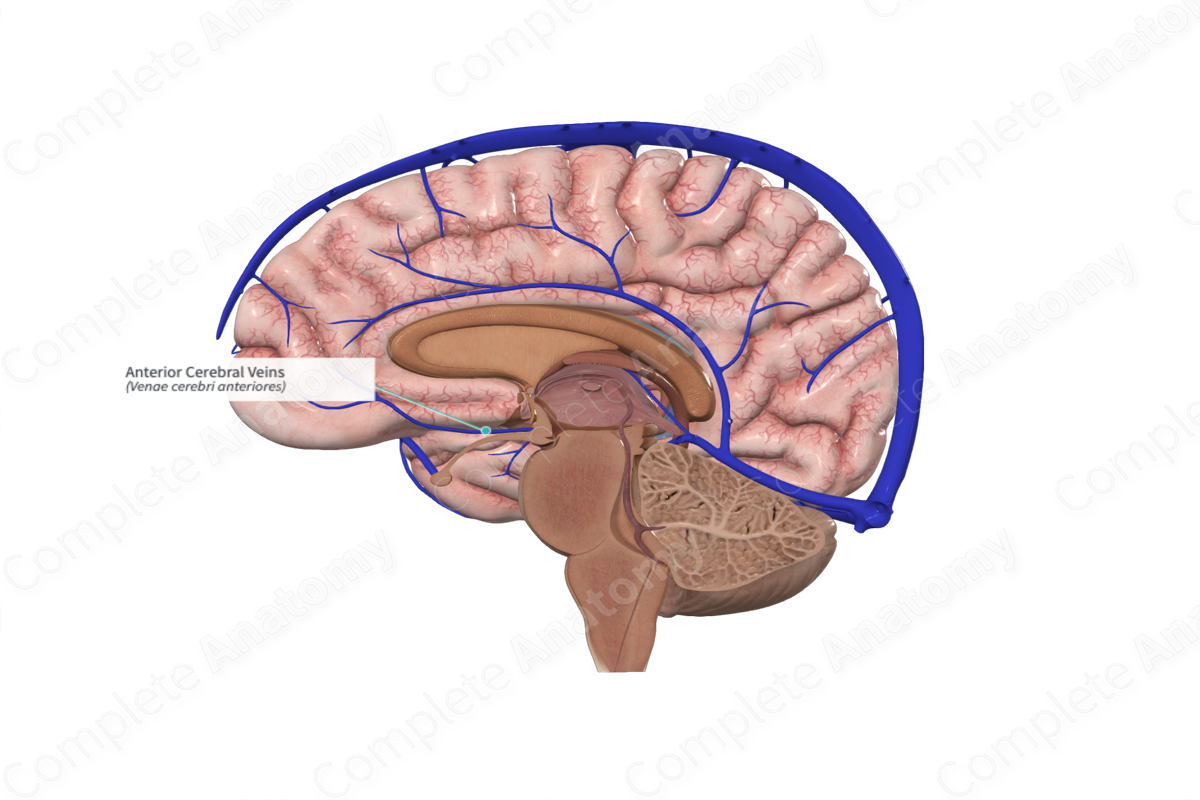
Where does the anterior cerebral vein empty?
Into the basal vein of Rosenthal.

What is the cerebral cortex?
The outer gray matter of the brain that controls higher cognitive and motor functions.
What type of matter is the cerebral cortex composed of?
Gray matter (neuronal cell bodies and synapses).
How many layers does the cerebral cortex have?
Six distinct layers.
molecular
external granular
external pyramidal
internal granule
internal pyramidal
multiform/ polymorph
Are all cortical layers equally developed in every region?
No — their thickness varies depending on function (motor vs sensory).
What is the molecular layer?
The outermost layer of the cortex.
What does the molecular layer contain?
Dendrites of pyramidal neurons and axons from thalamic neurons.
What is the function of the molecular layer?
It acts as a synaptic field for communication between neurons.
What cells are in the external granular layer?
Small multipolar neurons and interneurons
What is the main function of the external granular layer?
Local signal processing between nearby cortical neurons.
What cells are found in the external pyramidal layer?
Small pyramidal neurons
What is the main role of the external pyramidal layer?
Communication between different cortical areas (corticocortical connections)
What cells dominate the internal granular layer?
Small multipolar neurons and interneurons.
What is the main function of the internal granular layer?
Receives sensory input from the thalamus.
Which cortical areas have a prominent internal granular layer?
Sensory areas like the primary somatosensory and visual cortices.
What is found in the internal pyramidal / gnaglionic layer?
Large pyramidal neurons, including Betz cells. (UMNs)
What is the main function of the internal pyramidal layer?
Sends motor output to the brainstem and spinal cord.
Where are Betz cells found?
In the primary motor cortex (layer V).
What do Betz cells do?
Send axons down the corticospinal tract for voluntary movement control
What cells are found in the multiform layer?
Neurons of various shapes and sizes
What is the main function of the multiform layer?
Sends feedback to the thalamus.
What is homotypic cortex?
Cortex where all six layers are clearly visible.
Where is the homotypic cortex found?
In association areas involved in higher-order processing.
What is heterotypic cortex?
Cortex with certain layers more developed than others, depending on function.
What are the two types of heterotypic cortex?
Granular and agranular.
What are Betz cells?
Giant pyramidal neurons found in layer V of the motor cortex.(internal pyramidal)
What is the function of Betz cells?
Send long axons to the spinal cord to initiate voluntary movement.
Which cortical layers are most developed in sensory areas?
Layers II and IV (granular).
Which cortical layers are most developed in motor areas?
Layers III and V (pyramidal).
Which layer sends output to the thalamus?
The multiform layer (VI).
Which layer sends output to the spinal cord?
The internal pyramidal layer (V).
Which layer receives most input from the thalamus?
internal granular layer (IV).
Which cortical type is associated with higher-order thinking?
Homotypic (association cortex)
Where is the primary motor cortex located?
In the precentral gyrus and anterior paracentral lobule.
What is the main function of the primary motor cortex (Area 4)?
It controls voluntary muscle movements of the contralateral body.
What artery supplies the primary motor cortex?
The middle cerebral artery (MCA) for face/upper limb and anterior cerebral artery (ACA) for lower limb.
What happens if the primary motor cortex is damaged (e.g., MCA occlusion)?
Contralateral hemiparesis or paralysis.
Where is the premotor cortex located?
Anterior to the primary motor cortex.
What is the function of the premotor cortex? (6)
It plans and sequences movements and sends signals to the primary motor cortex for execution.
What condition results from a lesion in the premotor cortex? (6)
Dyspraxia — difficulty planning or performing coordinated movements.
Where is the frontal eye field located? (8)
Anterior to the premotor cortex in the middle frontal gyrus.