ARC 200 Exam #3 - Sites, Cultures, Periods, and Visual
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Mesopotamia
located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in the fertile crescent, north is rainy and fertile south is dry desert, first states developed in the south, used irrigation for agriculture, inter-regional trade, clay tablets as form of writing
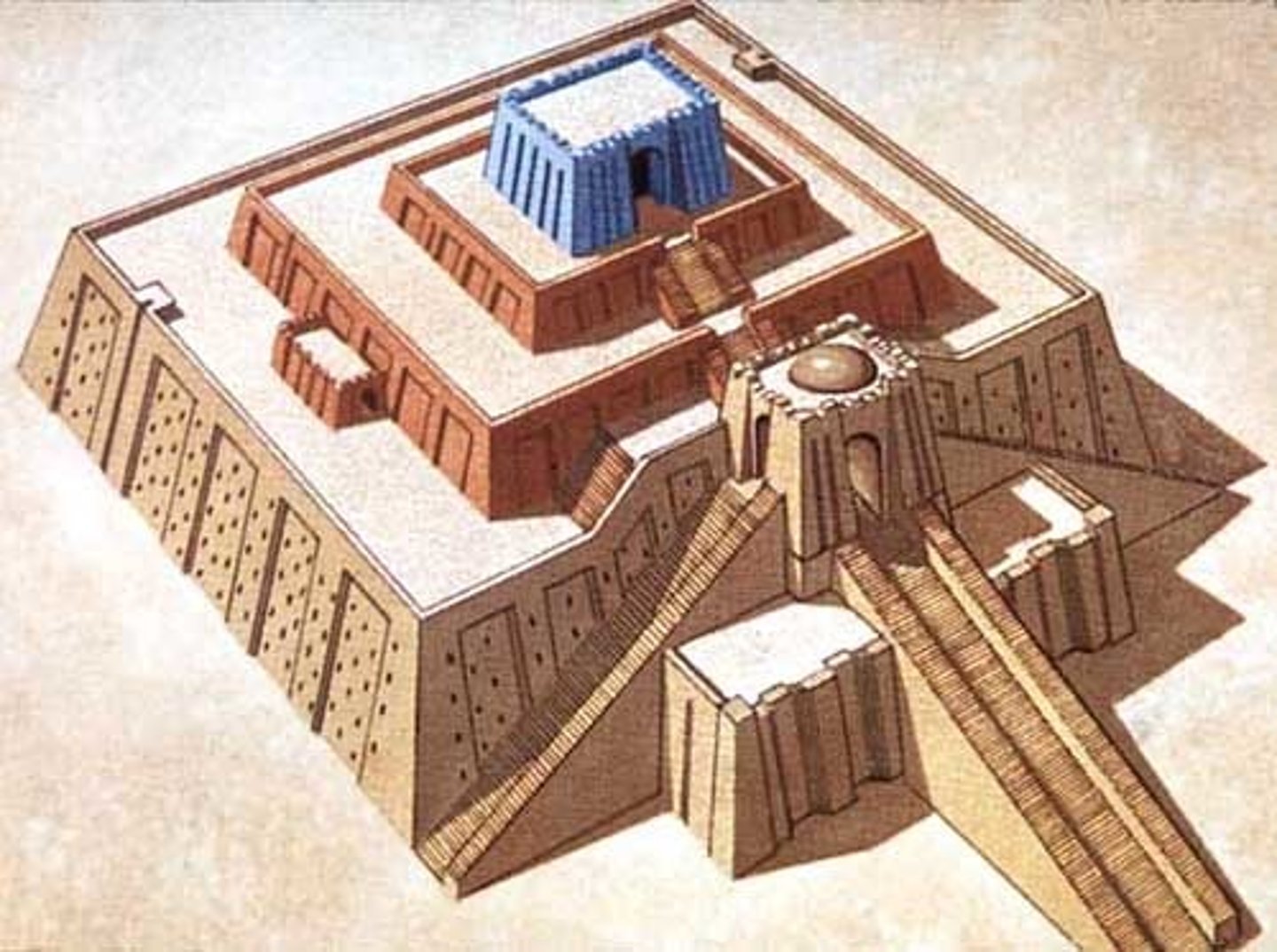
Ziggurat
Stepped pyramid. Used for food storage, religion, trade, and politics
Eridu
early urban center in Mesopotamia, powerful cheifdom, port and trade
Uruk Period
First states within the Mesopotamia period, found in south mesopotamia, monumental urban centers, plow and wheeled transport for agriculture, writing for administration, city-states, early Uruk brought Bullae Tokens and Cylinder Seals
Uruk City
first monumental urban center, palace/temple complex, over 10,000 people, Anu Ziggurat/White Temple, Eanna Temple, clay tablets
Early Dynastic Period
Mesopotamian, follows Uruk period, 10-15 competing city-states, military conquest & territorial expansion, bronze metallurgy alloy copper + tin, weapons and luxury goods, despotic rulers, harsh laws and punishment, king lists
Ur Royal Cemetery
-1922-1934
-2500 burials: 16 displayed wealth
-Elaborate funerary ritual involving human sacrifice on a mass scale
-Tomb of Queen Shub-ad
Ubaid Period
Earliest manifestation of classic Mesopotamian civilization (6200-4000BC) found in the lowest levels of Ur, Uruk, Eridu; reflects spread of farming throughout S. Mesopotamia
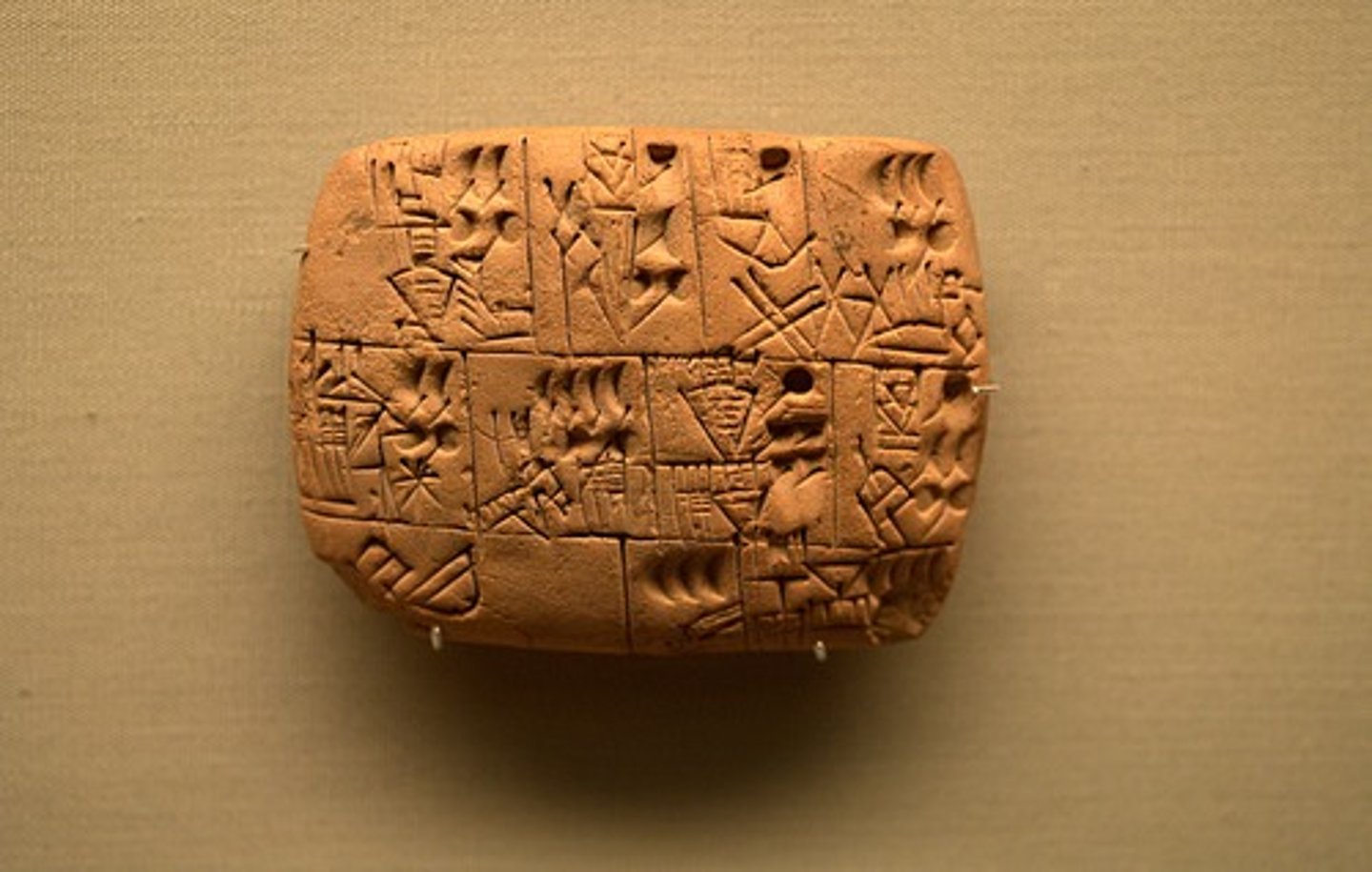
Mesopotamia Writing Sytem
Logo-syllabic writing system on clay tablets
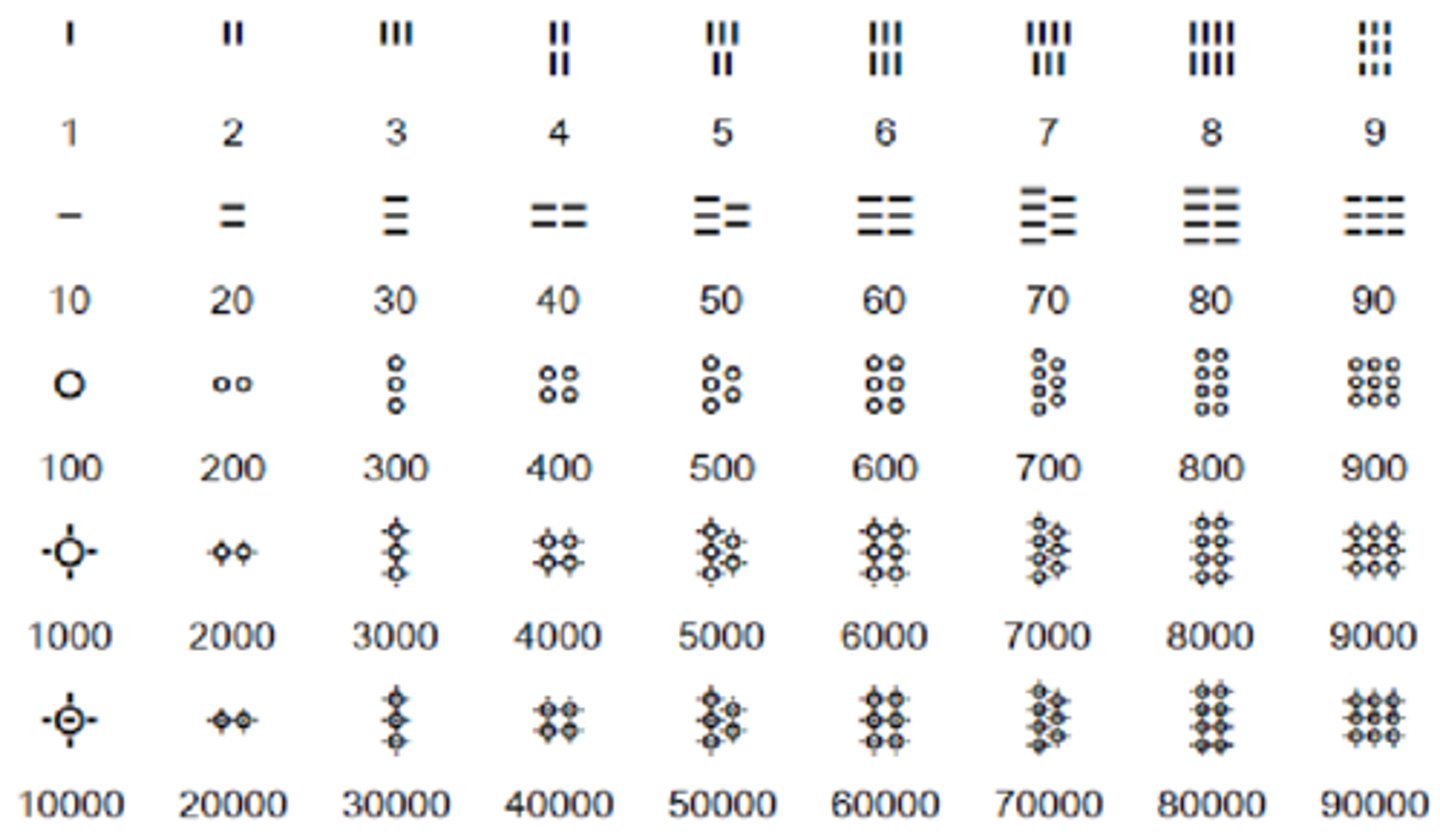
Mesopotamia Number System
-Base 60 number system
-Easily divisible
-Used today for time, circular measurements etc
Cuneiform
A system of writing in which wedge-shaped symbols represented words or syllables

Indus Valley
-Specialized craft production: fine painted pottery, bronze metallurgy, ornaments
-long distance trade of exotic goods: copperm marine shell, gemstones
-Mature Harappan: states, 4-8 major urban centers
-Stone and faience and jewelry, metal ornaments, weapons, terracotta figurines molded tablets
Mohenjo-Daro
-one of the earliest and largest Harappan urban centers
-"Mound of the Dead"
-modern day Pakistan
-Over 40,000 people
-Upper citadel (political and ritual center) and lower town (gridded streets, elites in courtyard compountes, specialized artisan sectors)
-Specialized city sectors and laid out on grid
-"Great Bath": first large water tank in the world
-Early sewer system
Indus Valley Accounting Systems
-Standardized weights and measures (base unit .5 oz)
-Stamp seals (impress in clay, ownership of goods, carved images and inscriptions)
Indus Valley (Harappaan) Writing
-Independent of Mesopotamian writing
-Over 4000 seals, tablets, sign boards
-400 symbols, longest inscription 21 signs, has not been deciphered
Indus Valley (Harappan) Elites and Rulers
-Little known about rulers, "preist kings"
Egyptian Period
-Divided into Upper and Lower Egypt, terms relative to flow of Nile River
Lower Egypt
North, fertile Nile River delta, "black land"
Upper Egypt
South, desert, narrow band along Nile River flood plain, "Red land"
Predynastic Egypt
Early
-intensive agriculture
-population growth
-craft specialization
-copper mettalurgy
-increased inequality
-powerful rulers "chiefs"
Late
-economic expansion
-increased trade (upper and lower egpyt, mesopotamia)
-state formation
-symbols of power (crowns, maceheads, "smiting" pose
-King Scorpion I & II, united much of Upper Egypt
Hierakonpolis (Nekhen)
-Earliest major town
-Center for pottery production
-Elites and traders in seperate, larger compounds
-Elaborate tombs
-Art depictions of war and boats
Early Dynastic Period - Egypt
-Unification of Upper and Lower Egpyt
-Single territorial state under one king
-first pharaohs (term not used until New Kingdom)
-double crown
-creat stabiloty in centralized govern.
-established Memphis as capital
-mortuary ritual (hreat tombs)
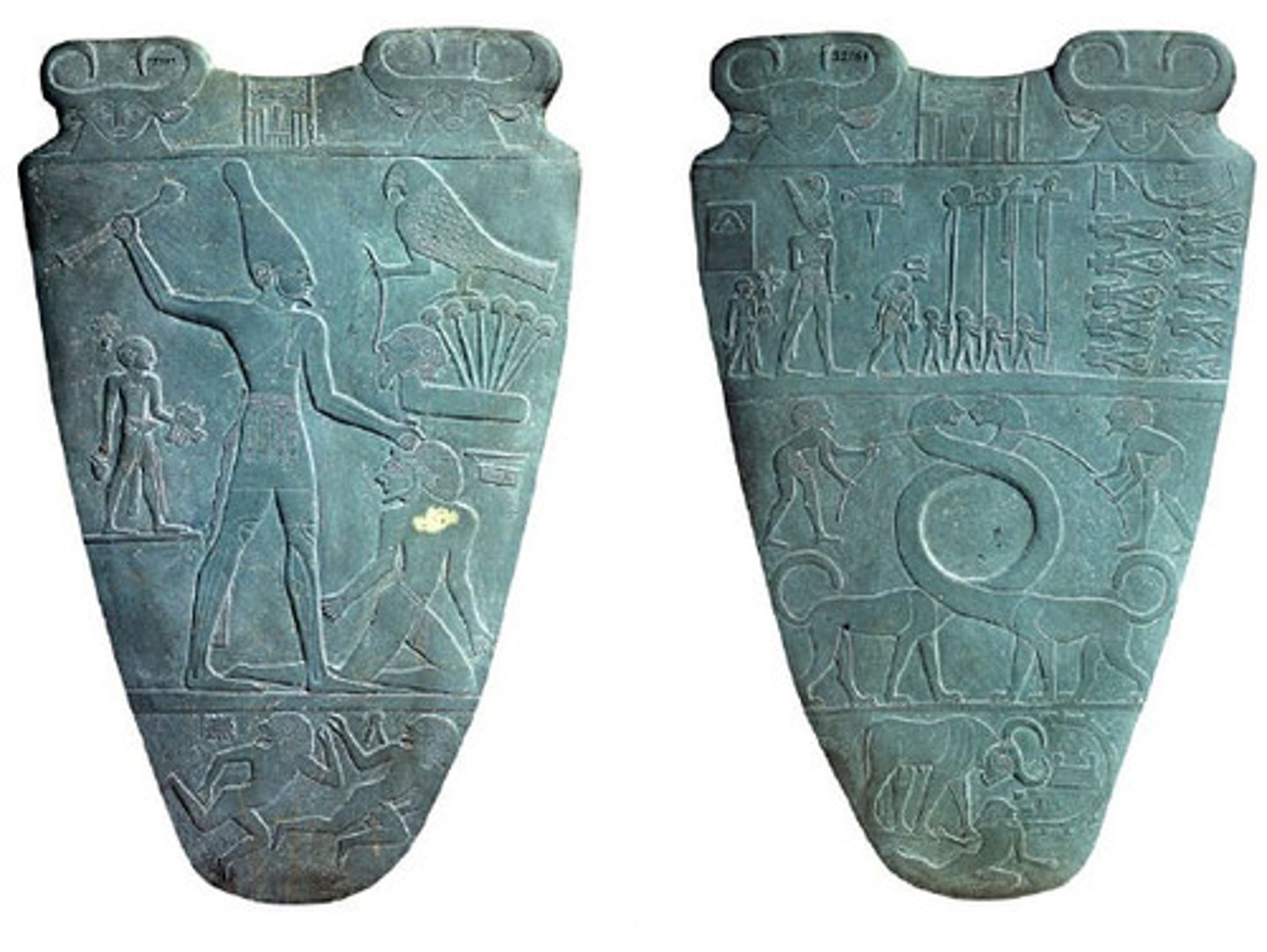
Palette of Narmer

Old Kingdom - Egypt
-despotic pharaohs
-pyramid construction
-divine god-kings
-bureaucracy
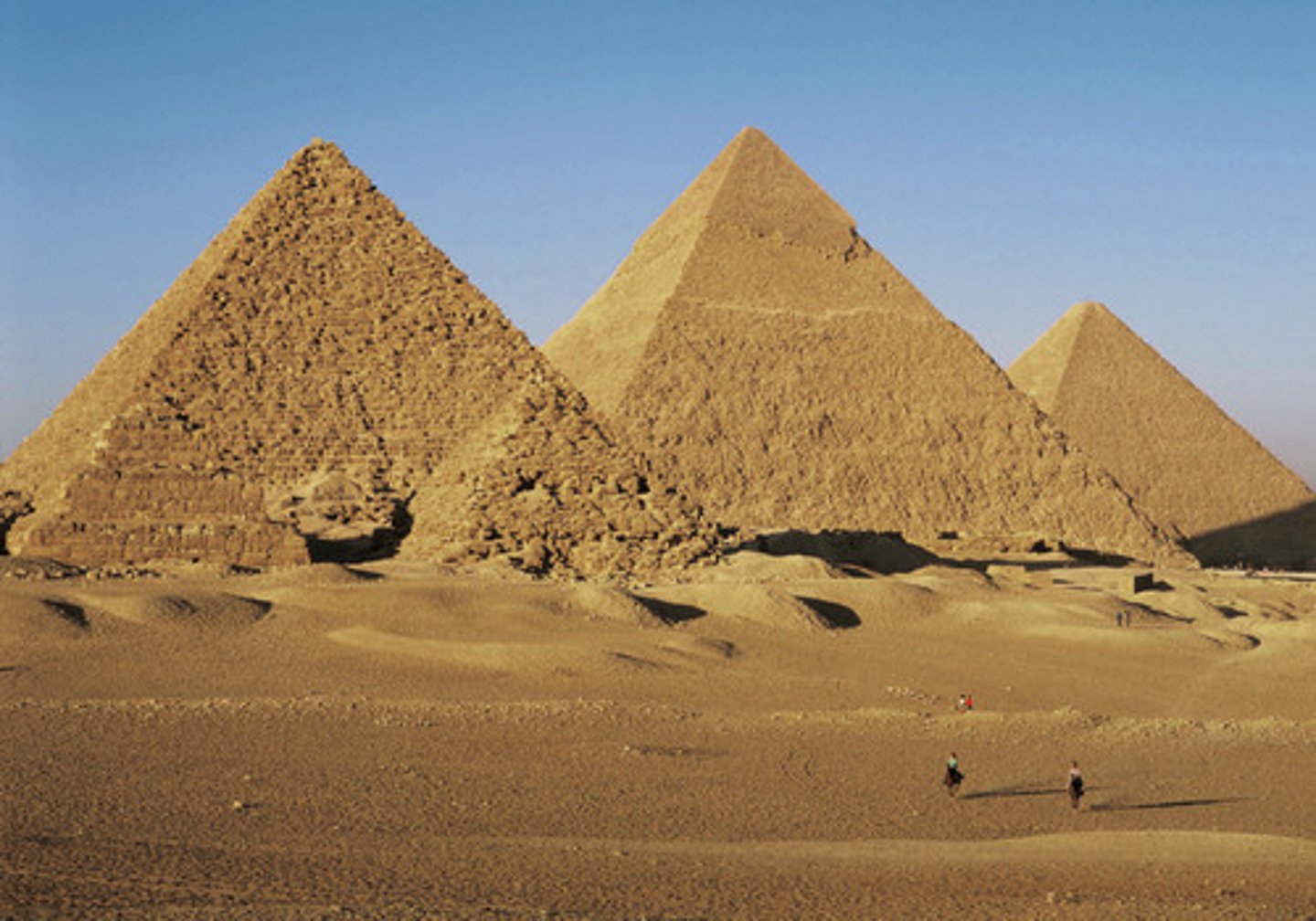
Giza Pyramids
The largest and best-preserved pyramids. Consists of the Pyramid of Khufu, the Pyramid of Khafre, the Pyramid of Menkaure and The Great Sphinx.

Egyptian Hieroglyphics
pictures and symbols to represent words and ideas; written on the walls of the tombs to guide the pharaohs through the afterlife

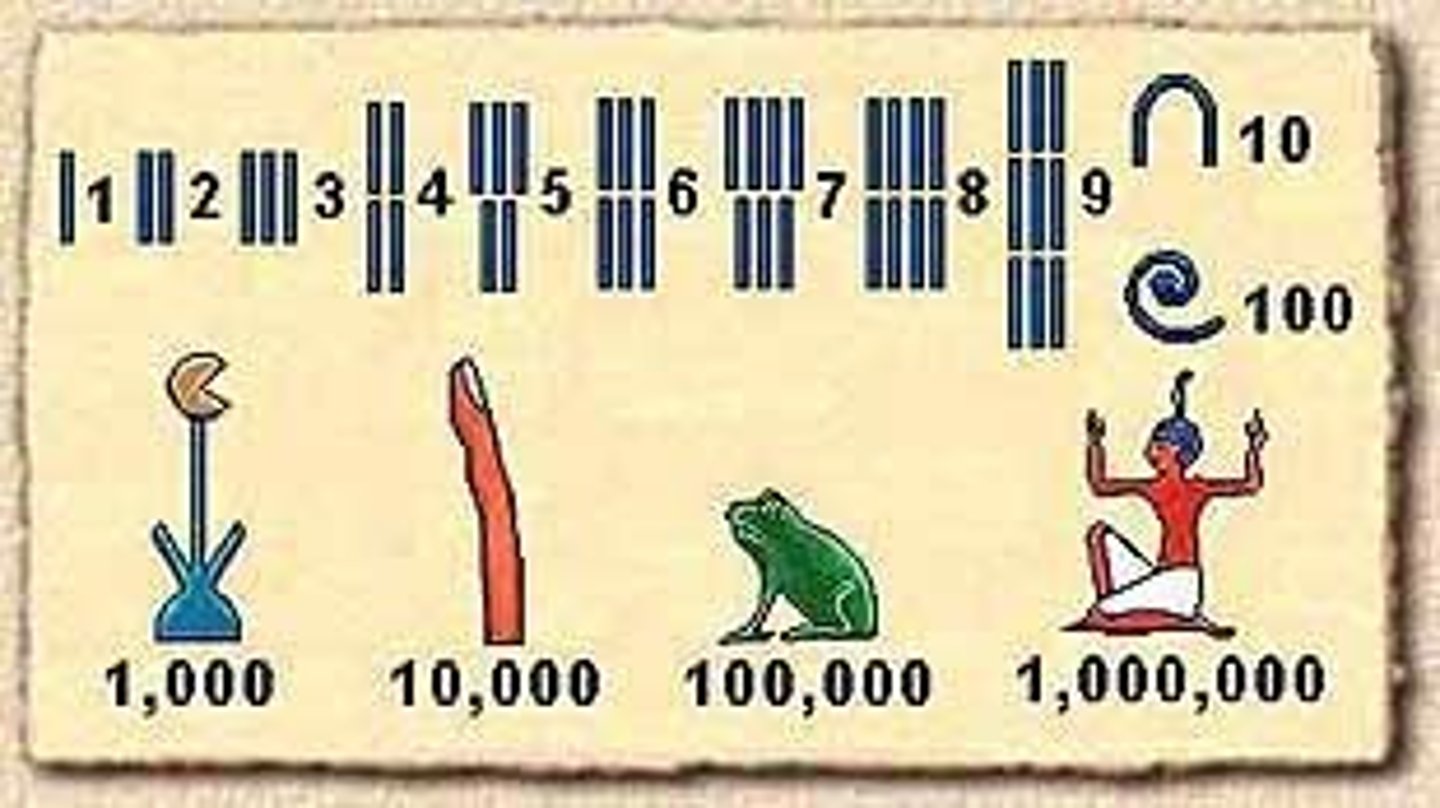
Egyptian Number System
-Base 10
Egyptian Writing Systems
-earliest preserved Egyptian writing: ivory tags
-development poorly known
-writing on perishable materials
-earlist preserved writing for ritual and royal gifts
-also governement accoutning
Rosetta Stone
a huge stone slab inscribed with hieroglyphics, Greek, and a later form of Egyptian that allowed historians to understand Egyptian writing.

Chinese "3 Dynasties"
Xia, Shang, Zhou
Xia Dynasty
-state formation
-small territorial state
-not city states
Shang Dynasty
-first preserved writing
-Anyang (early royal capital)
-logographic, characters simplify over time
-early: ritual, late: political administration
Zhou Dynasty
-many smalle, partially independent states
-competition and warfare between states
-Qin state conquers other states
-establishes 1st chinese empire
Qin Dynasty
-empire: aggregate of territorial states
-different cultures/languages
-complex admin systems
-moved capital to Xianyang (strong centralized government)
-forced relocation of rivals
-concentrate political and economic power
-chinas first standing army
-standardization: written language, code of laws, weights and measurements, coinage
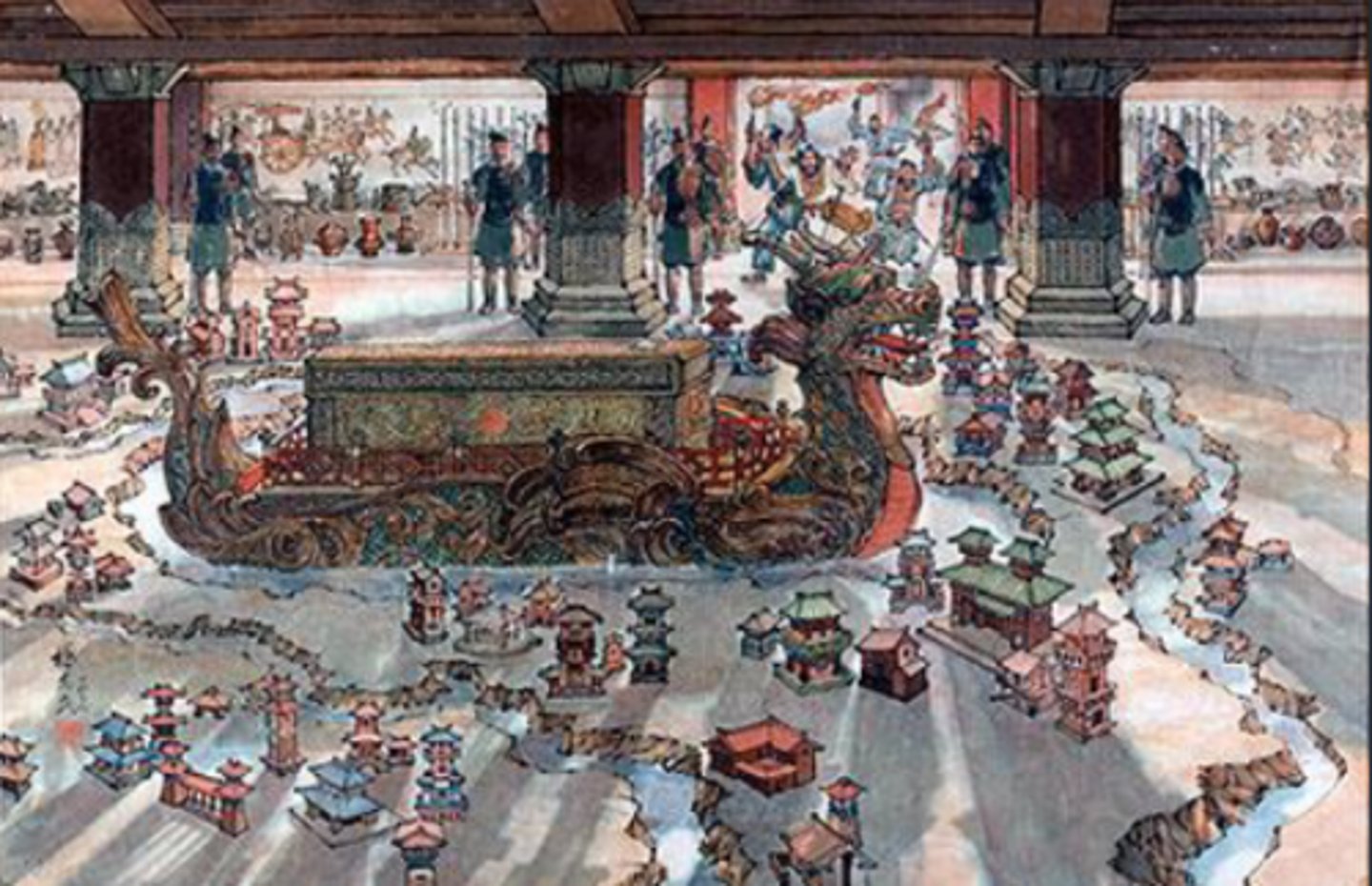
Mount Li Mausoleum
-miniature model of "universe"
-waterways and oceans of mercury, constellations on ceiling
-copper coffin, rich grave goods

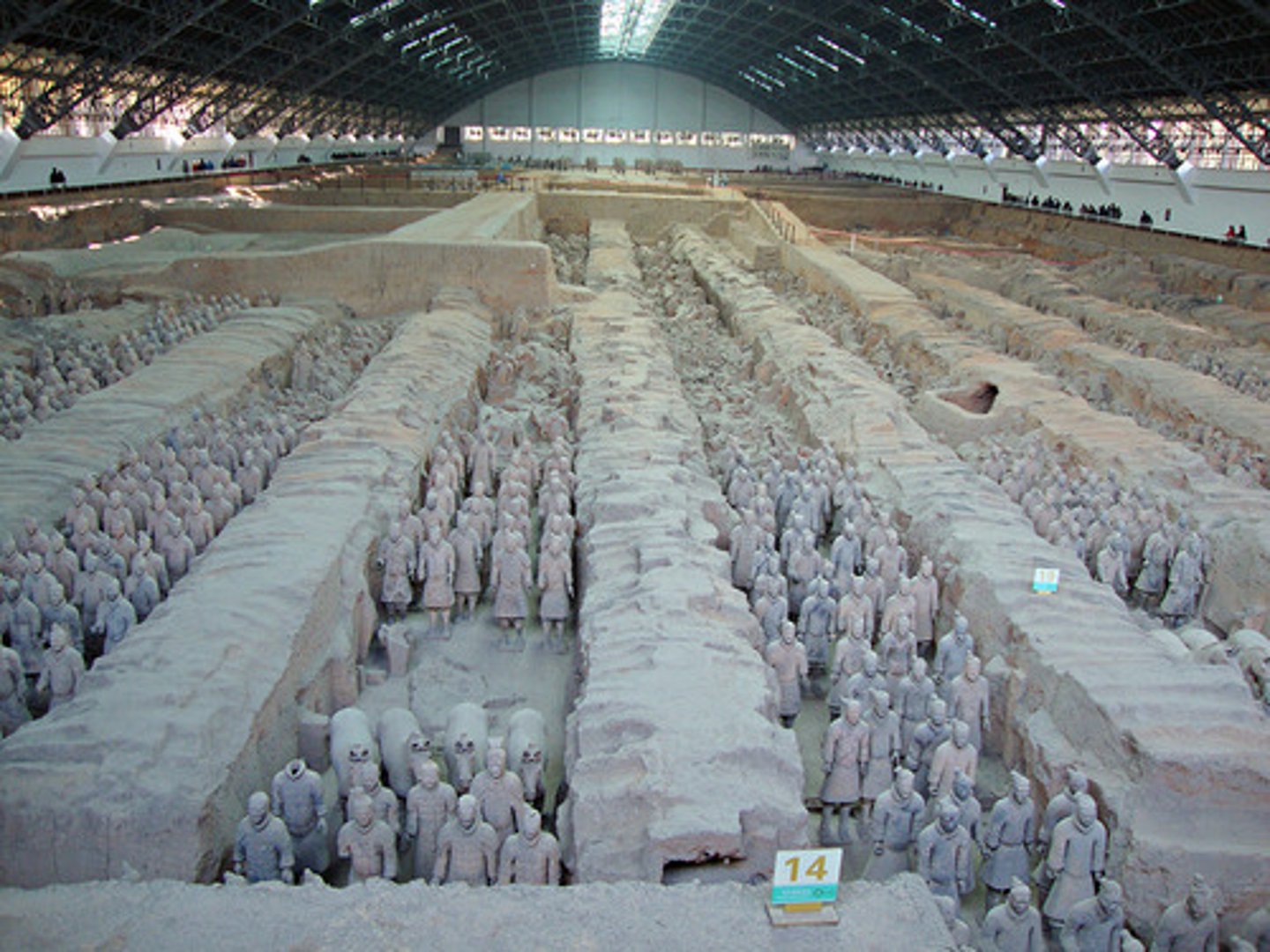
Mount Li Terracotta Army
-8000 figures exposed to date
-larger than life
-"unique" faces
-painted, real weapons
-chariots

Minoan
-Crete (Not Greek)
-Control of sea trade
-Palaces: seats of regional power (city-states)
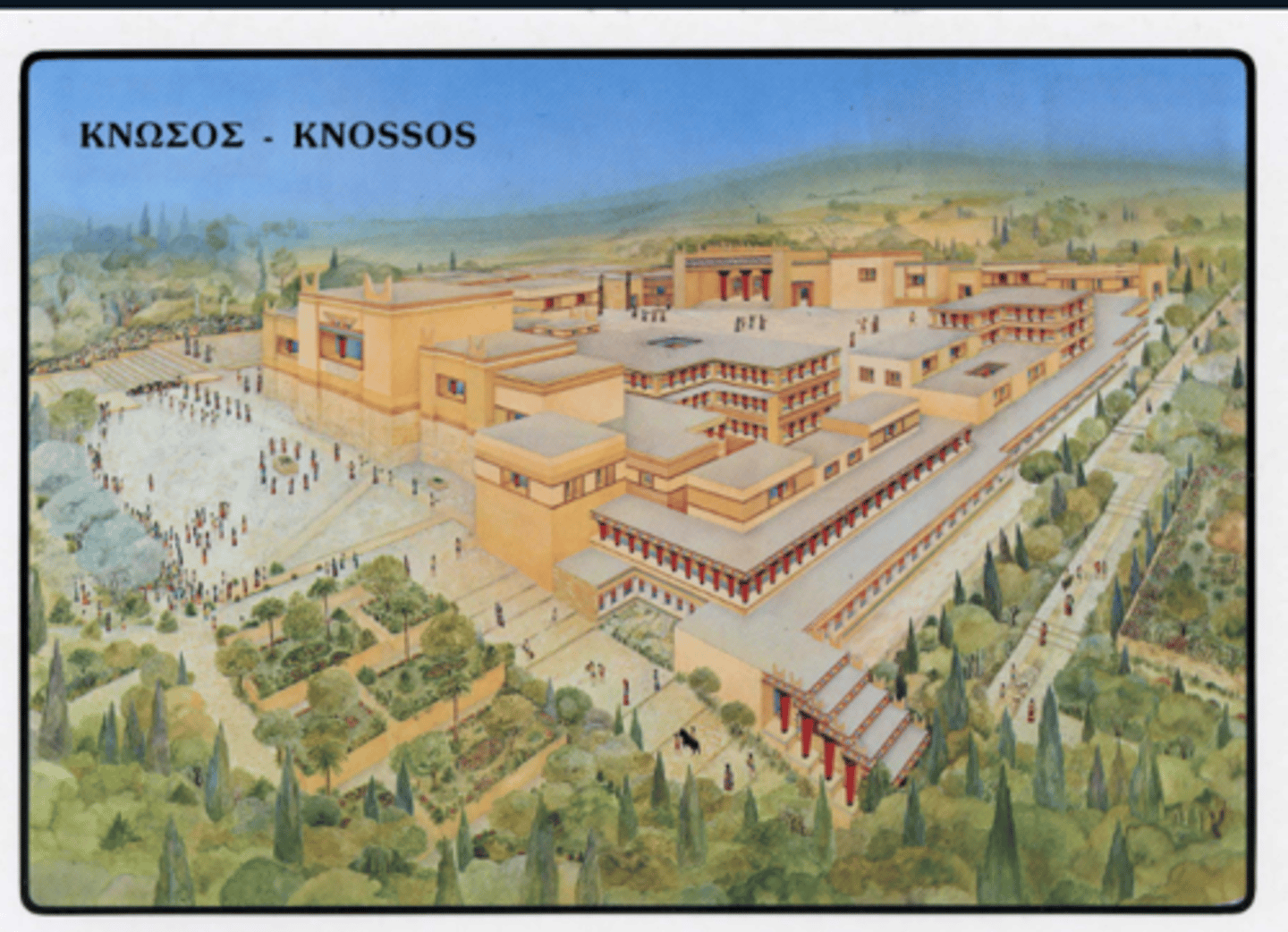
Knossos
-Largest , most important palace
-King Minos and the Minotaur
-Elaborate temple and royal quarters with frescoes
-Palace cult
-:Horns of consecration"
-Double axe
-Snake goddess
-SIgnet rings
Minoan writing systems
-Cretan hieroglyphics (pictographic)
-Linear A (pictographic and syllabic)
-Minoan language extinct and mostly undeciphered
Mycenaean
-Mainland Greece
-City-states
-Warrior-kings
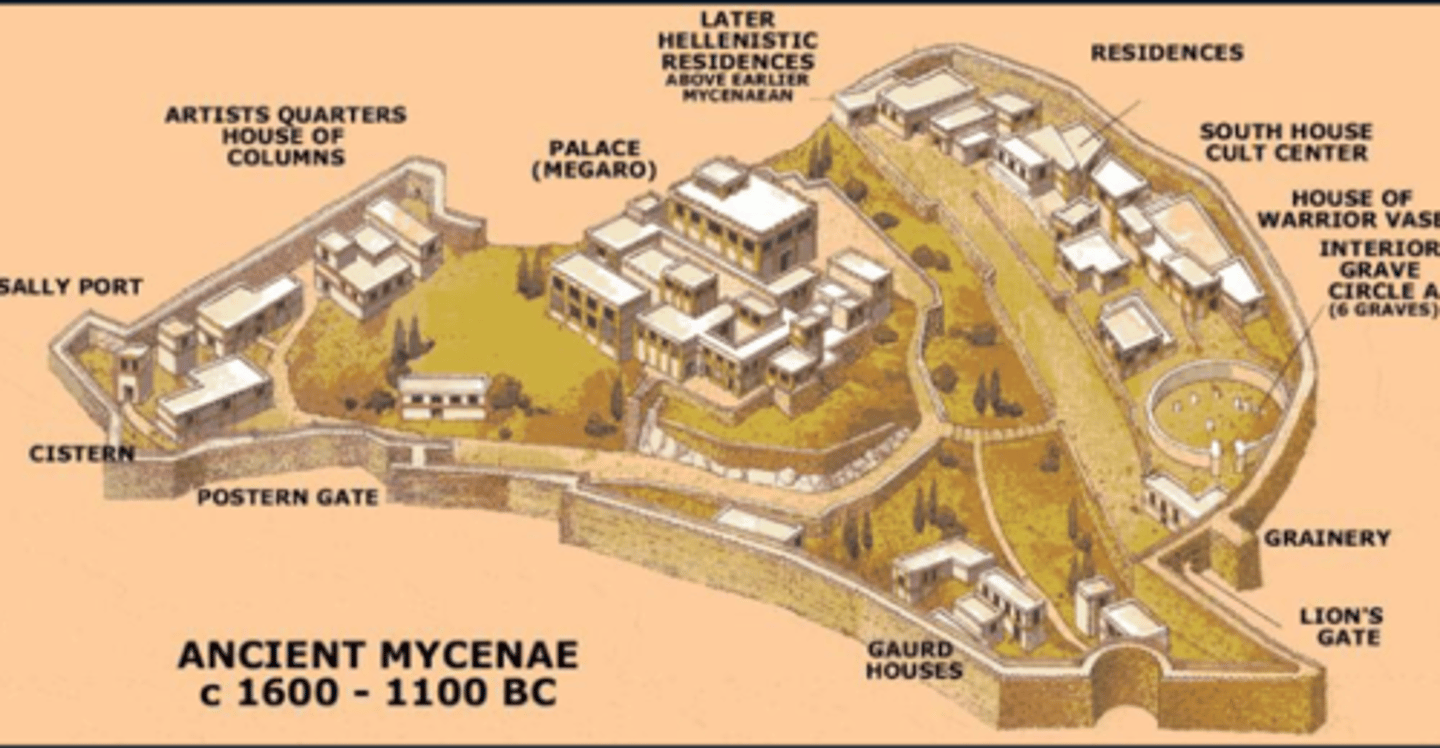
Mycenae
-Largest and most powerful of the city-states
-Heavily fortified admin center
-Megaron: audience hall of palace
-Circular complex of royal shaft graves
Mycenaean Writing
-Linear B
-Derived from Linear A
-Translated- form of ancient Greek
-Pictographic and syllabic
-Clay tablets, admin records
Linear B Counting Systems
-Base 10
-Large to small
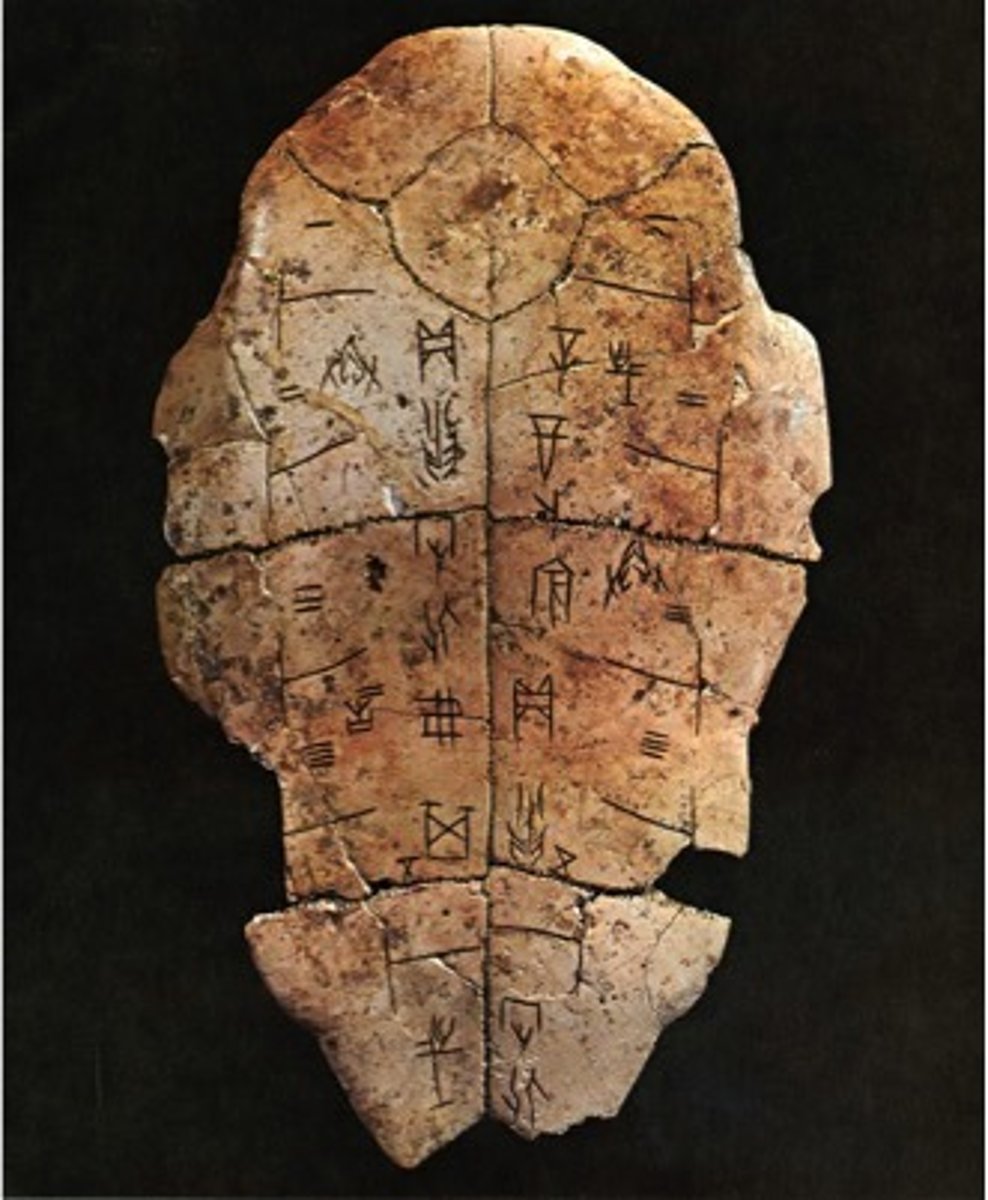
Oracle Bones
The earliest known Chinese writing is found on these from ritual activity of the Shang period.
Nubia (Kush)
-East Africa
-strong connection via trade: gold, ivory, ebony, live animals, slaves
Kerma
-early kushite capital
-state middle kingdom egypt
-large urban trade center
-frequent warfare with Egypt
-conquered in Middle and New Kingdoms
-incorporated into Egypt 1500 BC
Deffufa
-largest mudbrick structure in Africa
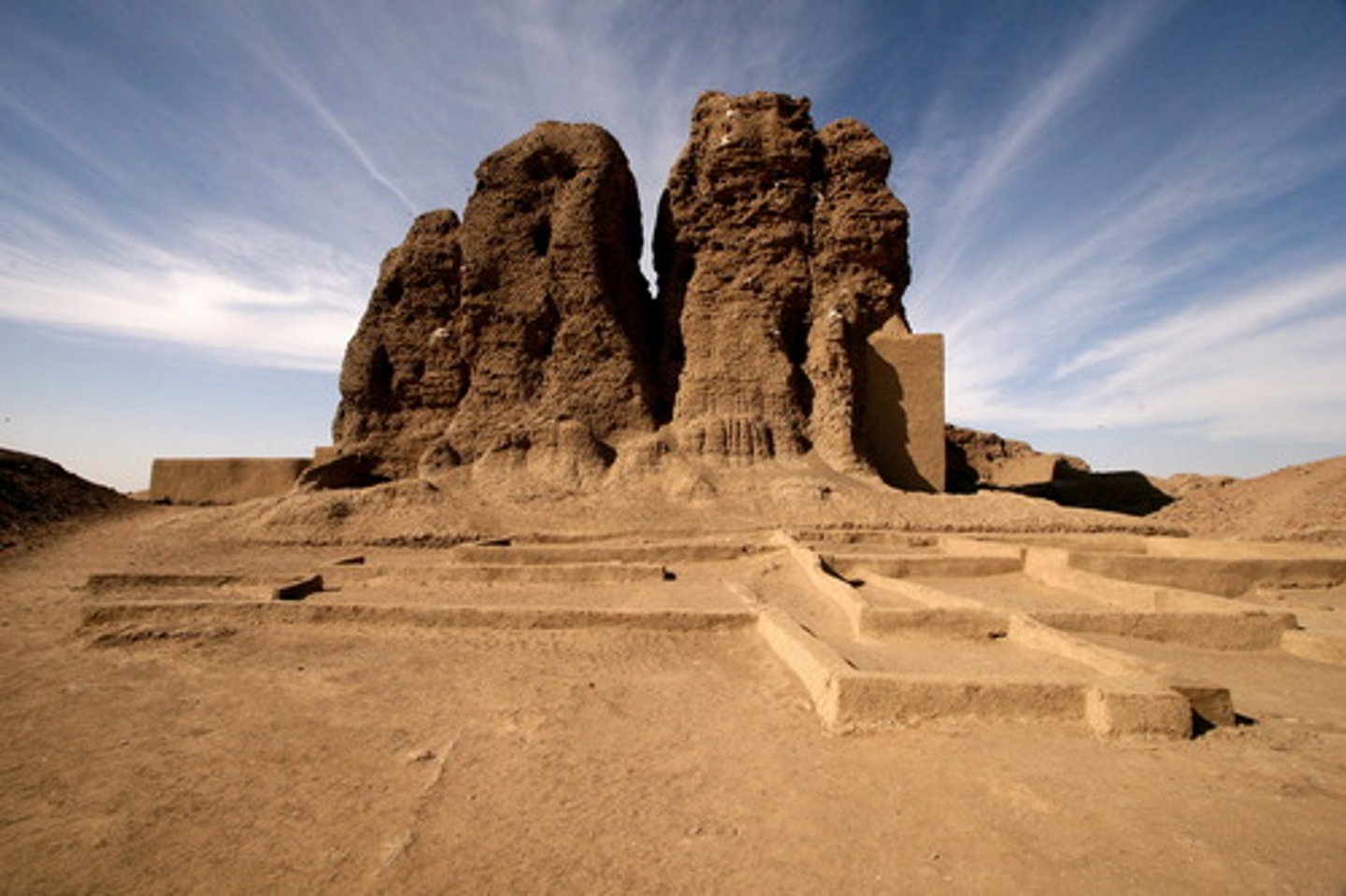

Kingdom of Kush
-regains independence 1100 BC
-capital at Meroe
-trade center
-influence of Egyptian culture, political systems, religion, and art
-independent writing systems: merotic
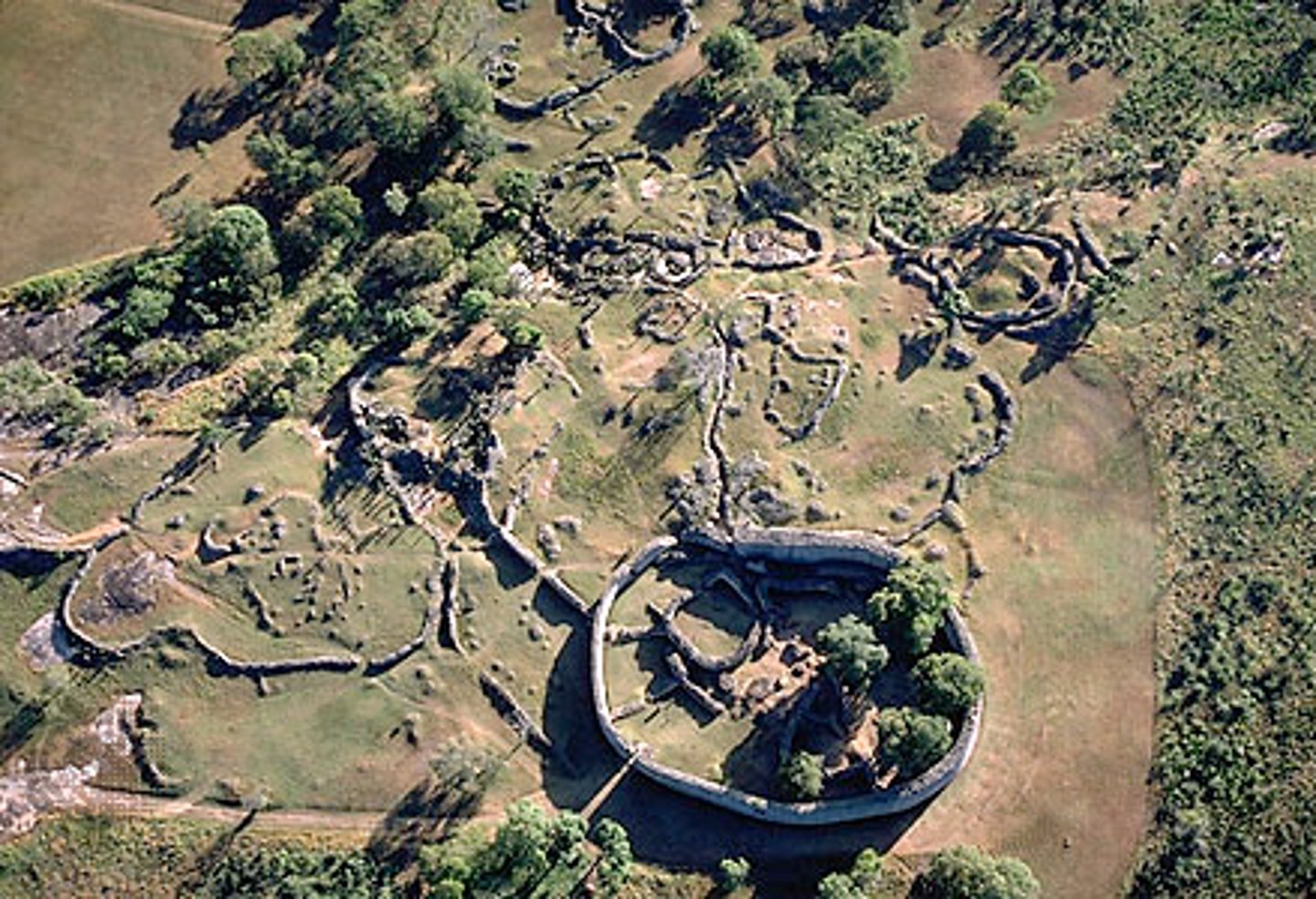
Great Zimbabwe
-Hill complex: king's palace, ceremonial center
-Great Enclosure: largest pre-colonial structure in sub-Saharan Africa, royal residence (1st queen)

Mali Empire
-West African: rich pastureland (cattle), abundant natrual and mineral resources
-Niger River region
-trade centers linking: sahara and equatorial africa, west africa to mediterranean world
-sahara: salt, minerals
-equatorial africa: gold, ivory, ebony, slaves
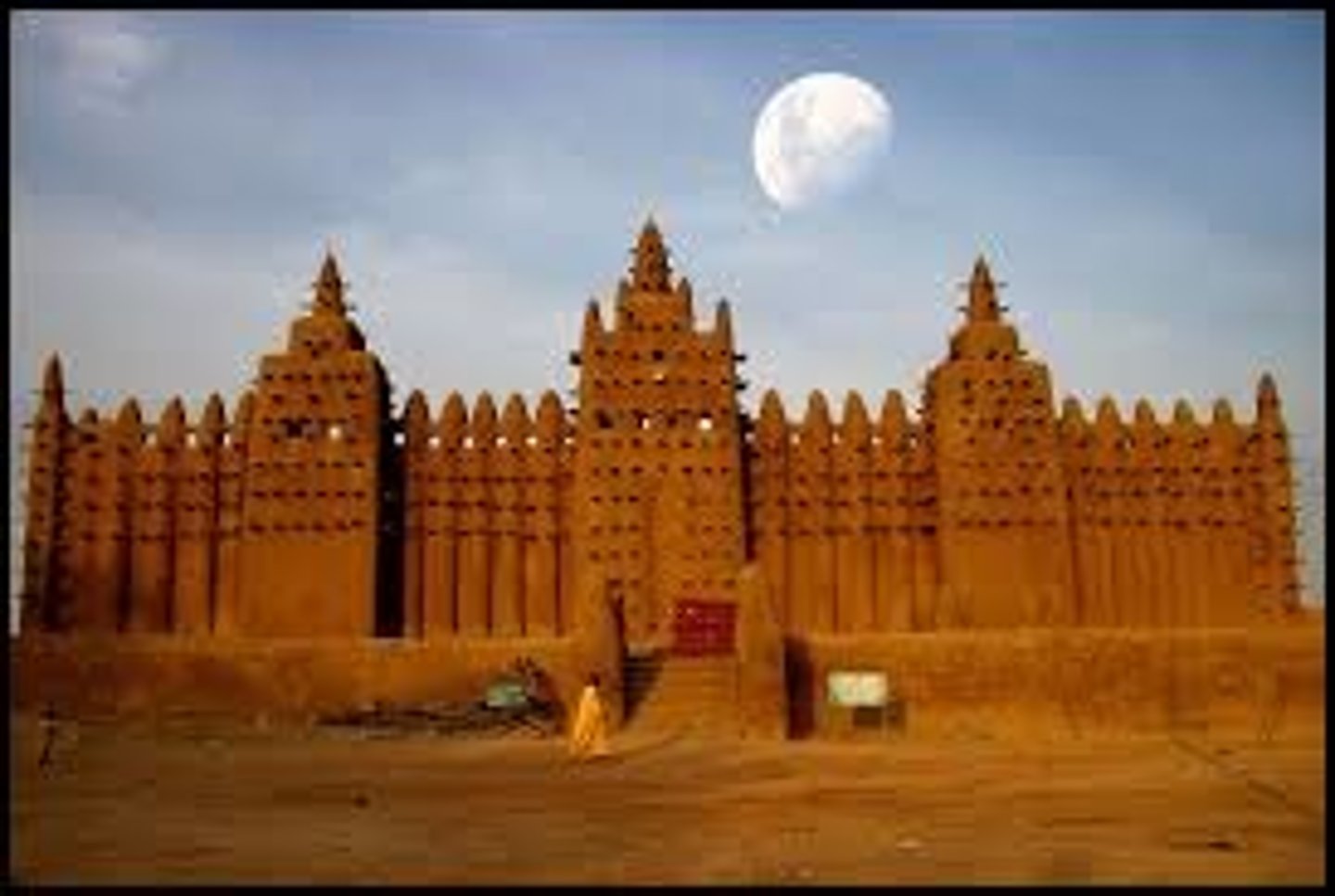
Djenne-deno
-eary capital
-fortified, mudbrick tell settlement
-trade center, camel caravans
-moved 2.5km SE to Jenne: defense
-trade center, center of Islamic learning (books)
Great Mosque of Djenne

The Maya
-Mesoamerica
-Tropical lowlands (north) and highlands (south)
-influenced but independent from the Olmec
-large scale reservoir systems
-raised field systems
Tikal
-one of the most powerful Maya city states
-trade center in heart of Maya world
-competition with neighboring city-states
-central acropolis and palace complex (elite residences and admin buildings)
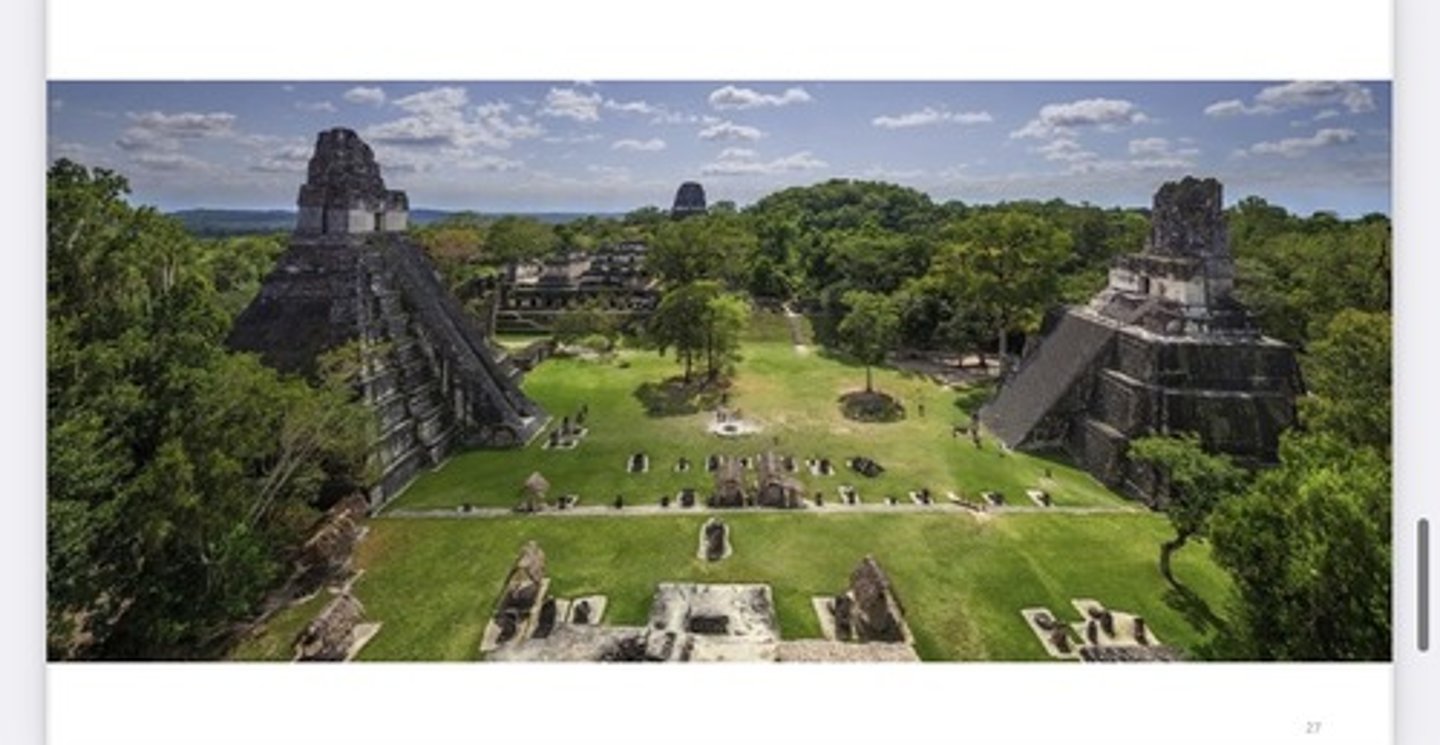

Tikal Elite Buildings
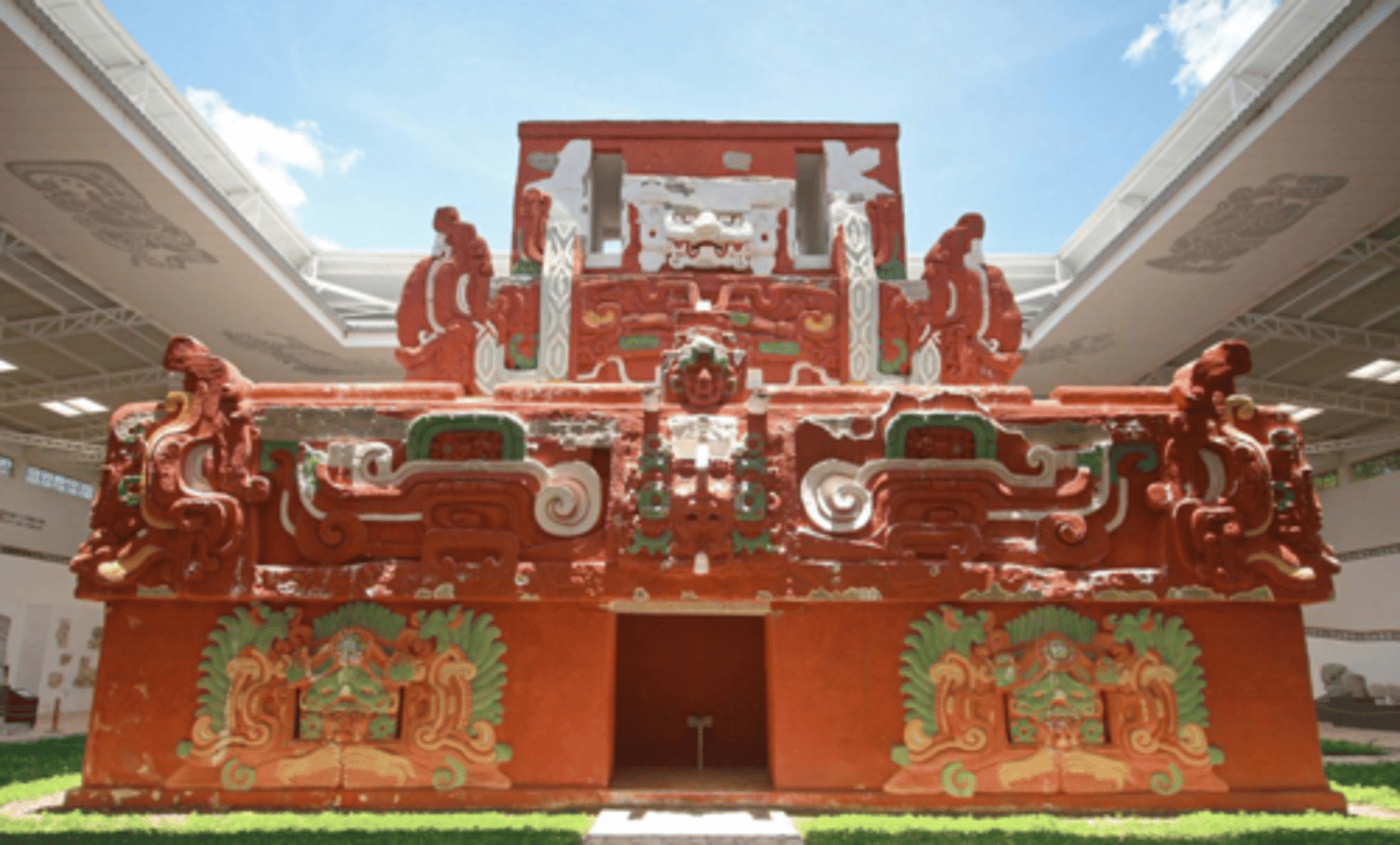

Tikal North Acropolis
Temples and royal burial complex
Tikal Great Plaza
Largest temples, courtyard, monuments
Mayan Writing
-Stele, codices
-logograms and syllables
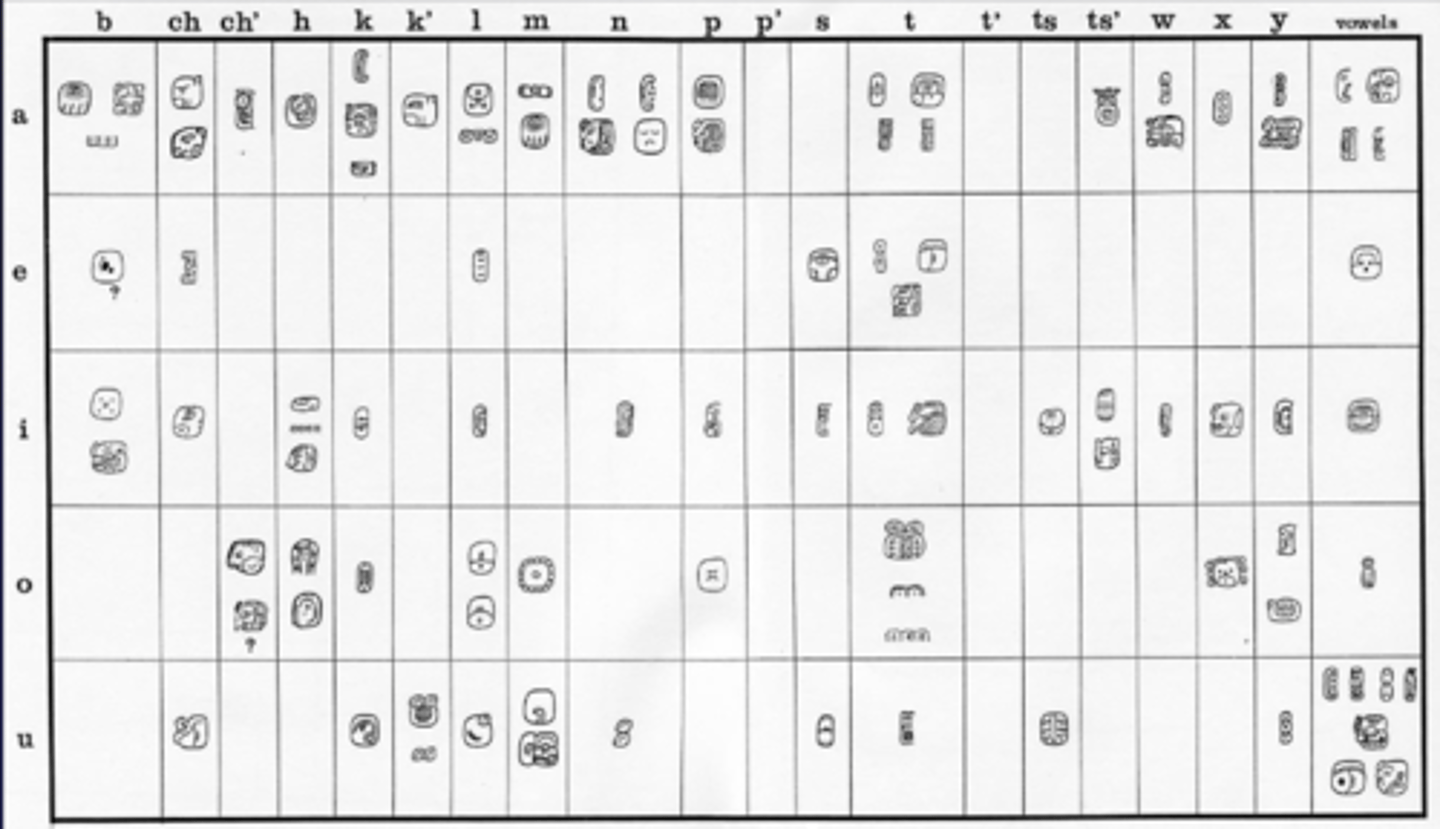
Mesoamerican Number Systems
-symbols for 0,1,5
-base 20 counting system

Mesoamerican Calendrics
-long count: linear time
-calendar round: cyclical time
-vague (solar) year 365 days
-18 months 20 days
-1 extra month 5 days (sacred month)
-260 day sacred almanac
-ritual calendar
-20 named days
-numbers 1-13
-each day combines 2 names
-vague year date AND sacred almanac date
Zapotecs
-Southern Mexico
-Oaxaca, semi arid enviornment
-settlements confined to river areas
-The Valley of Oaxaca
-long-term sequence from early domestication to small farming villages to chiefdoms to states
-first domesticated crop: pepo squash
-3 chiefdoms which causes conflict
-expand power beyond valley (territorial state)
-defensive walls 2 mi
San Jose Mogote
-largest of 25 villages in the Valley of Oaxaca
-capital of the most powerful of the 3 chiefdoms
-long distance trade of obsidian
-fortifications
-monumental architecture
Stele

Codex

Zapotec Writing
-hieroglyphics
-one of the two earliest writing systems in Mesoamerica
-Both developed prior to state formation
-syllabic and logographic
-only partially deciphered
-inscriptions recount major historical events
Zapotec Number/Calendar System
-Shared with other Mesoamerican groups
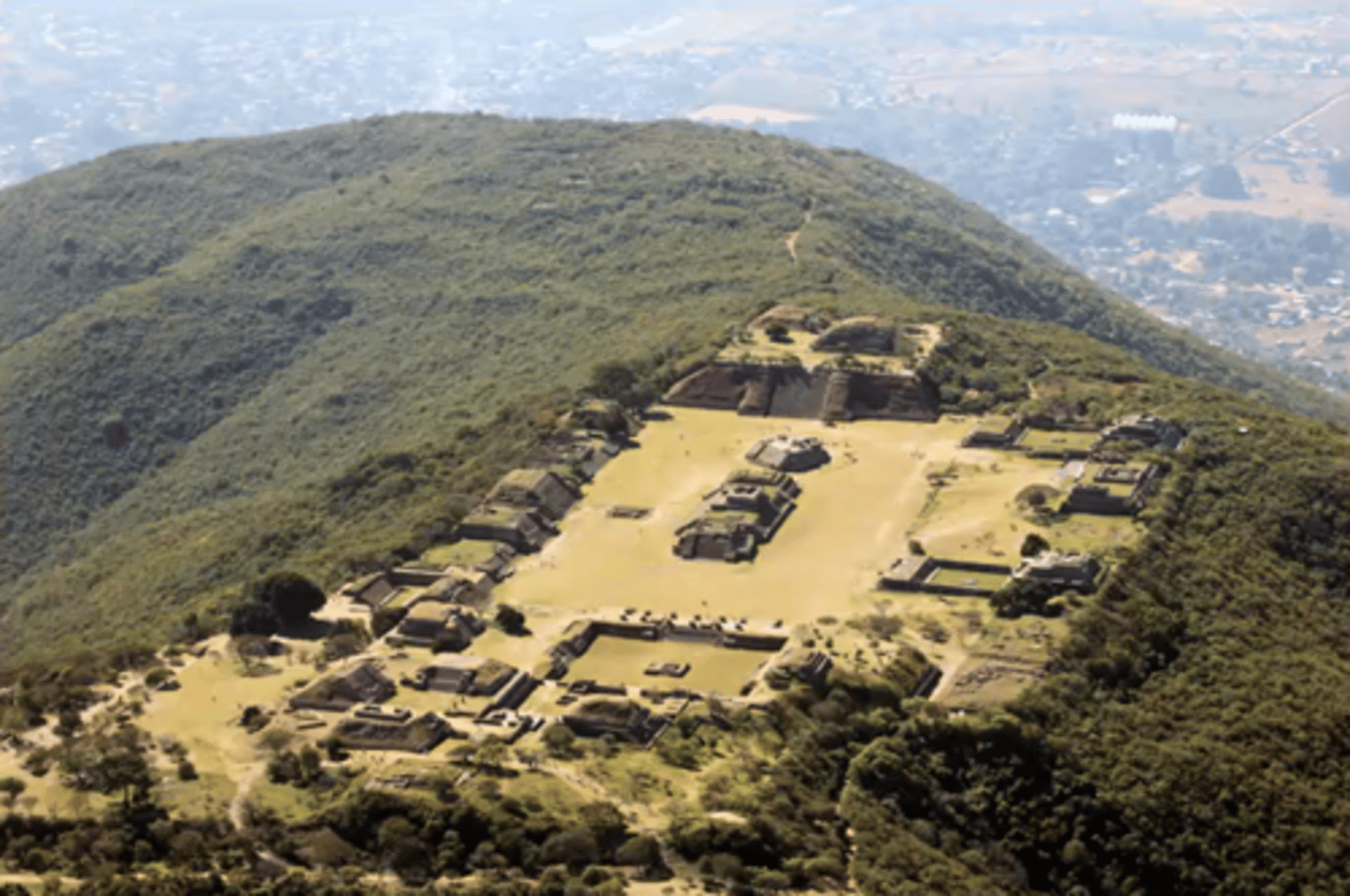
Monte Alban
-capital city of Zapotec, urbanized city
-early: city states
-built on a hill for a defensable location, and connection to gods
-same general plan as other Mesoamerican citites
-unique: citadel, defensive

Danzante
-images of war captives
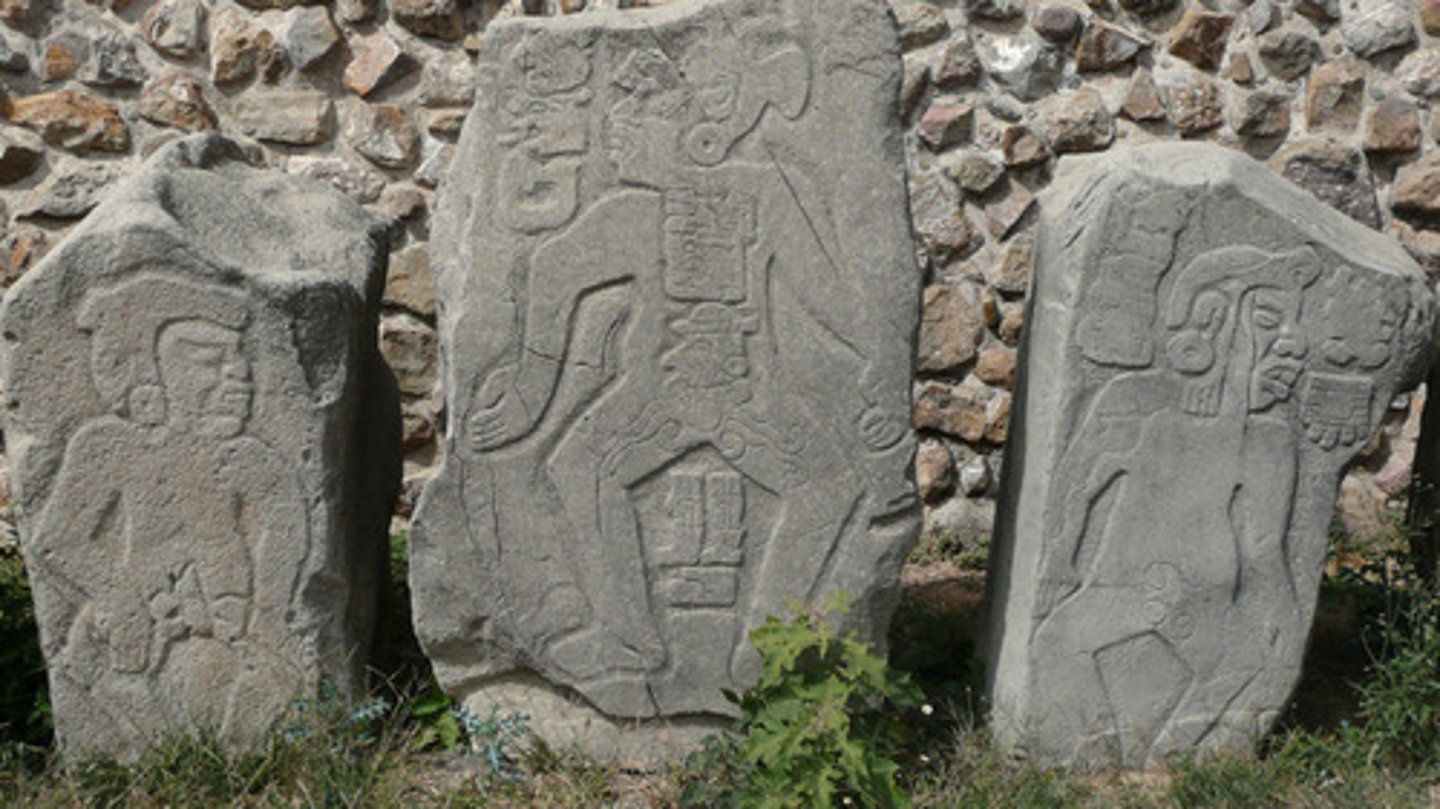

Building J
-unique building
-arrowhead shape
-offset orientation, astronomical alignment, venus?
-40 carved stone slabs
Spread of Zapotec Culture
-military expansion
-regional cultural influence
-pottery styles, architecture, conquest slabs
-trade, rital, art, ballgame
Teotihuacan
-one of the biggest cities in the americas
-Avenue of the Dead: mile and a half long strip in the middle of the city
-Pyramid of the Sun: largest pyramid in the americans, plastered and painted red with murals
-Pyramid of the Feathered Serpent: royal retainers and sacrificed victims
-Center for: pop.,admin, religion, economy
-2200 apartment complex, diff. in status, wealth, ethnicity
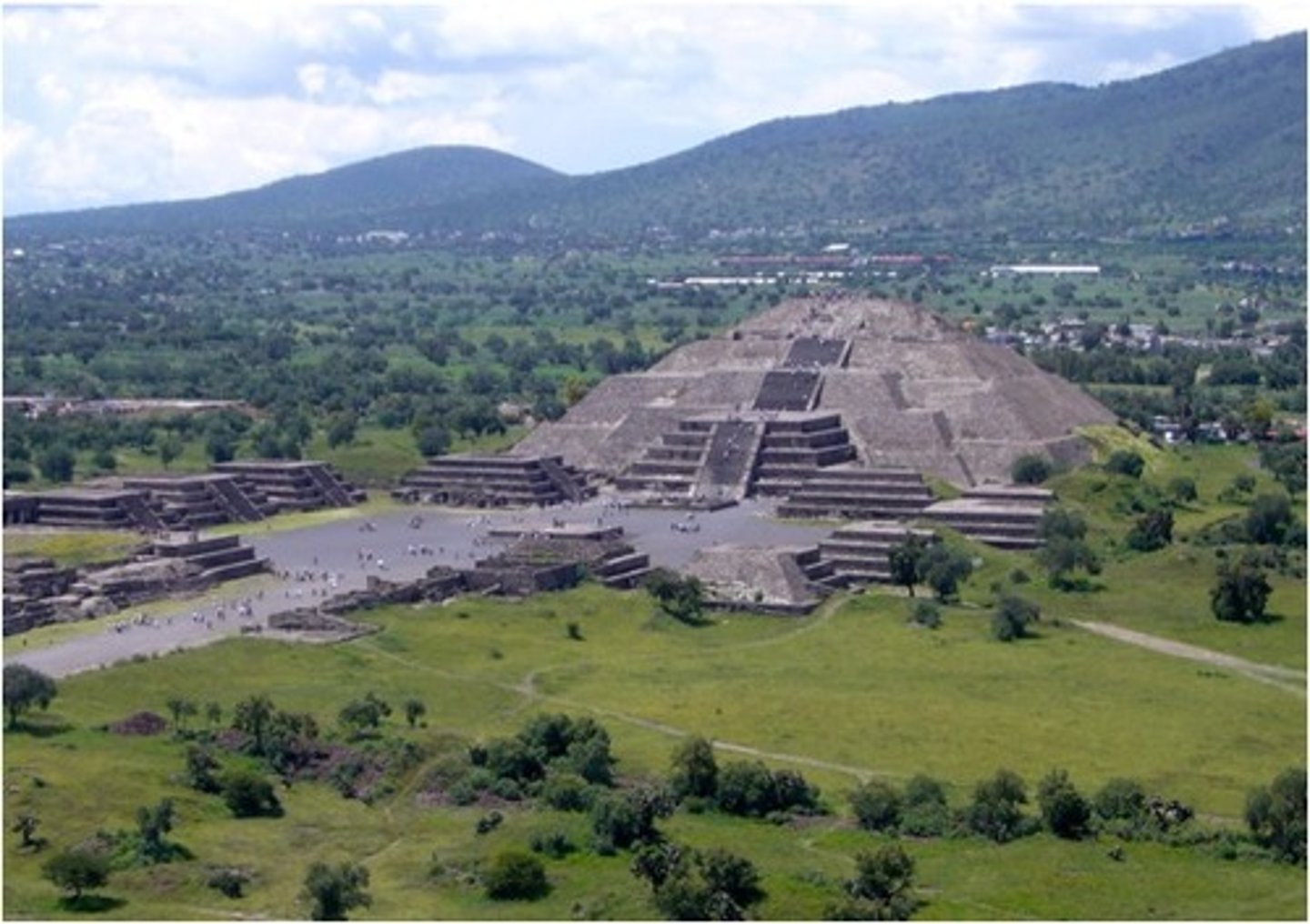

Teotihuacan Culture
-develops later than Maya and Zapotecs
-in the Valley of Mexico
-largest expanse agricultural land in highland mesoamerica
-rich central lakes
-basin (7000 ft) surrounded by volcanic mountains
-major exporter of obsidian
-urban center
-unclear political organization
-no named rulers
-most images are gods
-rulers in groups
-no elite burials or personal monuments
-most likelt not an empire
Teotihuacan Writing
-preserved writing is rare
-not used to record historical events on momuments
-only small portion "translated"
-language unknown, no modern speakers
Teotihuacan Collapse
-collapse in same period as both Classic Maya and Zapotecs
-No evidence of foreign invaders
-Burning of elite sectors only, internal revolution?
Incan Culture
-In South America: Andes, enviornment: deserts, forced cvilizations to rivers
-Empire
-very large territory, populations
-military expansion
-consolidation of territorial states
-different cultures, languages, governments, etc
-difficult to maintain order
-4 admin districts
-forced relocation (mitmaq)
-reduce ability to organize and rebel
-cultural hegemony
Cuzco
-the capital city of the Incan Empire, Located in present-day Peru
-largely destroyed by spanish
-parts integrated into modern city
-unique stone working
-puma shaped city walls
-Sacsahuaman fortess
Inca Road System
-25,000 miles of roads
-controlled by Inca state
-movement of military and state sanctioned trade
-creation of tampu, military outposts, roadside lodging and supplies
Andead (Incan) Recording Systems
-complex, bureaucratic administrative systems
-NO writing
Quipu
-knot/string recording system
-base 10
-number of knots each multiple of 10
-accounting, dates, people, places, simple messages

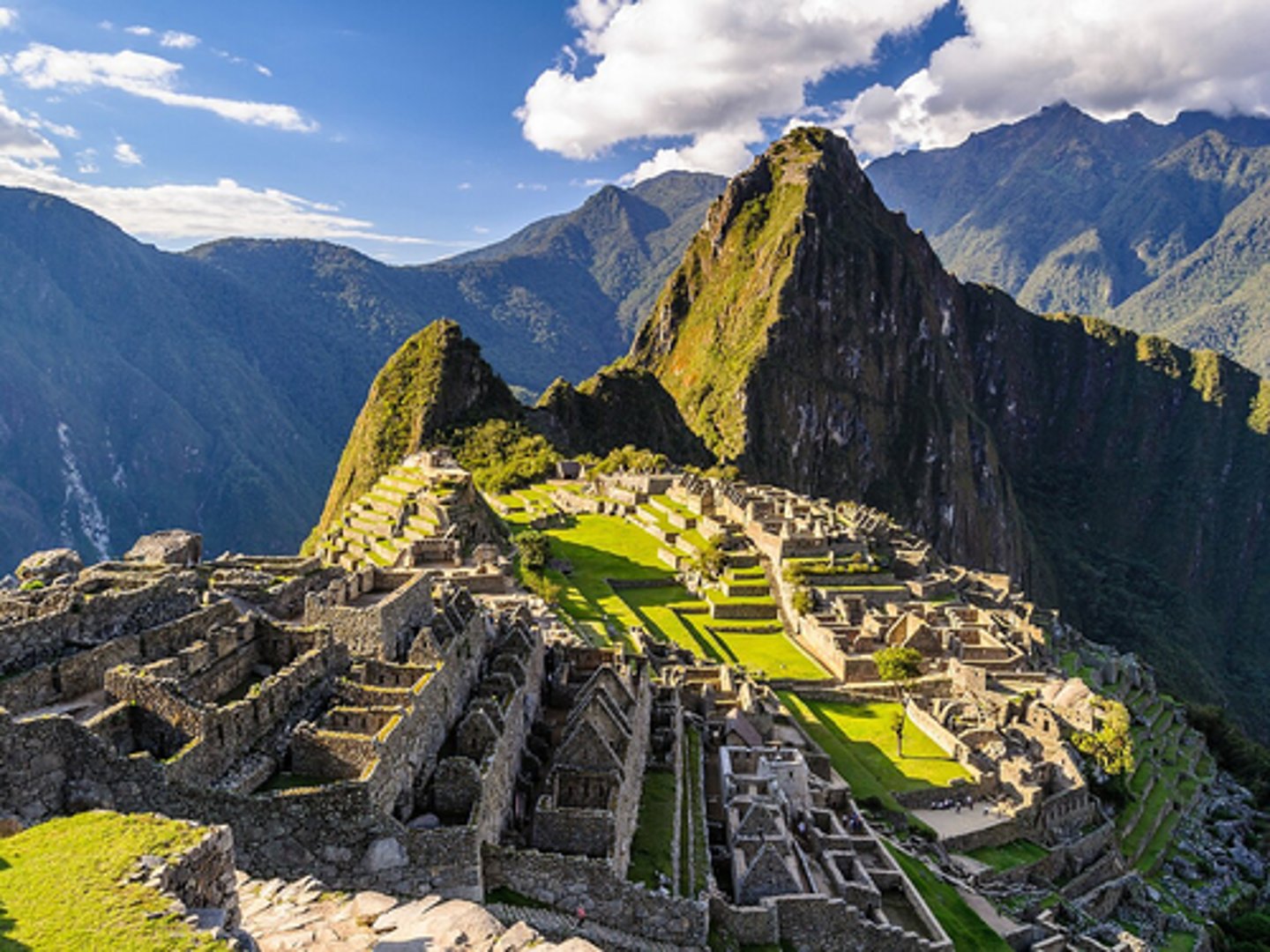
Macu Picchu
-royal estate
-ceremonial center
-astronomy

Inca Collapse
-Francisco Pizarro (spanish conquistador)
-period of civil unrest, smallpox
-captured Inca Atahualpa