Chemistry 1212: Reaction Rates and Kinetics Key Concepts
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is kinetics in chemistry?
The branch of chemistry or biochemistry concerned with measuring and studying the rates of reactions.
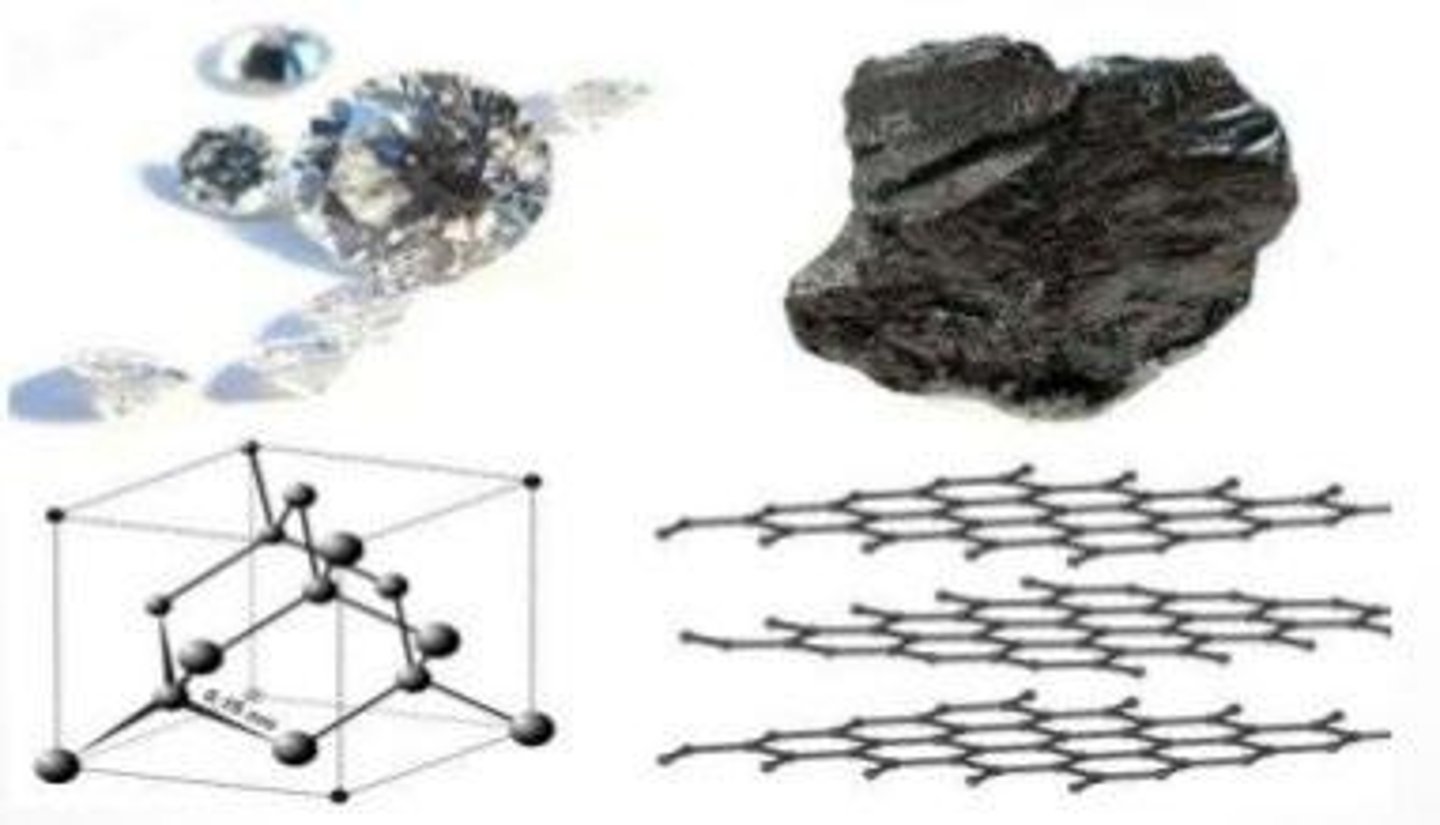
Give an example of a slow reaction.
Diamond converting to graphite.
Give an example of a fast reaction.
The reaction of sodium with water: Na + 2 H2O → H2 + 2 NaOH.
How is reaction rate defined?
Change in concentration of reactant or product per unit time, always expressed as a positive term.
What is the formula for the reaction rate of the equation A + 2B → D + 3F?
rate = - ∆[A]/∆t = -(1/2) ∆[B]/∆t = ∆[D]/∆t.
If C2H6 is consumed at a rate of 0.20 mol/Ls, how is CO2 produced?
CO2 is produced at a rate of 0.10 mol/Ls, based on stoichiometry.
What is the instantaneous rate of a reaction?
The rate at a given point in time, represented by the slope of the tangent line to the curve.
What is the initial rate of a reaction?
The instantaneous rate just after the reaction begins, dependent only on the concentration of reactants.
What factors affect the rates of reactions?
Temperature, concentration of reactants, and the presence of a catalyst.
How does the chemical nature of the reactant affect reaction rates?
Different reactants have varying reactivity, influencing the speed of the reaction.
What role does the physical state of the reactant play in reaction rates?
The physical state (solid, liquid, gas) can affect how reactants interact and react.
How does particle size of the reactant influence reaction rates?
Smaller particles have a larger surface area, leading to faster reactions.