L7 Language and Education
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What are the three components of language?
Form ⇒ syntax (grammar - rules for forming sentences), morphology, phonology
Content ⇒ semantics (meaning of words & sentences)
Use ⇒ pragmatics (how language is used appropriately in diff social contexts)
What is the difference between phonemes and morphemes? What is prosody?
Phonemes ⇒ basic units of sound that can change the meaning of a word
Morphemes ⇒ basic units of meaning that exist in a word (e.g. prefixes, roots, suffixes, or radicals in Chinese characters)
Prosody ⇒ melody of speech (e.g. pitch, intonation, pauses)
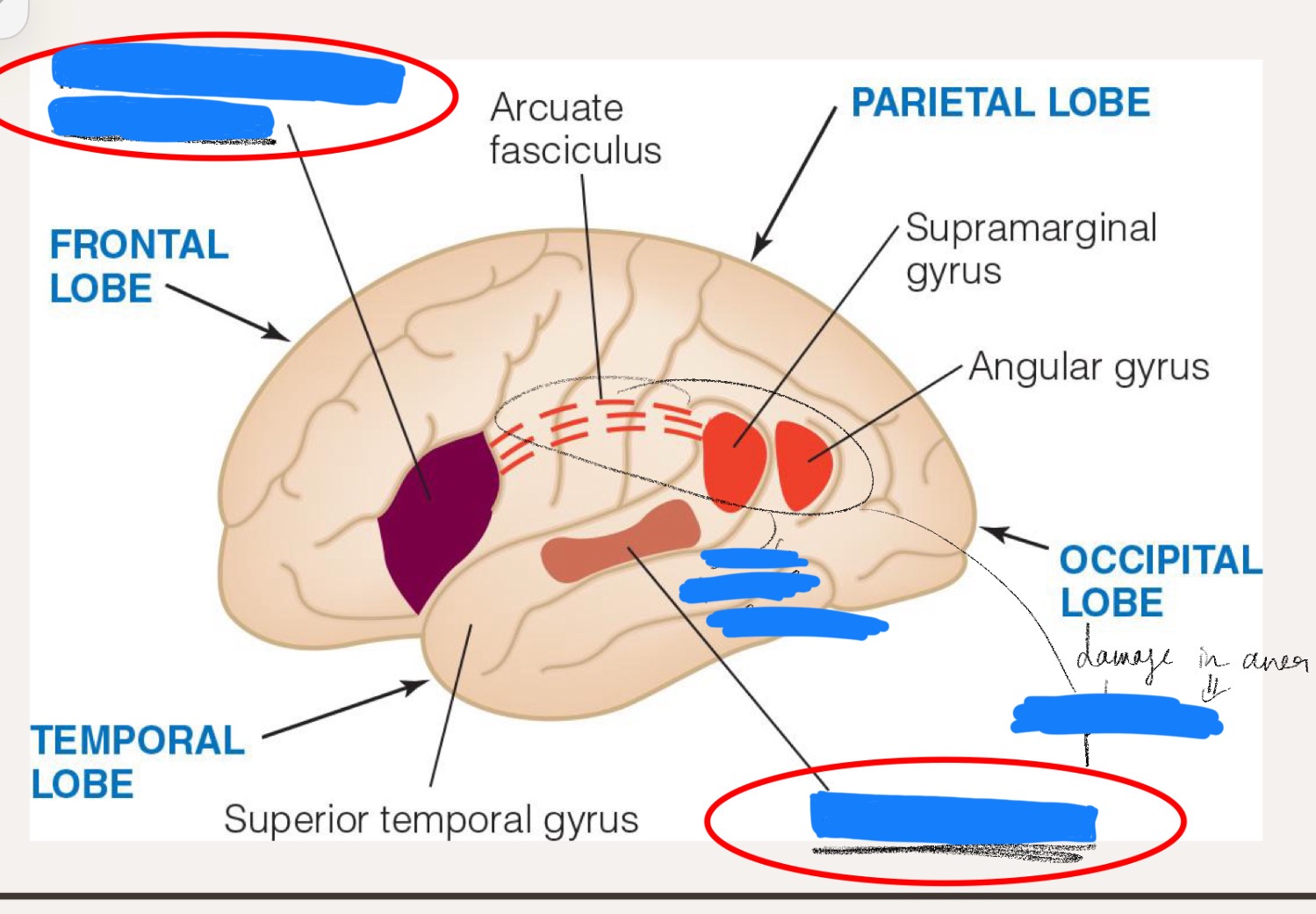
Fill in the blanks
Broca’s area (frontal area of left hemisphere - inferior frontal gyrus)
Broca’s aphasia = difficulty in speech articulation
Wernicke’s area (temporal lobe)
Wernicke’s aphasia = difficulty in speech comprehension
__________ connects Wernicke’s and Broca’s area
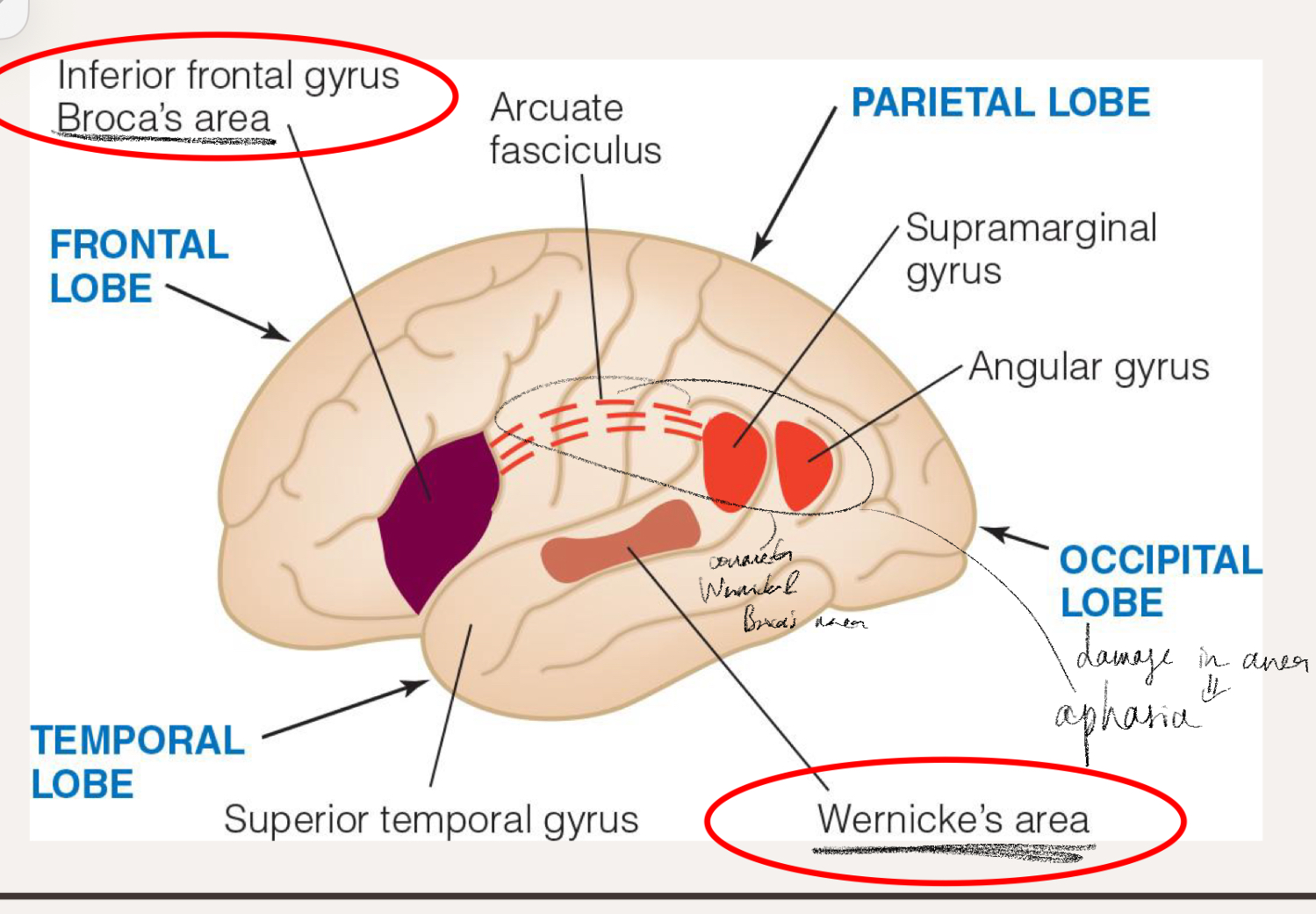
What is the general localisation of auditory functions for each hemisphere?
Left hemisphere ⇒ listening to speech
Right hemisphere ⇒ processing speech
Within the theories of nature and nurture, which supports the “nature” perspective?
Universal grammar ⇒ idea that there is a system of common rules and properties for learning any of the world’s languages
Language Acquisition Device ⇒ proposed that all people have LAD, though there is no specific associated brain region
LAD is area of brain that sifts through language, applies universal rules, and tailors system to specifics of language spoken in young child’s development
Nativist theory of language acquisition ⇒ children learn native language with ease due to innate biological/genetic predisposition
Within the theories of nature and nurture, which supports the “nurture” perspective?
Poverty of the stimulus ⇒ env stimulus of language input can be impoverished to support (activate LAD) the linguistic output that emerges
Learning perspective
observational learning - children learn words they hear spoken by others
operant conditioning - more likely to use new words if reinforced
Professional vs welfare family - amount of child-directed speech
What does the interactionist perspective say about language acquisition?
Biologically based competencies and lang env interact to shape lang development
Similar as Piaget/Vygotsky
lang dev depends on maturation of cog abilities + social interactions w adults contribute to dev
What is the name for special education needs related to language development?
Speech and Language Impairment (SLI) or Developmental Language Disorder (DSD)
not associated w known biomedical condition
What are the four categories of SLI?
articulation problems (speech sound disorder) - pronunciation issues
language problems (language disorder) - difficulty in comprehension and expression
fluency problem (fluency disorder) - stuttering
voice problem (voice disorder) - loss of voice, difficulty in volume control, etc

What are the neural bases of SLI?
inferior frontal gyrus
caudate nucleus
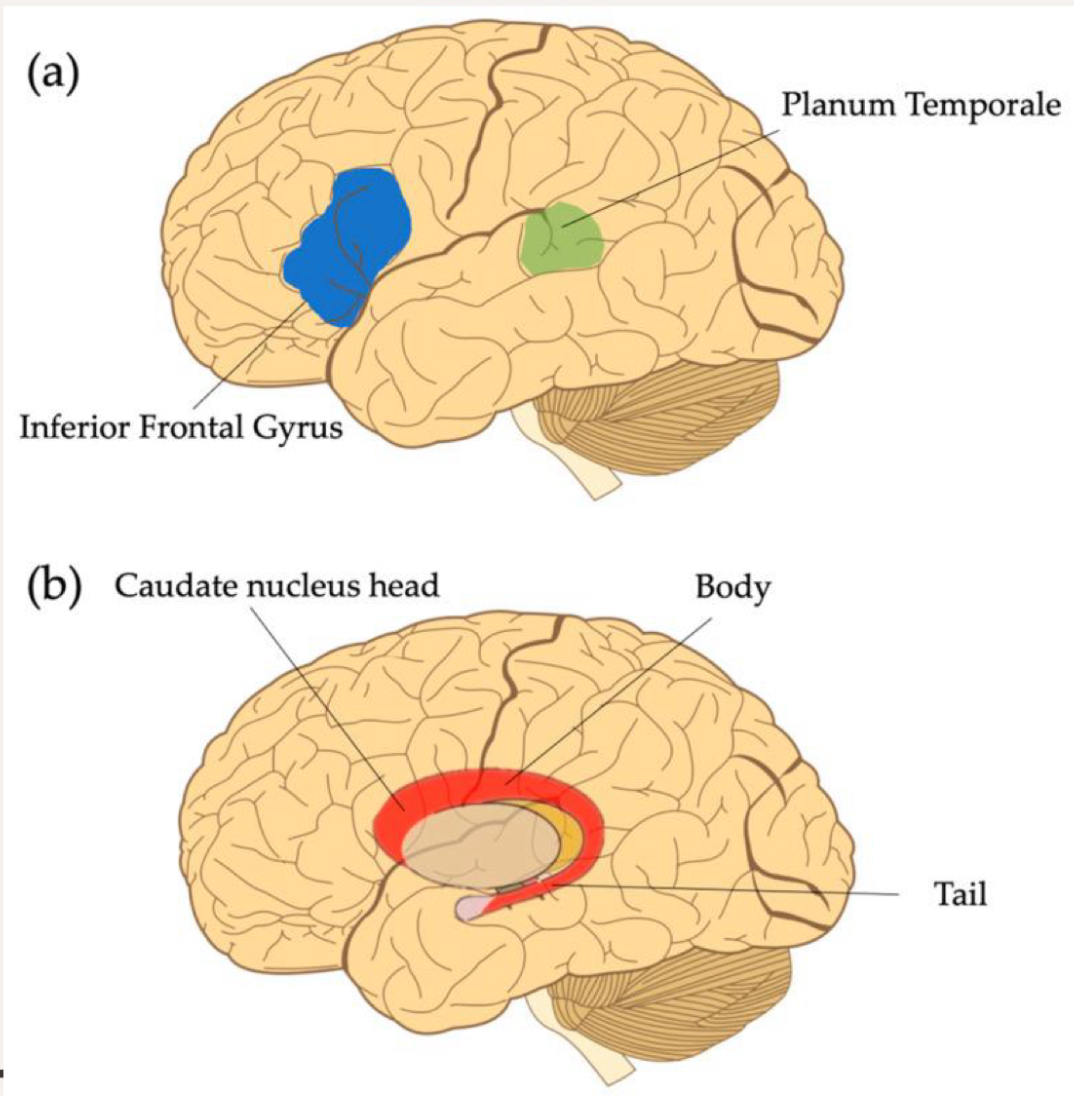
What kind of language disorder is dyslexia?
reading + visual/perceptive difficulties in reading (+ writing depending on cultural context)
specific learning disorder in DSM5 ⇒ 80% is dyslexia
prevalence of 10% globally
neurodevelopmental disorder
more cognitive resources and working memory
brain region: broca’s area, inferior frontal gyrus
Describe the stages of language development for babies
Birth - communicate through any sound
0-2 m/o - cooing
3-4 m/o - consonant sounds
4-6 m/o - babbling
7-12 m/o - word segregation (detect target word in stream of speech)
12 m/o - social and linguistic cues used (joint attention, syntactic bootstrapping), goes from receptive vocab → expressive vocab (choosing word from picture → showing picture to label)
first words (usually noun > verb)
12-18 m/o - holophrases (single word that functions as a complete phrase or sentence)
18-24 m/o - rapid expansion in vocab, telegraphic speech (early combination of 2-3 words), functional grammar (emphasis on semantics, meanings being expressed)
When does culture-bound listening begin to emerge?
between 6-8 m/o - infants can recognise sound changes regardless of language
culture-bound listening begins to develop at 10 m/o
What kind of mistakes do children make when first developing their language skills?
over extension - applying broader word category
under extension - referring to specific subset within broad category
over-regulation - over applying syntactic/language rules
What is mastery motivation and what does it impact?
striving for mastery - inborn & universal
some infants are more mastery oriented than others
affects later achievement behaviour
babies who attempt to master challenges at 6-12 m/o score higher on mental dev tests at 2 y/o
What effect does babies watching educational videos have on their language abilities?
for each hour spend watching videos, babies understood 6-8 fewer words
What effects does educational preschool programmes have on toddlers?
provides initial adv in basic academic skills
ultimately depends on quality of programme
sometimes may result in child being less creative and more anxious in test conditions
What kind of preschool programmes are the most beneficial?
programmes w mix of play and academic activities
Abecedarian Project → children showed cognitive gains during and after, completed more years of education than control
What conditions allow for early education to have positive effects?
stimulates cognitive growth
provides programming for parents
includes follow up in elementary school (to facilitate transition)
full-day programmes (routine, help w transition)
allow time for play and social interaction
What “awareness” increases during middle childhood?
metalinguistic awareness
knowledge of lang as a system
concept of words
defining words
grammar