BMGT 301 - wk. 7,8,9 (DBMS)
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to database management systems, including definitions of important terms and systems relevant to the course.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
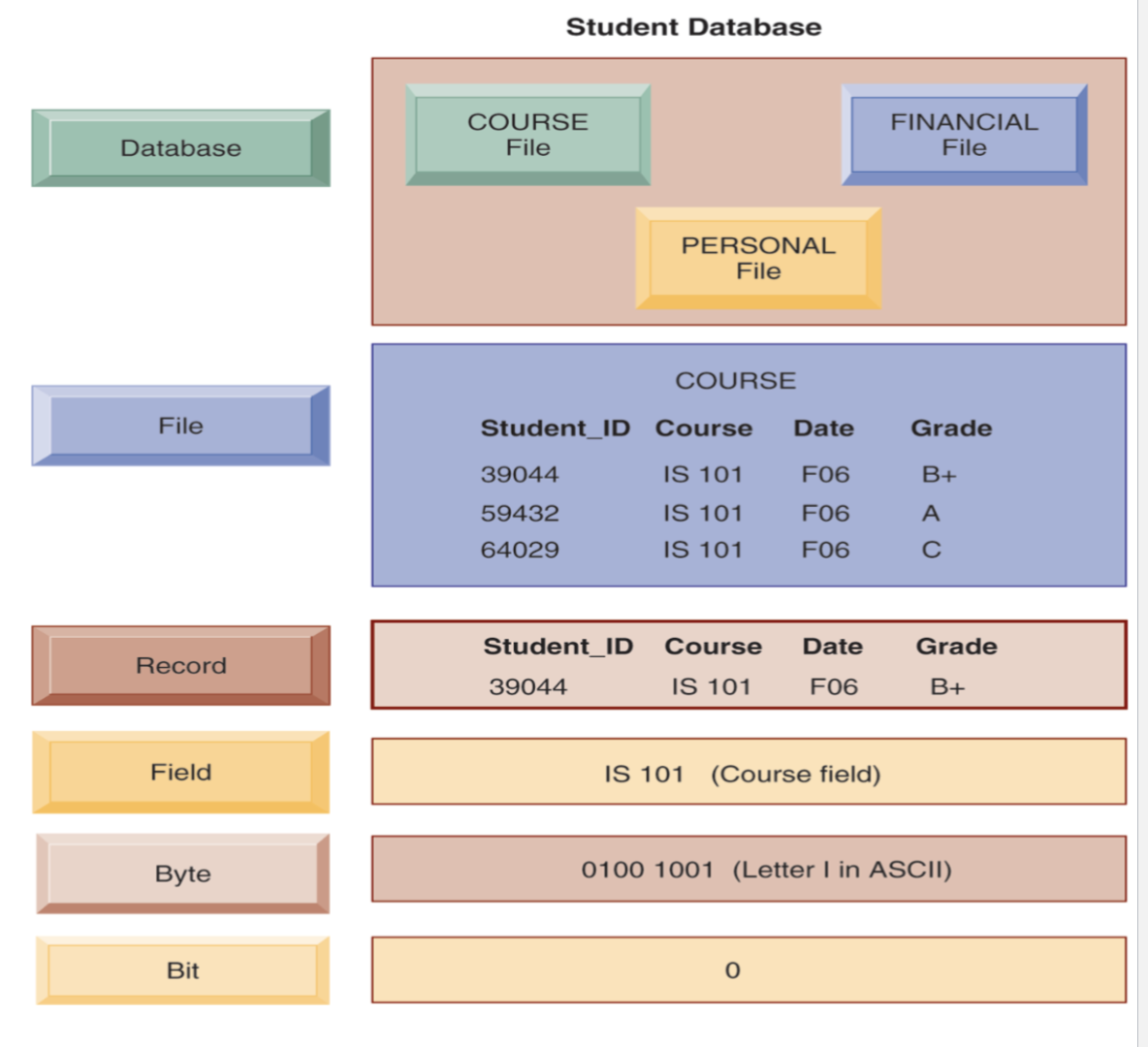
What’s a Data Hierarchy?
Organization of data in hierarchy: bits → bytes → fields → records → files → databases.
What’s a Database?
Serves many applications by centralizing data + controlling redundant data
What are the main functions of Database Management System (DBMS)?
interface between applications and physical data files
Separates logical and physical views of data
Solves problems of traditional file environment
What problems do DBMS solve in a traditional file environment?
Data redundancy, data inconsistency, lack of data integrity in traditional file-based systems → more efficient and organized way to manage data.
What are Relational DBMS?
A type of DBMS → organizes data into two-dimensional tables called relations/files
What’s a Table?
Grid of columns + rows
What are Rows, aka Tuples?
Records for dif entitites
What are Fields?
Attributes for each entity
Primary Key
Unique field in a table used to identify records
Foreign Key
Field in table that’s a primary key in another table → establish relationships between two tables.
What are the capabilities (and how many are there) of DBMS?
Data definition language → define data structures, used to make tables/define field characteristics
Data dictionary → automated/manually stores metadata about database elements, such as tables, fields, and relationships.
Data manipulation language → add, change, delete, retrieve data from databases (like SQL = structured query language)
What’s an Entity-Relationship Diagram
Used by database designers → represent the data model and relationships between entities.
Describe the relationships in DBMS between elements
one-to-one → each instance = one related instance
one-to-many → each instance = many related instances
many-to-many → many instances = many related instances
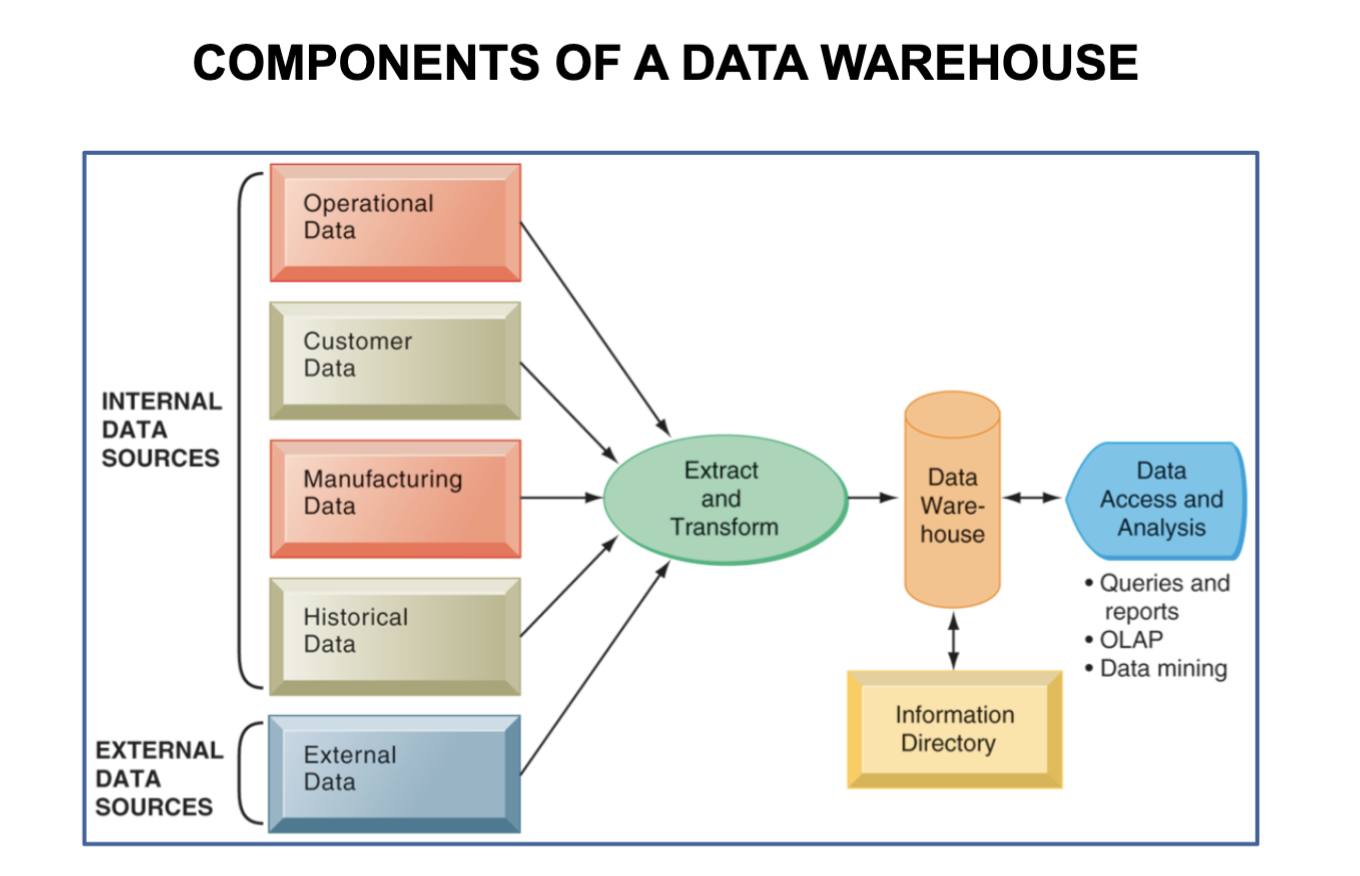
What is a Data Warehouse
Centralized repository → stores current/historical data from lots of core operational transaction systems for analysis and reporting
What is a Data Mart?
Subset of a data warehouse → focus on specific subject or line of business for a targeted group of users.
What’s text mining?
extracting key info from large unstructured data sets
What’s a Data Quality Audit
Structured survey → assess accuracy + completeness of data in information system.
How:
Survey samples from data files, or
Survey end users for perceptions of quality
What is data Cleansing
Detecting/correcting incorrect, incomplete, o redundant data in database.
True or False: A data dictionary is a language associated with a database management system that end users and programmers use to create data in the database.
False, data dictionary is centralized repository for information about data, not a language.
What is the schematic of the entire database that describes the relationships of entities called?
Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD).
True or False: In database systems, a column is also known as a key.
False, a column is not necessarily a key; it can contain data or be part of a key.
Which of the following is not a typical feature of DBMS?
A) DDL
B) DML
C) DICTIONARY
D) HDL
E) None of the above.
D) HDL (Hardware Description Language) is not a typical feature of DBMS.
In database systems, a ___ refers to a list of data describing an entity.
A) File
B) Record
C) Field
D) Column
E) Row
File.
In database terminology, what does a record represent?
A) A list of data, arranged in columns and rows.
B) All of the data in a given column.
C) A single instance of whatever the table keeps track of.
D) A field or combination of fields used to uniquely identify a file.
C) A single instance of whatever the table keeps track of.
When a customer uses a ___ and pays in cash, retailers can tie this to the customer and track their activity.
Loyalty card.
What area of application is referred to when data mining is used to determine which products customers buy together?
Market Basket Analysis.
Which of the following is a good candidate for a primary key?
A) A car model in a Motor Vehicle Department database
B) A State’s two-letter abbreviation
C) A student’s GPA
D) A student’s address
E) None of the above.
B) A State’s two-letter abbreviation.
What is the term for a field identified in a table as holding the unique identifier of the table's records?
Primary Key.
True or False: In database systems, a column is also known as a key.
False, while a column can be part of a key, it is not synonymous with a key.