Reaction Rates
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What factors affect the rate of reaction?
Concentration or pressure
Temperature
Catalyst
Surface area of solid reactants
What does the rate of reaction measure?
How fast a reactant is being used up, or how fast a product is formed, can be defines as a change in concentration of reactant or product in a given time
What methods can you use to follow the rate of reaction?
Monitoring the removal of reactant (decrease in concentration)
Monitoring the formation of product (increase in concentration)
If a reaction produces a gas:
Monitoring volume of gas produced, using a gas syringe
Monitoring loss of reactants, using a balance
What factors make an effective collision?
Particles must collide with the correct orientation
Particles must have sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy barrier of the reaction
How do you calculate the initial rate of reaction?
Plot a graph of volume (or concentration) against time
Draw a tangent at t=0
Calculate the gradient
Gradient = Rate of reaction
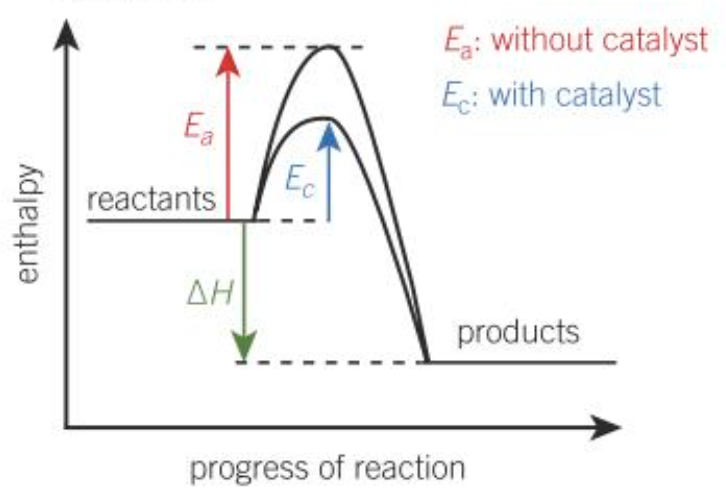
Activation energy (Ea)
The minimum amount of energy required to start a reaction by the breaking of bonds
Catalyst
A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up in the process; a catalyst provides an alternate reaction pathway for the reaction with a lower activation energy
Homogeneous catalysis
A reaction in which the catalyst and reactants have the same physical state (most frequently aqueous or gaseous)
Heterogeneous catalysis
A reaction in which the catalyst has a different physical state from the reactants
Adsorption
A process that occurs when a gas, liquid or solute is held to the surface of a solid (happens in heterogeneous catalysis)
Desorption
The release of an adsorbed substance from a surface (happens in heterogeneous catalysis)
Draw the enthalpy diagram for an exothermic reaction
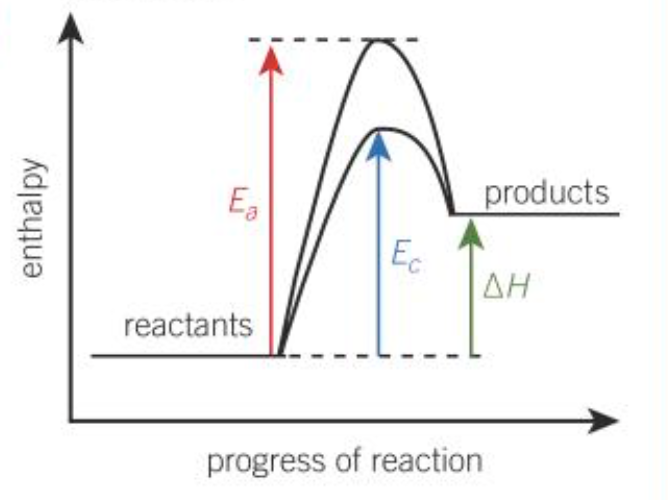
Draw the enthalpy diagram for an endothermic reaction
Is the change in enthalpy for an exothermic reaction positive or negative?
Negative
Chemical system loses energy
Surroundings gain energy
Is the change in enthalpy for an endothermic reaction positive or negative?
Positive
Chemical system gains energy
Surroundings lose energy
What is the economic importance of catalysts?
They lower activation energy, meaning that less electricity or fossil fuels are needed (to provide as much energy), cutting costs and increasing profit.
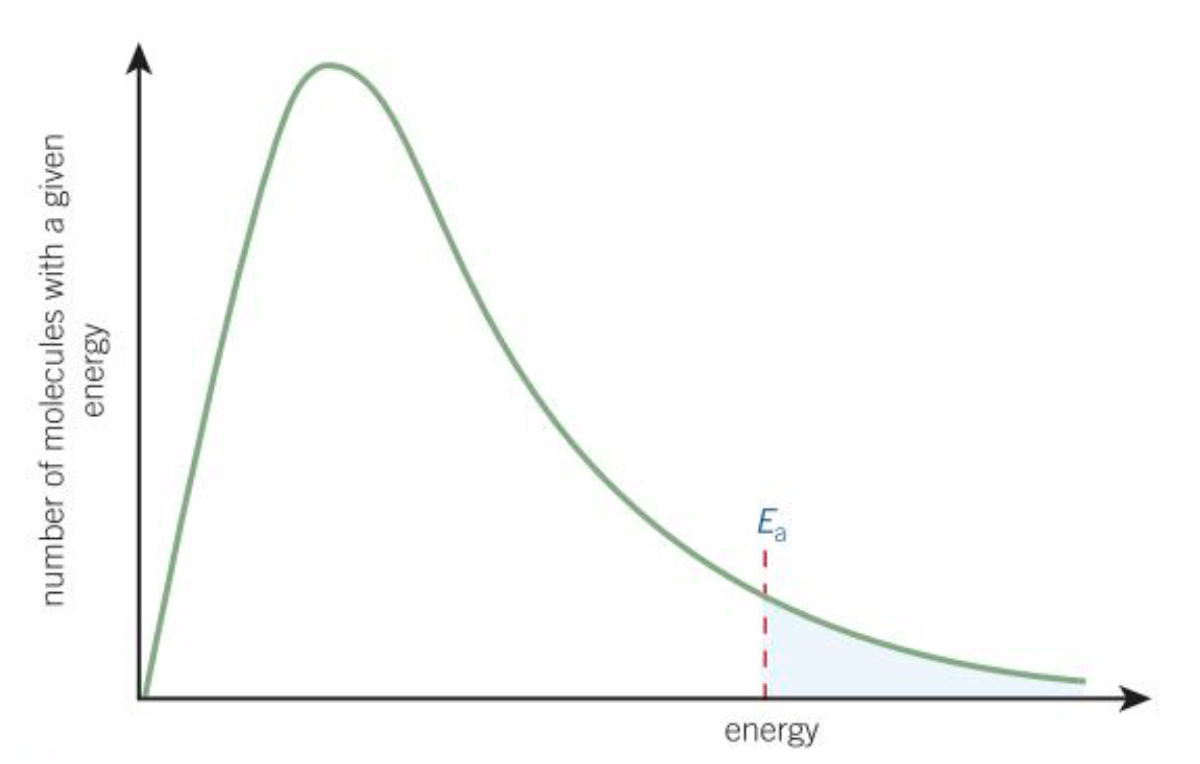
Boltzmann distribution
The spread of molecular energies in gasses
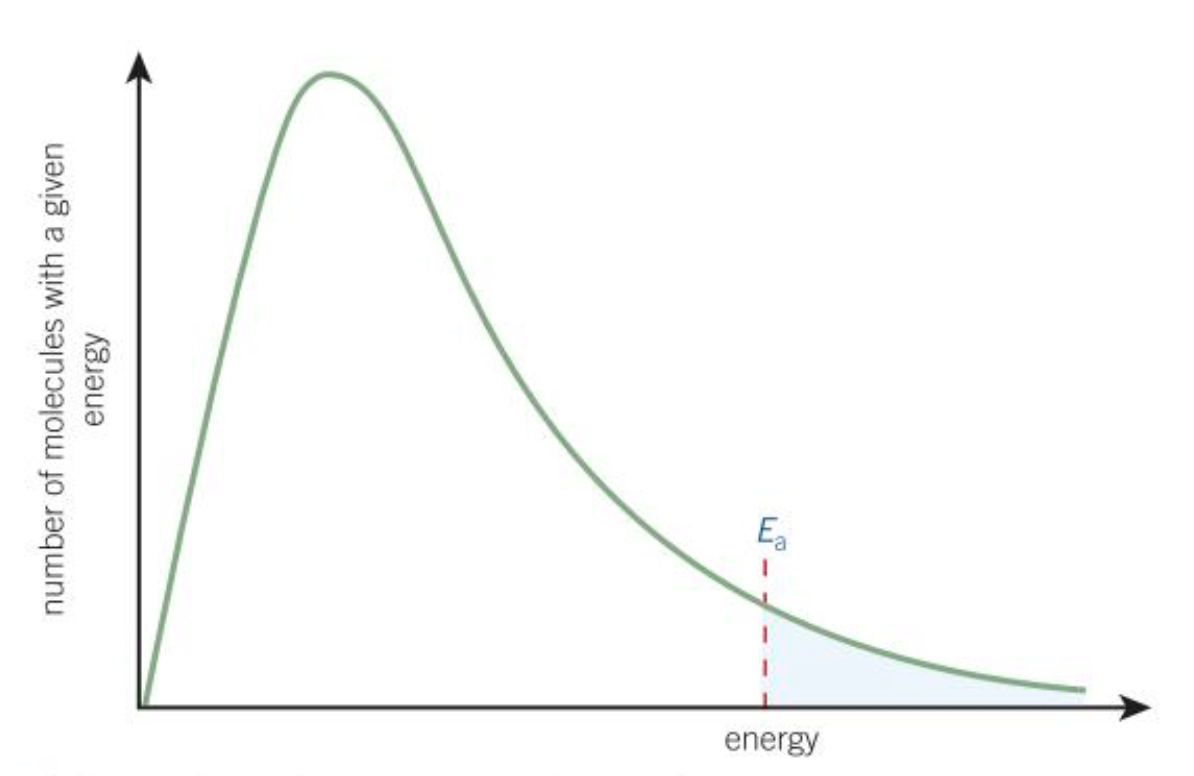
What does the area under the curve of the Boltzmann distribution represent?
Total number of molecules
Why does the Boltzmann distribution start at the origin?
No molecules have zero energy
Why does the Boltzmann distribution never cross the x-axis?
Theoretically, molecules can have infinite energy
What is the effect of temperature on the Boltzmann distribution?
At a higher temperature, the peak is lower and shifted right, this means that a greater proportion of molecules have the required activation energy. The means that a greater proportion of collisions result in a reaction. Also the frequency of collisions increases, as molecules are moving faster.
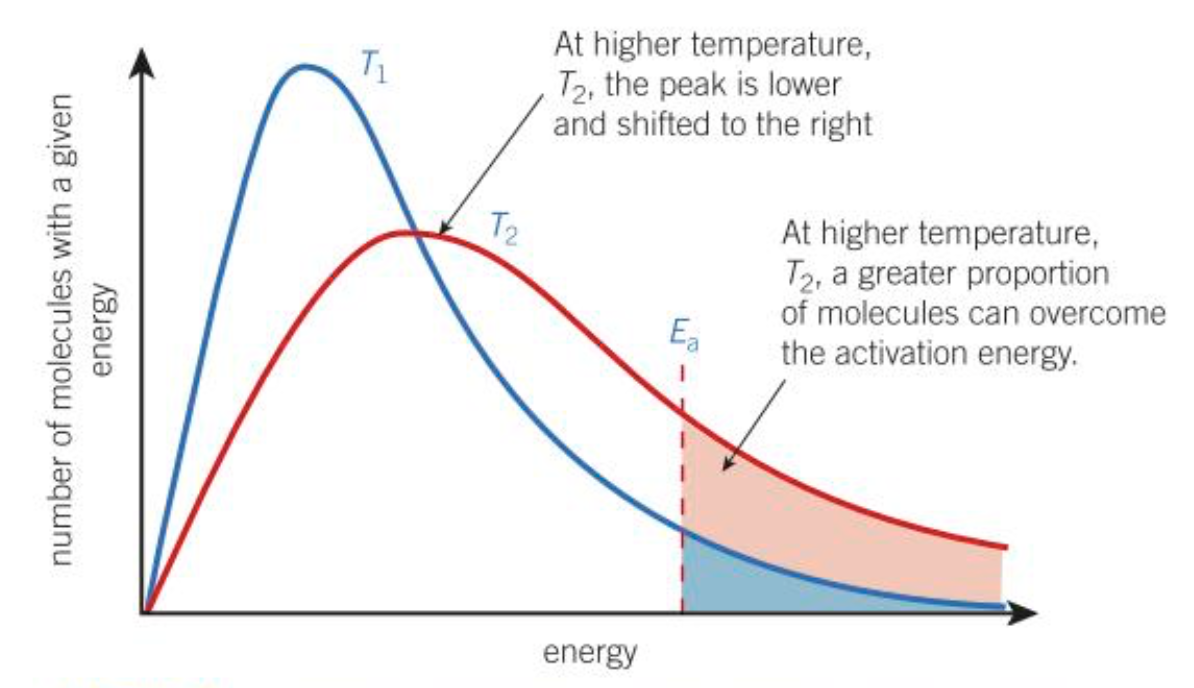
What is the effect of a catalyst on the Boltzmann distribution?
Higher proportion of molecules have the required activation energy with a catalyst. When molecules collide, they are more likely to react.
Catalytic converter
A device used to reduce the emissions of an internal combustion engine
Contains a ceramic honeycomb mesh coated in platinum and rhodium
Found in petrol engines
Heterogeneous catalyst
Reactant molecules adsorbed on the surface
They then leave ( after reaction) via desorption