transition metals part 2
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
what are the two types of limiting mechanisms?
dissociative and associative
what are dissociative mechanisms?
intermediate with lower coordination umber
similar to sn1
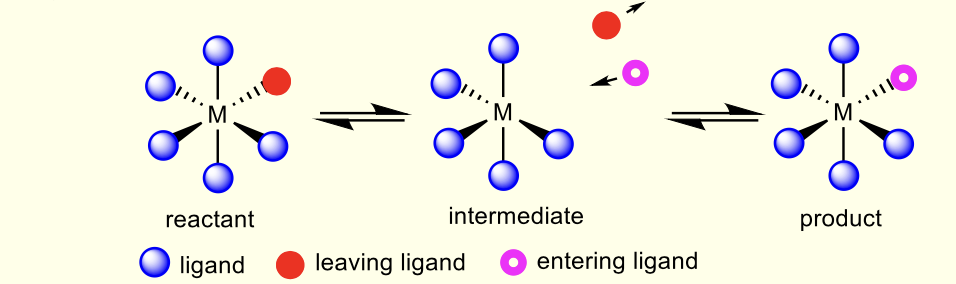
what are associative mechanisms?
intermediate has higher coordination number
similar to sn2
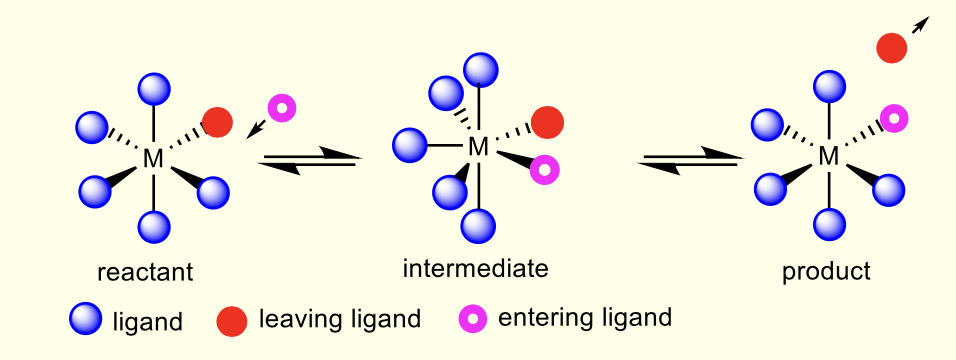
what is the most common substitution mechanism?
interchange
what is an interchange mechanism?
concurrent bond breaking and formation via transition state
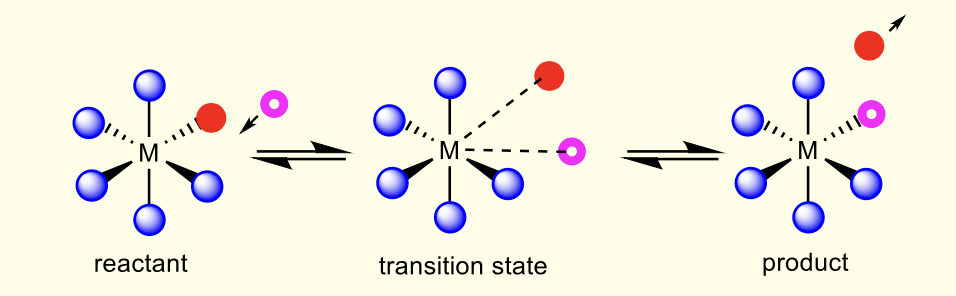
what is Ia? what is Id?
does bond formation or breakage dominate?
Ia = bond formation dominates over bond breakage
Id = bond breakage dominates
which mechanism is most common for square planar?
associative
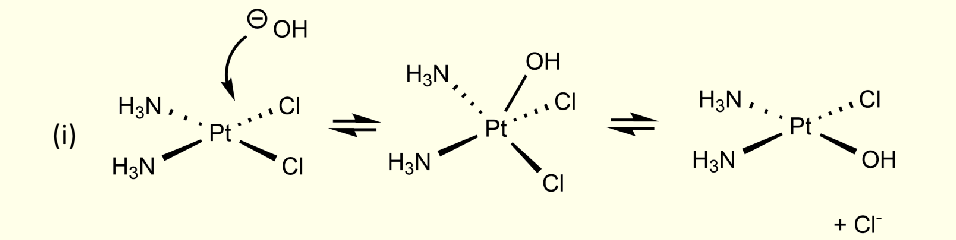
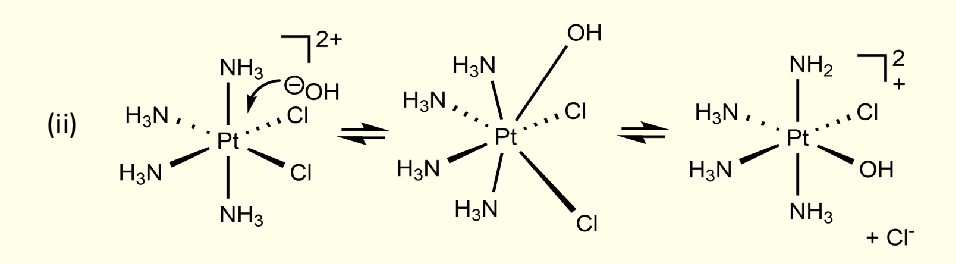
what type of mechanism is this?
interchange
bond is formed at same time as bond broken
what is the formation constant, Kf?
equilibrium constant
gives interaction strength of ligand to the metal relative to that of solvent
what does higher Kf mean in terms of stability?
higher = more thermodynamically stable complex
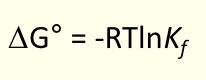
what is the general trend for stepwise formation constants?
decreases with each successive ligand exchange
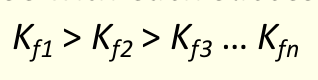
what is the overall formation constant βn?
product of equilibrium constants for stepwise reactions
multiply Kf’s together
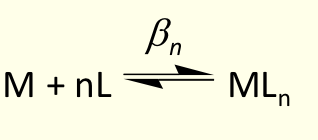
what is overall equation for βn?
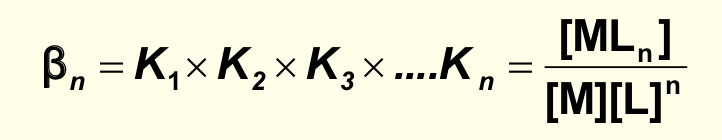
what is the chelate effect?
complex with one or more 5 or 6 membered chelate rings is more stable (higher β) than similar complex with no chelate rings
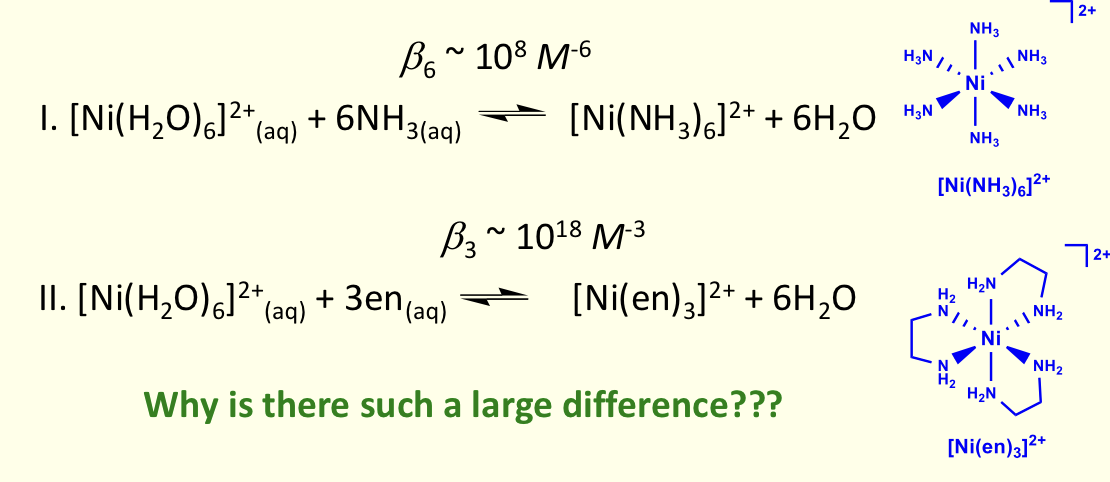
considering Gibbs free energy, why is the chelating complex more stable?
ΔH ?
ΔS ?
ΔH similar, as both involve breaking 6 Ni-OH2 bonds and forming 6 Ni-N bonds
gain in entropy favourable for cheating (more ways energy can be distributed)
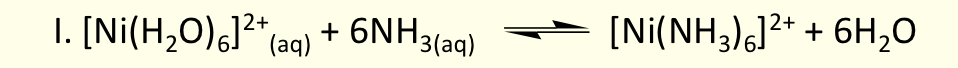
entropy change of this reaction?
no change in entropy
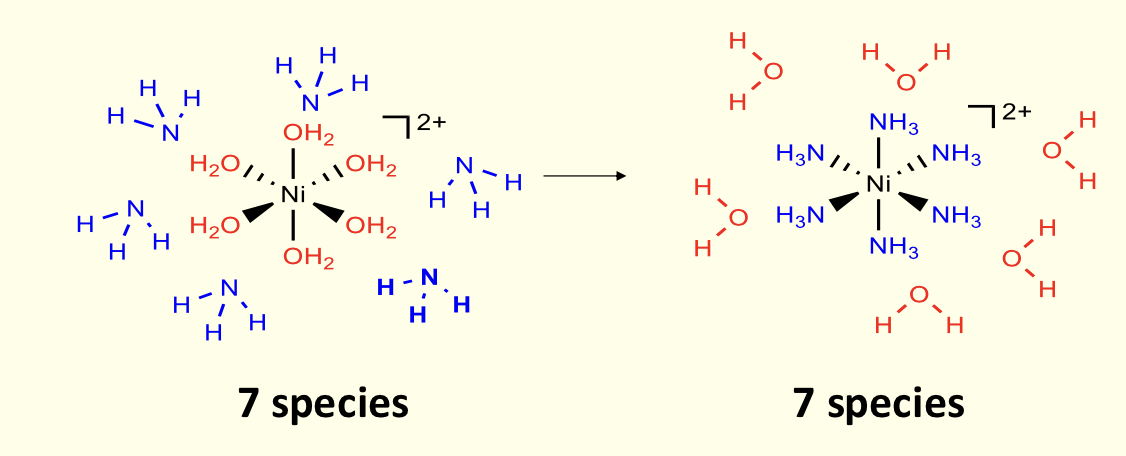
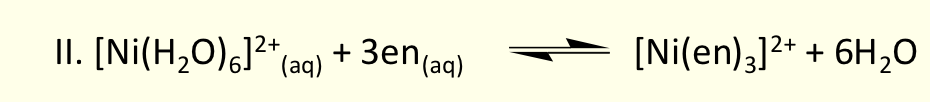
entropy change of this reaction?
there is an increase in entropy
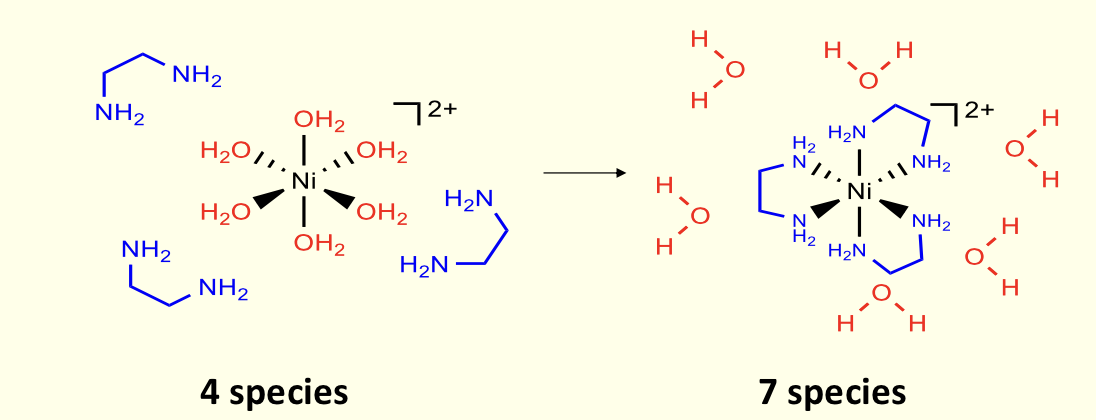
how does chelate effect change as number of members of ring increases?
greatest for 5 and 6 membered rings
marginal effect for 7
none for larger - entropy becomes negative as ligand loses degrees of freedom
why do smaller chelate rings not show chelate effect?
have steric strain (enthalpy unfavourable)
what does stable mean in terms of equilibrium?
Kf?
tendency to exist under equilibrium
Kf > 1
what does unstable mean in terms of equilibrium?
Kf?
tendency to not exist under equilibrium
Kf < 1
what does labile mean in terms of kinetics?
species that reacts rapidly
t<1min
what does inert mean in terms of kinetics?
species than react slowly
t>1min
what are general rules for lability?
most first row are labile
Cu(ii) and high spin Cr(ii) are extremely labile
Cr(iii), Co(iii) and low spin Fe(ii) are inert
some d8 and d6 2nd and 3rd row metals are very inert
are stability and kinetics related?
no
what does it mean if the incoming ligand doesn't have a large effect on kinetics?
dissociative
kinetics depend on breaking M-L bond
what does it mean if incoming ligand has a large effect on kinetics?
associative mechanism
what does associative mechanism need?
what orbital is this for octahedral?
available d orbital on metal
t2g for octahedral
what influences lability (3)?
charge density
Jahn-teller
CFSE
how does charge density affect lability?
increase in oxidation states reduce rate of exchange
how does Jahn-teller affect lability?
elongation of 1 axis for high spin Cr2+ and Cu2+ (d9) accounts for rapid kinetics
how does CFSE affect lability?
kinetically inert complexes have large CFSE
electron count and Δ are important
what is crystal field activation energy?
CFSE changes as geometry changes
ligand exchange intermediate/transition state have different geometry

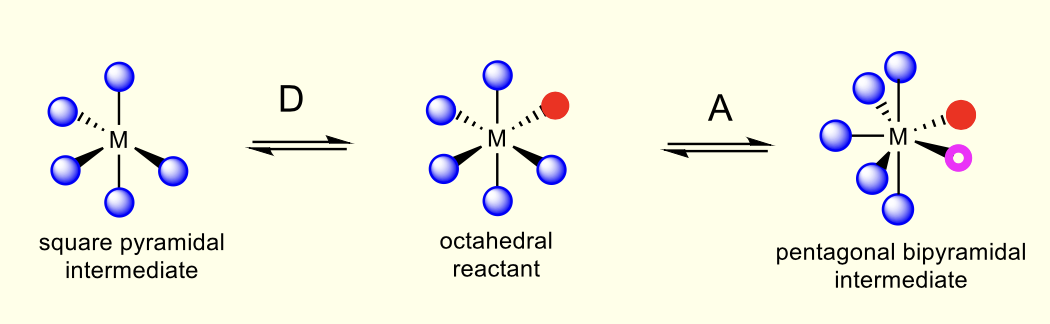
what are the crystal field splitting diagrams?
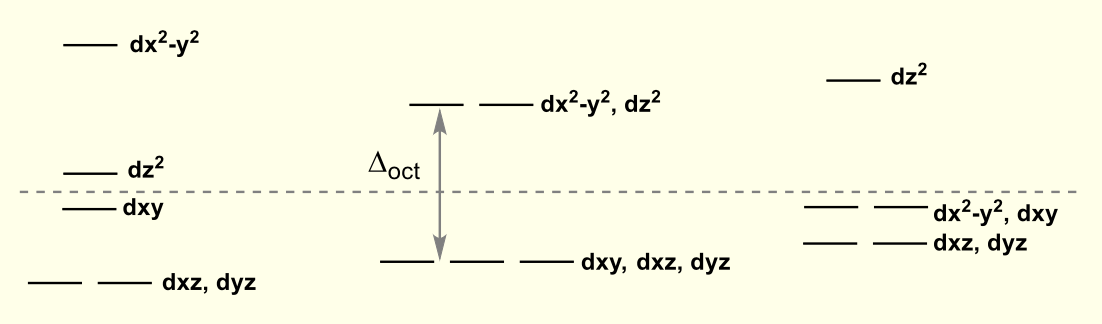
for octahedral, what configuration has the most negative CFSE?
what does this mean about ligand exchange?
low spin d6
CFSE is most affected by ligand exchange
what signifies inert complex (Δ and CFAE?)
large Δoct and positive CFAE
less stabilisation of intermediate compared to reactant