Energy Expenditure + Cardiovascular System
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy is neither created nor destroyed, it is transformed from one form to another.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
When energy changes form, the amount of entropy in a system tends to increase.
Much of the energy transformation occurring with the second law of thermodynamics results in…
Heat production.
Calorie
A basic unit of heat production, a measure of energy.
One calorie
The amount of heat energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of water from 14.5 to 15.5 degrees Celsius at standard atmospheric pressure.
Cal =
kcal (kilocalories)
Joule
Work done by a force of one newton (N) moving one meter.
Two methods of measuring heat expenditure
Direct measure via heat and indirect measure via oxygen consumption.
Direct measure via heat
Byproduct of hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis formula
H2o + ATP → (ATPase) = energy + ADP = Pi + heat
By measuring heat, we directly measure…
Energy expenditure (heat)
Indirect measure via oxygen consumption
(VO2) occurs in the last step of resynthesizing ATP via the oxidative energy system.
Oxygen reduction reaction
4H+ + O2 + 4e- → 2H2O
By measuring VO2, we indirectly measure…
Energy expenditure (VO2)
Calorimetry
The process of measuring heat production.
The human body uses…
<30% of the calories consumed to carry out cellular work.
Byproduct of every transformation
Heat.
Energy expenditure
The total amount of energy the body uses.
We can measure heat production as…
A direct measure of energy expenditure.
We can measure oxygen consumption as…
An indirect measure of energy expenditure.
Direct calorimetry
A way to measure the rate and quantity of energy production.
What does direct calorimetry measure?
Energy liberated via the amount of heat produced.
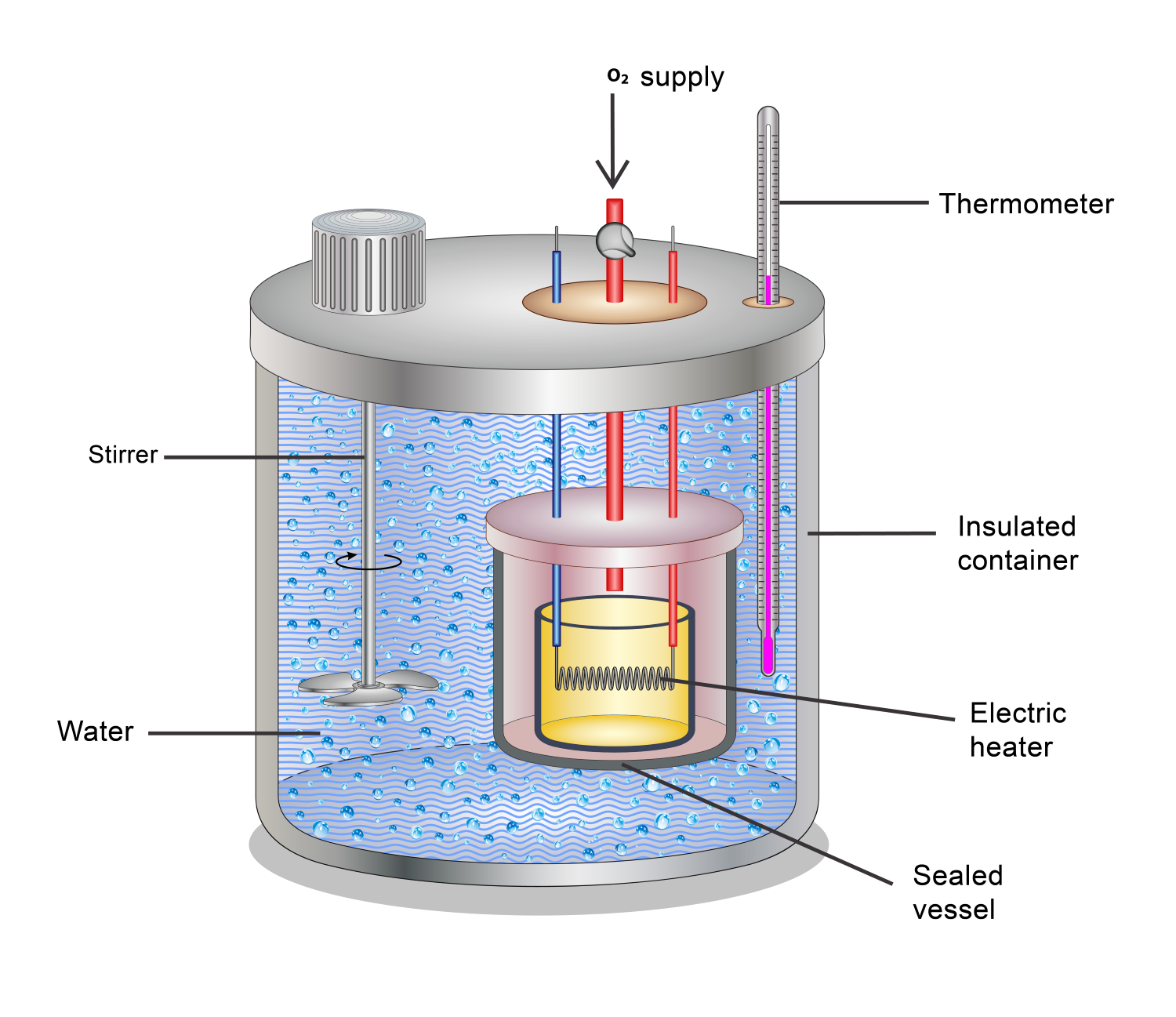
Bomb caloimeter
A device that measures heat (calories, heat) given off in food as food is burned up.
The amount of calories a given quantity of food contains is measured by what process?
A bomb calorimeter device.
Calorimetric chamber
Airtight chamber that measures heat released in body via change in water temperature passing through copper tubing in ceiling (expensive).
Indirect calorimetry measures…
The amount of oxygen consumed (VO2 + VCO2).
Oxidative phosphorylation requires oxygen to…
Be consumed in the final step of the electron transport system when resynthesizing ATP.
Oxidative phosphorylation products
ATP, CO2 and H2O.
By measuring the quantity of oxygen consumed…
We can indirectly measure the amount of energy (ATP) required for a given task.
Indirect calorimetry
Indirectly measures the amount of ATP required for a given amount of work.

Metabolic Cart
An indirect calorimeter that measures VO2, CVO2, and volume of air expired (VE).
Oxygen Consumption (VO2)
The amount of oxygen consumed in the last step of the electron transport chain.
VO2 indirectly reflects the amount of…
ATP resynthesized in the mitochondria for a given task at a given time.
VO2 is reported at?
Rate per minute.
A greater work rate leads to…
More ATP needed, (for cellular/muscular work) and greater VO2.
How is whole body VO2 measured?
Using a metabolic cart.
Each liter of oxygen consumed represents…
~5 calories/kcal.
Known when measuring VO2
Ambient air before inhaling air.
N2 = 79.03%
O2 = 20.93%
CO2 = 0.03%
Other gases = 0.03%
Unknown when measuring VO2
Volume of air we exhale and concentration of O2 and CO2 in expired air.
How are unknowns measured when measuring VO2?
Using metabolic carts and computer to calculate VO2 for a given task.
VO2 may be quantified as either:
Absolute or relative to one’s body mass.
Absolute VO2
Measured in absolute terms → measured in liters of O2 per minute.
Relative VO2
Expressed in relative terms, relative to body mass, measured in ml.
Relative formula
Absolute value divided by body mass (in kg).
Arteriovenous Oxygen Difference (AVO2D, AVD)
The difference in O2 concentration between arterial blood ejected from left ventricle (going to tissue) and (mixed) venous blood returning from tissue to right heart.
What does AVO2D represent?
How much O2 is extracted from blood and then consumed in ETC of cells’ mitochondria in order to make ATP.
Basal metabolic rate (BMR)
Minimum level of energy (VO2, ATP) necessary to maintain vital functions in waking state.
Mean basal metabolic rate
~3.5 ml of 2 per kg of body mass per minute (ml/kg/min).
Resting metabolic rate (RMR)
Similar to BMR, but does not require stringent standardized conditions to measure BMR (RMR has ~5-10% greater VO2 than BMR).
One metabolic equivalent (MET)
3.5 ml of 02 per kg of body mass per minute (3.5 ml O2/kg/min).
For cardiac rehabilitation, intensity of exercise is often assigned in…
Multiples of METs.
Constant load work
Work at a given work rate (WR) over a period of time (ex: jog 5 mph for 30 minutes).
During exercise homeostasis is…
Not possible.
During constant load work, we reach…
Steady state condition in attempt to reach state of equilibrium.
Steady-state condition
Occurs during constant load work of light or moderate intensity.
Oxygen deficit
The lag in VO2 at beginning of a constant-load exercise bout compared to VO2 (ATP) cost of exercise at that WR.
Maintaining the body function at rest requires:
A certain metabolic cost (ex: RMR, indirectly reflected in VO2).
(EPOC) Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption
The exaggerated level of VO2 upon cessation of exercise that is above the metabolic cost of VO2 at rest.
For several minutes to hours after exercise…
VO2 is higher than VO2 at rest in order to replenish the ATP, PCr, and glycogen used during the O2 deficit and remove metabolic wastes (lactate and H+).
Graded Incremental Exercise Test (GXT, stress test)
Multistage test where work rate starts at low intensity and then increases at regular time intervals until subject reaches predetermined end point.
GXT allows tester to observe…
Physiological responses to work at different intensities within a 8-13 minute test.
VO2 response to GXT
VO2 increases linearly with linear increase in work rate.
As exercise intensity increases…
More ATP resynthesis is required.
In GXT, greater VO2 is required in electron transport system because…
O2 needs to bind with 2H+ →H2O.
Peak VO2
Represents the peak ability of mitochondria to consume O2 and substrates in the process of resynthesizing ATP via the oxidative system.
Peak VO2 is the level at which the mitochondria reaches their…
Maximal ability to resynthesize ATP aerobically.
Best single indicator of maximal aerobic performance:
Peak VO2.
VO2 peak is often used to describe…
Aerobic fitness level.
Best indicator of submaximal aerobic performance:
Lactate threshold/breakpoint.
Intensity of exercise as % of VO2 peak
ACSM guidelines: work at 50-85% VO2 peak, depending on training level.
Lactic acid
An acid formed during fast anaerobic glycolysis (parent molecule).
Lactic acid immediately dissociates into…
H+ and lactate.
Hydrogen ion (H+)
A proton that is acidic and negatively affects PFK and other enzymes.
Lactate
An acid salt produced when the remaining compound binds with positively charged sodium or potassium ion.
What causes lactate production?
Breakdown of glucose (fast glycolysis).
Lactate threshold (LT)
Intensity during GXT at which there is an exponential rise in blood lactate concentration and H+ ion concentration in the sarcoplasm in conjunction with a linear increase in work rate.
At rest and during low-to-moderate intensity exercise (<60% VO2 peak), lipids act as…
Main substrate for generating ATP.
During high intensity exercise (>75% VO2 peak), glucose becomes…
Main substrate for generating ATP.
During rest through moderate intensity exercise, lactate is…
Cleared, reused, or recycled easily (slow glycolysis).
During rest and light intensity exercise…
More fat is used than CHO for energy, which leads to little lactate concentration in the blood.
Predominant energy source at high intensity work
CHO (Carbohydrate).
EPOC occurs in an attempt to…
Bring cells back to homeostasis through replenishment and repair.
Chronic aerobic training
Decreases deficit → decreases EPOC necessary to replenish homeostasis.
Accumulation of lactate (fast glycolysis) from muscle into blood →
Exponential rise in blood lactate.
Interval training
Exercise at high intensity interspersed with work at low intensity.
Aerobic exercise intensity is often measured by…
Heart rate achieved at lactate threshold during GXT.
For high intensity segment, train at work rate…
Above the lactate threshold (fast glycolysis).
For low intensity segment, train at work rate…
Below the lactate threshold (slow glycolysis).
Lactate Shuttle
Lactate produced via anerobic (fast) glycolysis can be reused within the same muscle group.
VO2
Oxygen consumed in electron transport system.
VCO2
Carbon dioxide produced from Cs and Os stripped from substrate, mostly in Kreb’s cycle.
Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER, R)
RER = VCO2/VO2