Cancer Chemotherapeutic Drugs 3: Alkylating Agents and Folate Analogs
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1. Describe the adverse effects associated with cisplatin. 2. Describe the mechanism of sodium thiosulfate as a chemoprotective agent with cisplatin. 3. Identify mechanisms of resistance to cisplatin. 4. Differentiate the structure-activity relationship of the platinum compounds. 5. Define the term “antimetabolite”. 6. Compare and contrast the structures of the folate analogs. 7. Describe the rationale of aggressive hydration and urine alkalinization with high-dose methotrexate therapy. 8. Compare and contrast leucovorin and glucarpidase use in methotrexate therapy. 9. Compare and contrast the mechanisms of action of the folate analogs.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
ADRs of Cisplatin
N/V (debilitating)
Nephrotoxicity (aquo species binds proteins in renal tubules causing necrosis)
Prevented by infusing chloride containing solutions to stabilize the inactive form.
Uses organic cation transporter-2 (OCT2) to be secreted into the renal tubule. Patients are given magnesium b/c hypomagnesemia upregulated OCT2 leading to increased cisplatin in the renal tubules increasing nephrotoxicity.
Neurotoxicity (peripheral sensory neuropathy)
Ototoxicity (loss of hearing in high frequencies)
aquo spp. increases reactive oxygen spp leading to cytotoxicity and damage to auditory cells.
Myelosuppression (due to the nature of alkylating agent)

Sodium thiosulfate (soln for inj): cisplatin is inactivated by sodium thiosulfate. It neutralizes the aquo species. This avoids: nephrotoxicity and prevent hearing loss. Treats extravasation of cisplatin.
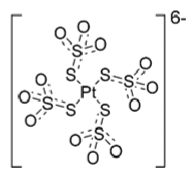
Neutralized aquo cisplatin species by sodium thiosulfate (excess)
Cisplatin resistance - intrinsic or acquired
downregulation of the carrier protein copper transporter 1 (CTR1) necessary for cisplatin to enter the cell
increased cellular efflux
drug detoxification via conjugation to glutathione and cysteine thiol rich metallothionein proteins
upregulation of DNA repair mechanisms or tolerance to cisplatin-DNA adducts
downregulation of mismatch repair (MMR) proteins. Normally, cisplatin-DNA adducts are recognized by MMR proteins. Cells then undergo several unsuccessful repair cycles, finally triggering apoptosis. If there is a decrease in MMR, then there is decreased apoptotic cell death.
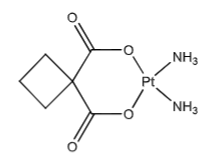
Carboplatin (Paraplatin): Decreased toxicity compared to cisplatin. Carboxylate leaving groups (instead of chlorines) hydrolyze much less rapidly than the chloro-platinum bonds. This decreases nephrotoxicity (nearly devoid), neurotoxicity, GI toxicity, and myelosuppression (dose-limiting ADR and presents as thrombocytopenia). Carboplatin needs 20-40x higher concentrations compared to cisplatin. Carboplatin’s aquo spp. forms 10x slower than cisplatin’s (efficacy is equal between the two).
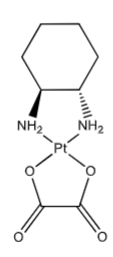
Oxaliplatin: “Carrier ligand” hydrophobic DNA intrusion, extends into the major groove of DNA when the platinum forms the crosslink within DNA. Contributes to its cytotoxicity—makes platinum-DNA adducts more effective @ blocking DNA replication than with cisplatin. May over common resistance mechanisms, effective in some cisplatin and carboplatin resistance cell lines. (not as dependent on CTR1 transporter as cisplatin and the oxaplatin-DNA adduct is not as recognized by repair proteins as the others. Larger volume of distribution—better tissue penetration.
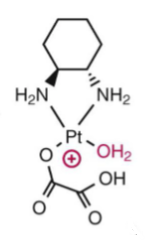
First step of oxaliplatin’s activation in a basic solution (unstable in basic soln)
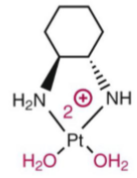
Active oxaliplatin diaquo form
Oxaliplatin and 5-fu clinical pearl
oxaliplatin is synergistic with 5-fluorouracil in the Tx of colorectal cancer. 5-fu is made in a basic solution therefore these two compounds are physically incompatible in solution together.
Nitrogen mustards for injection are acidic
They are formulated acidic to prevent premature cyclization into the aziridinium ion, which would cause degradation and loss of potency.
Hydration with cyclophosphamide/ifosfamide
Patients must drink water to prevent hemorrhagic cystitis by diluting urine and promoting excretion of acrolein, the toxic bladder metabolite.
Nitrosoureas cross the BBB
Carmustine and lomustine are highly lipophilic, allowing them to cross the blood–brain barrier and treat brain tumors.
Hydrolysis effects: nitrogen mustards vs. platinum
Hydrolysis inactivates nitrogen mustards by destroying the aziridinium-forming structure, but activates platinum drugs by replacing chloride ligands with water (aquation), making them reactive with DNA.
Hydration, chloride, and magnesium with cisplatin
Hydration increases urine flow to flush cisplatin out of the kidneys and reduce renal exposure; chloride decreases cisplatin aquation (activation) in the kidneys; and magnesium prevents hypomagnesemia-induced OCT2 upregulation, which increases cisplatin uptake into renal tubules and nephrotoxicity.
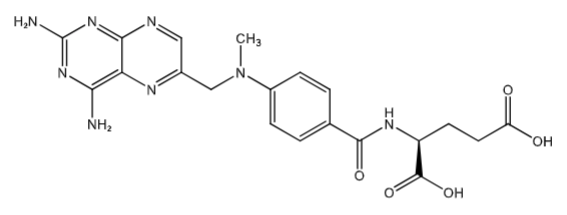
Methotrexate (PO- tablet, oral, IV/SQ): Folic Acid Antagonist, inhibits dihydrofolate reductase (human) DHFR. [MOA in RA]: inhibition of AICARFT (aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase) (which is involved in purine biosynthesis). Tx: PO-chemotherapy, rheumatoid arthritis SQ- rheumatoid arthritis (low dose). MTX get into the cells via RFC1 = Reduced folate carrier 1 (same carrier folic acid uses).
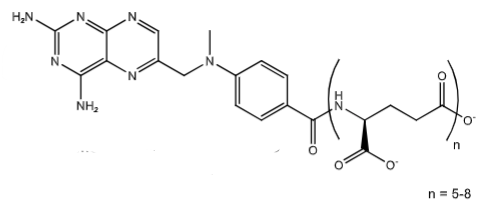
MTX-polyglutamate via folylpolyglutamate synthase. This traps MTX-PG inside the cell, [Main MOA in cancer chemotherapy] enhanced affinity to DHFR (increased inhibition), enhanced inhibition of other folate dependent enzymes (Ex. Thymidylate synthase AICARF)
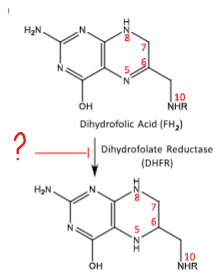
Methotrexate inhibits this conversion of DHFR to FH4. Downstream inhibits: methionine synthesis, thymidine synthesis, purine synthesis. Inhibits the folate cofactors that are one-carbon carrier units.
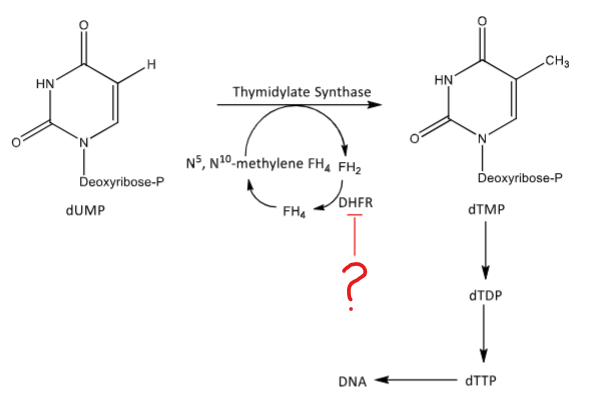
MTX inhibits thymidine synthesis by blocking DHFR from converting FH2 to FH4. This decrease DNA synthesis.
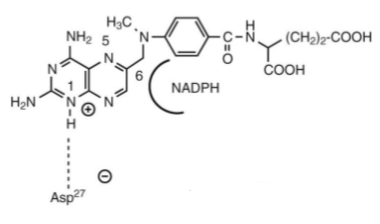
MTX (misoriented) in the binding site on dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) in relationship to the NADPH cofactor.
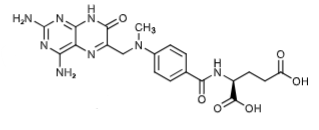
Metabolite of MTX (7-hydroxyMTX - 3-5x decreased water solubility than MTX)) via aldehyde oxidase. 80-90% of dose is excreted unchanged in urine (IV dosage form).
Preventing MTX toxicity with…
In high doses MTX and 7-hydroxyMTX can precipitate out into renal tubules. This causes crystal urea, damaging the kidneys. Patients need aggressive hydration and urine alkalinization (w/ sodium bicarbonate) to ensure MTX is ionized to increase water solubility.
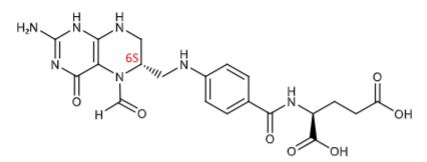
Leucovorin (folinic acid and N5- formyltetrahydrofolic acid): RESCUE MED, bypasses the inhibition of DHFR and provide an adequate FH4 pool to rescue cells. Folic acid itself will not rescue cells from MTX toxicity. Levoleucovorin is the active isomer. Serves as a cofactor involved in purine nucleotide synthesis.
Why is folic acid not considered a rescue medication but leucovorin is?
Why folic acid isn’t a rescue:
Folic acid is upstream of DHFR, so giving more folic acid does not bypass the DHFR block imposed by MTX. Cells still cannot make tetrahydrofolate, so DNA synthesis remains inhibited.
Why leucovorin is a rescue:
Leucovorin (folinic acid) is downstream of DHFR. It is already reduced to a form that can enter the folate cycle without DHFR, allowing nucleotide synthesis to continue and rescuing normal cells from MTX toxicity.
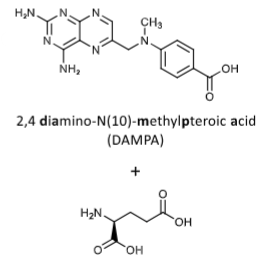
Inactive products of MTX when glucarpidase (Voraxaze) cleaves it. Used to rapidly decrease MTX levels in patients with renal dysfunction during high-dose MTX Tx. 97% decrease in MTX level in 15 mins.
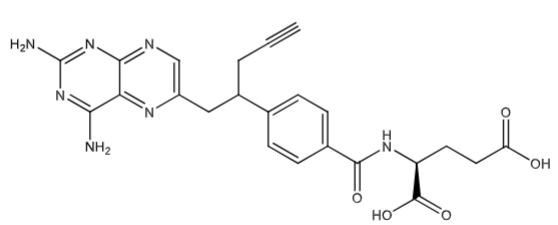
Pralatrexate (Folotyn soln for inj): inhibits DHFR. Contains a propargyl group that: increases polyglutamination in cells making it more active and stays in cell longer and increases uptake into tumor cells via reduced folate carrier 1 protein (RFC1)
Dosing limiting toxicity and required pretx for pralatrexate
Stomatitis (inflammation of the mouth) — occurred more frequently in pts with elevated pretx levels of homocysteine and methylmalonic acid. Give folic acid to replenish cofactor N5-methyl THF to convert homocysteine to methionine. Give vitamin B12 to convert methylmalonyl-CoA to Succinyl-CoA and activate methylcobalamin to convert homocysteine to methionine. Folic acid and Vit. B12 decreases the risk of stomatitis.
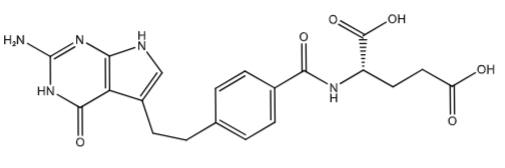
Pemetrexed (Alimate powder for soln for inj): inhibits thymidylate synthase (minor inhibition of DHFR) and inhibits GARFT & AICARFT (blocking purine synthesis). [Multi-targeted Antifolate] Pemetrexed uses RFC1 and PCFT (proton-coupled folate transporter) to get into the cells. It is also pentaglutamated via folylpolyglutamate synthase (FPGS). its polyglutamated 90-200x more than MTX. PreTX with IM vit B12 and folic acid to decrease ADRs.
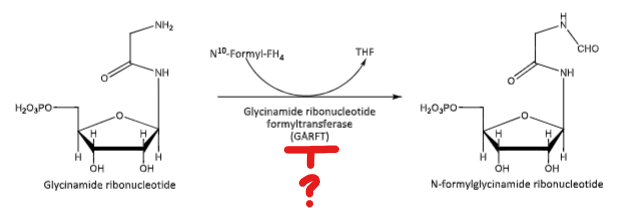
Pemetrexed blocks this conversion

Pemetrexed blocks this conversion
Can leucovorin be used for Pralatrexate and Pemetrexed toxicity?
Pralatrexate: ✅Yes
Pralatrexate is a folate analog and DHFR inhibitor like methotrexate.
Leucovorin can bypass DHFR, rescuing normal cells from toxicity.
Pemetrexed: ❌ No
Pemetrexed inhibits multiple folate-dependent enzymes (DHFR, thymidylate synthase, GARFT, AICARFT).
Leucovorin does not effectively rescue all inhibited pathways, so it is not routinely used for pemetrexed toxicity.