25.2 electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
conditions of nitrogenation of benzene and why they are important
catalysed by sulphuric acid
heating to 50 degrees
if heated above 50 degrees further substitution reactions may occur leading to the production of dinitrobenzene
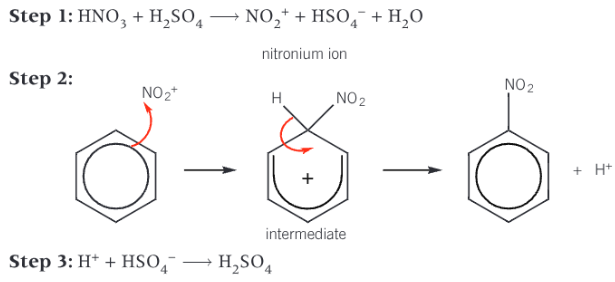
reaction mechanism for nitrogenation of benzene
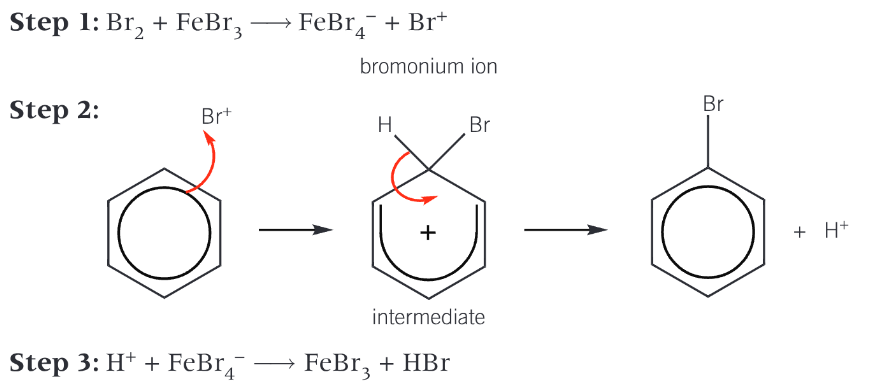
how is a halogen carrier used in the bromination of benzene
benzene is too stable to react with a non-polar bromine molecules
the electrophile is the Br+ which is generated when the halogen carrier reacts with bromine
the bromium ion accepts a pair of electrons from the benzene ring to form a dative covalent bond
the organic intermediate is unstable and breaks down to form the organic product bromobenzene and a H+ ion
The H+ ion reacts with the FeBr4- ion to regenerate the FeBr3 catalyst
bromination of benzene mechanism6
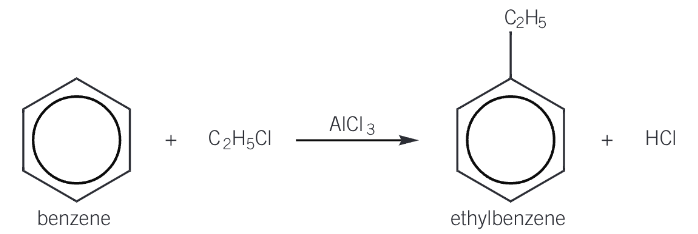
alkylation reactions
the substitution of a hydrogen atom in a benzene ring by an alkyl group
reacting benzene with a haloalkane in the presence of AlCl3, which acts as a halogen carrier catalyst forming the electrophile
comparing the reactivity of alkenes with arenes (using bromination reaction)
in alkenes
the pi bind in the alkene contains localised electrons above and below the plane of the two carbon atoms in the double bond. This produces an area of high electron density
the localised electrons in the pi bond induce a dipole in the non-polar bromine molecules making one bromine atom of the Br2 molecjules slightly more positive and the other slightly negative
the slightly positive bromine atom enables the bromine molecule to act like an electrophile
in arenes
benzene will not react with bromine unless a carbon carrier is present
this is because benzene has delocalised pi electrons spread above and below the plane of carbon atoms in the ring structure.
the electron density of carbons in benzene rings is less than in a c=c
when bromine approaches the benzene, there in insufficient pi electron density around two carbon atoms to polarise the bromine molecule. This prevents any reaction from taking place