Chemistry - moles 1 and 2
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what are moles
the amount of substance, the unit is moles or mol
what is the relative atomic mass
the mass found on the periodic table for an element
what is the relative formula mass
the sum of all the atomic masses of atoms represented in a chemical formula
what is the relative molecular mass
a term for formula that can be used with molecules
what is the empirical formula
shows the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms of different elements present in a compound
what is the limiting reagent
reactant that there are fewer moles than required by ratio given in equation
what is the reagent in excess
reactant that there are more moles than required by ratio in the equation
what is the reagent
reactant in chemical reaction
how to work out the percentage composition
Ar(of element in compound) x no. of atoms of the element in the compound/Mr of compound x 100
how to find the percentage composition of water
Mr of water x no. of water molecules in the compound/ Mr of compound x 100
what is a score of moles worth
20 units
what is Avogadro’s constant
6 × 10^23
how to find the moles of a substance
from the mass in grams and the relative formula mass
how to find the moles of an element
mass (g)/ Ar (g/mol)
how to find the moles of a compound
mass (g)/ Mr (g/mol)
how can the empirical formula be calculated
using either masses or percentage composition by mass
experiment for magnesium oxide
weigh a clean dry crucible
add a piece of magnesium ribbon and reweigh it with the lid on
using a pipe-clay triangle and a lid, strongly heat the magnesium
reweigh the crucible and lid
repeat steps 3-4 times until the mass remains constant
what could be some possible sources of error in the experiment of determining the empirical formula of magnesium oxide
not heated to constant mass or reaction incomplete, some MgO lost during the experiment, not weighing with the lid on consistently
experiment of copper oxide
weigh the empty reduction tube
add two spatulas of the copper oxide into the tube and reweigh.
turn on the gas and heat using a Bunsen burner until reaction is complete
reweigh the tube and its content.
repeat for the other copper oxide
what were the droplets of liquid seen at the end of the reduction tube before the apparatus became extremely hot in the copper oxide experiment
water
what did each copper oxide sample look like before and after reduction?
copper (ll) oxide - fine black powder at start, pink-brown metal at end
copper (l) oxide - fine red powder at start, pink-brown metal at end
why is methane passed over the product whilst it cools in the copper oxide experiment ?
to prevent the copper from reacting with oxygen in the air that would otherwise be sucked back into the tube
how to check that the pink-brown solid at the end of the copper oxide experiment is a metal ?
set up a circuit with a sample connected in the series and see if the light bulb lights up
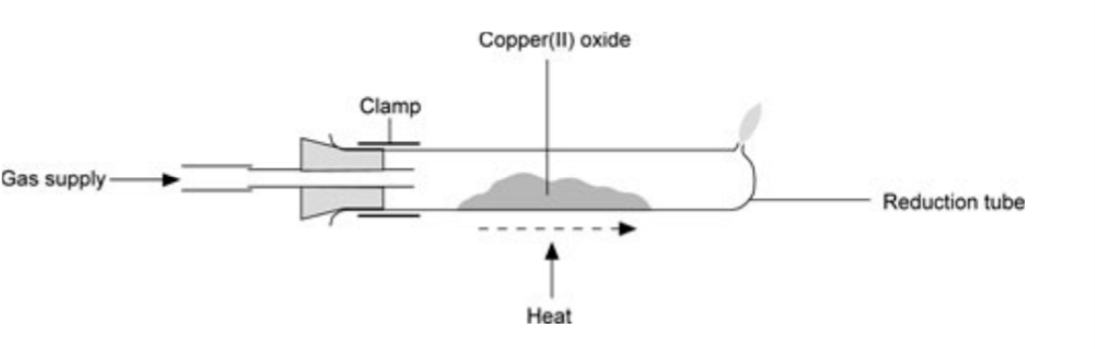
have you learn the picture
yes
experiment for reduction of tungsten oxide WO3
record the mass of a weighing boat
add tungsten oxide and record the mass again
heat the weighing boat and tungsten oxide strongly for two minutes, then allow to cool
record the mass of the weighing boat and its content
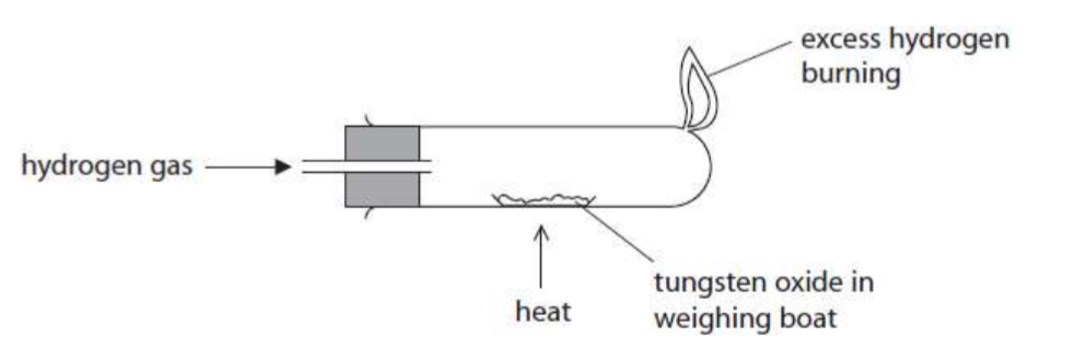
have you learnt the picture
yes
what could be an addition to the method to check that the tungsten oxide has been completely reduced
heat to constant mass
safety precautions for tungsten oxide experiment
lab coat, eye protection, use safety screen
what is molecular formula mass
number of atoms x empirical formula mass