Snakes
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
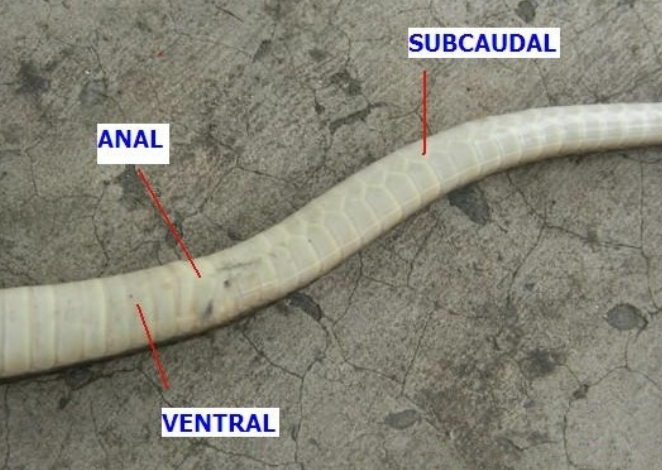
-ventral scales (gastrolia)
-large, rectangular
-fx: traction for land locomotion
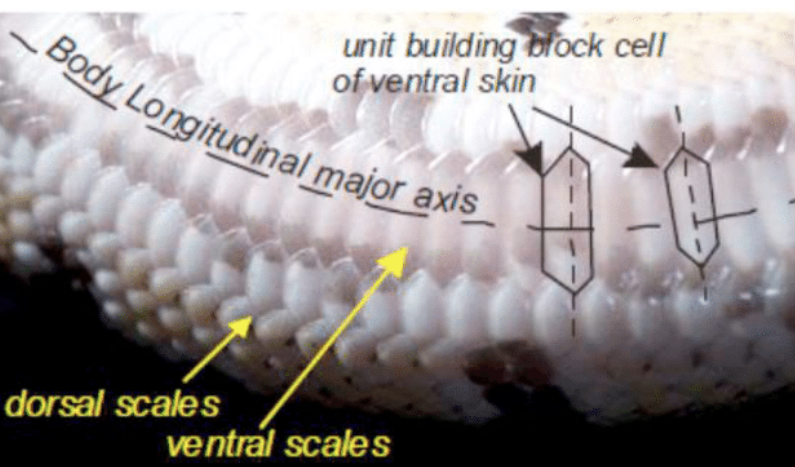
-dorsal scales
-overlapping
-fx: protection, camouflage, reduced friction
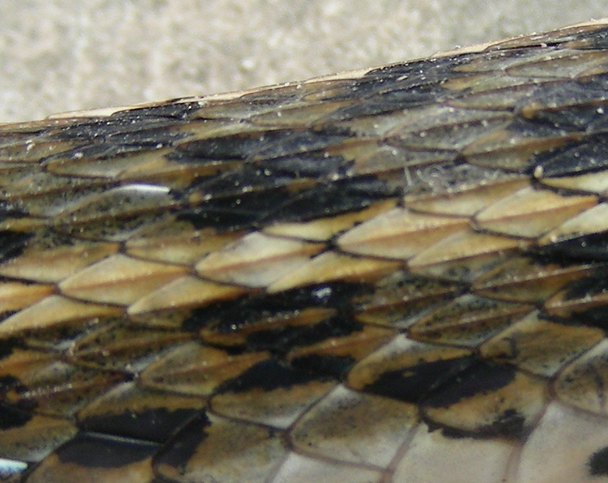

-keeled scales
-raised ridge in middle of scale
-fx: friction & grip (terrestrial snakes)

-smooth scales
-glossy, flat surface
-drag reduction in arboreal or aquatic snake
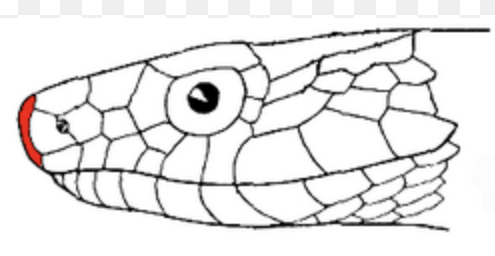
-rostral/labial scales
-enlarged scale on snout/lips
-fx: burrowing, prey handling
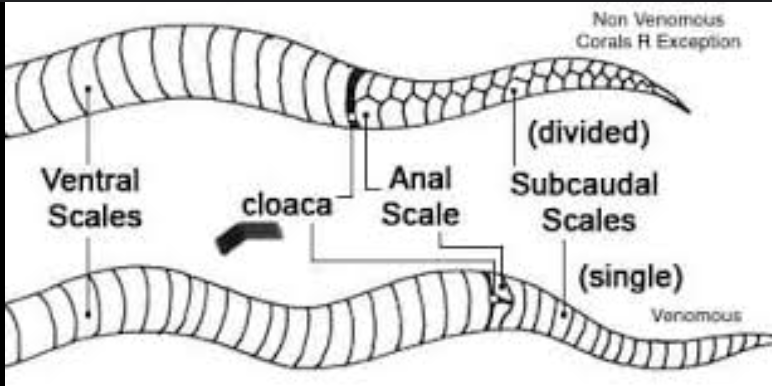
-subcaudal scales
-paired or single
-under tail
-ID
which spp do not have a parietal organ?
-snakes, birds, mammals
teeth:
Aglyphous
-non-venomous
-teeth are all similar
-no specialized fangs
-ex: pythons, boas, colubrids

aglyphous
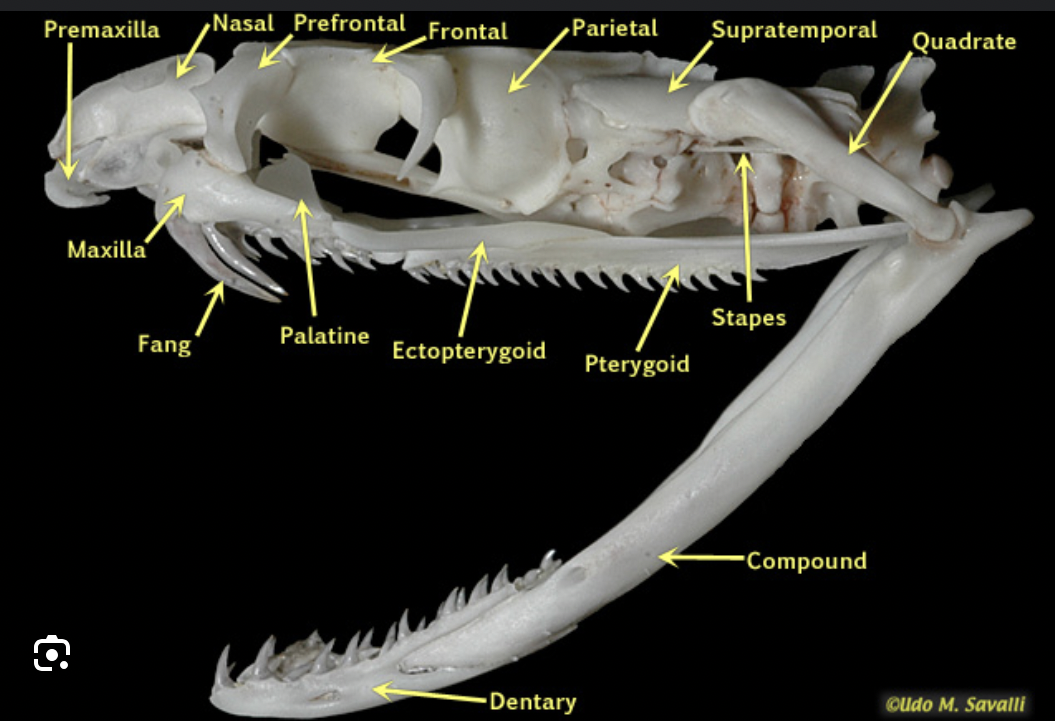
-opisthoglyphous
-nnlarged grooved fangs at the rear of the maxilla
venom along grooves, not thru a canal.
-some colubrids (e.g. Boomslang).
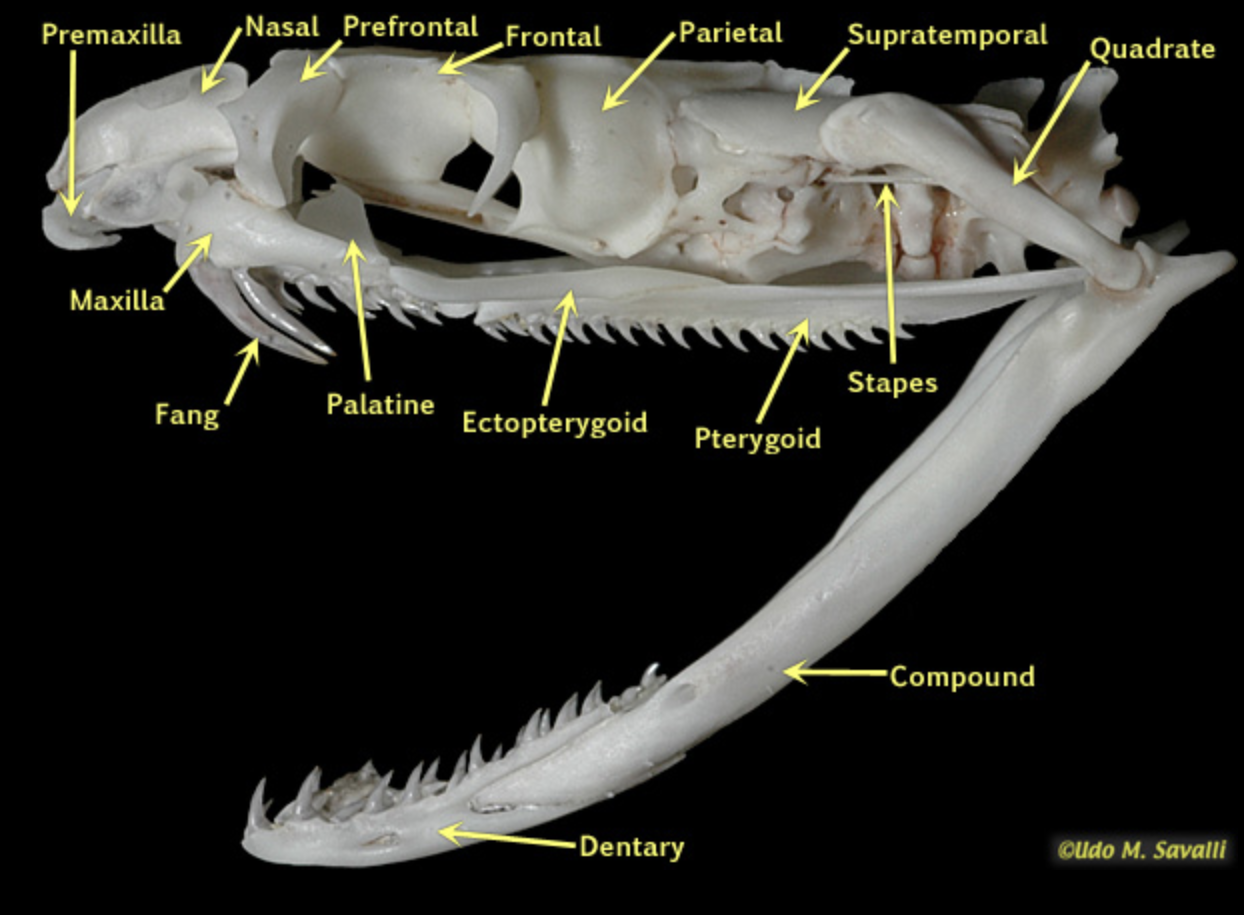
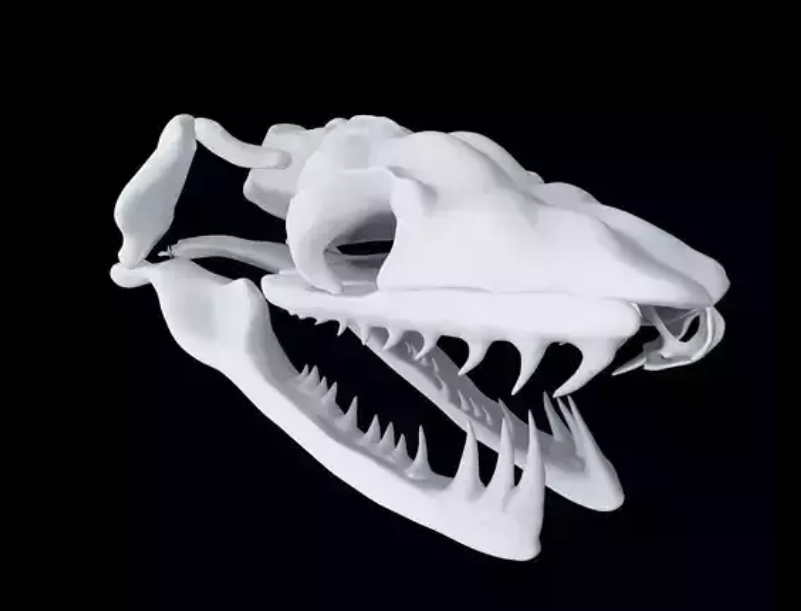
-Proteroglyphous
-short, hollow fangs at the front of the maxilla
-fixed in position
-venom injected through internal canal
-ex: Elapids — cobras, taipans, brown snakes, coral snakes
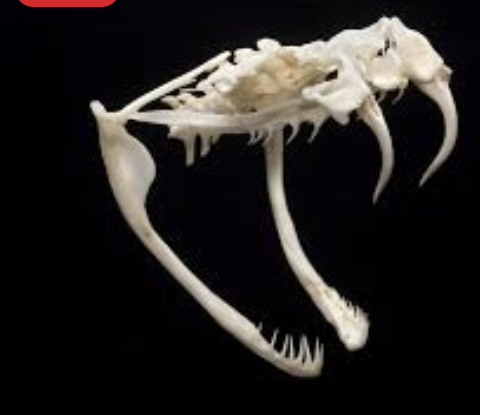

-solenoglyphous
-long, hollow fangs on a rotating maxilla — fold back when mouth is closed
-maxilla can swing forward to strike.
-ex: vipers, pit vipers
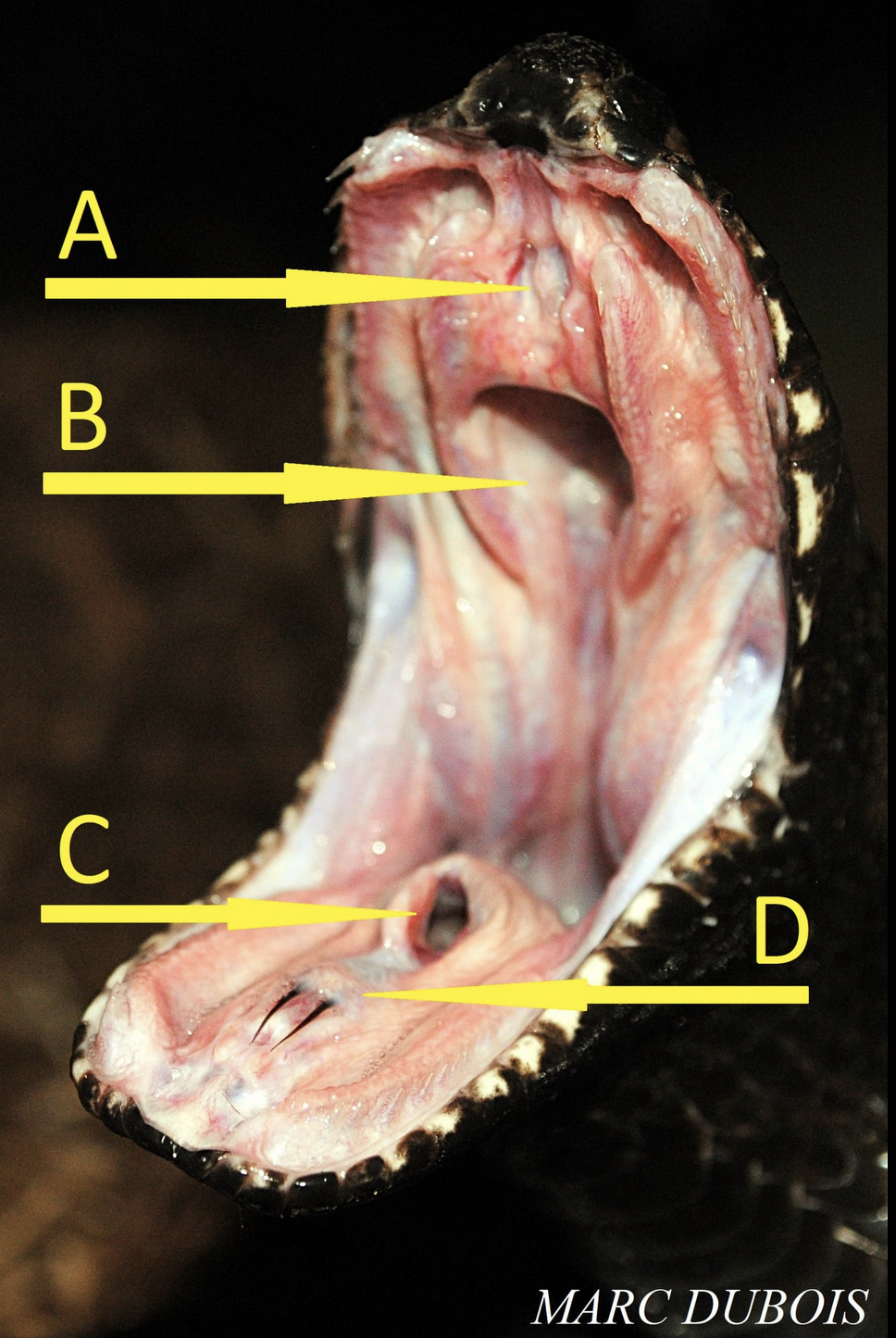
A - VO (Jacobson’s organ)
B - connects external nostrils to the internal part of the mouth (nasal cavity)
C - opening of larynx (glottis)
D - sheath covering forked tongue
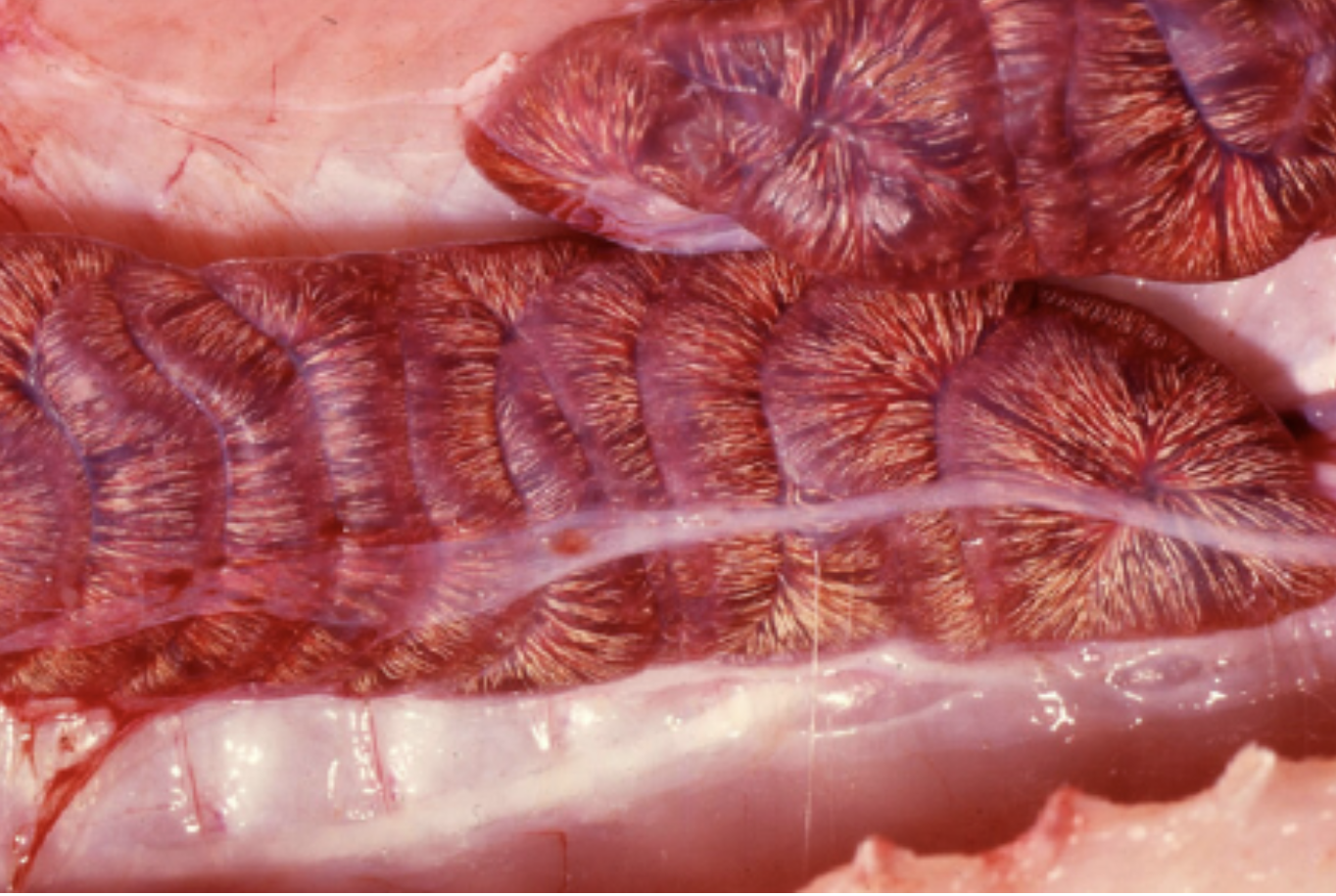
snake kidneys
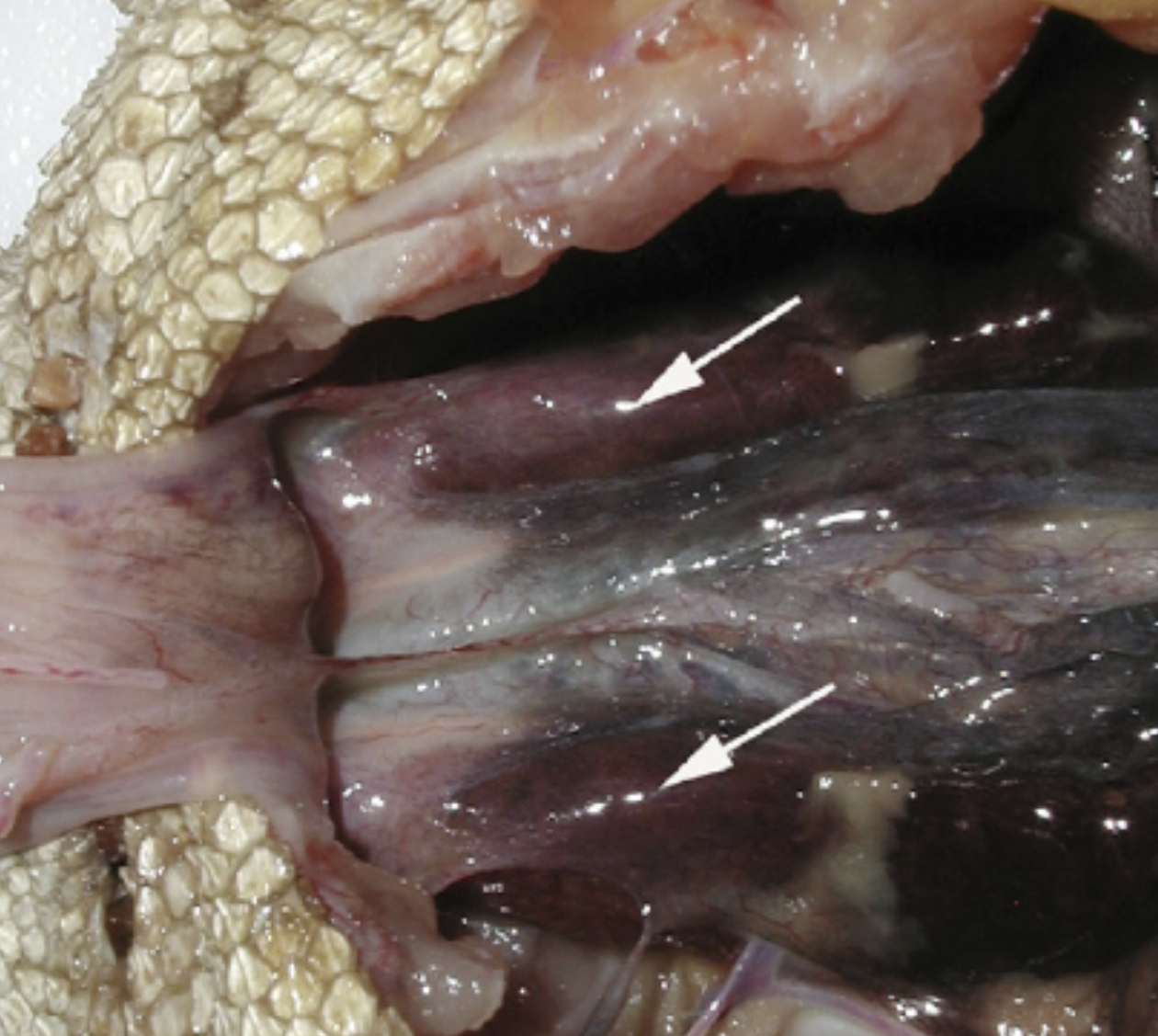
kidney