L11 Molecular Symmetry Representations
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
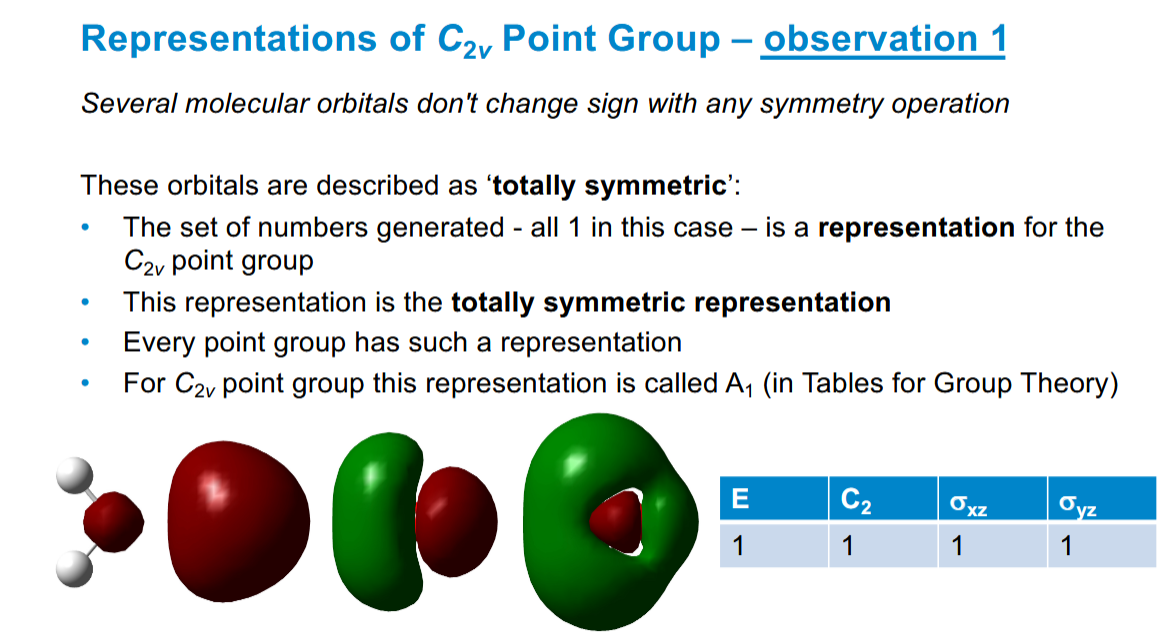
What are totally symmetric orbitals
Don’t change sign with any symmetry operation.
For water’s point group it is called A1
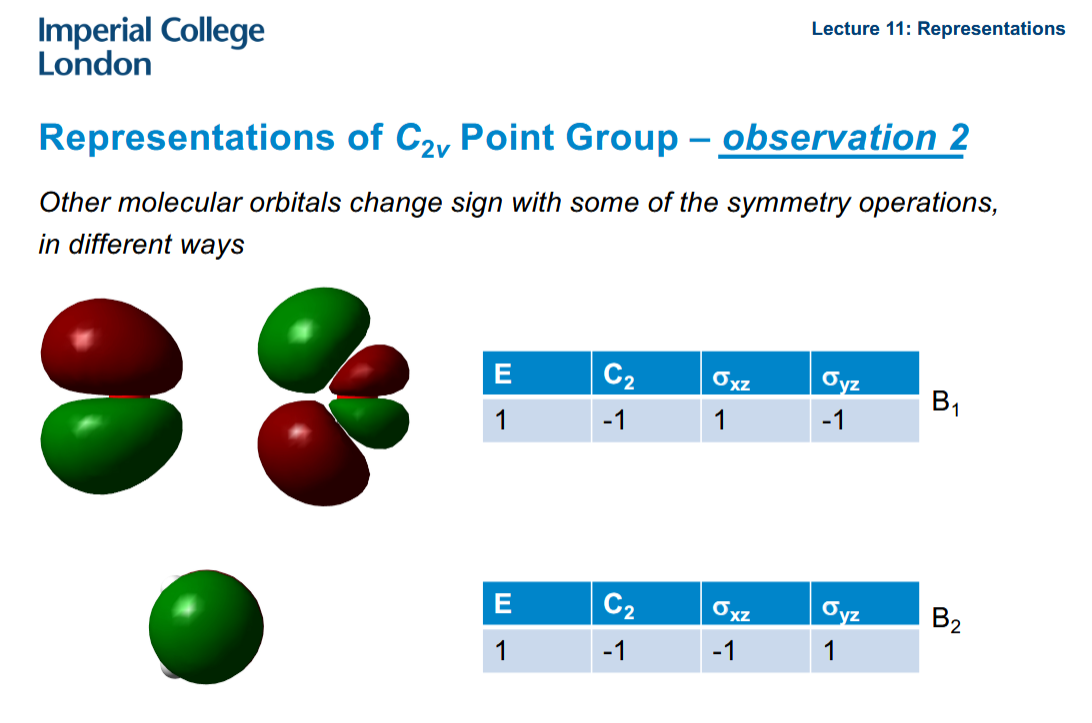
What about the other MOs
They change sign with different symmetry operations. Tables can be drawn out for them and a -1 written whenever a symmetry operation changes their sign. The B implies there is some anti-symmetry as opposed to A. The numbering is just to distinguish.
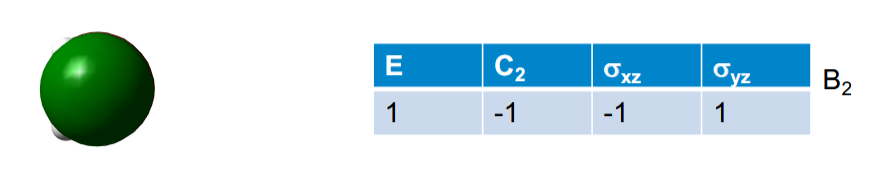
This p orbital has its own symmetry, what does that tell you
That it does not combine with any of the other MOs
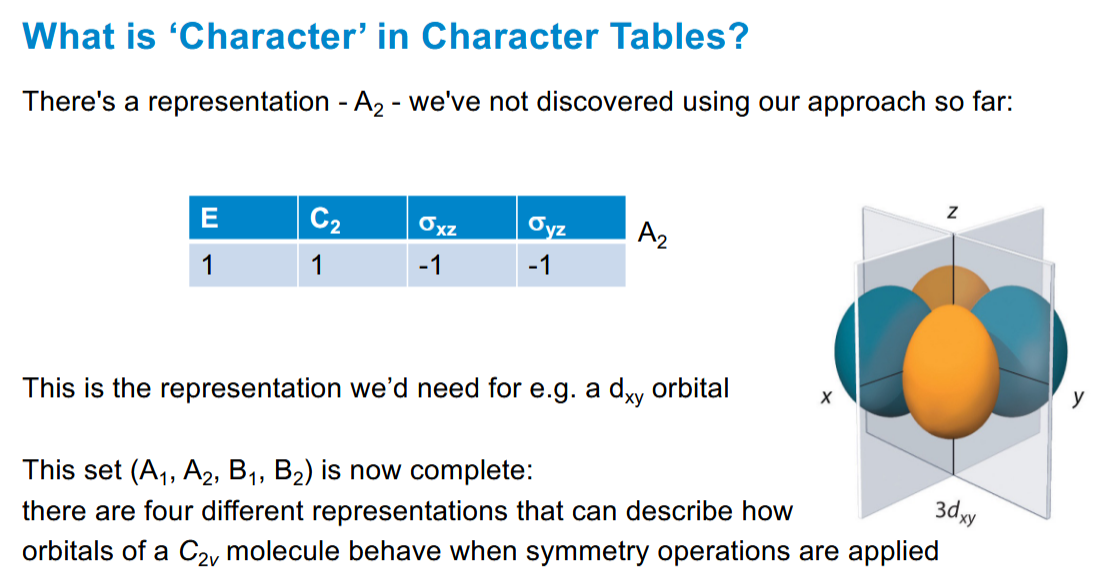
A2 character table
For d orbitals, hence it is not in water
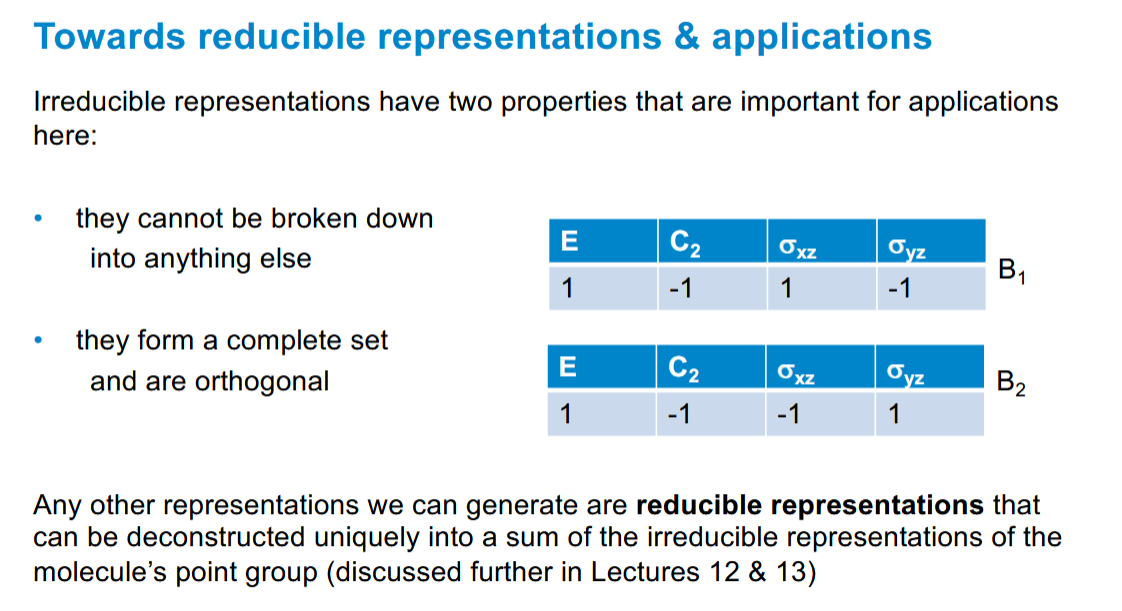
Irreducible representation properties
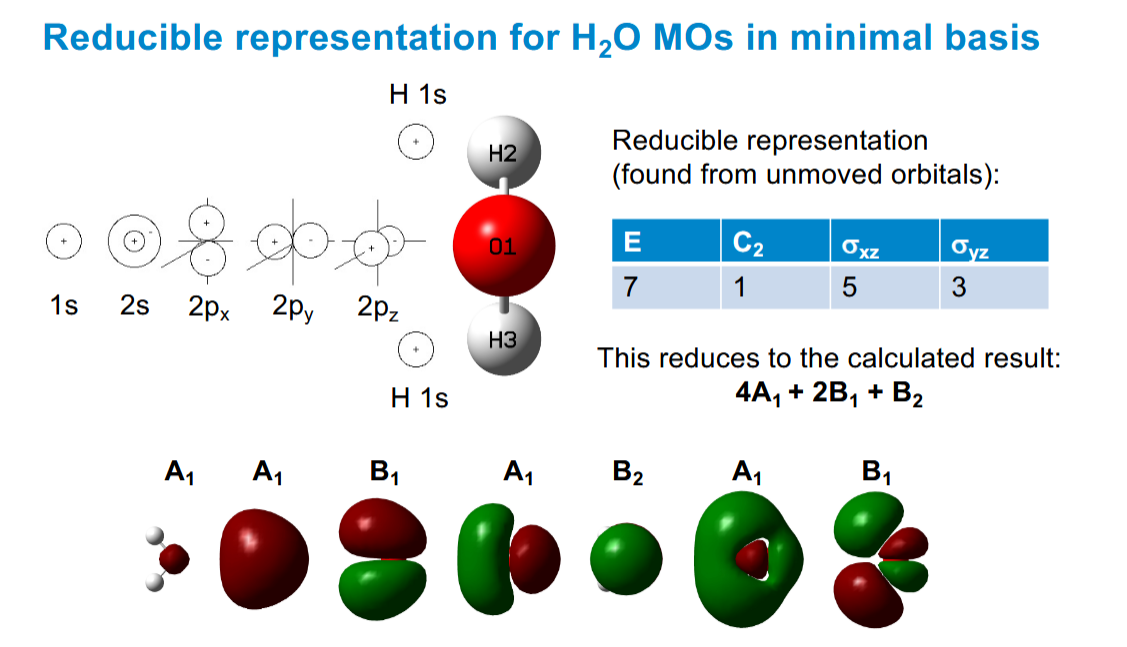
Finding the reducible representation from the atomic orbitals
You can sum up the result of symmetry operations form the atomic orbitals.
Add 1 if the sign does not chnage
Subtract 1 if the sign does change
Ignore it (0) if the orbital moves
Ther planes of symmetry go through the molecule, not the atom on which the orbital is centred.
How does increasing the n of the principal axis affect the irreducible representations
you can have numbers different from 1 and -1. The px and py orbitals can be rotated 90 degrees to give a 0, and they are no longer treated separately
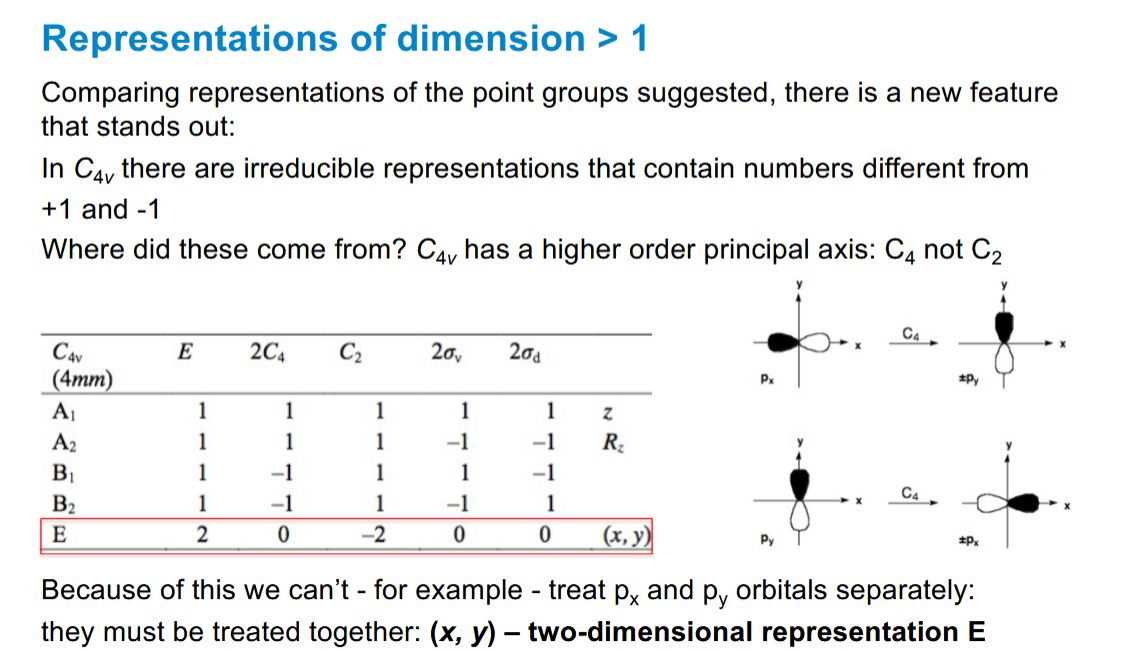
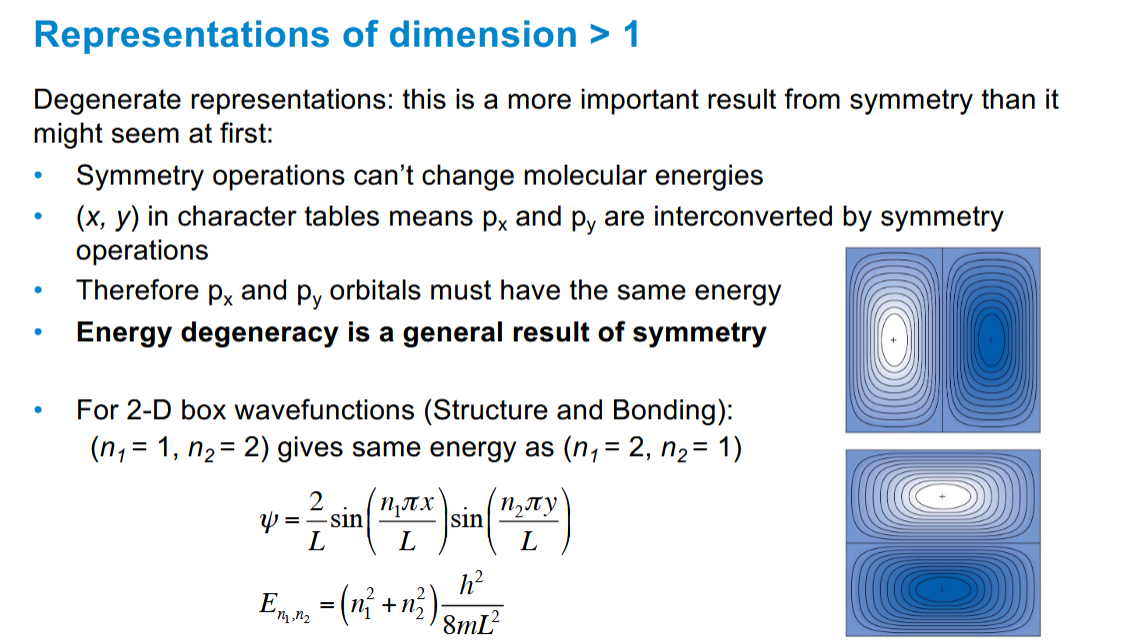
Consequences of x,y being treated together in representations of dimension > 1

Energy degeneracy relation to symmetry