Chapter 4: Problem Solving and Intelligence
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Intelligence
“The cognitive ability of an individual to learn from experience, to reason well, to remember important information, and to cope with the demands of daily living” - Robert Sternberg
Requires an operational definition: Allows for it to be measured and tested
Three Aspects of Intelligence
Analytic Intelligence
Creative Intelligence
Practical Intelligence
Analytic Intelligence
consists of analyzing, evaluating, and judgement
“Book smart” - academic problem solving
“To remember important information”
Creative Intelligence
consists of new ways to approach problems
Requires the use of existing knowledge and experiences
Functional fixedness is a good example of this
Practical Intelligence
involves individuals applying their abilities to the sorts of problems that face them in every-day life
“Street Smart”
“Cope with the demands of daily living”
Types of Biases
Functional Fixedness
Anchoring
Bounded Rationality
Framing
Confirmation Bias
Status Quo Bias / Stay Bias
Functional Fixedness
A bias where people only see an object working in its own particular way
Anchoring
A bias where People rely too heavily on the first piece of information (the “anchor”) when making decisions or estimates.
Even when the anchor is random or irrelevant, it pulls judgments toward it.
Bounded Rationality
A bias toward simplicity or convenience rather than full rational analysis
Shows that our decision-making is limited by the information we have, our cognitive ability, and time constraints.
where we often settle for “good enough” (satisficing) instead of making the perfect choice
Framing
A bias where People’s decisions are influenced by how information is presented (framed) rather than by the facts themselves
Eg 90% survival rate vs 10% death rate
Confirmation Bias
tendency to seek out information that supports our hypothesis
Status Quo Bias / Stay Bias
People prefer to stick with their initial choice rather than change it, even when switching is objectively better.
Modern Intelligence Testing
Wechsler Intelligence Scale, Common IQ test
Weschler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) and the Weschler Intelligence Adult Scale (WAIS)
Test: Short-term memory, verbal comprehension, processing speed and perceptual reasoning
Scores given for both specific intelligence
Standardized scale: With a mean of 100 and Standard Deviation of 15, average IQ regardless of how many people are achieving more or less
The Flynn Effect
the substantial and long-sustained increase in both fluid and crystallized intelligence test scores that were measured in many parts of the world over the 20th century
the phenomenon by which raw scores are increasing by roughly 3 points every 10 years
Reasoning: better access to nutrition, better healthcare, and better schooling
Myers Briggs Personality Testing
A personality test designed to identify how people perceive the world and make decisions.
Using four personality domains:
Extraversion (E) ↔ Introversion (I)
→ Where you get your energy (from others vs. from within).
Sensing (S) ↔ Intuition (N)
→ How you take in information (through facts/details vs. patterns/ideas).
Thinking (T) ↔ Feeling (F)
→ How you make decisions (logic vs. values/emotions).
Judging (J) ↔ Perceiving (P)
→ How you organize your life (structured/planned vs. flexible/spontaneous).
Intelligence Development
NAture: Environment plays a role on intelligence
Nurture: Genetics play a role on intelligence
Twin Studies:
involving comparing the similarity between monozygotic twins on a trait to dizygotic twins on a trait.
If monozygotic twins are more similar than dizygotic twins, we can assume that this trait is largely influenced by genetics.
Adoption Studies:
involve comparing a child to their biological parents and their adoptive parents on a trait.
If the child is more similar to their biological parents, we can assume that this trait is largely influenced by genetics
Confounding Factors: Increase difficulty to draw strong conclusions
Types of Problems
Distinguished by how defined they are → Some problems require overcoming functional fixedness
Well-Defined Problem
Aware of initial state, the allowable rules, and the desired end goal
Ill-defined problems
With unclear goals and ways to achieve it with a lack of specific rules, also an unclear start
Must be broken down into smaller more manageable sub goals to create well-defined problem to eventually fix the bigger one
Reasoning Styles
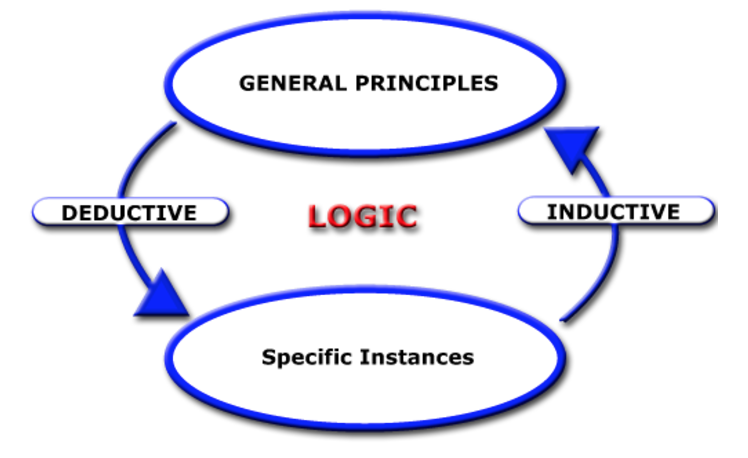
Deductive Reasoning:
Inductive Reasoning:
Deductive Reasoning:
A larger idea that is used to make smaller more specific conclusions
BIG TO SMALL
“using a theory—a general idea about how the world works—to arrive at a specific conclusion”
Inductive Reasoning:
Using small facts to form broader generalizations
SMALL TO BIG
“use specific observations to formulate a general theory or conclusion”
Arch of Knowledge
Works by using both inductive and deductive reasoning → USed in the scientific method
Deductive reasoning: allows the use of our current theories to generate specific hypotheses
Inductive reasoning: Then analyses collected data to update and revise current theories
Heuristics
mental shortcuts that we use to help us make decisions fast and reduce our cognitive load (can be incorrect) → Instead of the scientific method
Availability Heuristics
Tendency to make decision about the frequency of an event based on information most easily available
Your judgment based on tendencies that are more available in your mind
Representative Heuristics
The tendency to make decisions about the probability of an event based on information most easily available
Comparing an event to the “prototype” event in our mind
So like what we think is likely rather than what is actually likely based on probability
Reliability
The degree to which a test produces consistent results
Test-Retest Method
the participant takes the same test multiple times, and researchers examine whether the results are the same each time
Consistent results = reliable
Disadvantage: Hard to test reliability since scores can increase with the participant getting better with practice
Interrater Reliability
The degree of agreement between multiple observers witnessing the same event - higher degree of agreement the more reliable
Validity
The degree to which a test measures the construct it intends to measure
Predictive Validity
The extent to which a score on a test can be used to predict future behaviours
Francis Galton
Reaction time test for IQ
High reliability, poor validity
Alfred Binet
Binet’s test was meant to identify children with learning disabilities and assumed that intelligence develops with age
focussed on judgement, reasoning, and attention
Stanford-Binet Intelligence test:
computes a child’s mental age, and then compares this age to their true age
Ratio/Quotient: between the child’s mental age and their true age made up the final score for this test
“G”
MEasure of general intelligences that underlies specific types of intelligence → Coined by Spearman
People who do well in a certain test of intelligence are better at others
Eugenics…..Beleived only people with a minimum g level should vote or reproduce
HIerarchical Model of Intelligence
recognizes that there are specific types of intelligence, but also recognizes that these types of intelligences is related to a general, underlying intelligence (“g”)
Short term memory
Verbal Comprehension
Processing Speed
Perceptual Reasoning
Gardner’s Definition
Argued that there are multiple types of intelligence that are all independent from one another
Verbal
Mathematical
Musical
Spatial
Kinesthetic
Interpersonal
intrapersonal
Naturalistic
Piaget
Determined that Kids are active learners:
Schema
a mental framework for interpreting the world around us
Assimilation
incorporating new information into existing scheme
Accommodation
modifying existing schema to fit incompatible information
Cognitive Development
Children must develop their schema and overcome each level before they can go to the next stage
Declage: Some kids developing their skills out of order
Sensorimotor stage 0-2
Preoperational stage 2-7
Concrete operational stage 7-12
Formal operational stage 12+
Sensorimotor stage 0-2
Learn object permanence
Preoperational stage 2-7
Egocentrism: They are egocentric
Seriation: Logically order stuff
Reversible relationships: Can’t understand the other way around
Conservation task: Even if they watch they don’t get it
Concrete operational stage 7-12
Abstract terms
Formal operational stage 12+
Fully operational now!