General Histology (All)
1/448
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
449 Terms
Nephron
Functional unit of the kidney
Forms urine
T12-L3
The kidneys are located lateral to which vertebrae?
Renal fascia
Connective tissue layer that attaches to abdominal wall
Adipose capsule
Fat cushioning kidneyR
Renal capsule
Fibrous sac
Protects kidney from trauma and infection
Cortex
Composed of roughly 1.25 million nephrons
Renal papilla
Point of pyramid
Renal sinus
Surrounded by renal parenchyma
Contains blood & lymph vessels, nerves, urine-collecting structures
Blood vessels, renal corpuscle, renal tubule
3 main parts of nephrons
Glomerulus
Fenestrated capillaries
Initiates urine production
Filtrate lacks cells & proteins
Receives blood supply from afferent arteriole; drained by efferent arteriole
Renal corpuscle
The beginning of the nephron
the nephron’s initial filtering component
Renal corpuscle
Composed of glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule
Efferent arterioles
Which arteriole’s diameter is smaller? (Efferent/Afferent)
Bowman’s capsule
aka glomerular capsule
Surrounds the glomerulus
Composed of a visceral inner layer formed by podocytes
Parietal outer layer composed of simple squamous epithelium
Visceral layer of podocytes
Fluids from blood in the glomerulus are filtered through the _____, resulting in the glomerular filtrate
Renal tubule
Leads from glomerular capsule
Ends at tip of medullary pyramid
~3cm long
4 major regions:
Proximal convoluted tubule
Nephron loop
Distal convoluted tubule
Collecting duct
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
Arises from glomerular capsule
Longest, most coiled region
Lies in cortex
Lined by simple cuboidal epithelium with brush borders
Prominent microvilli
Loop of Henle/Nephron Loop
“U”-shaped, distal to PCT
lies in medulla
has ascending and descending limbs
Simple squamous epithelium
Lining of lower end of ascending limb of loop of Henle
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Lining of the distal portion of ascending limb of loop of Henle
Thick
(Thick/Thin) segment
active transport of salts
high metabolism, many mitochondria
Thin
(Thick/Thin) segments
permeable to water
low metabolism
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
coiled, distal to nephron loop
shorter and less coiled than PCT
very few microvilli
contacts afferent and efferent arterioles
contact with peritubular capillaries
Collecting duct
where DCTs of several nephrons empty into
passes into medulla
several merge into papillary duct (~30 per papilla)
drain into minor calyx
Ureters
pair of muscular tubules
extend from renal pelvis to bladder
oblique entry into bladder prevents backflow of urine
Transitional epithelium
Epithelium of ureter (mucosa)
Urinary bladder
collapsible muscular sac
stores and expels urine
Detrusor muscle
Muscle of urinary bladder
Internal urethral sphincter
retains urine in bladder
smooth muscle, involuntary
External urethral sphincter
Provides voluntary control over voiding of urine
skeletal muscle
Excretion
The removal of organic waste product from body fluids
Elimination
The discharge of waste products into the environment
Glomerular filtration
Creates a plasmalike filtrate of the blood
Tubular reabsorption
Removes useful solutes from the filtrate, returns them to the blood
Tubular secretion
Removes additional wastes from the blood, adds them to the filtrate
Water conservation
Removes water from the urine and returns it to blood, concentrates wastes
muscle
its main characteristic is the ability to contract and shorten, making movements possible
3 types:
Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth
skeletal muscle
attaches to the skeleton and enables the body to move
voluntary muscle
long, cylindrical, containing several nuclei per cell
striated (or banded) due to the arrangement of protein in the cell
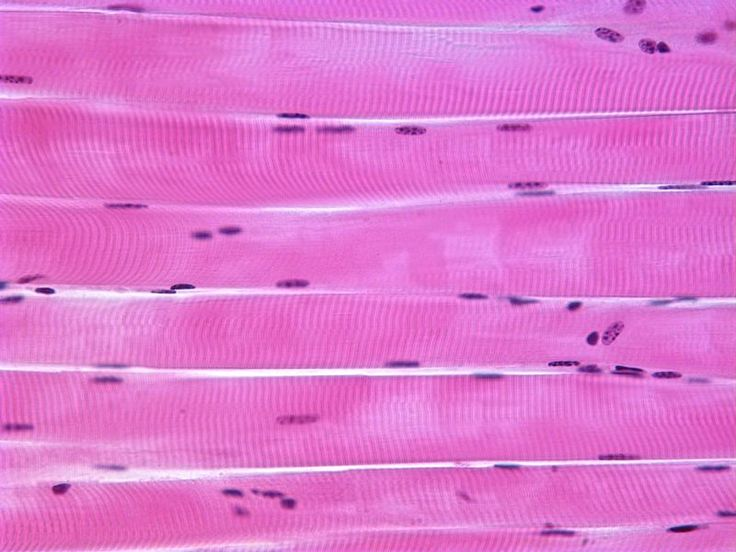
cardiac muscle
muscle of the heart
involuntary control, pumps the blood
cylindrical cells, shorter than skeletal muscle cells
striated, 1 nucleus per cell
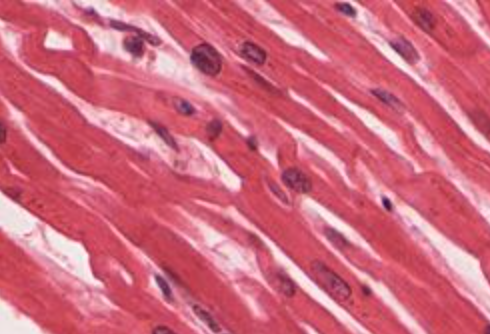
intercalated discs
gap junctions that link adjacent cardiac muscles so that electrical impulses can travel between cells and causes to contract almost simultaneously
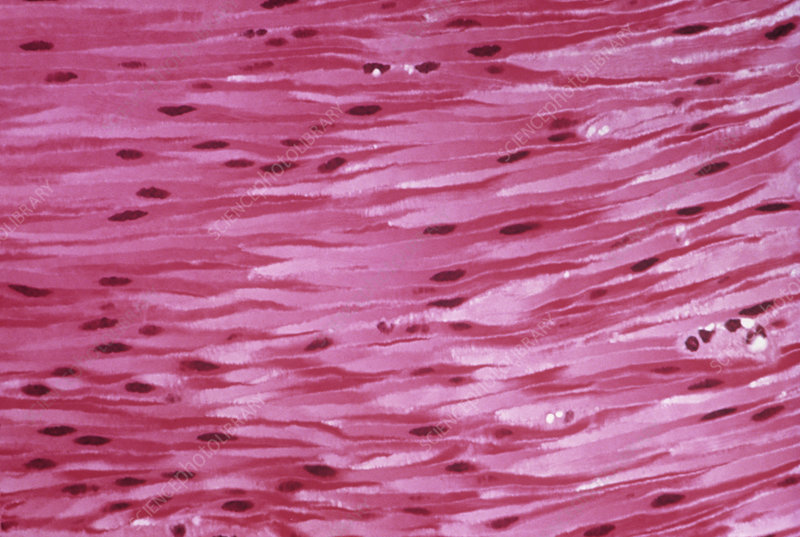
smooth muscle
forms the walls of hollow organs (except the heart)
found in the skin and eyes
moves food through the digestive tract
empties urinary bladder
involuntary control
cell has no striations, single nucleus, and tapered at each end (fusiform)
40%
about __% of the body is made up of skeletal muscle
10%
about __% of the body is made up of cardiac and smooth muscle
10-80
all skeletal muscles are composed of numerous fibers ranging from (?) micrometers in diameter
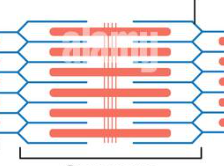
sarcomeres
a regular pattern of functional units — basic contractile unit of muscle fiber
epimysium
External sheath of connective tissue surrounding the whole muscle
separates whole muscles from one another
covered by fascia
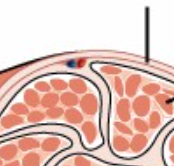
Whole muscle
Made up of multiple muscle fascicles
muscle fascicle
Bundles of individual muscle fibers
Surrounded by perimysium:
Thin sheaths of connective tissue
Continuous with epimysium at their ends
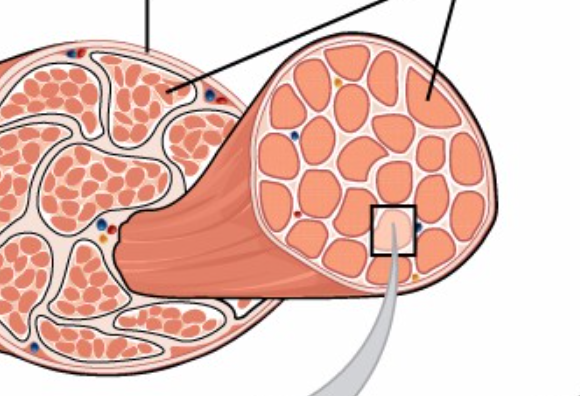
Muscle fibers
Individual muscle cells (but typically called “fibers” because they are so long)
Immediately encased by sarcolemma (muscle cell–specific
cell membrane)
surrounded by endomysium
Thin sheaths of areolar connective tissue
Contain capillaries and nerve fibers to supply each cell/fiber
Continuous with perimysium and epimysium at their ends
perimysium
Thin sheaths of connective tissue
Continuous with epimysium at their ends
sarcolemma
the plasma membrane of the muscle cell
myofibrils
Long functional subunits made up of myofilaments within a muscle cell
Surrounded by sarcoplasmic reticulum
Take up a majority of the sarcoplasm
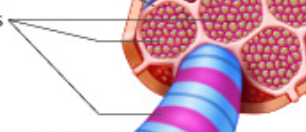
myofilaments
individual contractile proteins
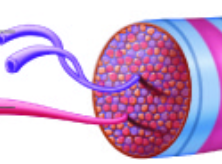
sarcoplasm
Muscle cell cytoplasm
Primarily filled with protein bundles called myofibrils
myoglobin
binds/stores O2 until needed
glycogen
used for energy
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Forms a network around each myofibril
myosin
thick straight filaments arranged in parallel
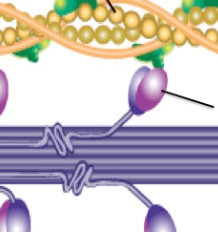
actin filaments
lighter band (microscopically)
Z-line
tails of actin filament
M-line
middle portion of sarcomere
H-zone
portion between m-line and z-line
Connective tissue
group of tissues in the body that:
maintain the form of the body and its organs
provide cohesion and internal support
ground substance
Unstructured material that fills the space between cells and contains all components of the extracellular matrix (ECM)
Collagen fibers
Consists mostly of cross-linked collagen protein
Provides high-tensile strength
Larger fibers consist of small cross-striated fibrils
The glycine-proline-hydroxyproline sequence is vital for its structure
glycine-proline-hydroxyproline
the amino acid sequence vital for collagen fiber structure
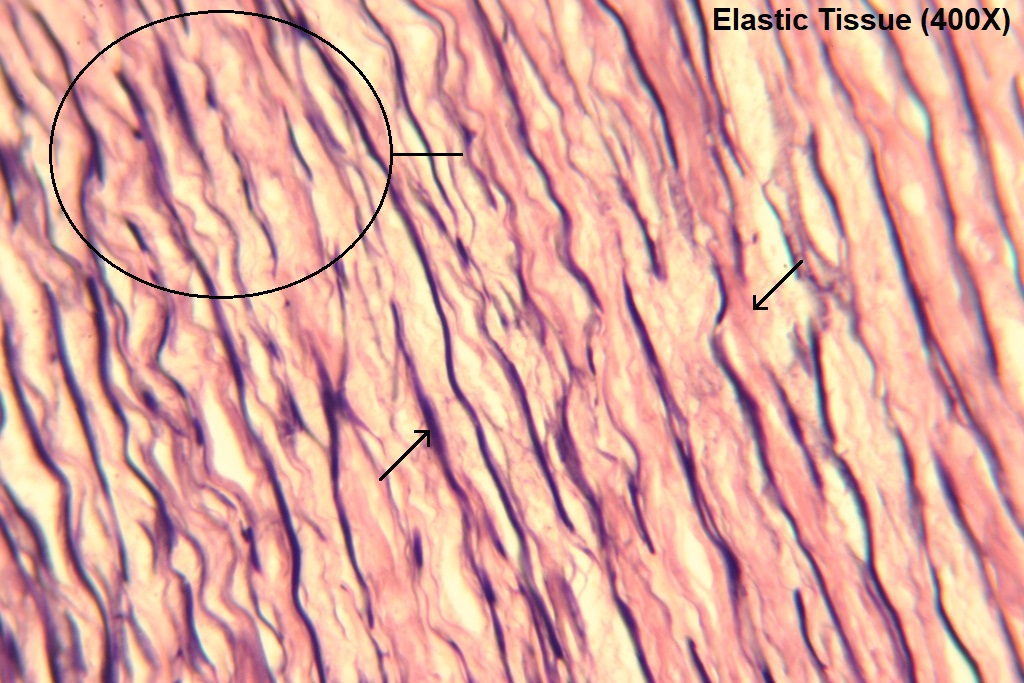
Elastic fibers
Consists of the rubber-like protein elastin
Long and thin branching fibers; highly distensible
Lack structural subunits (fibrils) unlike collagen
Rich in glycine and proline, but also contain large amounts of valine and the unique amino acid, desmosine
found in skin, lungs, blood vessel walls
skin, lungs, blood vessel walls
where are elastic fibers found?
fibroblasts
examples of stationary cells
lymphocytes, macrophages, mast cells
examples of migratory cells
stationary cells
cells that can be of the mature or immature types
the undifferentiated (immature) cell type has the suffix "blast":
connective tissue proper: fibroblast
cartilage: chondroblast
bone: osteoblast
fibroblasts
Major cell type of the prototypical connective tissue
Long and spindle-shaped cells
Secrete tropocollagen (a precursor of collagen) and constituents of the ground substance
tropocollagen
what do fibroblasts secrete?
retain water; support and cushion organs
Function of loose areolar connective tissue
loose areolar connective tissue
connective tissue that:
Support and bind other tissues
Hold body fluids
Defend against infections
Consist of fibroblasts, macrophages, fat cells, and occasional mast cells
Typical arrangement is that of loose fibers forming “empty spaces”: a
reservoir of fluid
High hyaluronic acid content
Retains water seen in edema
Lipid storage
Function of loose adipose connective tissue
Loose adipose connective tissue
Major function: lipid storage
Adipocytes are the predominant cell type (90%)
can develop anywhere there is areolar tissue
matrix is rare
cells are packed close together
richly vascularized
White adipose tissue
type of adipose tissue that stores energy that is used during periods of fasting
Brown adipose tissue
type of adipose tissue mainly located between the shoulder blades and in the neck and abdominal wall
structural support for liver, spleen, lymph nodes
Function of loose reticular connective tissue
loose reticular connective tissue
Fine fibers composed of collagen that form fine-meshed networks around cells and help maintain the integrity of organs
Function: structural support of the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes
Mostly made up of reticular fibers (type III collagen)
liver, spleen, lymph nodes
where is loose reticular connective tissue found?
Dense connective tissue
Function: support and transmit mechanical forces
Dense regular connective tissue
Closely packed collagen bundles
Fibers are arranged in the direction of the pulling forces
Fibroblasts are arranged between fibers
Present in tendons, aponeuroses, ligaments
tendons, aponeuroses, ligaments
where is dense regular connective tissue found?
Dense irregular connective tissue
Collagen bundles are thicker and the arrangement is multidirectional
Resists pulling forces from multiple directions
Present in organ capsules, dermis, joint capsules
organ capsules, joint capsules, dermis
Where is dense irregular connective tissue found?
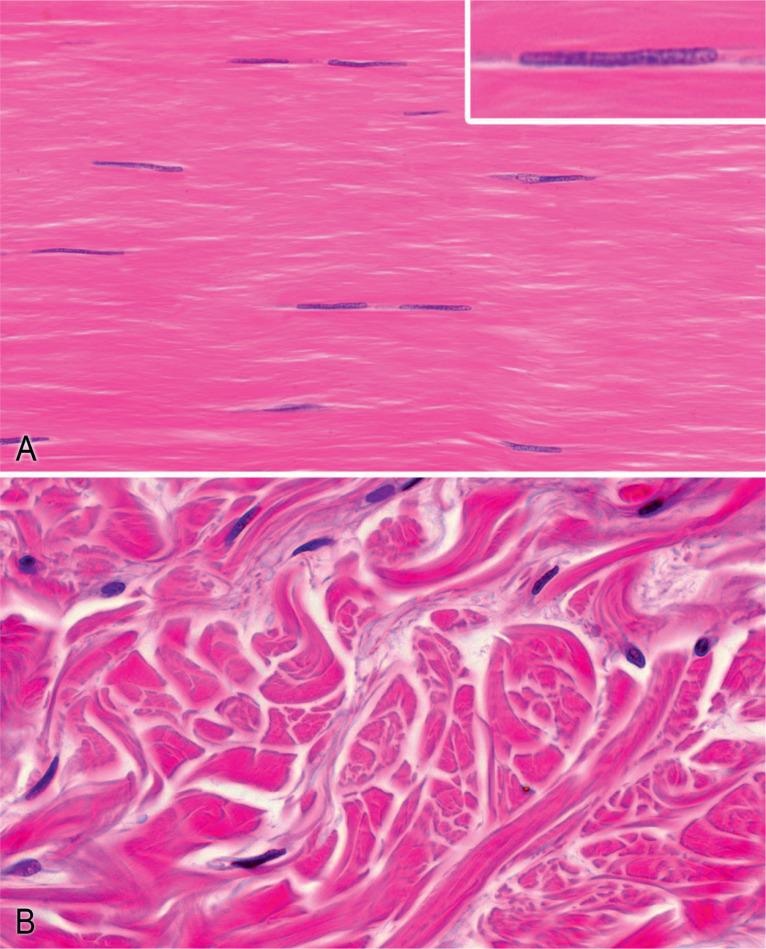
Elastic connective tissue
Extremely elastic connective tissue proper
Present in nuchal ligament and ligamentum flavum
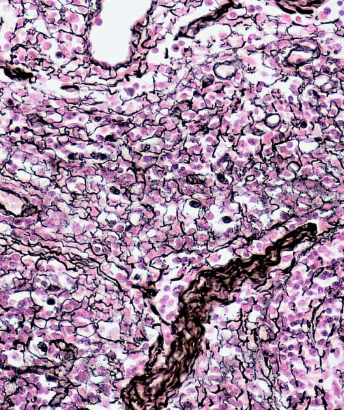
Reticular fibers
distinguished by their tendency to form fine-meshed networks around cells and cell groups and by virtue of their property of staining black, because of adsorption of metallic silver, when they are treated with alkaline solutions of reducible silver salts.
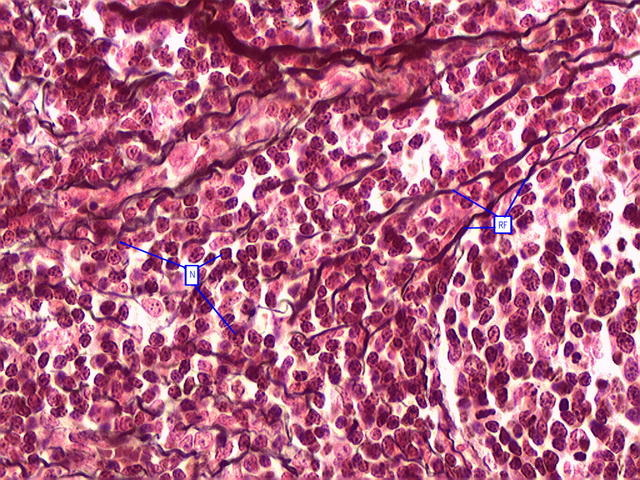
Ground substance
a transparent material with the properties of a viscous solution or a highly hydrated thin gel
Fibrocytes
They are stimulated to develop into fibroblasts
Mast cells
Cells that mediate inflammatory responses such as hypersensitivity and allergic reactions.
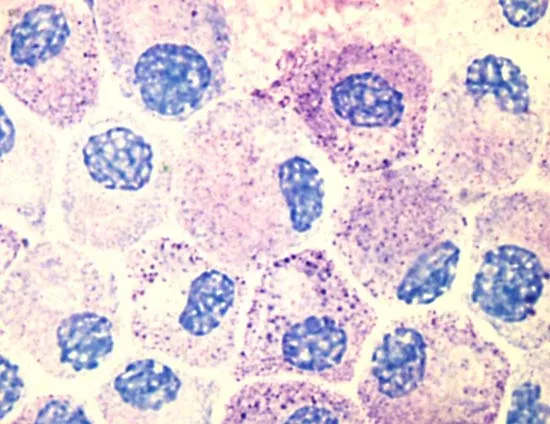
Macrophages
aka histiocytes
derived from circulating monocytes in the bloodstream
important for tissue repair and defense against bacteria
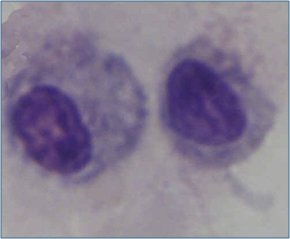
Synovial membrane
lines joint capsules
lubricant and nutrient of avascular joint surfaces
Cartilage
a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this tissue with unusual rigidity and resistance to compression.
Chondrocytes
cells of cartilage that are isolated in small lacunae within the matrix
Bone
consists of cells, fibres, and ground substance, but, in addition, the extracellular components are impregnated with minute crystals of calcium phosphate in the form of the mineral hydroxyapatite.
Histiocytes
macrophages are also known as (?)
Simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cube-like cells
carry out facilitated transport, active transport, or secretion
ex. kidney tubules that have large portion of walls
excretes the harmful by-products into the urine
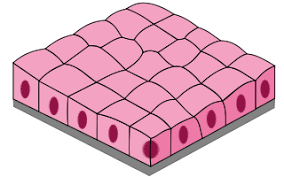
simple cuboidal epithelium
what type of epithelium lines the bronchioles of the lungs?