Institutions Ch 11 (Done)
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Commercial banks
________________ are the largest group of financial institutions in terms of the dollar value of assets
depository institutions
Also called _____________________ because a significant proportion of their funds come from customer deposits
loans | deposits
Major assets are ______ (financial assets), and major liabilities are ________
Perform services essential to U.S. financial markets
Play a key role in the transmission of monetary policy
Provide payment services
Offer maturity intermediation services
disruption
Banks are regulated to protect against a __________ in the provision of these services and the cost this would impose on the economy and society at large
Differences in Balance Sheets of Commercial Banks and Nonfinancial Firms
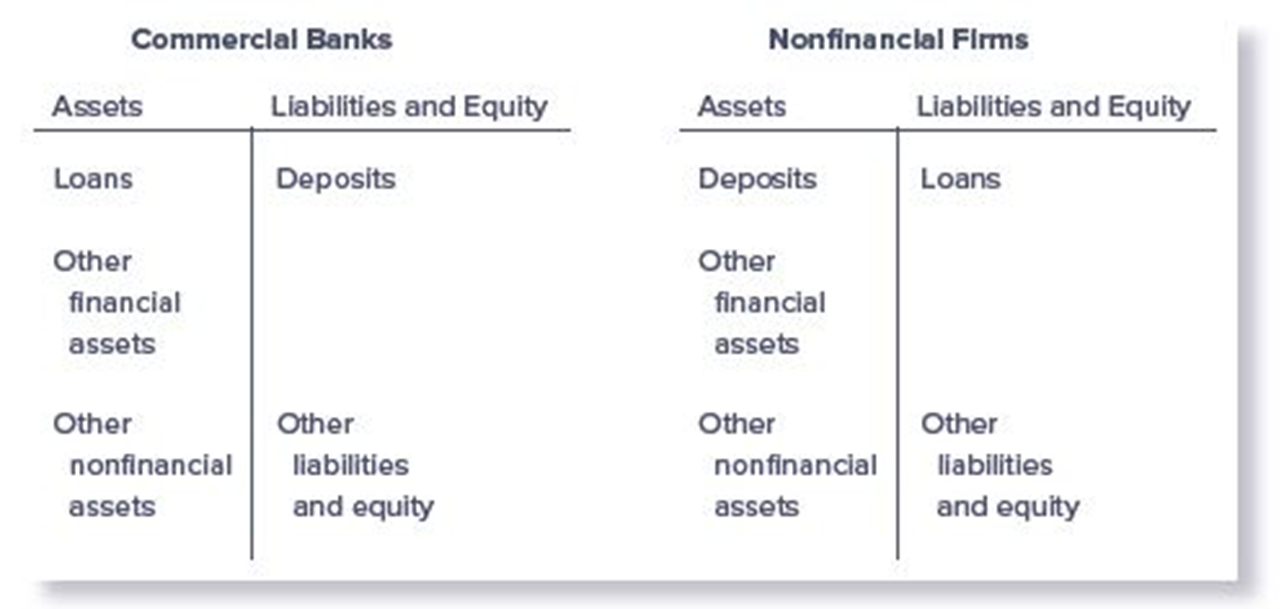
loans
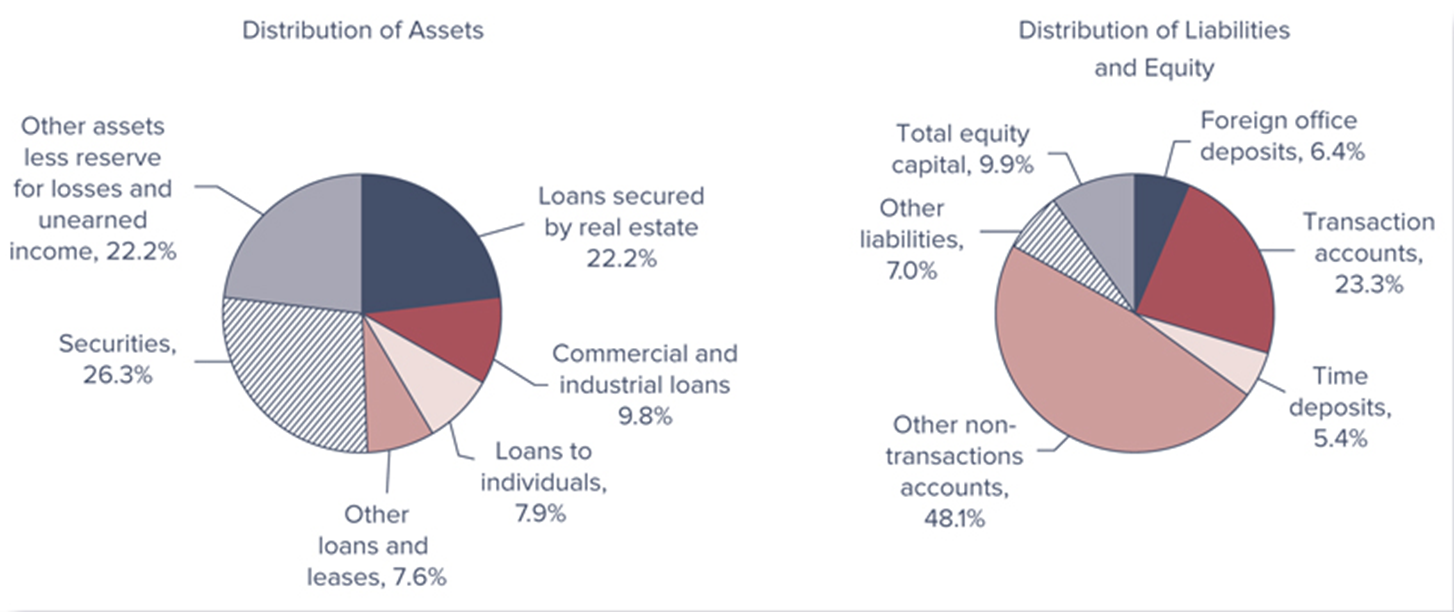
Majority of the assets held by commercial banks are ______
In 2021, net loans and leases amounted 46.7% of total assets
Bank premises and fixed assets, other real estate owned, intangible assets, and all other assets
___________________________________________________________________________________ amounted to 27.0% of total assets in 2021
Investment securities
___________________ generate interest income and provide banks with liquidity
Investment securities generate interest income and provide banks with liquidity
Include interest-bearing deposits purchased from other FIs, federal funds sold to other banks, repurchase agreements, U.S. Treasury and agency securities, municipal securities issued by states and political subdivisions, mortgage-backed securities, and other debt and equity securities
In 2021, the investment portfolio totaled 26.3% of total assets
Distribution of Commercial Bank Assets, Liabilities, and Equity, 2021
Commercial banks face unique risks because of their asset structure:
Credit (i.e., default) risk is the risk that promised cash flows from loans and securities held by FIs may not be paid in full
Liquidity risk is the risk that a sudden and unexpected increase in liability withdrawals may require an FI to liquidate assets in a very short period of time and at low prices
Interest rate risk is the risk incurred by an FI when the maturities of its assets and liabilities are mismatched and interest rates are volatile
Credit, liquidity, and interest rate risk all contribute to a commercial bank’s level of insolvency risk, the risk that an FI may not have enough capital to offset a sudden decline in the value of its assets relative to its liabilities
Credit (i.e., default) risk
______________________ is the risk that promised cash flows from loans and securities held by FIs may not be paid in full
Liquidity risk
______________ is the risk that a sudden and unexpected increase in liability withdrawals may require an FI to liquidate assets in a very short period of time and at low prices
Interest rate risk
________________ is the risk incurred by an FI when the maturities of its assets and liabilities are mismatched and interest rates are volatile
insolvency risk
Credit, liquidity, and interest rate risk all contribute to a commercial bank’s level of _____________, the risk that an FI may not have enough capital to offset a sudden decline in the value of its assets relative to its liabilities
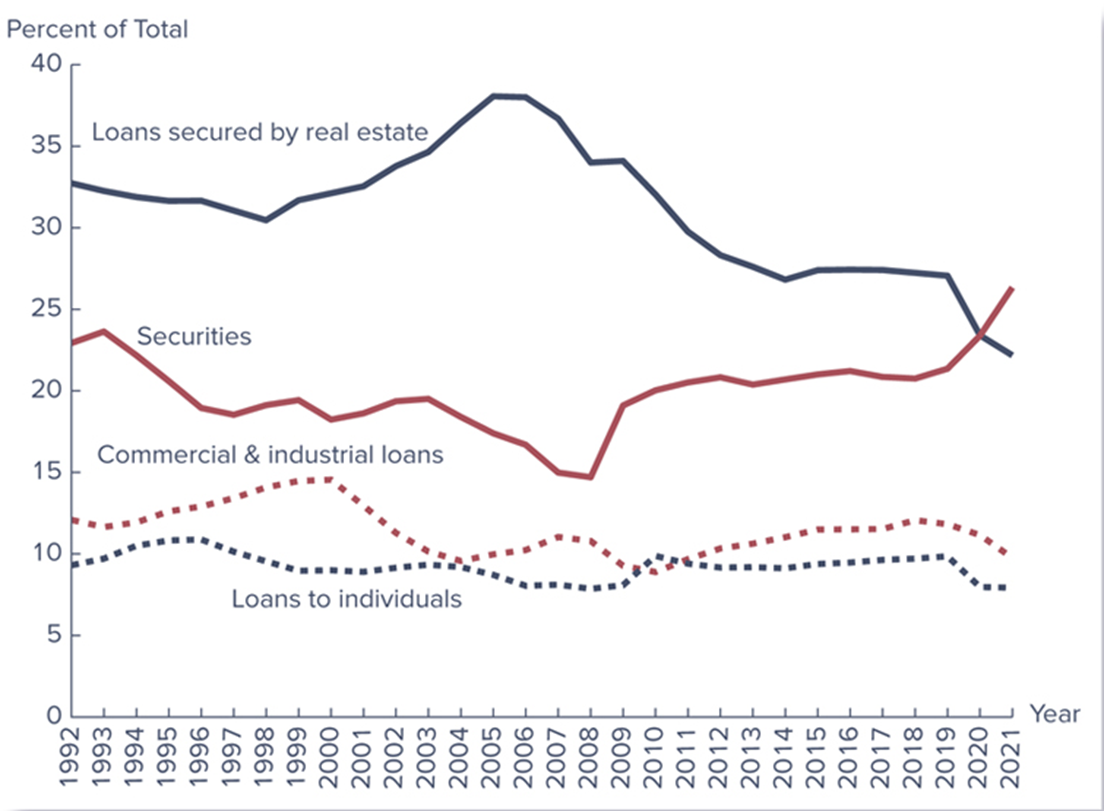
Loans and investment securities continue to be the primary assets of the banking industry
Loans secured by real estate have consistently been the largest asset class for commercial banks over the 1992–2019 period, but real estate loans have been shrinking steadily from 2007 to 2014
In 2016, the volume of 1–4 family mortgages originated by nonbanks surpassed the volume originated by banks
Nonbanks accounted for 52.5 percent of the volume of 1–4 family mortgages originated in 2017, up significantly from the financial crisis-era low of 23.5 percent in 2007
declining
Proportion of commercial and industrial loans have been _________ since 2000
Portfolio Shift: U.S. Commercial Banks’ Financial Assets
Commercial Bank Liabilities: Deposits
Transaction accounts are checkable deposits that are either demand deposits or NOW accounts
Transaction accounts are about 28.0% of total deposits
Interest-bearing checking accounts are called negotiable order of withdrawal (NOW) accounts
Household savings and time deposits (normally individual account holdings of less than $100,000)
Important components of bank retail savings accounts are small nontransaction accounts, which include passbook savings accounts and retail time deposits
Large time deposits ($100,000 or more)
Primarily made up of negotiable CDs, fixed-maturity interest-bearing deposits with face values of $100,000 or more that can be resold in the secondary market
Transaction accounts are checkable deposits that are either demand deposits or NOW accounts
Transaction accounts are about 28.0% of total deposits
Interest-bearing checking accounts are called negotiable order of withdrawal (NOW) accounts
Transaction accounts
___________________ are checkable deposits that are either demand deposits or NOW accounts
negotiable order of withdrawal (NOW) accounts
Interest-bearing checking accounts are called __________________________________
Household savings and time deposits (normally individual account holdings of less than $100,000)
Important components of bank retail savings accounts are small nontransaction accounts, which include passbook savings accounts and retail time deposits
Large time deposits ($100,000 or more)
Primarily made up of negotiable CDs, fixed-maturity interest-bearing deposits with face values of $100,000 or more that can be resold in the secondary market
negotiable CDs
Primarily made up of ____________ , fixed-maturity interest-bearing deposits with face values of $100,000 or more that can be resold in the secondary market
Nondeposit liabilities include a broad array of instruments:
Shorter maturity instruments
Purchase of federal funds (bank reserves) on the interbank market
Repurchase agreements (temporary swaps of securities for federal funds)
Longer maturity instruments
Issuance of notes and bonds
Shorter maturity instruments
Purchase of federal funds (bank reserves) on the interbank market
Repurchase agreements (temporary swaps of securities for federal funds)
Longer maturity instruments
Issuance of notes and bonds
shorter maturity structure
Liability structure of banks’ balance sheets tends to reflect _________________ than that of their asset portfolio
Relatively more liquid instruments, such as deposits and interbank borrowings, are used to fund relatively less liquid assets, such as loans
Interest rate risk—or maturity mismatch risk—and liquidity risk are key exposure concerns for bank managers
Commercial bank equity capital consists mainly of common and preferred stock (listed at par value), surplus or additional paid-in capital, and retained earnings
Commercial bank equity capital was 9.9% of total liabilities and equity in 2021
Troubled Assets Relief Program (TARP)
Capital Purchase Program, part of _________________________________ , was intended to encourage U.S. FIs to build capital and increase flow of financing to U.S. businesses and consumers to support the U.S. economy
Largest banks subject to annual stress tests, designed to ensure that the banks are properly capitalized
2010 Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act
Banks engage in many fee-related activities off the balance sheet, such as the following:
Issuing various types of guarantees (e.g., letters of credit)
Making future commitments to lend
Engaging in derivative transactions – futures, forwards, options, and swaps
Off-balance-sheet (OBS) assets
When an event occurs, this item moves onto asset side of balance sheet or income is realized on income statement
Off-balance-sheet (OBS) liabilities
When an event occurs, this item moves onto liability side of balance sheet or an expense is realized on income statement
“tax-avoidance”
Banks have both earnings and regulatory __________________ incentives to undertake OBS activities
Use of derivative contracts accelerated during 1992–2010 period; accounted for much of the growth in OBS activity
Notional value of OBS activities at commercial banks was $10,252.8b in 1992 compared to $4,593.0b of on-balance-sheet activities
By 2010, the notional value of OBS bank activities was $254,731.5b (compared to the $13,254.2b value of on-balance-sheet activities) before falling to $180,421.6b in 2019
At the heart of the financial crisis were losses from OBS mortgage-backed securities, created and held by FIs
Losses from the falling value of OBS securities reached over $1 trillion worldwide through 2009
TARP gave U.S. Treasury funds to buy “toxic” mortgages and other securities from FIs
Trust services are offered by only the largest banks
Trust department of a commercial bank holds and manages assets for individuals or corporations are offered by only the largest banks
Individual trusts represent about one-half of all trust assets managed by commercial banks
Pension fund assets are the second largest group of assets managed by trust departments of commercial banks
Trust services
______________ are offered by only the largest banks
Trust department of a commercial bank holds and manages assets for individuals or corporations are offered by only the largest banks
Individual trusts represent about one-half of all trust assets managed by commercial banks
Pension fund assets are the second largest group of assets managed by trust departments of commercial banks
Correspondent banking is the provision of banking services to other banks that do not have the staff resources to perform the services themselves
Services include check clearing and collection, foreign exchange trading, hedging services, and participation in large loan and security issuances
Correspondent banking
_____________________ is the provision of banking services to other banks that do not have the staff resources to perform the services themselves
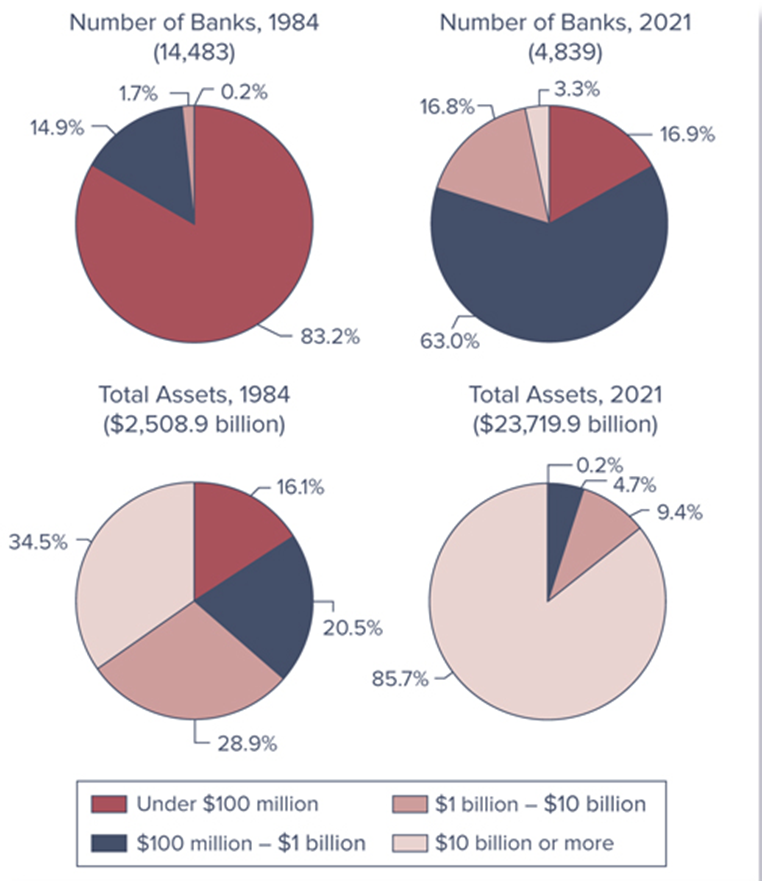
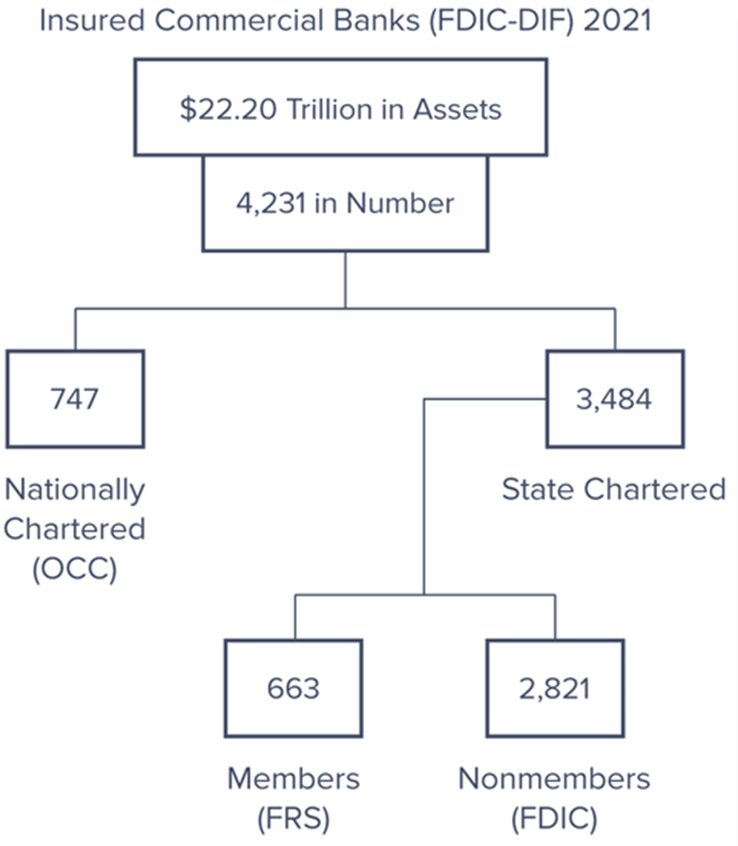
Number of commercial banks in U.S. has been declining, though much of this is due to mergers and acquisitions
2021 – 4,231 banks
1984 – 14,483 banks
It was not until the 1980s and 1990s that regulators allowed banks to merge with other banks across state lines (i.e., interstate mergers)
In 1994, Congress passed legislation (the Reigle-Neal Act) easing branching by banks across state lines
It has only been since 1987 that banks have possessed powers to underwrite corporate securities
Full authority to enter the investment banking (and insurance) business was received only with the passage of the Financial Services Modernization Act in 1999
Activities of nonfinancial service firms that perform banking services have been termed shadow banking
Shadow banking system intermediates the flow of funds between net savers and net borrowers
Credit intermediation is performed through a series of steps involving many nonbank financial service firms
Face significantly reduced regulation than traditional banks
Can often perform credit intermediation process more cost efficiently than traditional banks
shadow banking
Activities of nonfinancial service firms that perform banking services have been termed ______________
2010 Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act
_____________________________________________ called for regulators to be given broad authority to monitor and regulate nonbank financial firms that pose risks to the financial system
Community banks have less than $1 billion in asset size and tend to specialize in retail banking
Retail banking is consumer-oriented banking, such as providing residential and consumer loans and accepting smaller deposits
Decreasing both in number and importance, as asset share has dropped from 36.6% in 1984 to 4.9% in 2021
Community banks
_________________ have less than $1 billion in asset size and tend to specialize in retail banking.
Retail banking
_________________ is consumer-oriented banking, such as providing residential and consumer loans and accepting smaller deposits
Relative asset share of largest banks (over $1 billion in size) increased from 63.4 percent in 1984 to 95.1 percent in 2021
Regional or superregional banks engage in a complete array of wholesale banking, or commercial-oriented, activities
Have access to the markets for purchased funds (e.g., interbank or federal funds market), to finance lending and investment activities
wholesale banking
Regional or superregional banks engage in a complete array of ________________, or commercial-oriented, activities
federal funds market
Have access to the markets for purchased funds (e.g., interbank or _________________), to finance lending and investment activities
Money center banks
__________________ engage heavily in wholesale activity in money markets, with retail banks and large firms as clients
U.S. Bank Asset Concentration, 1984 versus 2021
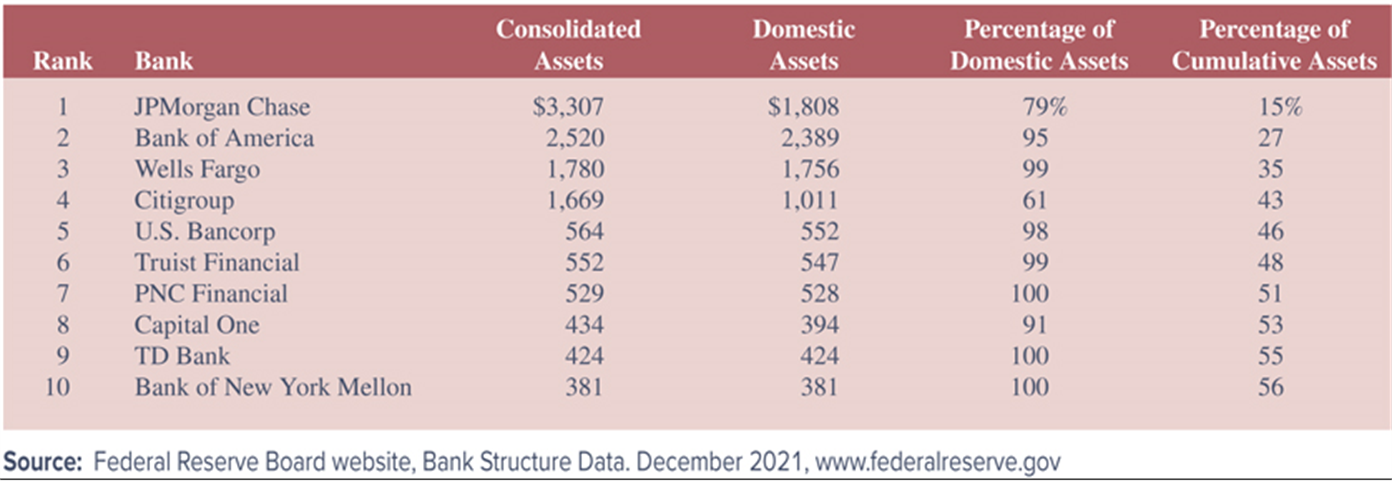
Top Ten U.S. Banks Listed by Total Assets, 2021 (in billions of dollars)
Size
_____ has traditionally affected the types of activities and financial performance of commercial banks
Small banks typically focus on the retail side
Generally hold fewer OBS assets and liabilities than large banks
Rarely hold derivative securities
More sheltered from competition in highly localized markets
Lend to smaller, less sophisticated customers than do large banks
Large banks usually engage in both retail and wholesale banking, but focus on the wholesale side of the business
Operate with lower amounts of equity capital than do small banks
Tend to use more purchased funds and have fewer core deposits
Lend to larger corporations, which means their interest rate spreads (i.e., the difference between their lending rates and deposit rates) and net interest margins (i.e., interest income minus interest expense divided by earning assets) have usually been narrower than those of smaller regional banks
Pay higher salaries and invest more in buildings and premises
Diversity their operations and services more than small banks
Generate more noninterest income than small banks
interest rate spreads | net interest margins
Lend to larger corporations, which means their ________________ (i.e., the difference between their lending rates and deposit rates) and ________________ (i.e., interest income minus interest expense divided by earning assets) have usually been narrower than those of smaller regional banks
Strong performance of commercial banks during early 2000s
Federal Reserve cut interest rates 13 times during this period
Lower interest rates made home purchasing more affordable
Development of new financial instruments helped banks shift credit risk from their balance sheets to financial markets and other FIs, such as insurance companies
Improved IT helped banks manage their risk better
Rising interest rates in mid-2000s caused performance to decline, but not significantly
Third quarter 2006 earnings represented the second highest quarterly total ever reported by the industry
Industry’s core capital ratio increased to 10.36%, the highest level since new, risk-based capital ratios were implemented in 1993
No FDIC-insured banks failed during 2005 or 2006
Performance deteriorated in late 2000s as U.S. economy experienced its strongest recession since Great Depression
For all of 2007, net income was $99.94 billion, a decline of $45.28 billion (31.1 percent) from 2006
Average ROA for 2007 was 0.81 percent, the lowest yearly average since 1991 and the first time in 15 years that the industry’s annual ROA had been below 1 percent
One in four institutions (25.0 percent) was unprofitable in 2008
Bank performance slowly recovered in 2010 – 2016
2010 industry ROA and ROE increased to 0.65% and 5.85%, respectively; by 2016, industry ROA and ROE increased to 1.04% and 9.27%, respectively
By the end of 2019, 96.4 percent of banks were profitable
ROA and ROE declined due to COVID-19 but fully recovered to pre-pandemic levels in 2021
U.S. banks may be subject to the supervision and regulations of as many as four separate regulators:
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) was established in 1933 and insures deposits of commercial banks
Acts as receiver and liquidator when insured bank is closed
Manages the Depositors Insurance Fund, or DIF
Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) is the oldest U.S. bank regulatory agency, established in 1863
Primary function is to charter (and close) national banks
Federal Reserve System (FRS) serves as the country’s central bank, has regulatory power over some banks, and where relevant, their holding company parents
State bank regulators perform function similar to those the OCC performs, but only for state-chartered commercial banks
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)
______________________________________ was established in 1933 and insures deposits of commercial banks
Acts as receiver and liquidator when insured bank is closed
Manages the Depositors Insurance Fund, or DIF
Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC)
______________________________________ is the oldest U.S. bank regulatory agency, established in 1863
Primary function is to charter (and close) national banks
Federal Reserve System (FRS)
_________________________ serves as the country’s central bank, has regulatory power over some banks, and where relevant, their holding company parents
State bank regulators
___________________ perform function similar to those the OCC performs, but only for state-chartered commercial banks
Bank Regulators
Global Issues
Advantages of international expansion
Risk diversification
Economies of scale
Innovations
Funds source
Customer relationships
Regulatory avoidance
Disadvantages of international expansion
Information/monitoring costs
Nationalization/expropriation
Fixed costs
Advantages of international expansion
Risk diversification
Economies of scale
Innovations
Funds source
Customer relationships
Regulatory avoidance
Disadvantages of international expansion
Information/monitoring costs
Nationalization/expropriation
Fixed costs
The financial crisis of 2008-2009 spread worldwide and banks saw losses that were magnified by illiquid markets
Largest banks in the Netherlands, Switzerland, and the U.K. had net losses in 2008
Banks in Ireland, Spain, and the U.K. were especially hard hit because they had large investments in mortgages and mortgage-backed securities, both U.S. and domestic
central banks and national governments
Many European banks averted outright bankruptcy thanks to direct support from their __________________________________
Greece suffered a severe debt crisis in the spring of 2010
Problems from the Greek banking system then spread to other European nations, such as Portugal, Spain and Italy
The situation stabilized after 2012, but a major debt payment was due from Greece to creditors on June 30, 2015
Deal was reached that required Greece to surrender to all its creditors’ demands, including tax increases, pension reform, and the creation of a fund (under European supervision) with state-owned assets earmarked to be privatized or liquidated
European banking system was rocked again in June 2016 with “Brexit”
The EU and the UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement was signed on December 30, 2020, and entered into force on May 1, 2021