NURS 211 Statistics Full review
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio
What are the 4 Levels of Measurement?
Hint: N.O.I.R
Categorical variable
A variable that has a finite number of classification groups/ categories, which are usually qualitative in nature
Continuous variable
A variable that has a infinite number of potential values, with value being measured falling somewhere on a continuum containing in-between values.
Empirical method
What method is a way of gathering information through systematic observation and experimentation?
Parameter
___________ is a measurable characteristic of a population
Statistic
_____________ is an estimate derived from a sample
- numerical measurement describing some characteristic of a sample
Estimate
_____________ is a preliminary approximation
Qualitative measure
What measure describes or characterizes an attribute?
- data in words
ex. The day is "warm" or "cold"
Quantitative measure
What measure reflects a numeric amount?
- data in numbers
ex. writing down the temperature for the day
Nominal
Marital status: you're either married (together)/ divorce(not together) Is an example of what level of measurement?
Hint: sounds like "Name/Nom"
- no order, either has it or doesn't
Ordinal
Pain scale, stress scale (ex: low, medium, high stress level) is an example of what level of measurement?
Hint: sounds like "Ordered"
- no equal interval between the values
- Comparison between smaller value to bigger value
Interval
Temperature and Student tests are examples what level of measurement?
- Ordered,
- Equal ___________ between values
- No true "zero"
Ratio
Tests such as: Blood pressure, (if patient's BP is 0 then they're in trouble, heart isn't beating, dead = true zero),
- blood sugar, renal function, glascow coma scale, BMI etc. Are examples of what level of measurement?
-Ordered
- Equal interval between values
- Has a true zero
- Very precise, accuracy (best for healthcare)
- bodily measures ex.) there can be 0 weight gain
Dependent variable
The _________________ is the outcome factor.
- The variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
- Depends on independent variable
Independent variable
The _______________ is the variable that experimenter can change
- influences dependent variable.
Mean
____________(M)
- average,
[Calculation: add all numbers then, divide by number of values]
Ex: Videos, Reading
- Good for interval and ratio data
- Best measure for symmetrical distribution of data
Median
___________- middle (Medium)
[Calculation: Arrange in order,
Number is odd = middle value
Number is even = mean of the middle values]
Ex: Odd (reading), Even (videos)
- Works for Ordinal, interval and ratio data
- Good for asymmetrical data distribution
- Not appropriate for nominal data
Mode
___________ - sounds like "Most", most frequent number
[Calculation: arrange number in order, count the number that shows up most frequently]
- Only appropriate for nominal data
- Can also be used for ordinal, interval and ratio data
(Patients score - Sample mean) ÷ (Standard deviation/ SD)
Z-score
Points out outlier patients/ defiant patients
Ex) patients way below or above a scale
captures how much people deviate from the mean/defy the average
What is the formula for Z-scores?
Formula:
___________ ÷ ___________ = Z-score
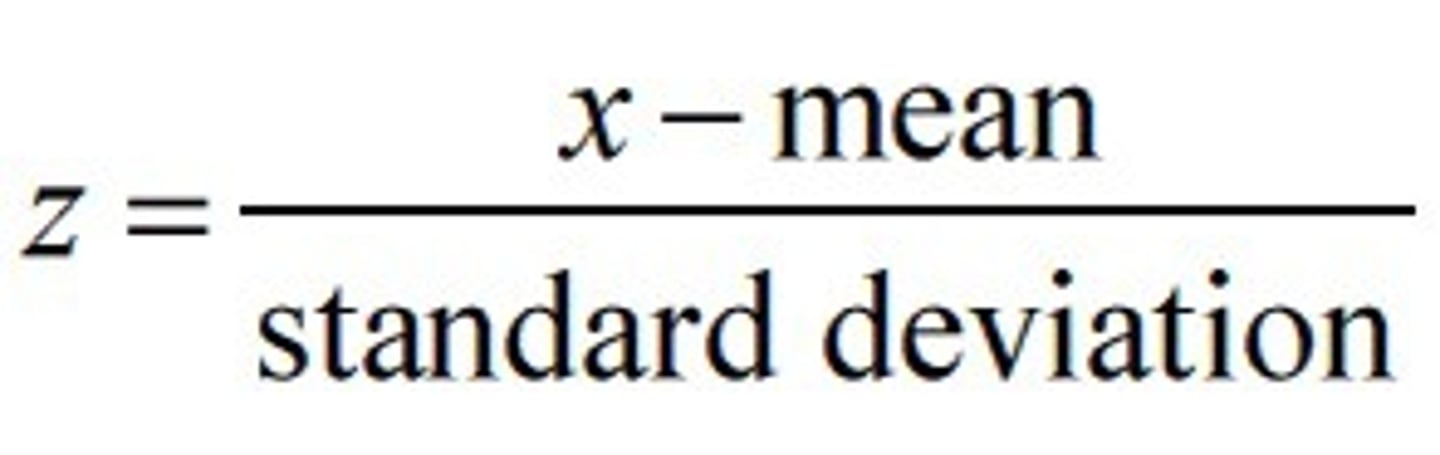
Normal distribution
What kind of distribution has the:
- Measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) all fall in the same midline point? (ALL EQUAL)
- Bell shaped
- Has a mean of 0 and Standard deviation of 1
Standard Deviation (SD)
- The average distance that values in a distribution are from the centre
- Indicates how many far a value is from the mean value.
Low SD = values are close to the mean (homogenous sample)
High SD = values spread out over a large range (heterogenous sample)
What measures how much variation exists in distribution?
Probability
The chance that a particular outcome will occur
ex.) 75 students in class and 69 are female and 6 are males - what is ___________ of a male student being randomly selected from a seminar group?
[6/75 = 0.08 x 100 = 8%]
0.05 or 95%
Alpha = the probability of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis or making a type 1 error
The significance level of Alpha is usually: ___________.
0.20 or 20%
Beta = the probability of accepting the null incorrectly or making a type 2 error
The significance level of Beta is usually: __________.
1 - 80 = beta
How would you calculate Beta if the power of the study is 0.80?
p-value
the probability of finding the outcome you observed if the null hypothesis is true
- The probability you got your finding due to chance (don't want result to be due to chance so p-value should be low)
Low value = low probability
High value = high probability
Reject the null hypothesis
If the p-value is LESS than the alpha, you should _____________.
Fail to reject the null hypothesis
If the p-value is GREATER than the alpha, you should ____________.
- there is no relation
Probability Sample
______________ is a technique where the probability of selecting each subject is known (Randomized)
Simple Probability Sampling
______________ = All individuals in a population have an equal probability of being selected
ex) Randomly picking from a CARNA list
Systematic Probability Sampling
______________ = Probability sampling involving selecting subjects according to a standardized rule
ex) Picking every 5th person in a population
Stratified Probability Sampling
______________ = A probability sampling technique where a researcher begins by identifying subgroups (or strata) and then randomly samples from each subgroup.
ex) Identifying nurses that have worked for 1 year and randomly selecting 20% of your sample from this group
Cluster Probability Sampling
________________ = Randomly selecting a group or unit rather than a individual
ex) Geography, randomly selecting nurses from Rural hospitals or Urban hospitals
Non-probability sampling
______________ are methods in which subjects DO NOT have the same chance of being selected (NOT Randomized)
Convenience probability sampling
______________ = Selecting & collecting data from a population that is available
ex) Doing a study on the nurses in your clinical group
Quota probability sampling
______________ = Selecting proportion of the sample for different subgroups.
- Similar to Stratified sampling but is NOT randomized
ex) After deciding on your proportion of the sample, you collect data continuously until you meet your set goal (until you reached your quota)
Range
_____________ is the difference between maximum and the minimum values in a distribution
Central Limit Theorem
- states that the sampling distribution of the sample means approaches a normal distribution as the sample size gets larger — no matter what the shape of the population distribution.
- If the number in your sample is around 30 your data will likely approximate to normal distribution
30
Central Limit Theorem
→ if the number in your sample is around _______ your data will likely approximate to normal distribution.
Sample mean will be approximately normally distributed for larger sample sizes, regardless of the distribution from which we are sampling.
As you take more samples, especially large ones, your graph of the sample means will look more like a normal distribution.
What is the ideal number of people to have in a study?
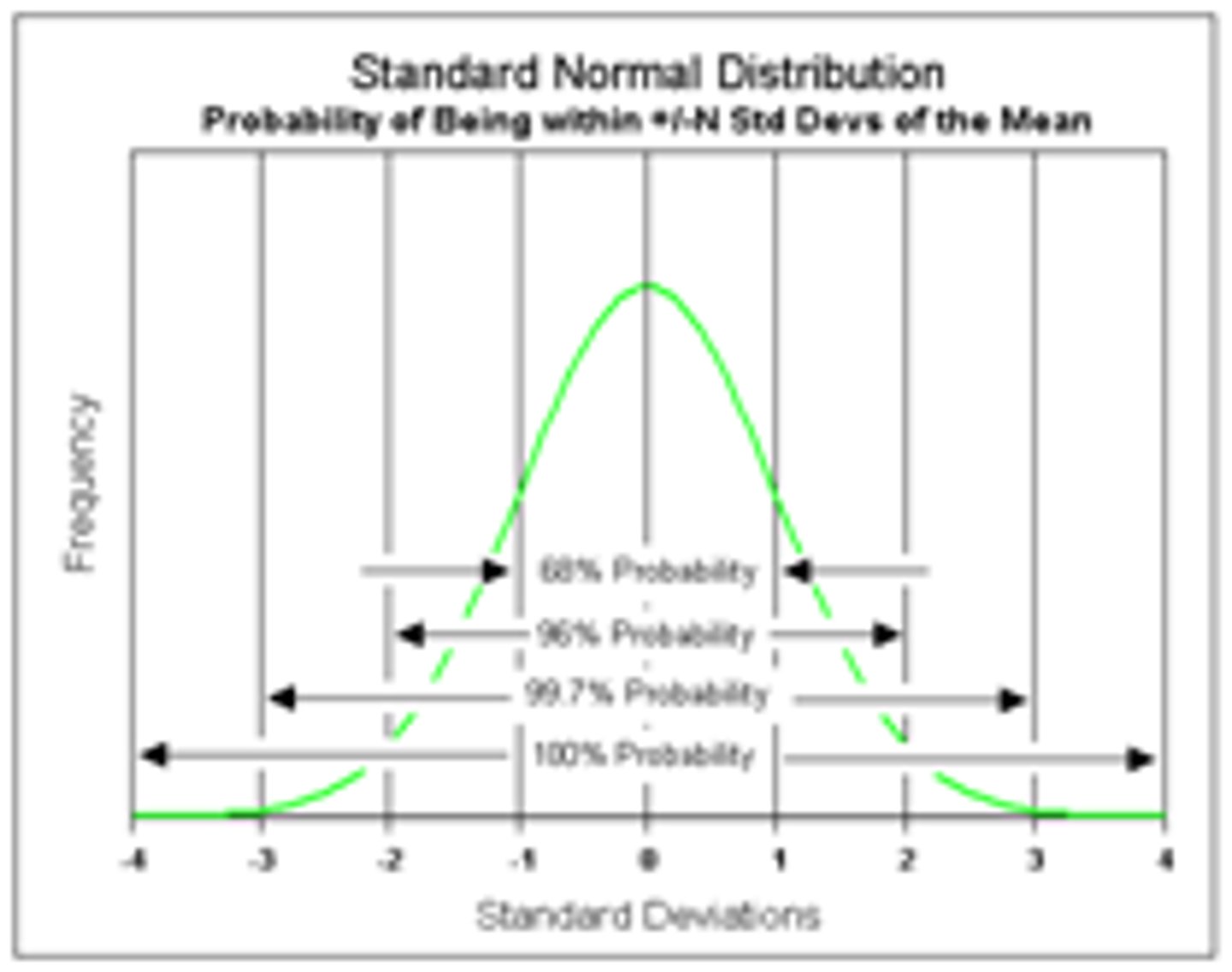
68-95-99.7 rule
in a normal model, about 68% of values fall within 1 standard deviation of the mean
about 95% fall within 2 standard deviations of the mean
99.7% fall within 3 standard deviations of the mean
--> More than 3 SD above or below average is "Outlier" or "weirdo"
anyone deviates that far out should be investigated further
Inclusion criteria
characteristics a subject must have to be eligible to participate in a study
Exclusion criteria
Characteristics that eliminate a potential subject from the study
Sampling error
The differences between the sample and the population that occurs due to randomization or chance
- Errors made by chance alone
Sampling bias
Systematic error made in the sample selection that results in a nonrandom sample
- something that has gone wrong while conducting a sample
- Error you're making on purpose
- Errors YOU make that result in a non-random sample
Data collection error
Data handling error (made when processing data)
Reporting error (reporting something untrue)
What are three examples of sampling bias?
1.
2.
3.
Effect size
<.30, .30-.50, >.50
The extent to which a difference or relationship exists between variables in a population (size of the difference you are attempting to find)
Weak Effect _______ (Want LARGER sample size)
Moderate Effect _______
Large Effect _______ (Want SMALLER sample size)
Sample size
The number of subjects used in an experiment or study. - Generally, the larger the better.
- Calculated by: Power analysis
Smaller sample size
- less info
- wider confidence intervals
- greater chance of making a type 2 error
Larger sample size
- more info
- sampling error reduced
- narrow confidence interval
- greater chance of making a type 1 error
Confidence interval
Variation of population
Size of sample
- Communicates how accurate our estimate is likely to be
What two things affects the width of ________________?
1.
2.
Type 1 error (alpha)
- Incorrectly REJECTING the null hypothesis
- Rejecting null hypothesis when it is true
- When data is true => reject data
ex) Think you got the cure for cancer but you actually don't.
Type 2 error (beta)
- Incorrectly ACCEPTING the null hypothesis
- Missing an association that is really there
- When data is false => accept data
ex.) Got the cure for cancer but then got insecure and trashed it.
Type 2 error is 4 times more serious
Which type of error is more serious to make in a healthcare setting and why?
20% chance of committing vs. 5%chance of committing
Power
______________ is the ability to find a difference/association when one really exists
- has a significance level of usually: 0.80 or 80%
- When sample size increases = Power of study is increased = likelihood of correctly rejecting null hypothesis also increases.
Reliability
What is it called when your measurement tool is consistent or repeatable?
- Measure has good reproducibility
Test-retest reliability
- Correlation of the scores obtained by a measure at two different times
- Participants are given the same test at 2 different times
Correlation between test 1 and test 2 (testing twice)
Inter-rater reliability
Correlation of measurements observed by two or more raters
Ex. asking two people about their pain and they say around the same value
Internal consistency
All the items in a survey tool measure the same concept (i.e., coping).
Equivalence reliability
Different forms of your survey tool yield matching (consistent) scores.
Validity
- The extent to which a measurement measures what it intends to measure
Ex. a questionnaire about self-esteem should be capturing self esteem, not other concepts like extroversion
Divergent validity
- The degree to which results of a measure do NOT correlate with other variable or measures
Covergent validity
- a determination that the test results obtained are similar to the results obtained with another previously validated test that measures the same thing
Predictive validity
Measurement of how accurately an instrument suggest future outcomes/behaviours
- How scores predict a health outcome
ex) People with high serum cholesterol scored low on exercise
Construct validity
the extent to which variables measure what they are supposed to measure
- Do the items in your tool 'stick together' in an expected way.
Yes, a measurement can be Reliable and not Valid BUT CAN'T be Valid and not Reliable.
- For something to be valid, it needs to be reliable and accurate
Can a measurement be Reliable but not Valid?
Dependant samples
- When members of one sample are related to members of the other sample.
-NOT random
-Sample B depends on the result of sample A because they are related.
ex.) Sample A is taken from husbands and Sample B is taken from their wives. (related)
Independent samples
- RANDOM, Unrelated
- There is no relationship between sample A and B
Null
Nothing, Not different
No difference or association between variables that is any greater or less than would be expected by
chance.
Alternative
Opposite of the null
Alternative POV
Usually the relationship or association or difference that the researcher actually believes to be present.
Parametric statistics
What kind of statistics need....
- Needs to be ratio or interval LOM
- Normally distributed
- No outliers
- Homogeneity of variance
- Sample sizes larger than minimum for many nonparametric tests
______________________
- More powerful, more likely to detect a difference that truly exists
Less likely to make a type 2 error
Nonparametric statistics
Random independant Samples
______________ - small sample, non normally distributed date
- More conservative
- Less statistical power
What kind of statistic is more likely than a parametric test to produce type 2 error?
One-tailed test
A hypothesis test in which rejection of the null hypothesis occurs for values of the test statistic in one tail of its sampling distribution.
Two-tailed test
A hypothesis test in which rejection of the null hypothesis occurs for values of the test statistic in either (both) tails of its sampling distribution.
Chi-square (x^2)
2 independent samples of nominal or ordinal level data
- Looks for associations or relationships between groups
-Highly sensitive to sample size
- Samples should be Random & Independent
Change in (observed - expected)^2 / expected
What is the formula for Chi-square?
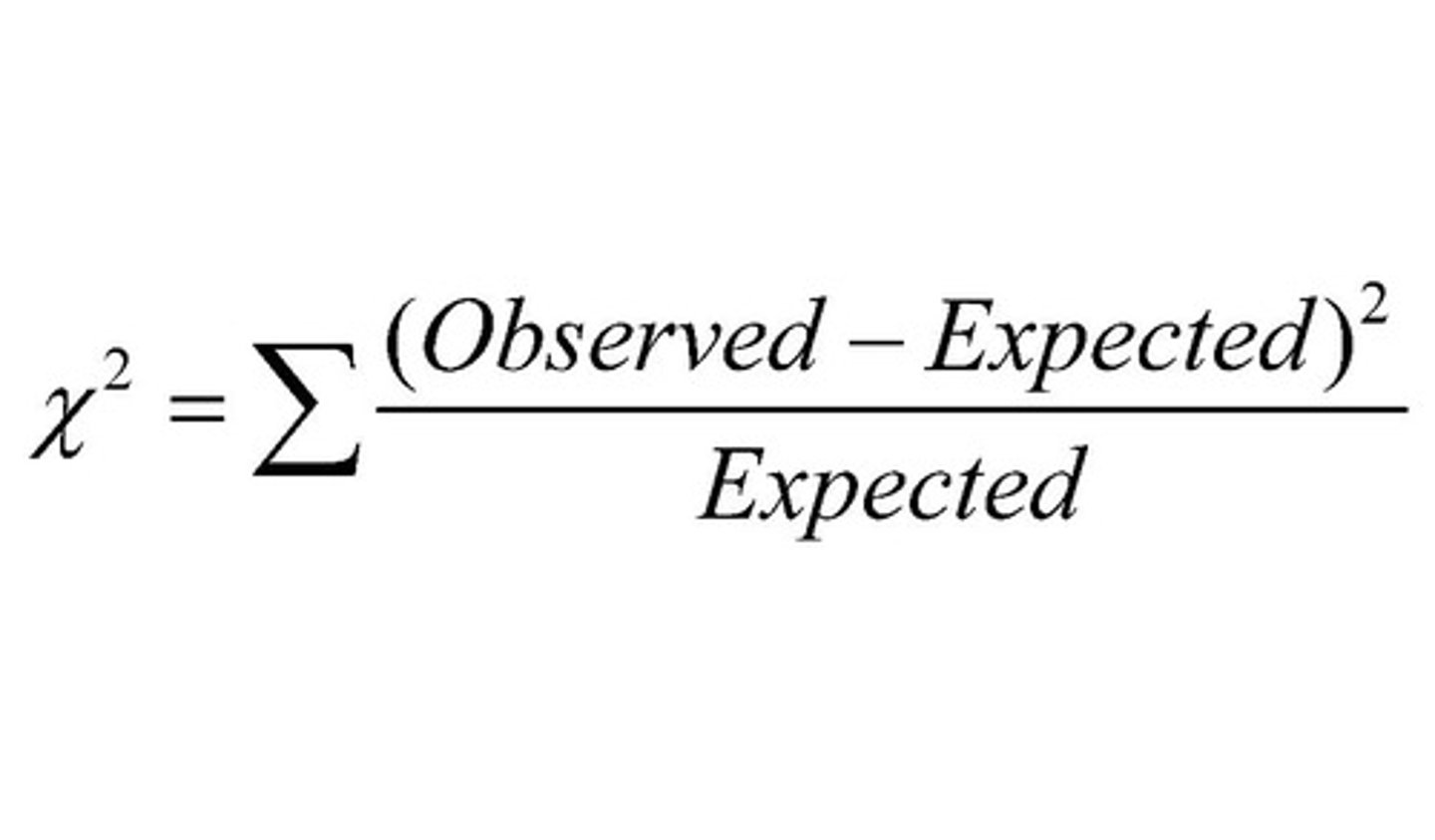
Expected Frequency
____________ = (Row total x Column total)/ Grand total
Reject the Null hypothesis
(P-value is less than 0.05/alpha)
- There is an association
If X2 result has a p-value that is LESS than alpha you should....
Fail to reject the null hypothesis
(P-value is greater than 0.05/alpha, Ex) p-value is 0.09)
- There is not enough statistical strength to say the variables are not related.
If X2 has a p-value GREATER than the alpha you should....
Degrees of freedom (df)
the values that are "free to be unknown"
(df = n-1 )
df for a 2x2 is always "1"
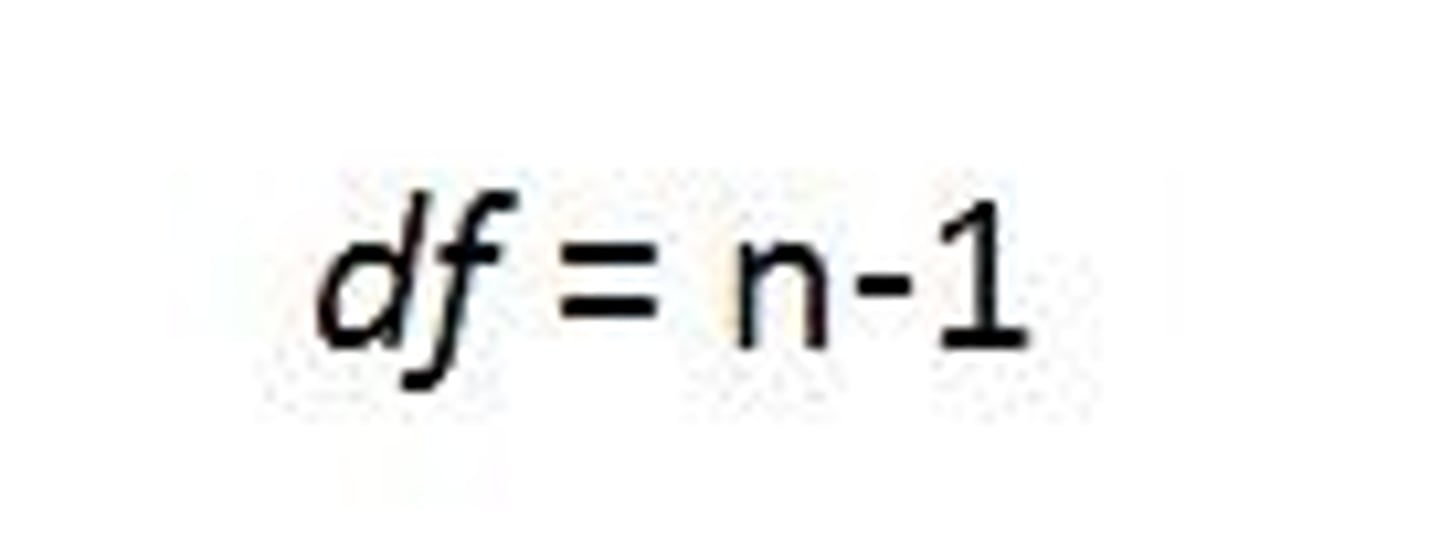
Student t-test
A test used when you are looking for a difference in the MEAN VALUE of an interval-level or a ratio-level variable.
- Interval or Ratio level
- Two samples
- Random and independent samples
Degrees of Freedom (t-test)
DF = [(# of total subjects in sample1) + (# of total subjects in sample2)] - 2
![<p>DF = [(# of total subjects in sample1) + (# of total subjects in sample2)] - 2</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5a5205c7-7339-41af-a4fe-fd0cdc3ae98d.jpg)
t-value
Mean difference / Standard error
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
A test used when comparing the means from a single dependent variable among TWO OR MORE groups of samples
-Detect differences between continuous variables when there are two or more groups
Variance
differences, how much that persons score is different between the average score.
- The square of the standard deviation
Levene's Test for Equality of Variances
A method that tests the null hypothesis that the variances in the two groups being compared are NOT DIFFERENT
- tests for the homogeneity of variance (variances are somewhat similar)
Levene's test
If _________ ______ has a significant p-value, you do not assume equal variances.
If the _________ ______ does not show a significant p-value, you can assume equal variances.
F ratio
Compares between-groups variance to within-groups variance
Formula:
F= (Between group variation) / (Within group variation)
Can also think of it as:
F = (Treatment / sampling error)
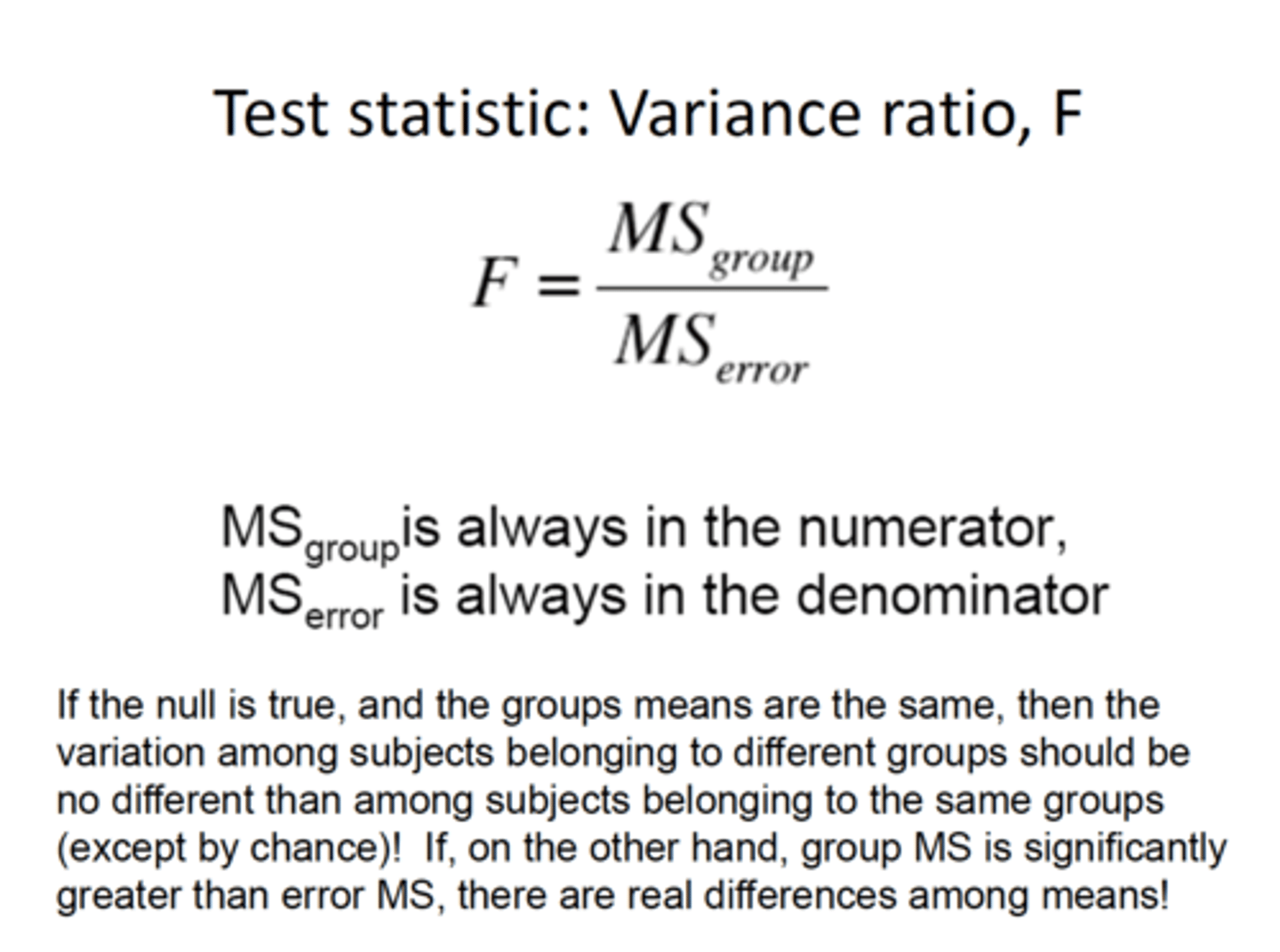
What is the ideal F-ratio?
F-ratio greater than 1.0 is ideal --> Larger F-ratio is more likely to have a significant p-value
- 'between group' variation should be higher
- (Numerator should be bigger than the denominator)
Appropriate use of ANOVA (4)
1. Sample should be INDEPENDENT (ideally random)
2. Measure must be in INTERVAL or RATIO level
3. Sample should be NORMALLY DISTRIBUTED
4. HOMOGENEITY of variance (scores need to vary similarly among the 3 groups)
Repeat-measures ANOVA
Examines a change over time in the same sample population
- one group with outcomes at multiple points in time
- Useful for dependent samples
- Compound symmetry
- Be aware of Latency effects and Carry over effects.
What are Assumptions used for Repeat ANOVA?
Compound symmetry
measurements are correlated and of equal variances
Latency Effects
When a subject is being exposed to more than one treatment overtime and order of the treatment effects the outcome.
Carry over effects
When previous treatments continue to have an effect in the next treatment
Correlation
A measure of the relationship between at least two variables
- Strength of relationship
Direction of Relationship
Is either positive or negative
Positive: Two variables tend to increase or
decrease TOGETHER
Negative: Two variables tend to move in OPPOSITE directions
Pearson's correlation coefficient (Pearson's r)
Used when looking for a relationship between two variables that are:
- Normally Distributed
- Interval or Ratio level
Spearman correlation coefficient (⍴)
Used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables but don't meet Pearson's assumptions:
- NOT Normally distributed
- Ordinal, Interval or Ratio level
Correlation Coefficient
Always Range From -1 to +1
-1 = Perfect negative relation
0 = No relation
+1 = Perfect positive relation
Positive correlation: Coefficient is also Positive
- Ex) Time studying for an exam and exam grade is positively correlated
Negative correlation: Coefficient is also Negative
- Ex) When Smoking increases, Life expectancy decreases & vice versa
Percentage of Variance
The amount of variance in one variable that is explained by the second variable.
Formula: Coefficient of determination x 100
- ** r > 0.3 is considered clinically important