digestive system + enzymes + organic molecules
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Nutrients
Chemical building blocks our bodies need to live, grow, and repair themselves, also providing energy.
Energy
The ability to do work, powering activities and helping build complex muscles.
Macronutrients
Chemical building blocks provided by food in large quantities, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
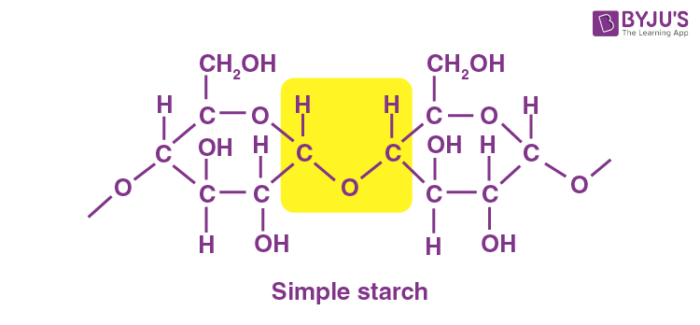
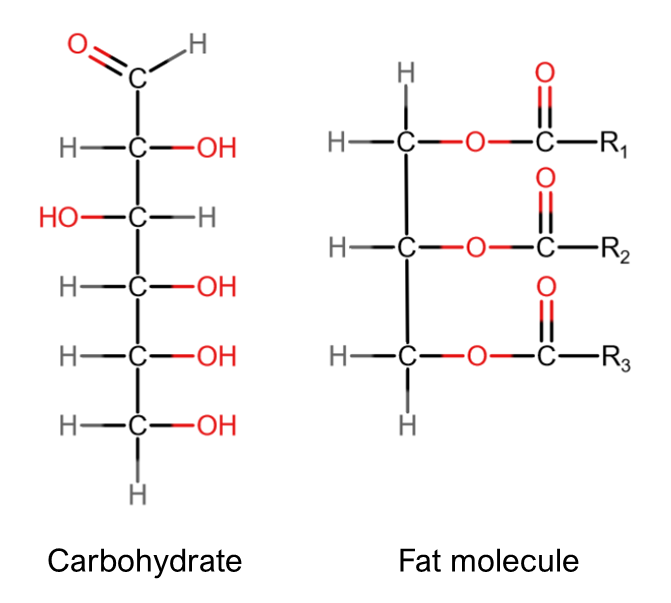
Carbohydrates
Macronutrients broken down into simple sugars, used to build cell-surface markers and energy-storage molecules.
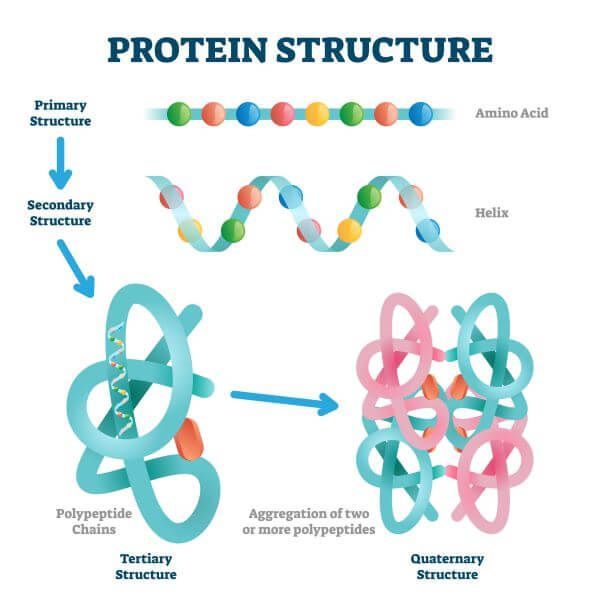
Proteins
Macronutrients broken down into amino acids, used to assemble new proteins with many different functions in the body.
Fats
Macronutrients broken down into fatty acids and glycerol, used to build molecules that form cell membranes.
Nucleic Acids
Components provided in smaller amounts (not macronutrients), broken down into individual nucleotides, used to build DNA and RNA.
Essential Nutrients
Nutrients that cells cannot synthesize and must be obtained through diet.
Essential Amino Acids
Nine specific amino acids out of 20 that cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through diet.
Digestion
The process of breaking down huge food molecules into smaller pieces through a series of chemical reactions, starting in the mouth.
Enzyme
A protein that catalyzes (speeds up) a chemical reaction.
Substrate
A molecule to which an enzyme binds and on which it acts.
Active Site
The specific part of an enzyme that binds to the substrate.
Catabolic Reactions
Metabolic reactions that break down larger structures into smaller ones (bond breaking).
Anabolic Reactions
Metabolic reactions that build new structures from smaller subunits (bond building).
Activation Energy
The energy required for a chemical reaction to proceed.
Catalysis
The process of facilitating a chemical reaction without the catalyst itself being used up in the reaction.
Denatured Protein
A protein whose shape and function have been disrupted, often by extreme environmental conditions like heat or pH.
Micronutrients
Nutrients required by organisms in smaller amounts than macronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, important for maintaining health and playing structural and functional roles.
Minerals
Inorganic elements required by organisms for normal growth, reproduction, and tissue maintenance (e.g., calcium, iron, potassium, zinc).
Vitamins
Organic molecules required in small amounts for normal growth, reproduction, and tissue maintenance.
Coenzymes
Small organic molecules (often vitamins) required to activate enzymes.
Cofactors
Inorganic micronutrients (often minerals like zinc, copper, iron) required to activate an enzyme.
organic molecules
molecules that contain carbon and hydrogen
Why does carbon bond with four other elements?
It is to gain four more electrons since Carbon only has four electrons in its outer shell. Carbon normally shares electrons with Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen.
Hydrocarbons
Chains composed of carbon and hydrogen
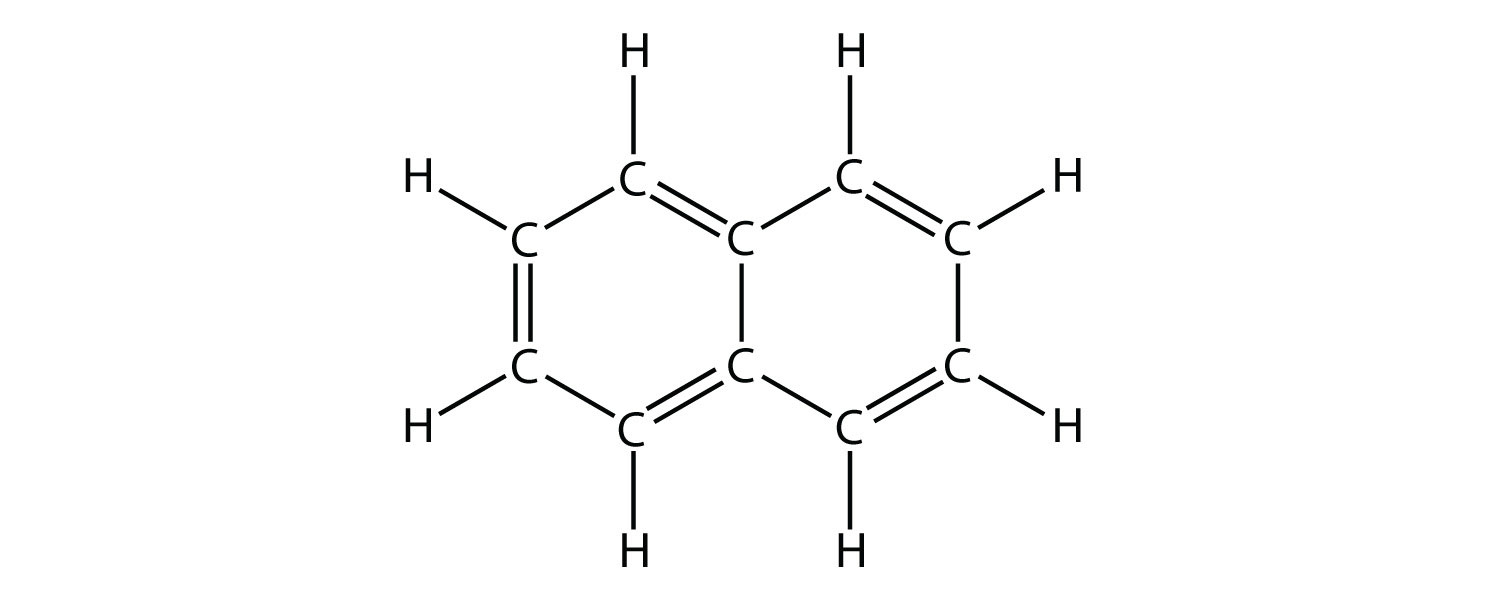
Functional Groups (R-groups)
molecules that are attached to hydrocarbons that gives them their properties.
Monomer
small chemical unit that makes up a polymer
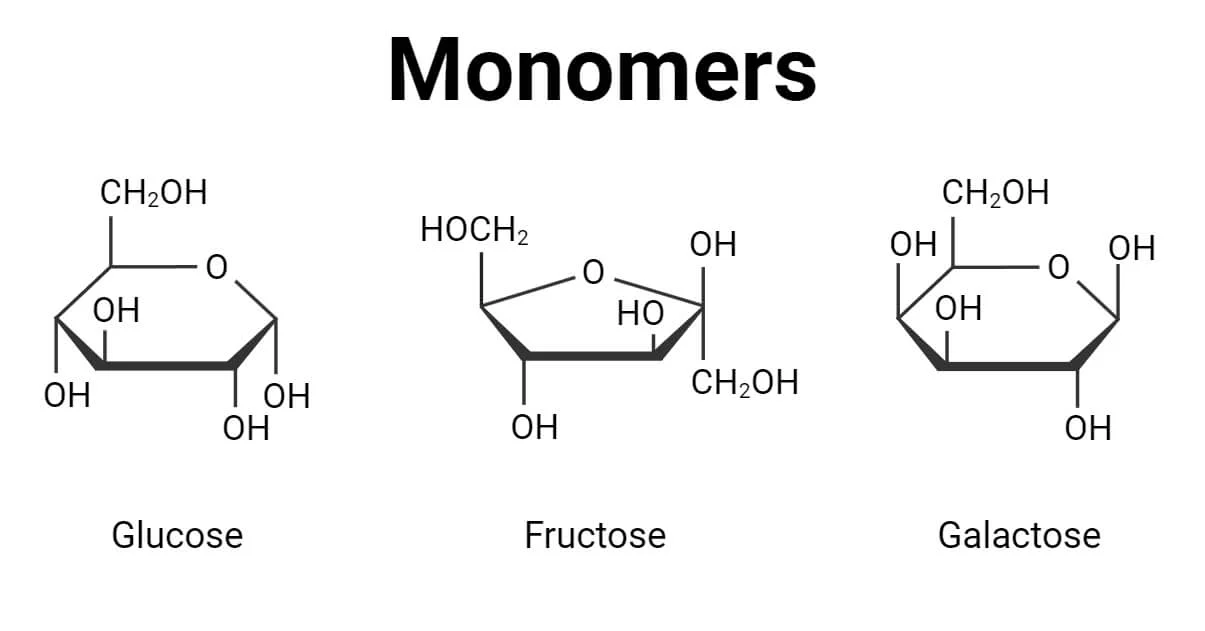
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
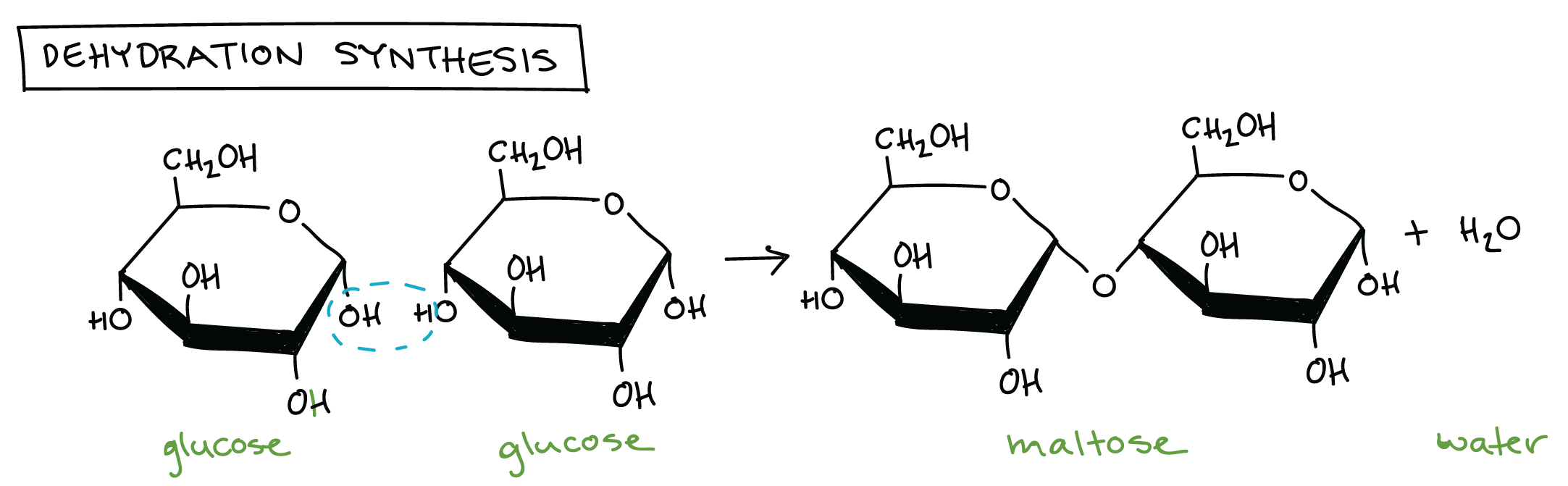
Dehydration Synthesis
WATER is REMOVED from the chemical reaction, which then allows monomers to bond
Hydrolysis
WATER is ADDED to break bonds.
Polymers => Monomers
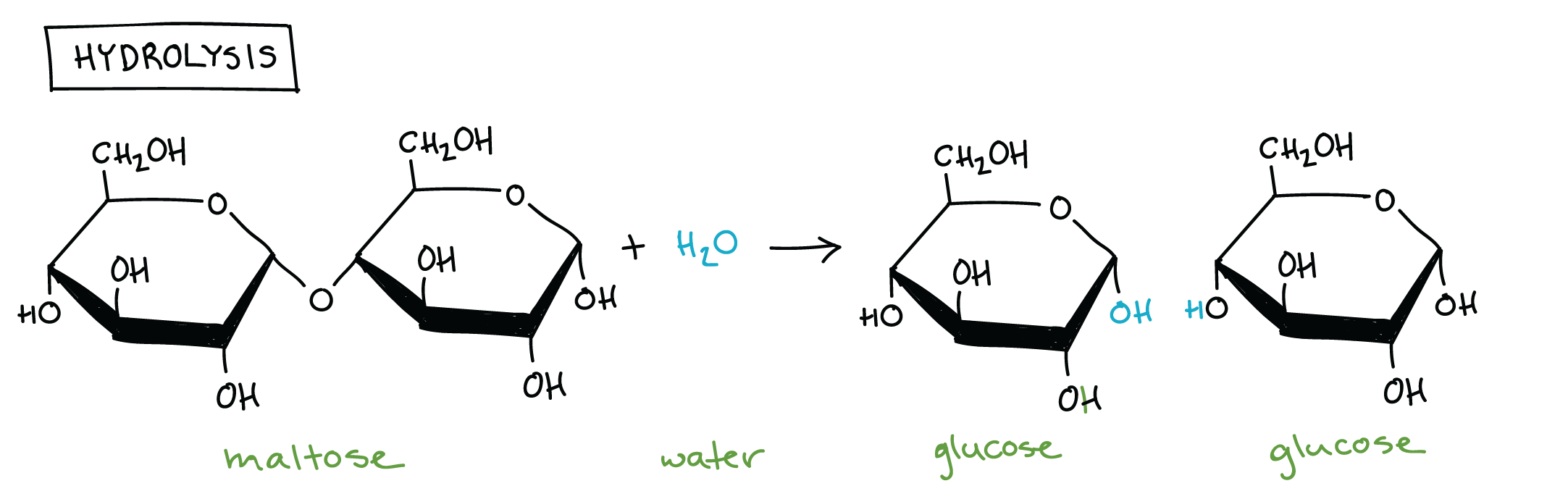
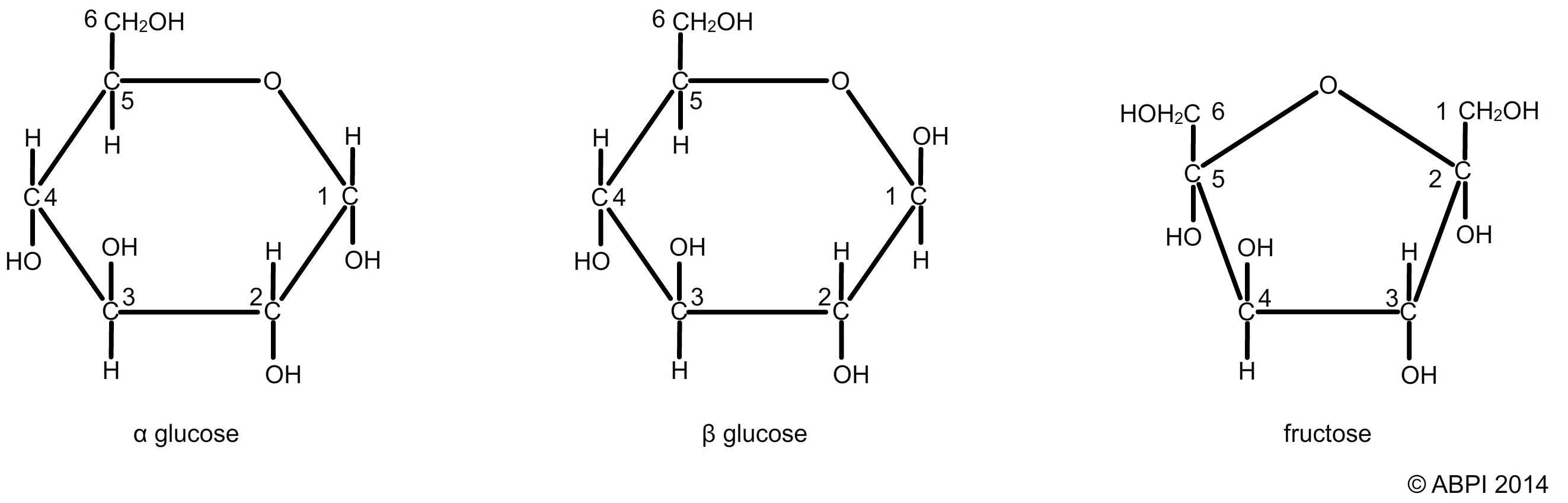
monosaccharides
single molecule (simple sugar)
ex. glucose
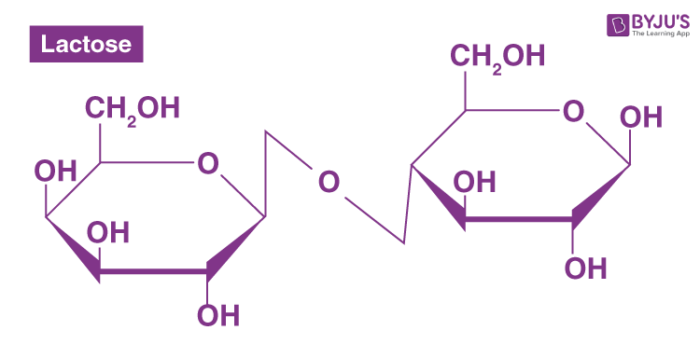
Disaccharides
two monosaccharides bonded together
ex. Maltose (glucose + glucose)
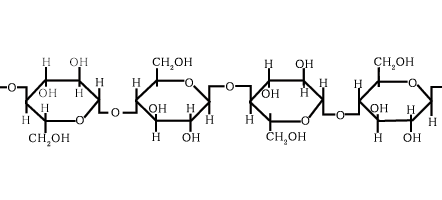
Polysaccharides
large molecules formed by multiple monosaccharides. Energy storage molecules
Starch = glucose storage for plants
Glycogen = glucose storage for animals
Structural: cellulose for plant walls and chitin for lobsters
Lipids
long chains of carbon and hydrogen
used for: cell membrane, waterproof skin, hair, feathers. Also used for long-term energy storage
ex: steroids, fats, phospholipids
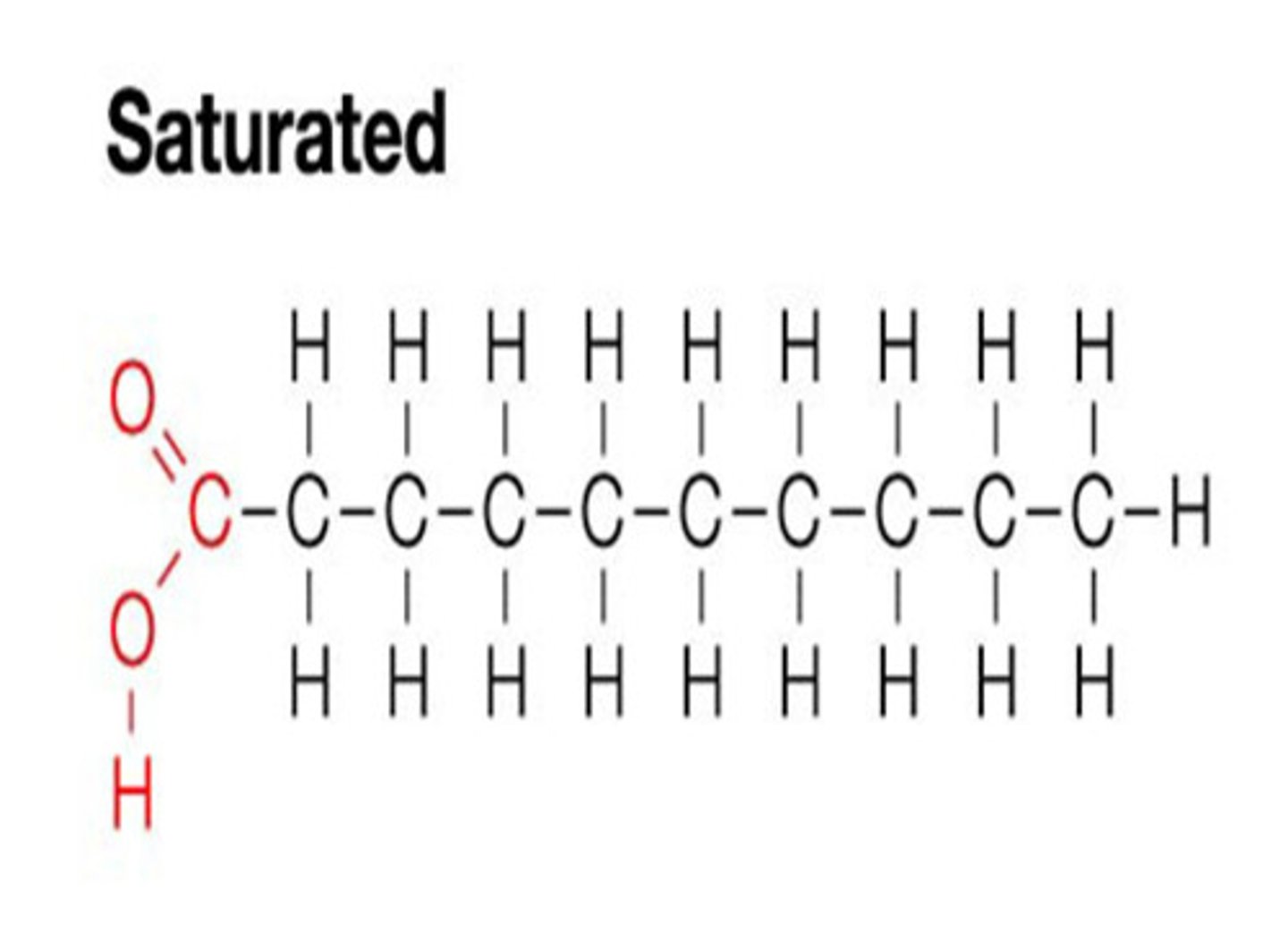
Saturated Fats
SOLID at room temperature. It does not have double bonds.
ex: Butter
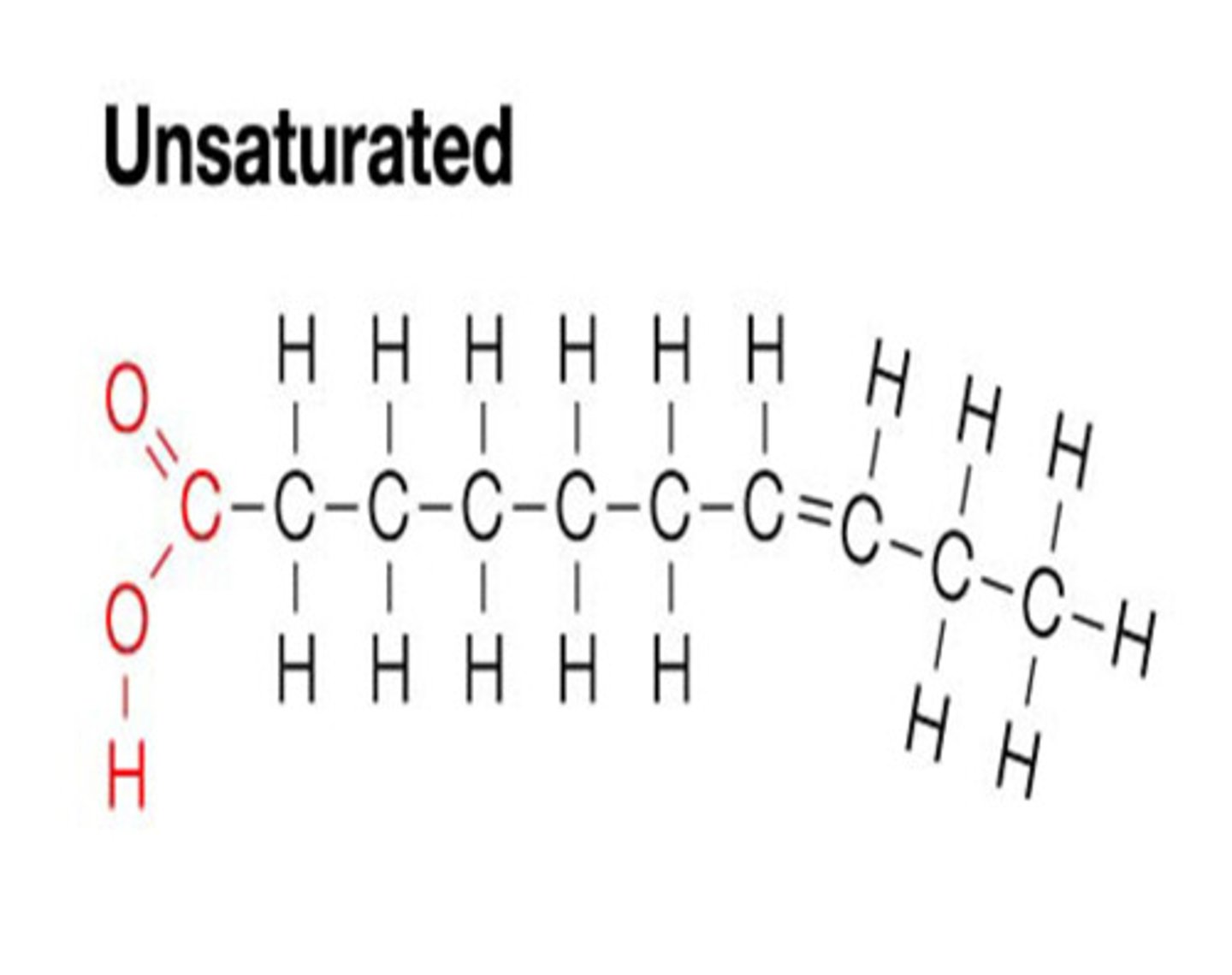
Unsaturated Fats
LIQUID at room temperature. Has double bonds.
ex: oil
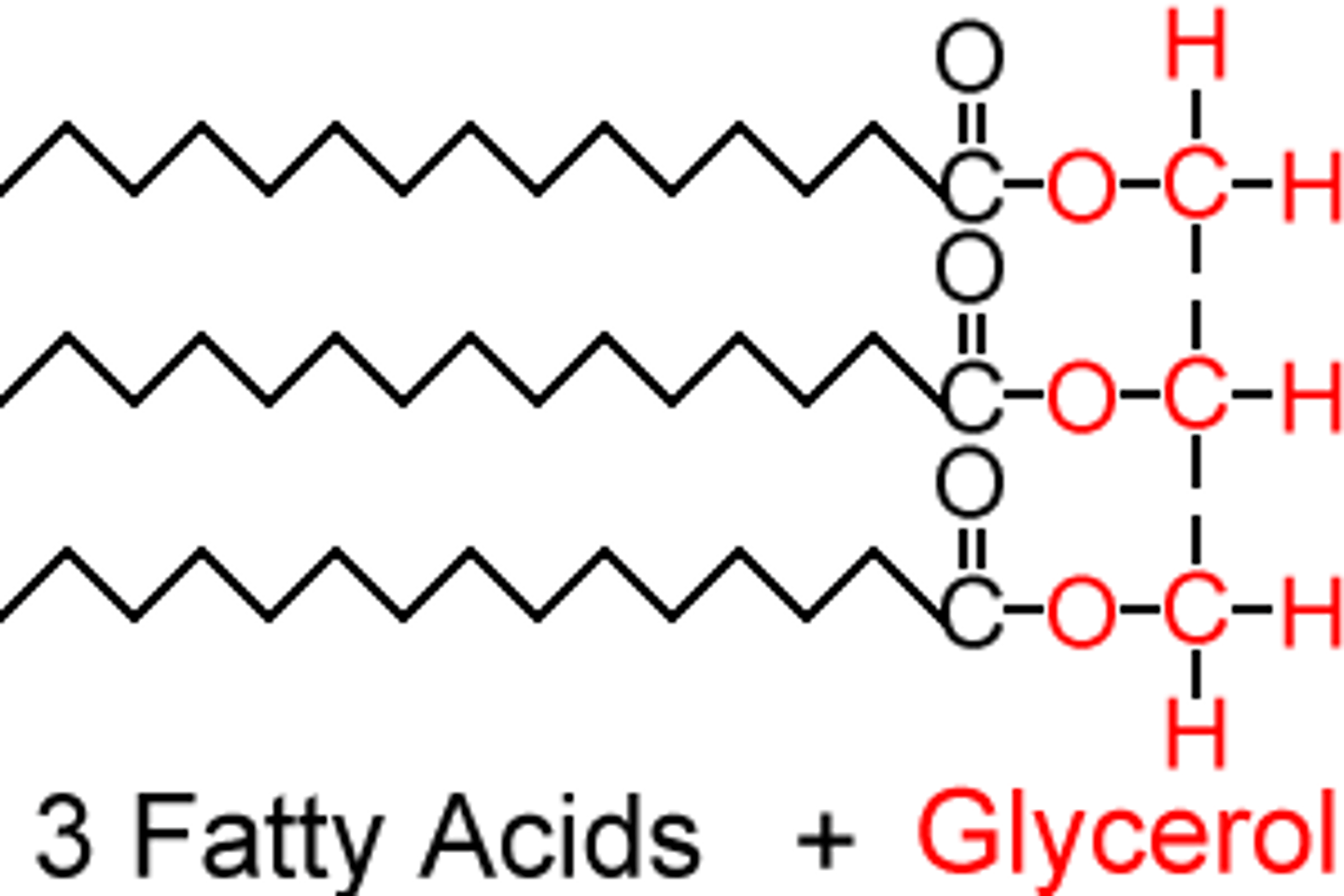
Triglycerides
composed of 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids.
storage for extra calories
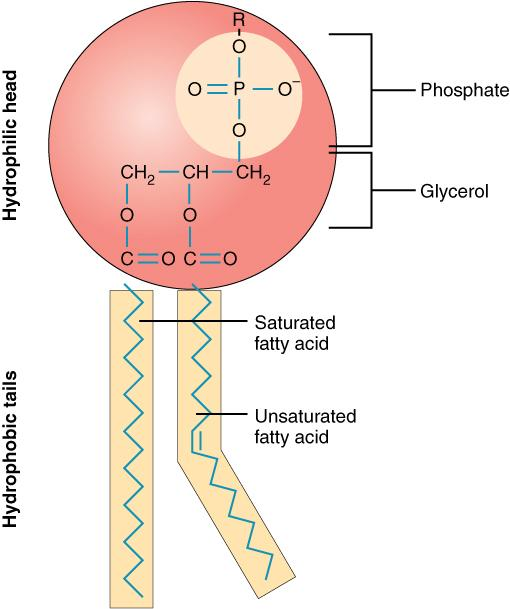
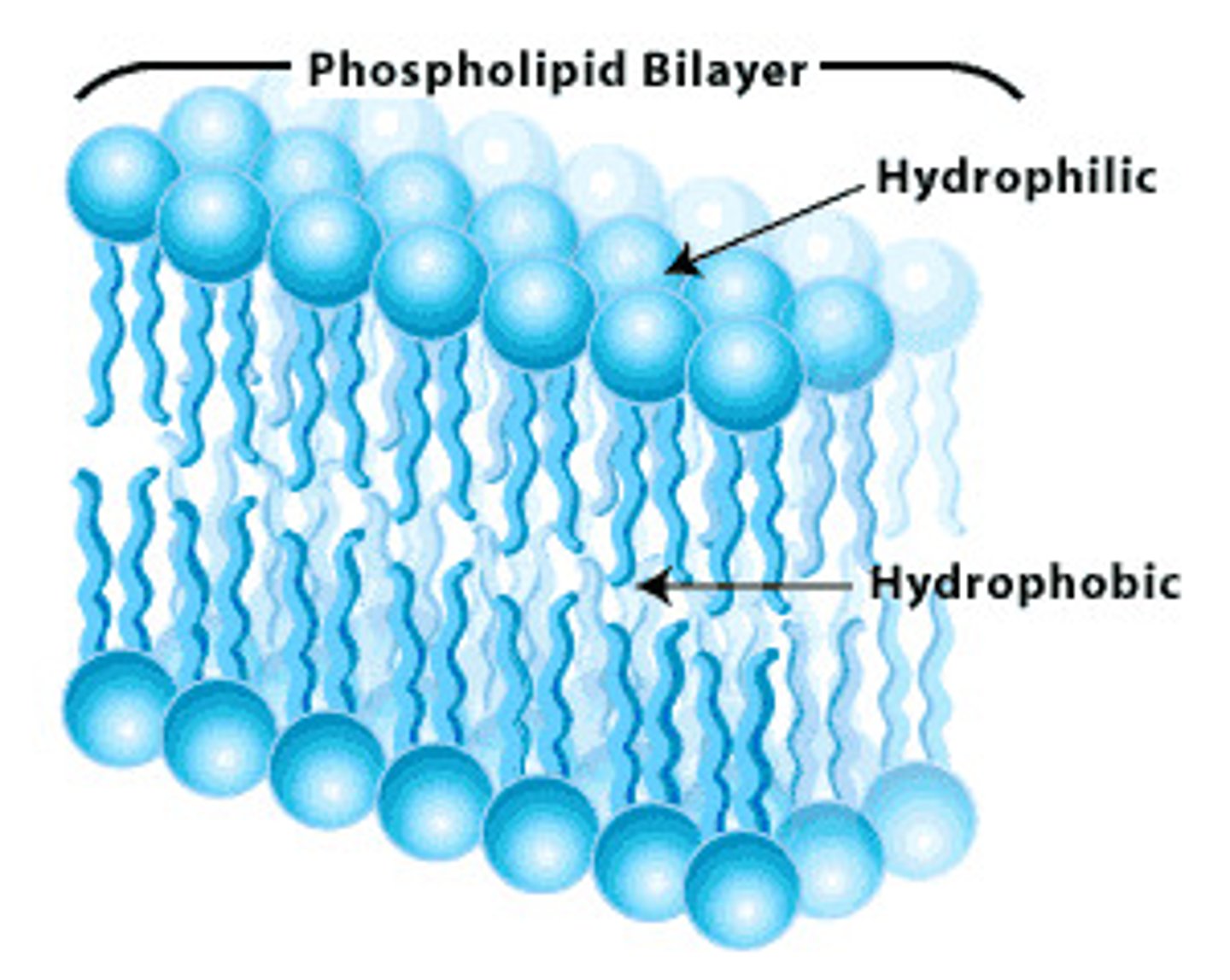
Phospholipids
a lipid consisting of a glycerol bound to two fatty acids and a phosphate group.
Present in the cell membrane: Polar head and non-polar tail
Sterols
lipids with four fused ring carbon skeletons
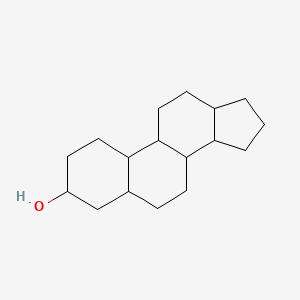
Cholesterol
Sterol common in cell membranes, also in many hormones.
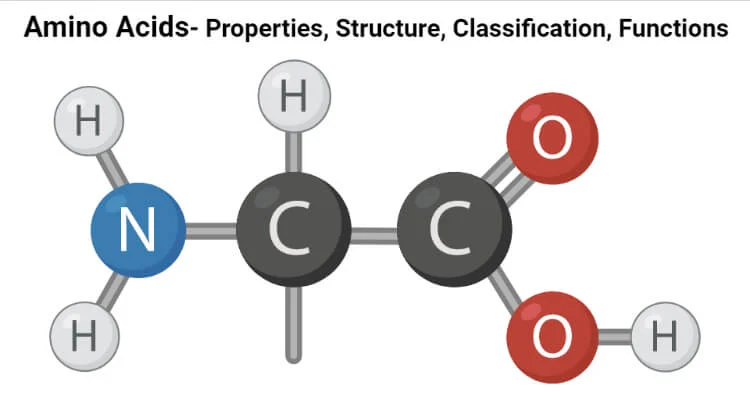
Amino acids
organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups
r group determines its properties
It is a monomer
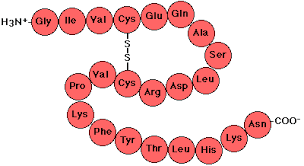
Polypeptides
long chains of amino acids
it is a polymer
Four levels of protein structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
primary structure
sequence of amino acids
secondary structure
Either an alpha helix (coils) or beta pleated sheet (folds) in polypeptide chain. (via H-bonds)
tertiary structure
interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
quaternary structure
Results from two or more polypeptide subunits.
nucleic acids
Polymers of nucleotide monomers.
DNA and RNA
composed of phosphate, 5-carbon sugar, and nitrogen base
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acids
Sugar: Deoxyribose
Double Helix
stores genetic information
(Bases: Guanine, Adenine, Thymine and Cytosine)
RNA
ribonucleic acid
Sugar: Ribose
Single-stranded
helps to make protein
(Bases: Guanine, Adenine, Uracil and Cytosine)
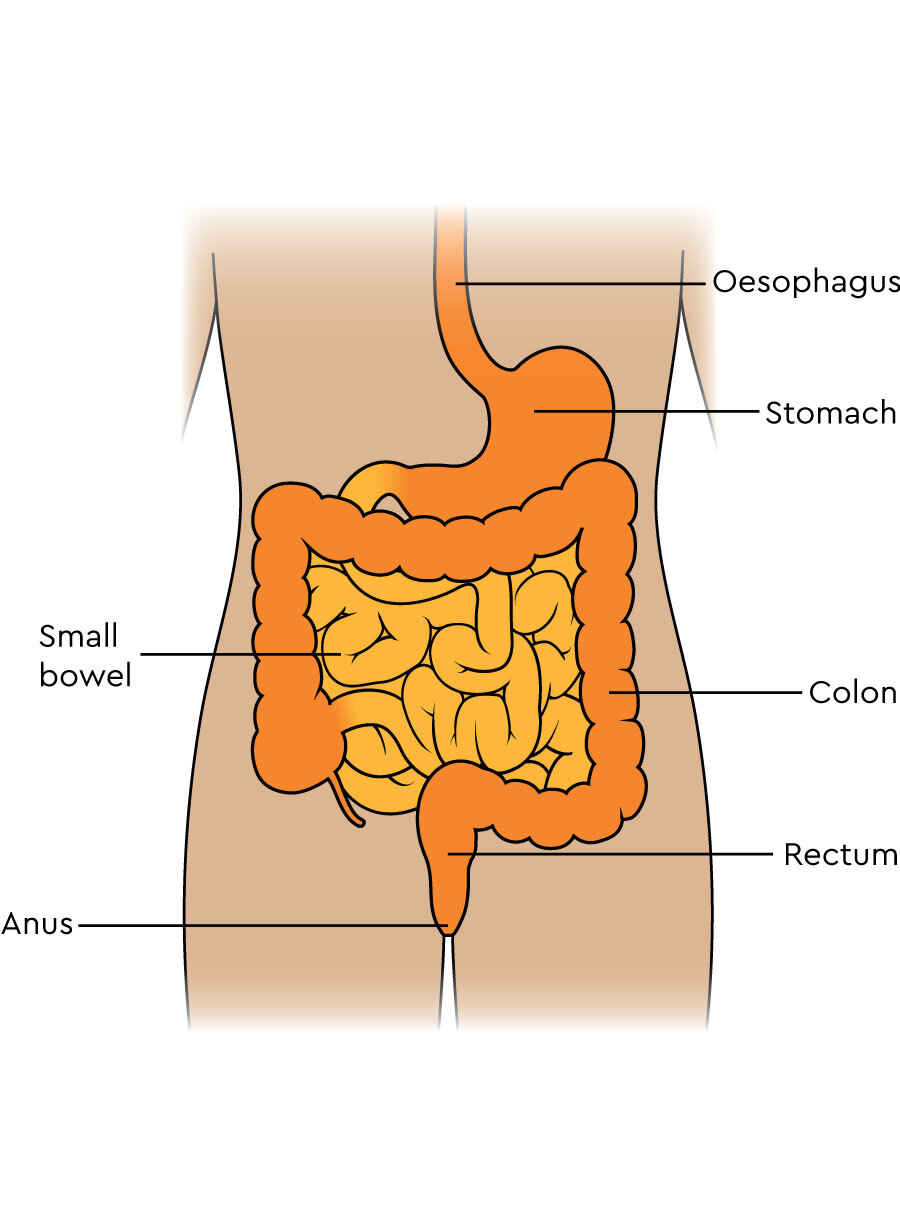
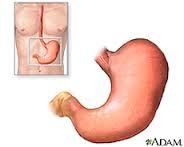
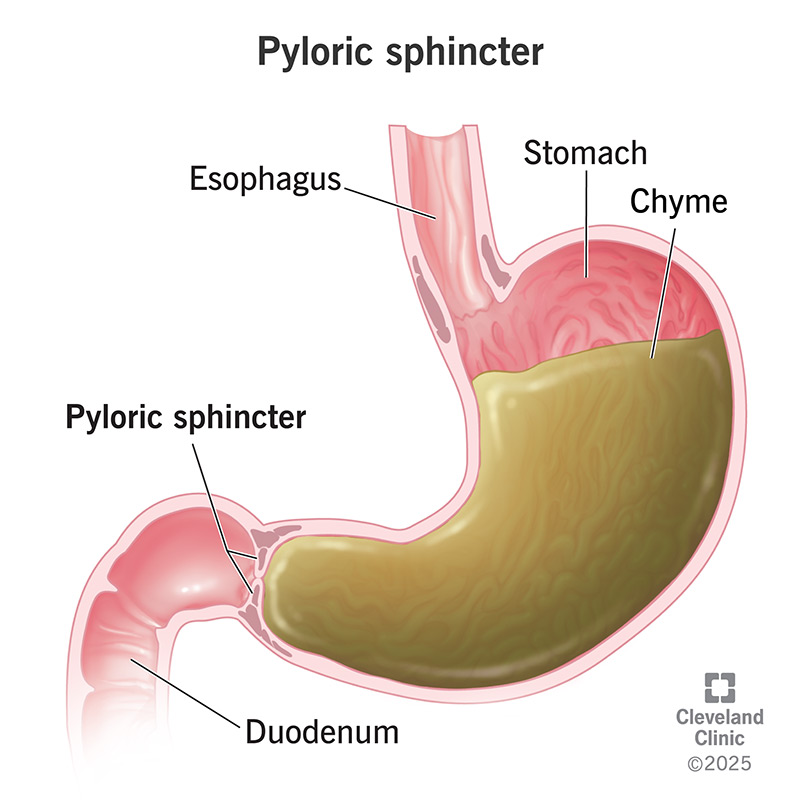
stomach
An organ of the digestive system where mechanical and chemical breaking down of food happens
Mucus lning produces gastric juices, HCl (hydrochloric acid), and pepsin
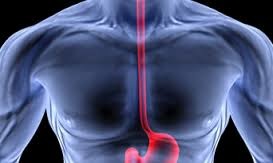
esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach
Performs peristalsis to pump the food through the tube
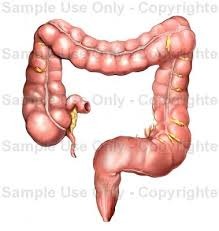
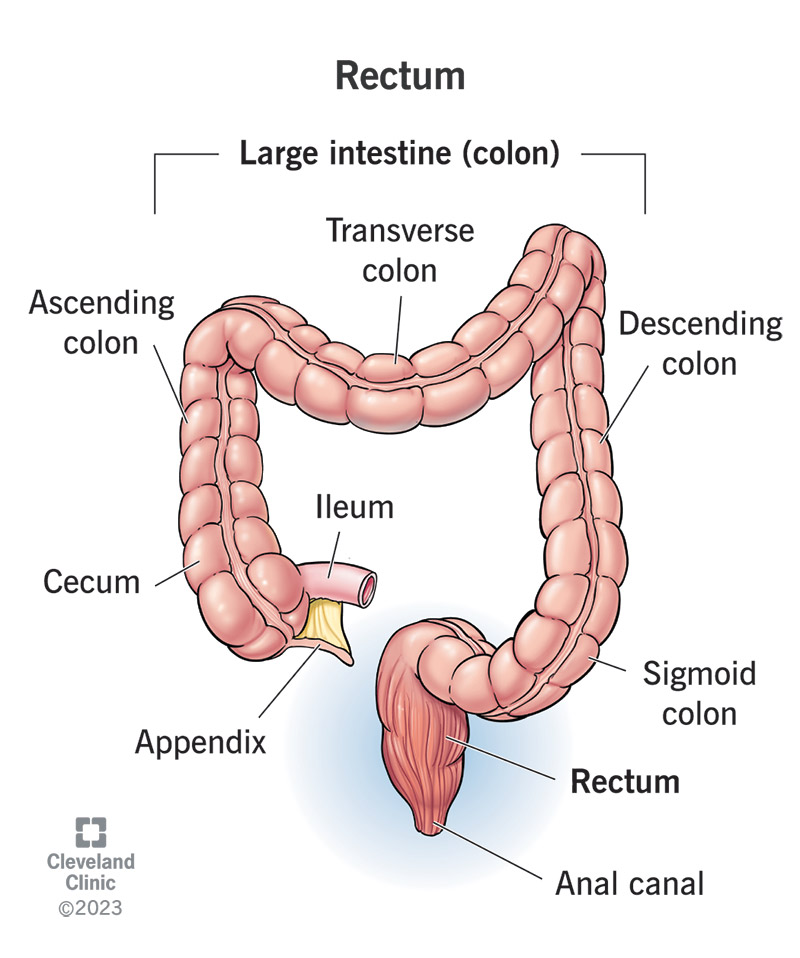
large intestine
Absorbs water and forms feces (hardens it)
Removes toxins
Makes short-chain fatty acids
E.Coli live in here to feed on undigested lactose
Trachea
Windpipe
Helps prevents choking
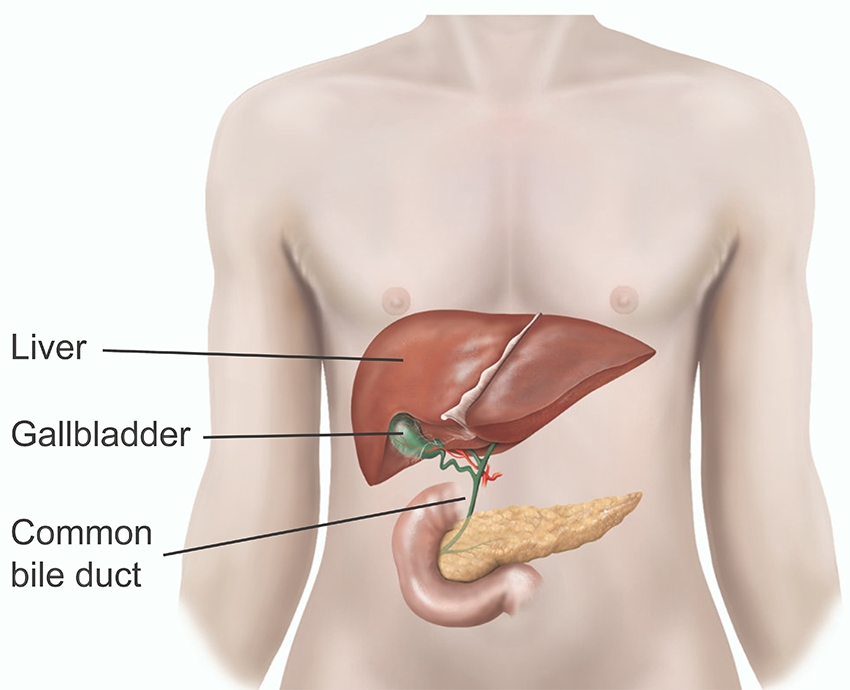
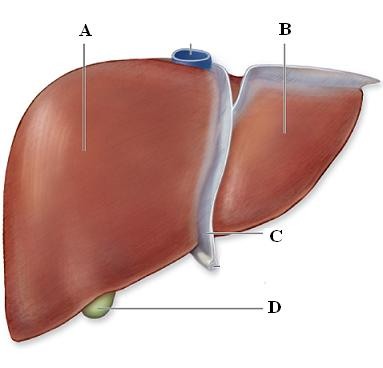
Bile duct
Transports bile from the liver and gall bladder to the small intestine
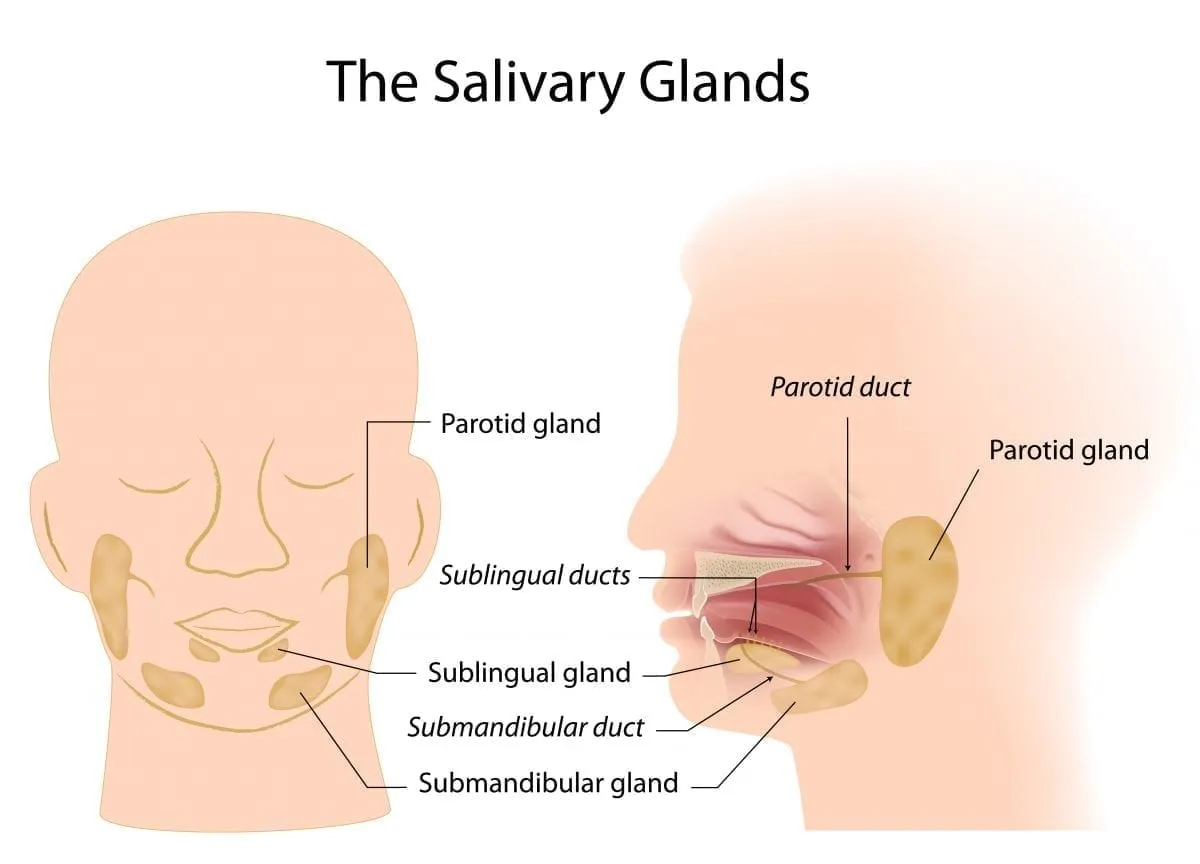
salivary glands
Makes saliva
Lysozymes break down chemical bonds
Saliva breaks down polysaccharides into disaccharides
Starts chemical digestion
Saliva has amylase
Liver
Breaks down and filters toxins
Produces bile
Stores nutrients
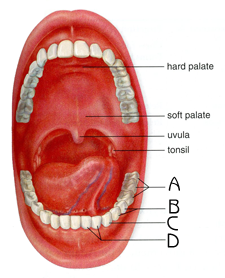
mouth
where digestion begins
small intestine/duodenum
Long hollow tube where most absorption of nutrients occurs
Starts the break down of chyme
Uses bile from liver and gall bladder
Uses trypsin (proteins), lipase (fats), and amylase (carbs) from pancreas
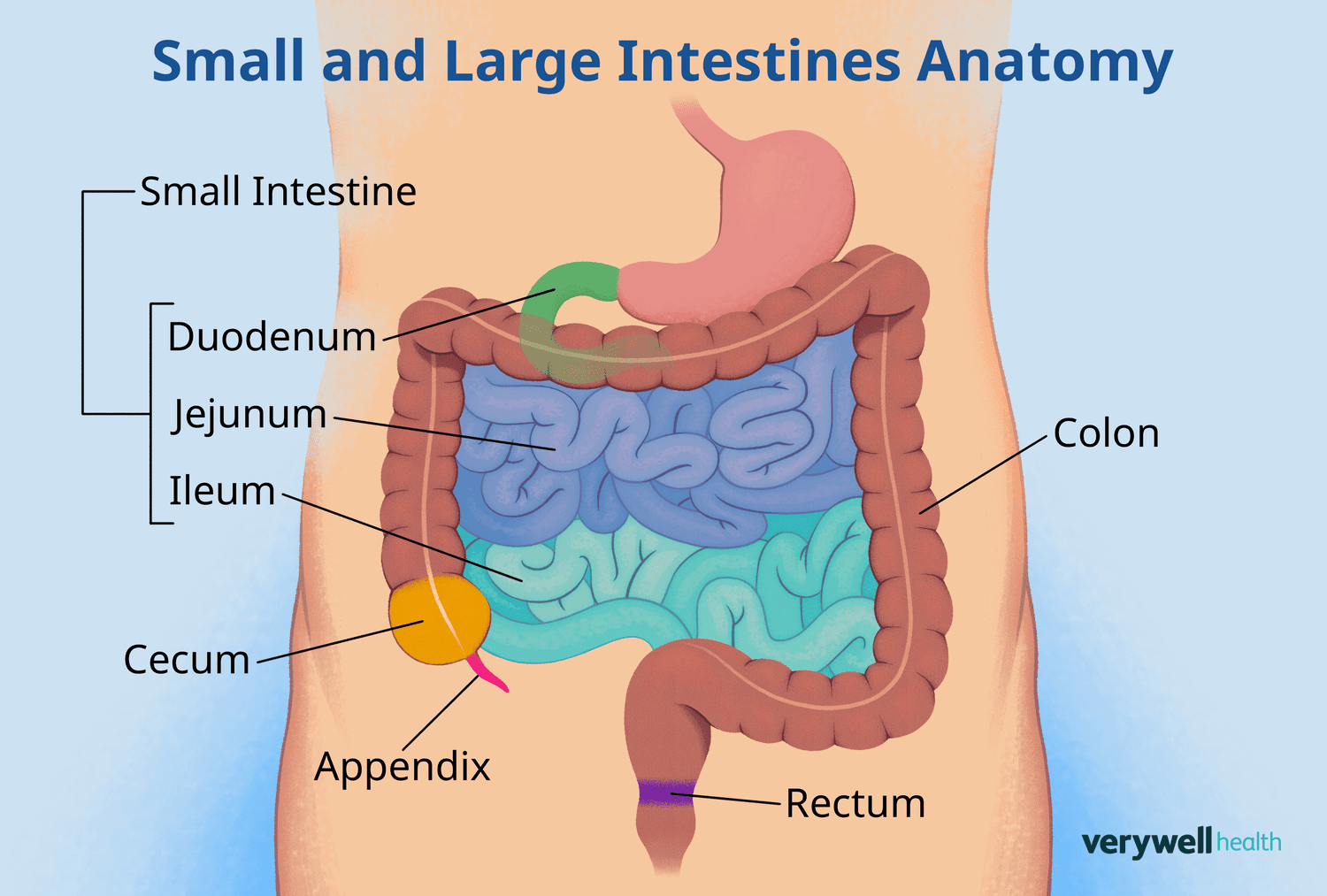
pancreas
Produces amylase to break down carbs in the small intestine
Produces trypsin to break down proteins in the small intestine
Produces lipase to break down fats in the small intestine
Sodium bicarbonate has a high pH, neutralizing the chyme
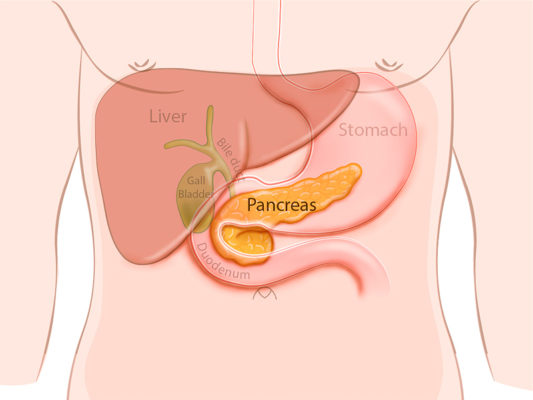
gall bladder
Stores and concentrates bile from the liver and brings it to the bile duct
rectum
stores solid waste and compresses into more solid form
Has 2 sphincters, one where the poop is brought to anus, other is the elimination of poop
Feces made of cellulose and bacteria
chemical digestion
breaking down food with enzymes
mechanical digestion
physically crushing, mashing or breaking down food into smaller pieces
chyme
thick slippery paste of food molecules formed from the broken down pieces of food in the stomach
hydrochloric acid
kills bacteria in stomach and gives an acidic environment for enzymes to work
villi
fingerlike projections in the small intestine that increase surface area
peristalsis
the process of food being pumped through the esophagus
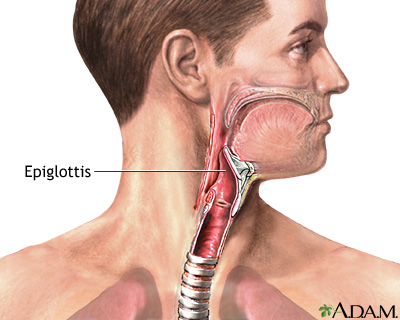
epiglottis
flap of tissue that covers the trachea when swallowing food
Makes sure food and liquids go to the esophagus not the respiratory system
bacteria
organisms found in the large intestine that help with digestion of solid matter
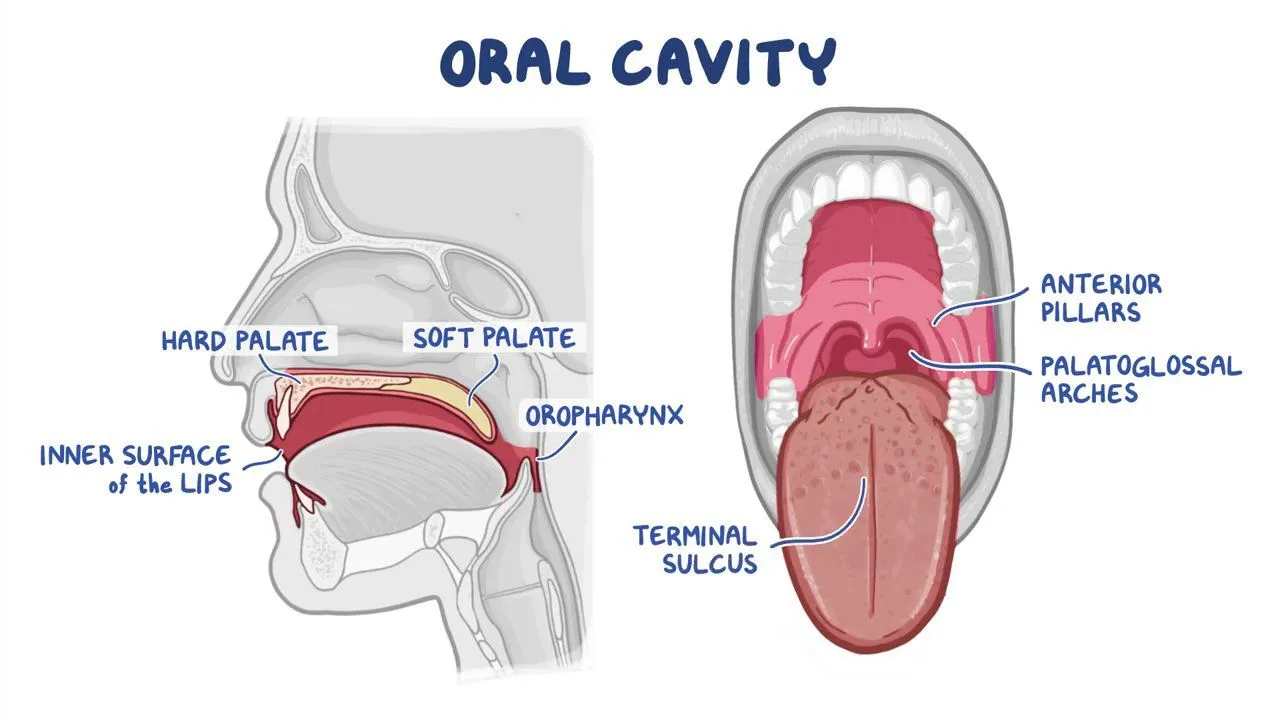
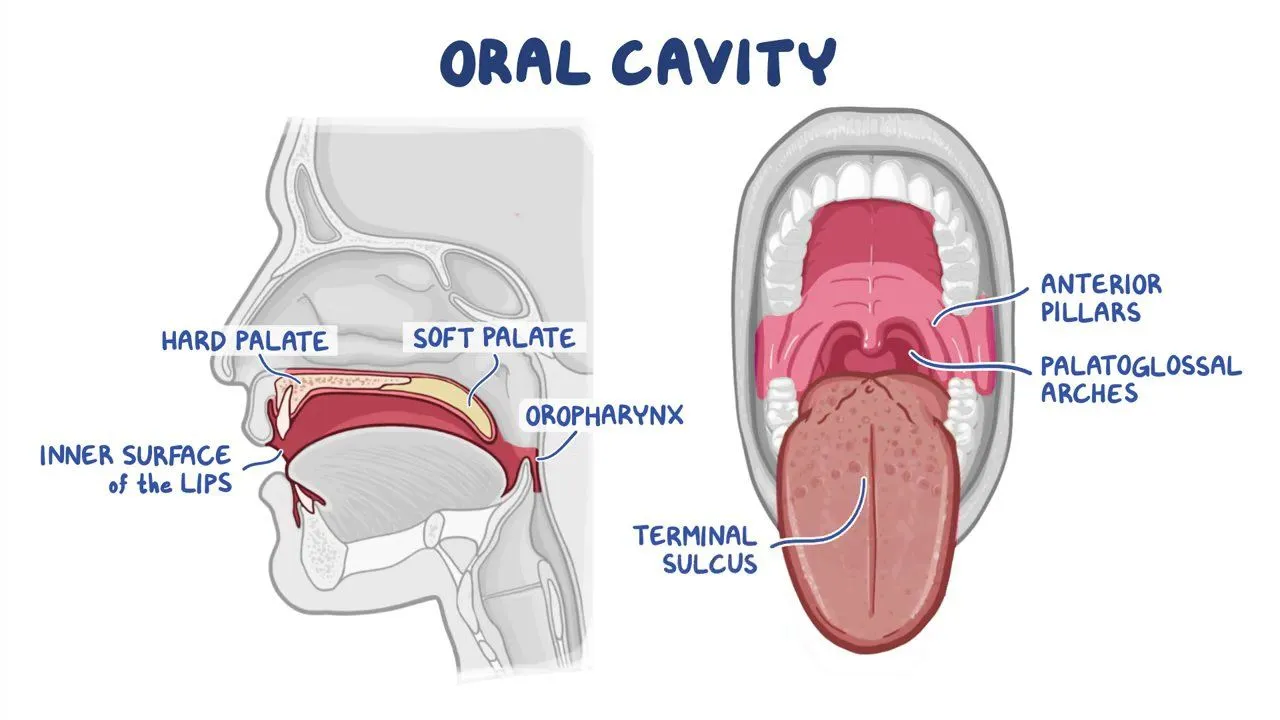
oral cavity
Mechanical and chemical digestion
Uses teeth and enzymes in saliva to break down starches and fats
Substrate is amylose (carbs)
tongue
Helps with mechanical digestion
Moves food around for chewing and swallowing
teeth
Anchored in the jaw
Does most of the mechanical breakdown
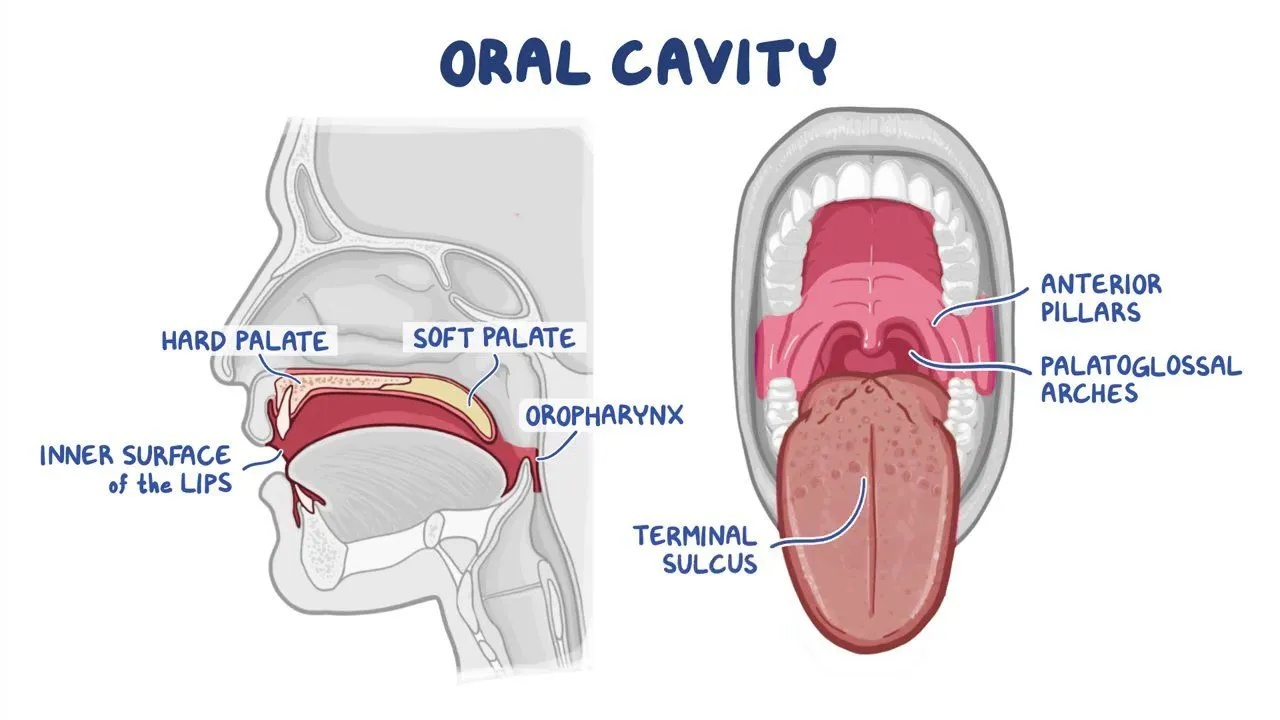
soft palate
Blocks food and liquids from entering the nasal tube when swallowing
Prevents choking
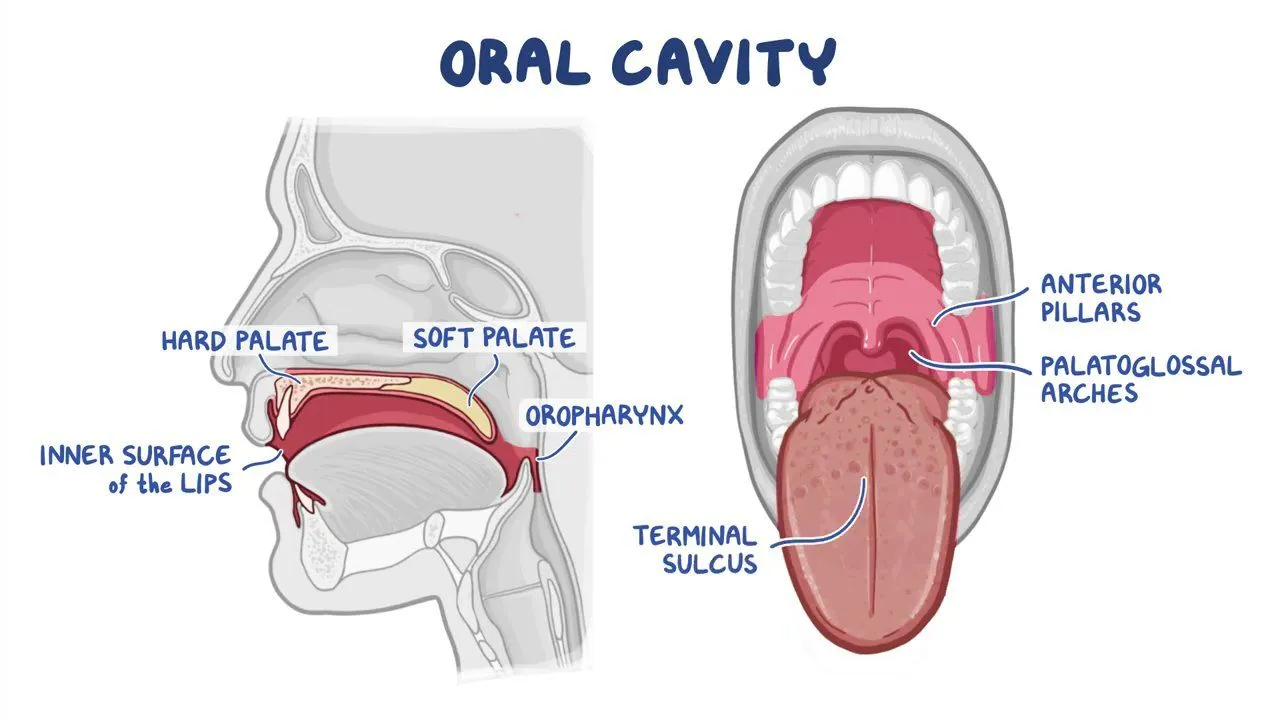
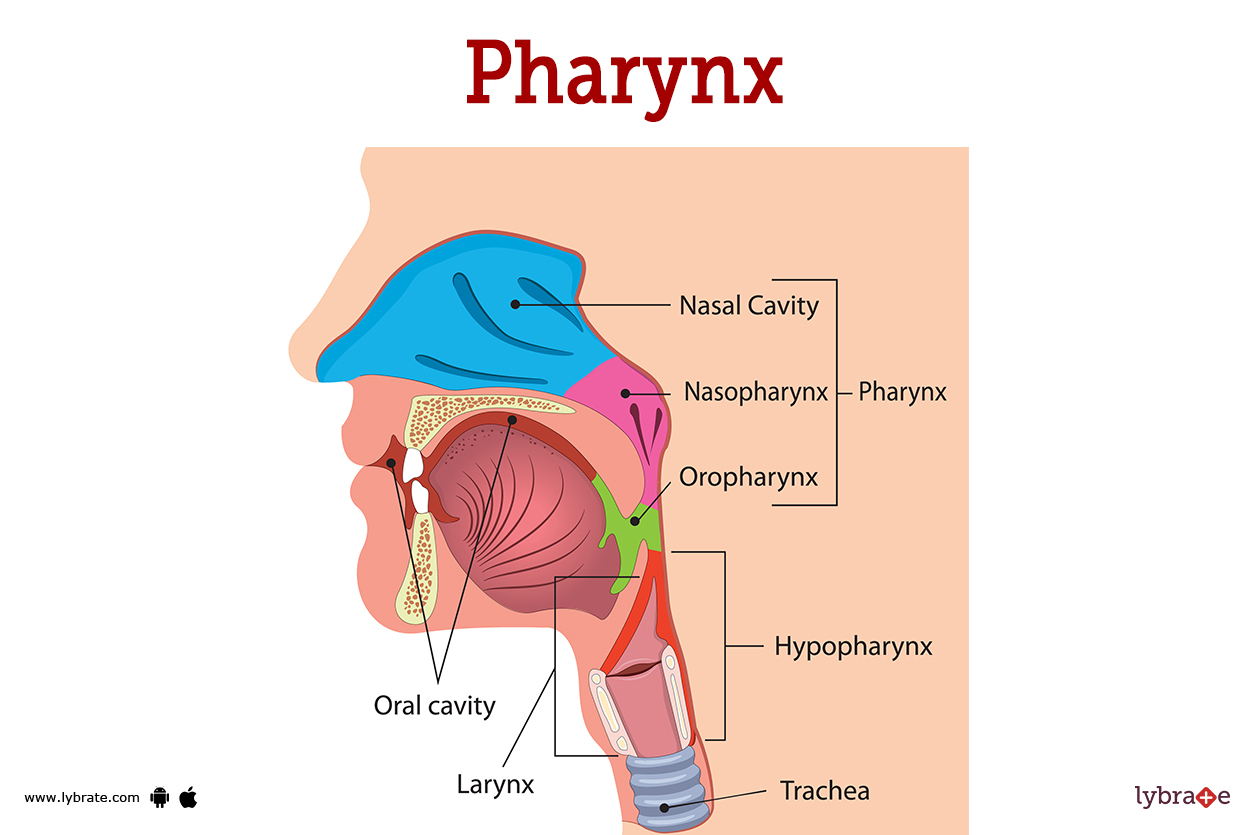
Pharynx/Throat
Tube that connects the mouth or trachea to the esophagus
Pyloric sphincter
Controls the passage of chyme from the stomach to the small intestine
pepsinogen
pre enzyme of pepsin
pepsin
enzyme that helps digest proteins turns proteins into long-chain polypeptides
trypsinogen
pre enzyme to trypsin
trypsin
enzyme used to digest proteins. turns long-chain polypeptides into short-chain polypeptides
Cardiac/Esophageal Sphincter
Prevents chyme in the stomach from going back up the esophagus
Controls what goes from the esophagus into the stomach
cecum
Absorbs fluids and electrolytes
Mixes remaining waste with mucus to lubricate it
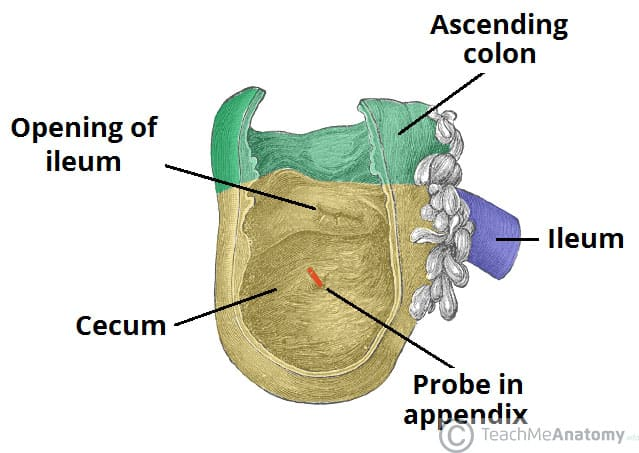
appendix
Regulates the movement through the digestive tract
Produces mucus
Stores and releases bacteria when stressed/ill
Jejunum
Absorbs carbs, proteins, fats, and vitamins from chyme
Has muscular contractions
Where the most absorption happens in the digestive system
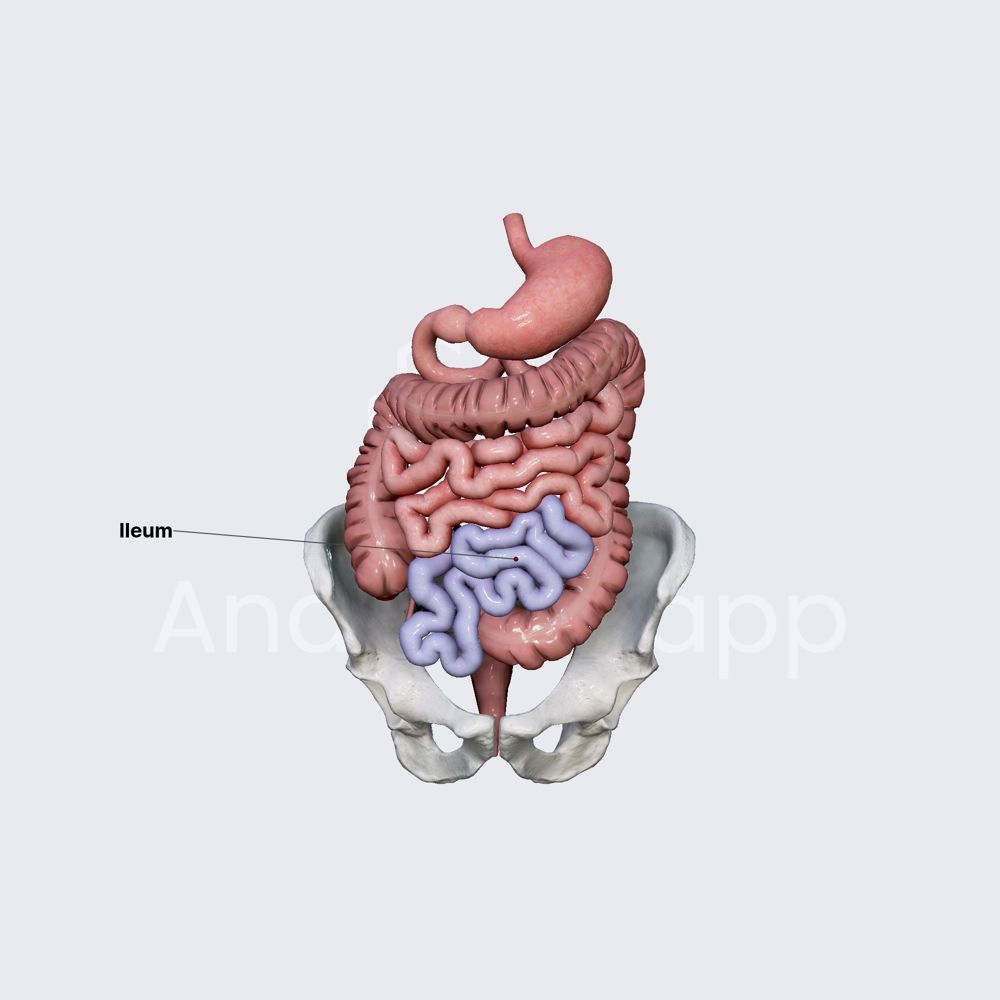
ileum/ileocecal sphincter
Completes absorption of carbs, proteins, fats, water, and vitamins from chyme
Anus
Responsible for eliminating waste products
Holds feces
Has a mucus membrane
Prevents bacteria and pathogens from entering the body