Stoichiometry
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
What does the ‘amount of substance’ mean?
-Number of moles e.g. n(Cl)= amount or moles of chlorine atoms
How many molecules does 1 mole of ANY substance contain? What is the mass of 1 mole of a substance?
6.022×1023 molecules (Avogadro’s constant)
the mass of 1 mole of a substance= its Mr e.g. 148g is its mass
Give the 4 equations for calculating amount of substance
C1V1+C2V2=total amount/moles
amount is in g. conc in g/L unless m/m, w/w etc
e.g. ‘amount of aspirin in solution’=CxV

The radioactive isotope technetium-99m is widely used in radiopharmacy. A typical technetium injection might contain 2.5×1012 entities of sodium pertechnetate (NaTCO4 Mr=185.99). Calculate the mass and amount of sodium pertechnetate used.
amount=4.15×10-12 mol
mass= 7.72×10-10 g
You have 0.5mol sodium sulphate decahydrate (Na2SO4.10H2O). Calculate the amount of water. Mr(H2O)=18.015
-for every 1 mole of Na2SO4, there are 10 moles of H2O (in terms of ratio). So, amount of H2O= 0.5molx10=5 mol
-answer=5mol
State the unit conversions for cm3,dm3,ml and L
cm3=ml
dm3=L
1dm3=1000cm3
Give the 3 equations for calculating concentration
C1V1=C2V2

Calculate the amount of sodium in 10mL of a 0.1 m sodium sulphate (Na2SO4) solution
-amount concentration=n/v
-but we want amount of sodium.
amount= moles
amount of sodium= cv= 0.1×0.01=1×10^-3 mol BUT there are 2 Na’s in Na2SO4, so answerx2= 2×10^-3mol
mol=mol
m=concentration
25mL of a 0.30m sodium chloride solution, plus 50mL of a 0.15m sodium chloride solution are mixed together. Calculate the total amount of sodium chloride and the concentration of the final solution
c1v1+c2v2 to find total amount/moles (because CxV=mol). Always convert mL to L
(0.30×0.025)+(0.15×0.05)=0.015mol
concentration= moles/volume (this equation because we haven’t been given mass. 0.015/(0.05+0.025) [total vol of sol.]=0.20M
When you calculate conc., answer is M not m usually
What equation should you always remember in calculations?
C1V1=C2V2 or C1V1+C2V2=total amount/moles
1.775g of a pure sample of potassium iodate (KIO3) was dissolved in water and made up to 500mL with water. Calculate the molarity of the solution.
-molarity=g/L=concentration
-mol=mass/Mr=1.7753g/214.001=8.29576×10-3mol
-molarity=moles/vol=moles/0.5L
ALWAYS L
this is molarity!!!
10mmol of glucose was dissolved in water to give 25mL of solution. The solution was then divided into 5mL aliquots. Calculate the glucose concentration and amount of glucose in an aliquot.
-concentration of glucose=mol/vol=0.01/0.025=0.4M
-Dividing a solution into aliquots does NOT affect concentration. It’s the same in all of them.
-amount of glucose=moles=CxV=0.4Mx0.005L=0.002mol
How do you calculate %m/m (percentage of mass in mass)?
mass of substance/mass of sample x1001.4326g of a zinc oxide and salicylic acid paste was found to contain 0.3425g of zinc oxide. What is the percentage of zinc oxide in the sample?
%zinc oxide=mass of zinc oxide/mass of sample x100
0.3425/1.4326 x100=23.91%m/m
How do you calculate %m/v (percentage of mass in vol)?
mass of substance(g)/volume of solution(L) x100
How do you calculate %v/v?
volume of substance/volume of mixture x100
What does this mean in terms of volume: 1:5 ?
1ml in total vol of 6ml
What does 1 in 5 mean in terms of volume?
-1ml in 5ml NOT the same as 1:5
What are the 8 factors that affect the success of a chemical reaction/percentage yield?
-the reaction conditions (e.g. temperature, pressure, time, solvent)
-choice of reactants and reagents
-properties of starting material
-activation energy of chemical reaction
-stability of the starting materials and products
-side reactions
-ease and efficiency of product isolation
-operator-related factors e.g. loses due to handling etc
How do you calculate percentage yield? (2)
-moles of actual/moles of theoretical x100
or molarity or mass
OR moles of product/moles of limiting reagent x100
What 3 factors could cause a percentage yield of greater than 100% (even though it should be less than or equal to 100%)?
-contamination of the product
-the product isn’t dry
-weighing error
What is the concentration of water in water?
55.56M
Give the equation that links mass, density and volume?
mass (g)=density(g/mL)x volume (mL)
How do you calculate the number of molecules?
number of molesx A.C
What are convergent reactions?
-When 2 products from 2 different reactions combine together to form a new product.
-not all reactions are linear i.e. A—→B——>C
If the yield for each step is 90%, what’s the overall yield?:
A——→B——>C——>D——>E——>F
0.9×0.9×0.9×0.9×0.9 x100= 59% (because there’s 5 arrows)
If the yield of the first step is 50% and the other steps is 90%, what is the overall yield?:
A——>B——>C——>D——>E———>F
33%
DO NOT DO 0.9X4… you do 0.5x(0.9^4)
What is an indicator? What is the aim of an indicator?
-a chemical added into a chemical reaction that changes colour depending on the conditions of the reaction.
-the aim is to for the indicator to change colour (end-point) as close as possible to the equivalence point. The difference between the equivalence point and endpoint is known as titration error.
What is equivalence point?
-The point at which the chemical reaction stops and the moles of the two reacting solutions are equal. All the unknown has reacted with all the standard
What is endpoint?
-the stage in the titration when the colour change from the indicator occurs.
What is titration?
-the slow addition of one solution of a known concentration (called a titrant) to a known volume of another solution of unknown concentration (titrand) until the reaction reaches neutralization in order to determine the volume of the titrant needed to react with the titrand.
What is a titrant?
-the solution with the known concentration in the titration
What is a standard solution (or volumetric standard)?
-solutions with a known concentration (titrants are solutions with a known conc. in the titration but ss is in general).
What is a primary standard?
-a pure substance that is used to create a standard solution.
What are the 6 requirements that substances should have to be used as a primary standard (which most of them don’t)?
-more than 99.9% m/m purity
-heat-stable so that they may be dried. This allows any moisture absorbed to be removed
-don’t absorb/react with water or CO2 or anything else from the air
-have a high molecular mass so that weighing errors are small
-readily soluble in solvent for titration
-easily tested for impurities
What is a secondary standard?
-a material or solution used that has a known concentration or quality, but its accuracy has been determined by comparing it to a primary standard. Gets its value from being checked against a more reliable, main measurement.
What are the 4 main types of reactions that can be involved in titrations?
-acid-base reactions
-redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions
-complexation reaction
-precipitation
What is an acid-base reaction?
acid+base——>salt+H2O
What is acidimetry?
-the titration of free bases with a standard acid
What is alkalimetry?
-the titration of a free acid with a standard base
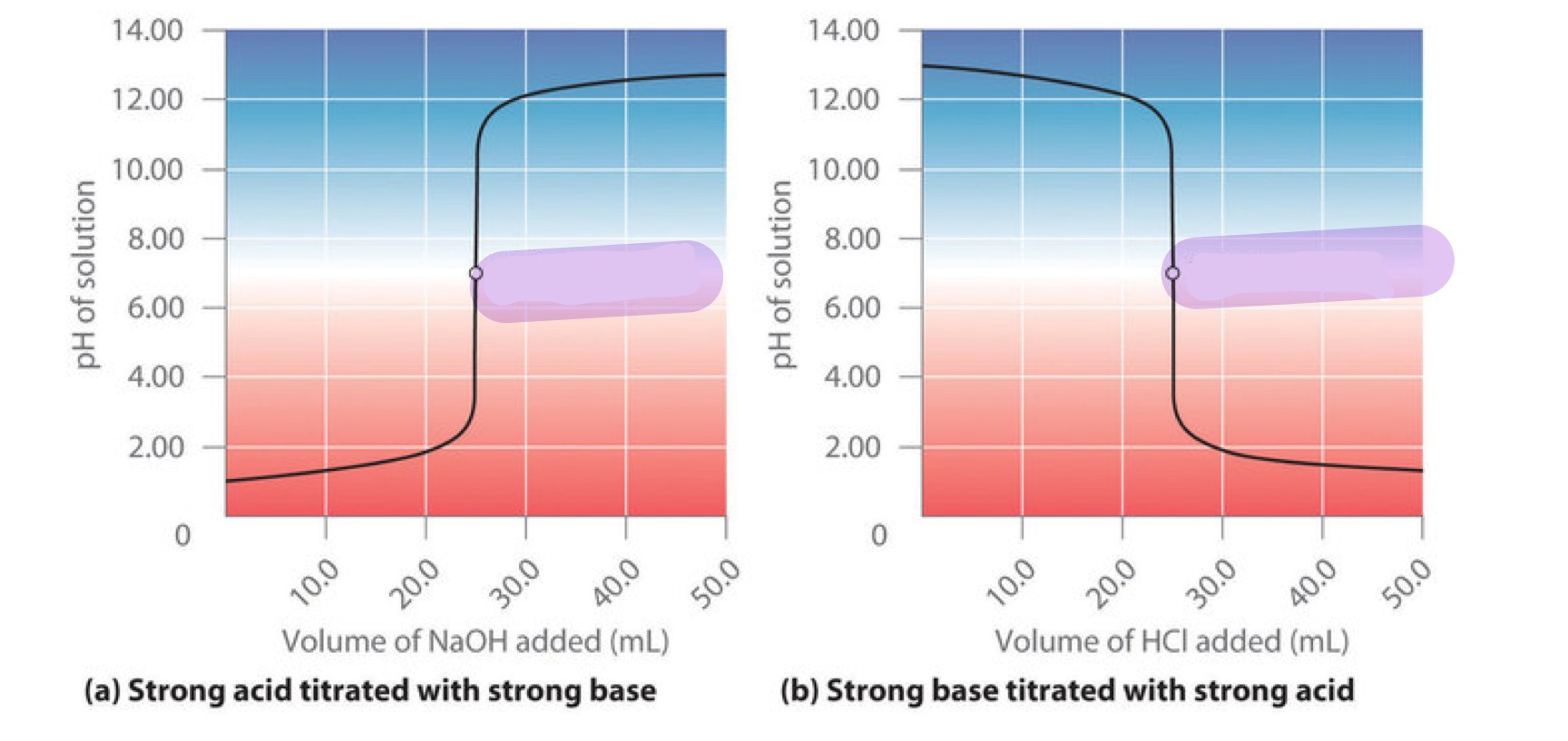
label this graph
equivalence point
What is a redox reaction?
-one component is being reduced and the other oxidised.


What is a complexometric reaction?
-a reaction where a complex is formed as a result of a metal ion and chelating agent reacting

What is a precipitation reaction?
e.g. Ag+ + Cl- ——>AgCl (s)
What are argentometric methods?
volumetric methods in which silver nitrate is used
What is a titrand?
-a solution whose concentration is unknown and is being analysed in a titration experiment
Briefly state the steps of a typical titration
a known mass or volume of titrand is measured in conical flask. If solid, dissolved first and then added,
indicator added
titrant added from burette until indicator changes colour (endpoint).
from the volume of the titrant, the amount of substance is calculated
What are the 2 ways that titrations can be performed?
-direct and indirect (back)
What’s the difference between a direct and indirect titration?
Direct titration
A known concentration solution is added directly to a sample. The titrand and titrant react directly. (typical titration from school)
-Indirect titration
- an excess of a reagent is added to a sample, and then the excess is titrated with another solution. Back titration involves two known compounds, while direct titration involves a known compound and an unknown compound.
Explain the steps of calculating the molarity of the unknown solution in a direct titration
write down balanced equation of the reaction
Calculate the moles of the substance that has the known volume and concentration
use stoichiometry to find the moles of the other substance
calculate molarity=moles of substance/volume on substance (L!!!)

0.1027M

write balanced equation. blank titration usually means do reactions happened
C10H15NO+HCl—→C10H15NOH+ +Cl-
NaOH+ HCl—→H2O+HCl
find moles of HCl in the beginning:
0.02×0.098=0.00196mol
calculate the moles of excess HCl:
nHCl=nNaOH because of 1:1 ratio. nNaOH=0.110×0.00715=0.0007865mol=nexcessHCl
find the nHCl that reacted with the sample: intial moles of HCl-final moles of HCl=0.001175mol
calculate moles of sample that reacted=moles of acid reacted because of 1:1 ratio=0.001175mol
calculate mass of sample after reaction=nxMr=0.19387g
percentage content=mass of sample after reaction/mass of sample before reaction x100=0.1938/0.198 ×100=97.87% m/m

What is a blank titration?
-it’s part of back titration. It’s the part where there is a titration without the sample
What is the strongest acid in water?
H3O+ ion
What is the strongest base in water?
OH-
What is an amphiprotic solvent?
-solvents that possess both acidic and basic properties and undergo auto dissociation e.g. 2H2O (Eq arrow) H3O+ +OH-
2NH3 (eq arrow) NH4+ +NH2-
2CH3COOH (eq arrow) CH3COOH2+ +CH3COO-
What is an aprotic solvent?
-a solvent with no acidic or basic properties e.g. hydrocarbons
-aprotic=no H bonding

-always write balanced equations
-for blank, usually 2 equations. for direct, usually 1.
-make sure equation is balanced
-when it says approximately, that is NOT definite. you must work out actual value

How do you calculate loss of drying?
difference in mass/mass of sample x100
1.0345g of a sodium sample decreased to 0.9542g on drying at 105 degrees. Calculate the loss on drying
(1.0345-0.9542)/1.0345 x100= 7.76% m/m
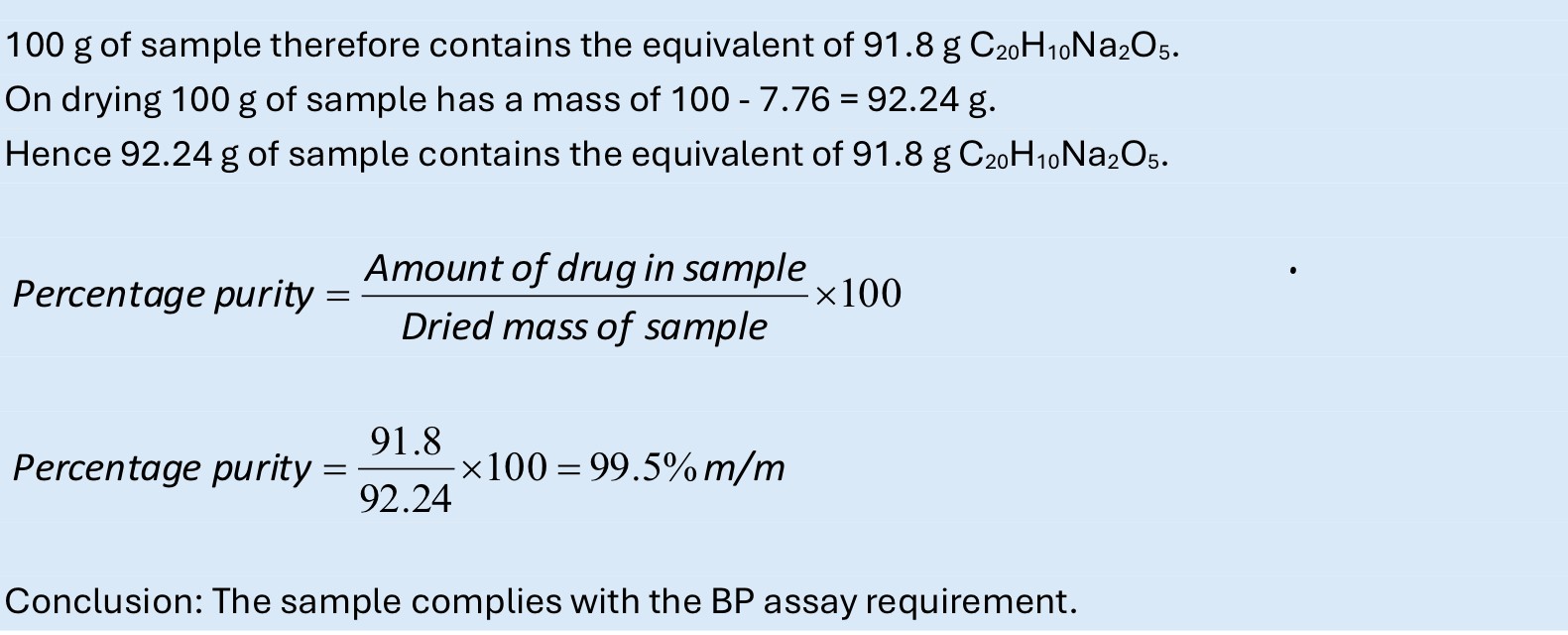
How do you calculate % purity?
-(amount of drug in sample/dried mass of sample) x100

What are 4 advantages of classical analytical techniques?
• Robust methods that can be carried out very precisely
• Automation is possible (e.g. automatic titrators etc.)
• Fairly cheap, little specialist equipment is required
• The methods do not depend on instrument calibration (but they do require pure substances for standards…)
What are the 3 disadvantages of classical analytical techniques?
• Require relatively large amounts of sample
• Procedures are time consuming and depend upon the skill of the analyst
• Methods can be relatively non-selective and are often unsuitable for complex mixtures of ingredients in formulated medicines
How do you calculate mass when given conversion factor?
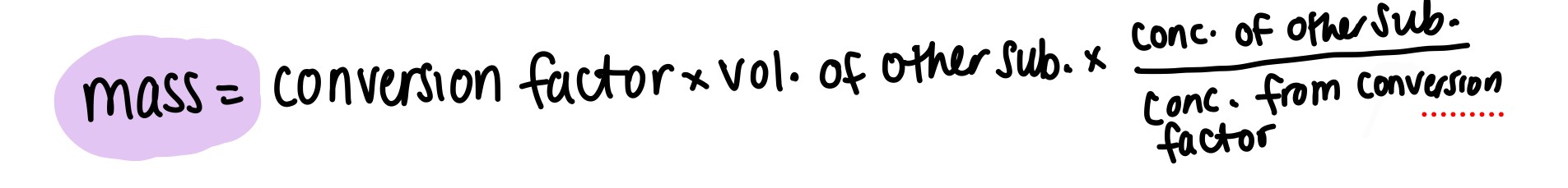

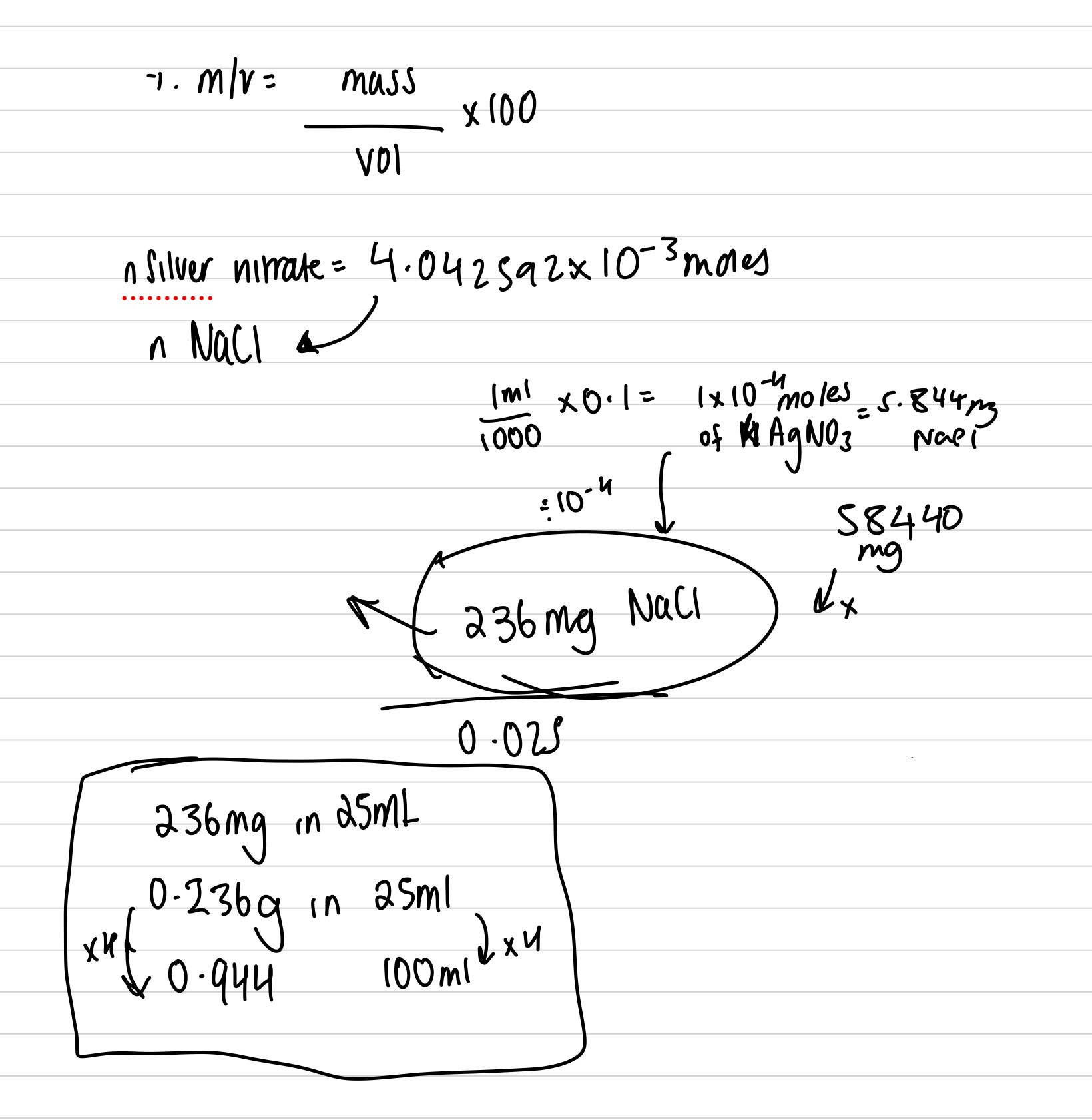
0.945% m/v

91.81% m/m percentage in sample usually means m/m
On periodic table, which number is atomic mass and which is atomic number?
atomic mass=bigger number
If N has 3 bonds, does it have a lone pair?
yes. 4 bonds, then no
What is the hybridisation of C in C=O bond?
sp2
Give 2 factors that indicate if a molecule is polar or not?
symmetry
polar groups
What is a hydrogen bond donor?
any H attached to F, O or N
What is a hydrogen bond acceptor?
F, O or N atom attached to H atom
What does it mean if a molecule is polar in terms of solubility?
-higher solubility
If the structure of 2 drugs is similar, what does this mean about how similar they work?
-it often suggests that they may have similar mechanisms of action or interact with the same biological targets, such as receptors or enzymes. (not definite though)
When calculating m/v, v/v etc what must the units of volume be?
mL
The local anaesthetic lidocaine is required by the BP to contain not less than 99% and not more than 101% of C14H22N2O, calculated with reference to the anhydrous substance. 0.2093g of a lidocaine sample was dissolved in anhydrous acetic acid and titrated with 0.1025M perchloric acid. 8.53mL was required. Another sample of the lidocaine from the same batch was found to contain 0.78% water. Does the sample meet the BP requirements?
should be 96 ish percent

The BP requires ephedrine (C10H15NO.1/2H2O) to contain not less than 99% and not more than 101% C10H15NO with respect to the anhydrous substance. Use the data below to see if the sample complies with this requirement. (a) loss on drying: 0.3152g of sample had a mass of 0.2991g after drying. (b)assay: 0.3751g was dissolved in ethanol and 25mL of 0.0935M hydrochloric acid added. The excess acid was back titrated with approximately 0.1M sodium hydroxide and 1.93mL was required. A blank titration was performed and required 24.17mL of the sodium hydroxide.

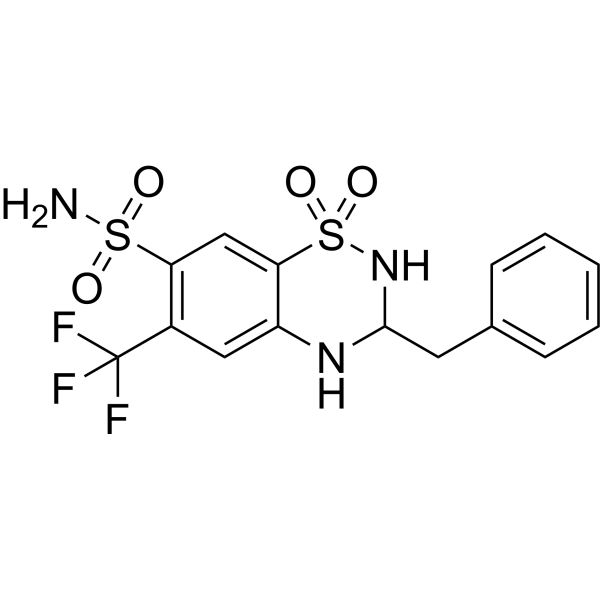
How many HBD in this molecule?
4 (N has 2 hydrogens)

97.48% remember Iodine exists as a diatomic molecule (I2)
How to know which is the limiting reagent
The reactant that produces the smallest amount of product is the limiting reagent
A buffer solution is made up with 0.0074 mol of potassium dihydrogen phosphate and 0.0175 mol of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate hexahydrate. Calculate the total mass of potassium in the final solution.
-Potassium dihydrogen phosphate: 0.0074 mol KH2PO4 contains 1 x K per mole => 0.0074 mol K
-Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate hexahydrate: 0.0175 mol K2HPO4.6H2O contains 2 x K per mole => 2 x 0.0175 = 0.035 mol K
-Total amount of K = 0.0074 mol + 0.035 mol = 0.0424 mol
-Molar mass of K = 39.0983 g/mol
-Mass of K = amount x molar mass = 0.0424 mol x 39.0983 g/mol = 1.658 g
If you mix 50 mL of a 2% w/v solution of ephedrine hydrochloride with 24 mL of a 5% w/v solution of ephedrine hydrochloride, what will the final % strength be? Calculate the molarity of the final mixture. Mr=201.69
final percentage strength= total mass from both w/v/total volume x100
50+24=74ml
50ml of 2% w/v= 1g
24ml of 5% w/v= 1.2g
total mass= 1+1.2= 2.2
2.2/74 x100= 2.97% w/v
moles of ephedrine hcl=2.2/201.69=0.01091 moles
-molarity=0.01091/0.074=0.147M
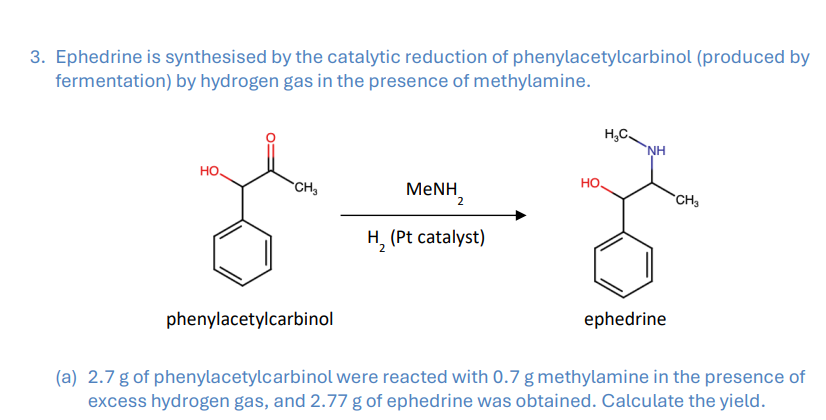

A 0.2077 g of iodine sample was dissolved in potassium iodide solution and titrated with 0.0848 M sodium thiosulphate solution, 17.64 mL was required. Calculate the iodine content of the sample (% m/m). Sodium thiosulphate and iodine react in a 2:1 ratio.
Remember I is a diatomic molecule, so Mr= I x2
-91.4% m/m
1.0748 g of a sample of Quinidine Sulphate after heating at 130°C for 2 h had a mass of 1.0106 g. Calculate the percentage loss on drying.
5.97%
Calculate the % m/m of water in sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2CO3.10H2O).
63.0% m/m
Step 1: Determine the Molar Mass
The molar masses of the components are:
Na₂CO₃ (Sodium carbonate):
105.99 g/mol10H₂O (Water of crystallization):
180.16 g/mol
So, the molar mass of Na₂CO₃·10H₂O is:
286.15
Step 2: Calculate the % m/m of Water
62.94%
Final Answer:
The % m/m of water in sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na₂CO₃·10H₂O) is 62.94%.
mr of water/total mr x100
3.1128 g of zinc metal was dissolved in dilute sulphuric acid and then made up to 371 cm3 with water. What is the percentage mass in volume composition in terms of zinc sulphate (ZnSO4.7H2O).
3.69%
moles of Zn= 3.1128/65.38=0.0476 moles
Mr of ZnSO4.7H2O=287.56 g/mol
mass of ZnSO4.7H2O=0.0476×287.56=13.69 g
13.69/371×100=3.69% w/v
remember, must be in mL
The BP(2008) specifies that ferrous gluconate should contain not more than 1.0% Fe(III).
5.1781 g of sample was dissolved in dilute hydrochloric acid and excess potassium iodide added. 7.42 mL of 0.0997 M sodium thiosulphate solution was required to titrate the liberated iodine.
What is the percentage content of iron (III)? Sodium thiosulphate and Fe(III) react in the equivalent of a 1:1 ratio.
0.798%
Mr of Fe is exact same as Fe (III)
Twenty tablets (labelled 300 mg aspirin per tablet) had a total mass of 6.8862 g. The tablets were powdered and 0.5424 g of powder was added to 30.0 mL 0.497 M sodium hydroxide solution and the mixture boiled gently for 10 minutes. The excess alkali in the cooled solution was titrated with 0.489 M hydrochloric acid solution and 20.56 mL required for neutralization. Given that aspirin (C9H8O4) and NaOH react in a 1:2 ratio calculate the percentage of aspirin as compared to the labelled claim.
Aspirin Mr(C9H8O4) = 180.2
92.58-92.63

Twenty vitamin C tablets (total mass = 6.3677 g) were powdered and 0.3218 g dissolved in dilute sulphuric acid. This solution was then titrated with 0.0974 M ammonium cerium (IV) sulphate and 23.23 mL required to reach the end-point. Given that ammonium cerium(IV) sulphate reacts with ascorbic acid in a 2:1 ratio, calculate the mass of ascorbic acid (in mg) per average tablet. Mr (Ascorbic acid, C6H8O6) = 176.12
197.1
1.26mmol of drug (Mr=221) was dissolved and made up to 250mL with water. What is the concentration of the prepared solution in %m/v? Give your answer to 3 sig figs
0.111% m/v