Path Cardioresp: investigating resp outbreak in ruminants
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What to check during group clinical examination
increased respiratory rates
Behavioural change - ear position, not rising
Evidence of open mouth breathing
Coughing
Examine proportion of the group further
What to check during individual clinical exam when investigating resp disease in ruminants
Body condition score
Respiratory rate and lung auscultation
Pyrexia
ID affected age group
Estimate the number affected with clinical signs
Normal respiratory and heart rate, and rectal temperature of sheep
Resp = 16-34
Heart = 70-80
Temp = 38.3-39.9
Normal respiratory and heart rate, and rectal temperature of cattle
Resp = 26-50
Heart = 48-84
Temp = 38-39.3
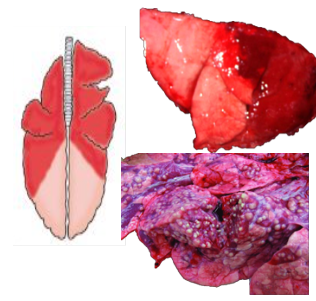
What pattern of lung pathology? Describe it. 2 example causes and possible differential
Suppurative bronchopneumonia (bacterial)
Neutrophilic inflammation
Cranioventral lung reddening, due to consolidation
Examples: Pasteurella multocida, Mycoplasma
Ddx = aspiration pneumonia
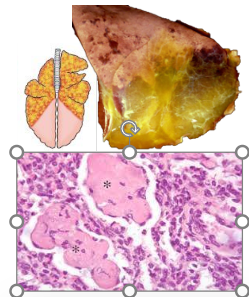
What pattern of lung pathology? (2 names). Describe it. 1 example cause.
Fibrinous bronchopneumonia or Lobar pneumonia/pleuropneumonia
Fibrinous exudate predominates in the cranioventral lung/consolidation
Cause: Mannheimia haemolytica
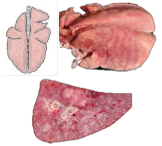
What pattern of lung pathology? Describe it. 2 example causes.
Interstitial pneumonia
Affects alveolar and interlobular septae.
Lungs fail to collapse
Rib impressions
Lacks visible exudates
Rubbery/elastic/meaty texture
Causes: Maeda Visna virus, fog fever/acute bovine pulmonary emphysema
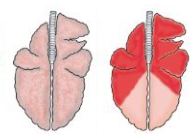
What are these lung patterns together? Describe it. 3 example causes.
Bronchointerstitial pneumonia.
Affects cranioventral lung lobes with bronchopneumonia, and the alveolar and interlobular septae
Causes:
Bovine respiratory syncytial virus
Parainfluenza 3
Mycoplasma bovis
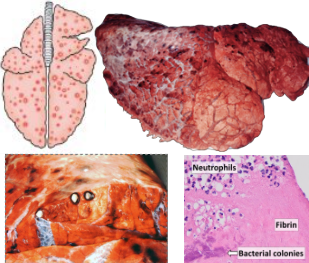
What pattern of lung pathology? Describe appearance and pathogenesis. 2 example causes.
Embolic pneumonia
Multifocal random distribution on all lobes
Caused by haematogenous injury on arterioles/capillary beds = trapping bacterial emboli
Can progress into abscesses
Causes:
Omphalophlebitis (umbilical infection)
Vegetative endocarditis
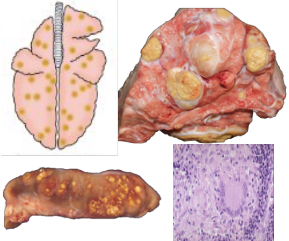
What pattern of lung pathology? Describe appearance and pathogenesis. 3 example causes.
Granulomatous pneumonia
Caused by aerogenous or haematogenous injury by particles that cannot be eliminated or phagocytosed.
Randomly distributed granulomas.
Macrophages predominate. Giant multinucleated cells possible.
Causes: Mycobacterium bovis
Parasite migration e.g. liver fluke
Aspergillus/systemic fungal infection
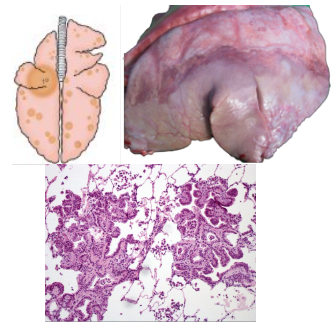
What pattern of lung pathology? Describe appearance and pathogenesis. Example cause (cattle)
Tumour metastases - secondary to malignant neoplasm elsewhere.
Unusual in farm species.
Causes multiple randomly distributed lesions throughout all lobes.
Lesions have variable size and appearance depending on cell type.
Cause: Lymphoma - Enzootic Bovine Leukosis (notifiable)
What pattern of lung pathology? Describe appearance and pathogenesis. Give an example cause.
Primary neoplasia with metastasis.
Random or cranioventral distribution.
Often has secondary bacterial infection.
Variable size and shape
Firm grey/cream mass
Cause: Ovine Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma/Jaagsiekte retrovirus
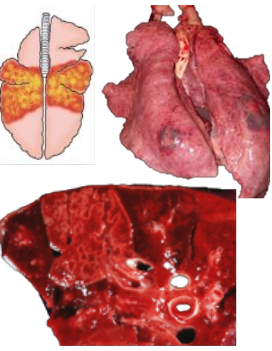
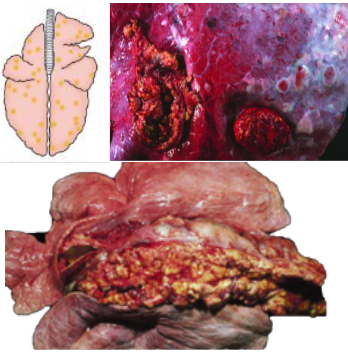
What pattern of lung pathology? Describe appearance. Give example cause in pigs.
Dorsal diaphragmatic pneumonia
Locally extensive distribution on dorsal aspect of caudal lung lobes
Well demarcated areas of necrosis when cut
Cause: Actinobacillus pleuropneumonia (APP)
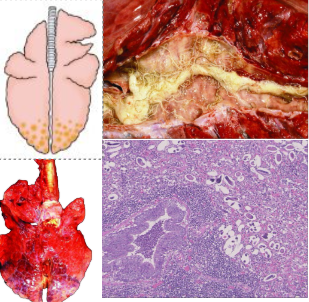
What pattern of lung pathology? Describe appearance. Give 3 example causes.
Verminous pneumonia
Locally extensive consolidation of dorsal caudal lung lobe
Adult worms present in bronchus
Pneumonia can be: interstitial (migration), chronic bronchitis (adults in airways) or granulomatous (dead parasite/larvae)
Causes: Dictyocaulus viviparus (cattle), Dictyocaulus filaria (significant, sheep), Muellerius capillaris (incidental, sheep)
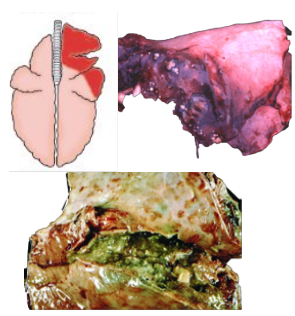
What pattern of lung pathology? Describe it and pathogenesis. 4 example causes and 1 differential diagnosis.
Aspiration pneumonia
Usually cranioventral and unilateral.
Caused by foreign material reaching lung through inhalation. Can cause septic or gangrenous pneumonia.
Causes:
Stomatitis (pharyngitis/laryngitis)
Regurgitation of ruminal contents
Metabolic disorders
Iatrogenic (feeding tube_
Differential = suppurative bronchopneumonia
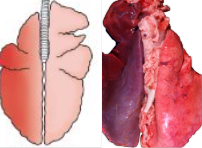
What is this?
Hypostatic congestion.
Normal post mortem change caused by pooling of blood. Depends on how the carcass is laying down
Helps demonstrate rib impressions if lungs fail to deflate (MV)
Will float as air spaces still present. Blood is pooling in capillaries.
What lung histopathology samples should be taken at post mortem?
1cm strips of lung.
3 sections from 3 different lobes
Include edge of lesion with some normal tissue
1:10 tissue: formalin ratio
Same sample to be frozen
What are the diagnostic samples and tests are used for bacterial disease?
Bronchoalveolar lavage or tracheal wash/nasopharyngeal swab in cattle
Aseptic technique on post mortem samples - bacteriological swabs
lung - boarder of affected and unaffected lung, or middle of affected tissue if on antibiotics
sample from heart blood or liver - septicaemia
centre of abscess
Cranioventral lung tissue for PCR if Mycoplasma suspected
Histopathology of samples
What diagnostic tests and samples are used for viral diseases?
Use sterile dry swab. Not charcoal, or wooden.
Sample spleen for bovine viral diarrhoea virus PCR
Sample clotted blood post mortem for serology of MV in sheep
Histopathology
What diagnostic tests and samples are used for parasitic disease?
Baermann test = separates lungworm larvae from faecal material (live animal)
Histopathology to show larvae/other stages, infiltrating eosinophils within pulmonary parenchyma.