MEDRADSC 3K03 Lecture 9 - Image Display
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Back projection
Process of converting data from the attenuation profile to a matrix
Compiles all info from all attenuation profiles to create image
Problems with back projection
Does not produce a sharp image (star pattern)
Back projection is a ___ method
Summation
Filtered back projection is a ___ method
Convolution
Filtered back projection steps
All projection profiles gathered
Log of data obtained
Log values multiplied by a convolution filter to generate a set of filtered profiles
Filtered profiles are back-projected
Filtered profiles are summed. -ve and +ve components canceled → image free of blurring
ASIR stands for
Adaptive statistical iterative recon
ASIR
Start w assumed image → compare measurements/projections of actual data with expected → update image based on differences
Advantages of using ASIR
Can reduce noise and pt dose up to 50% currently
ASIR steps
Input
Std filtered back projection algorithm utilized
Image reconstruction loop
Output
Final back projection image prod
What is a recon filter?
Mathematical pre-processing function applied to each detector value in each attenuation profile, involving intentional distortion of 1 value by adding weighted neighbours’ values
Function of recon filter
Deblurring filter to undo blur effect during back projection; converts raw data into image data
2 types of recon filter
Smoothing and enhancing
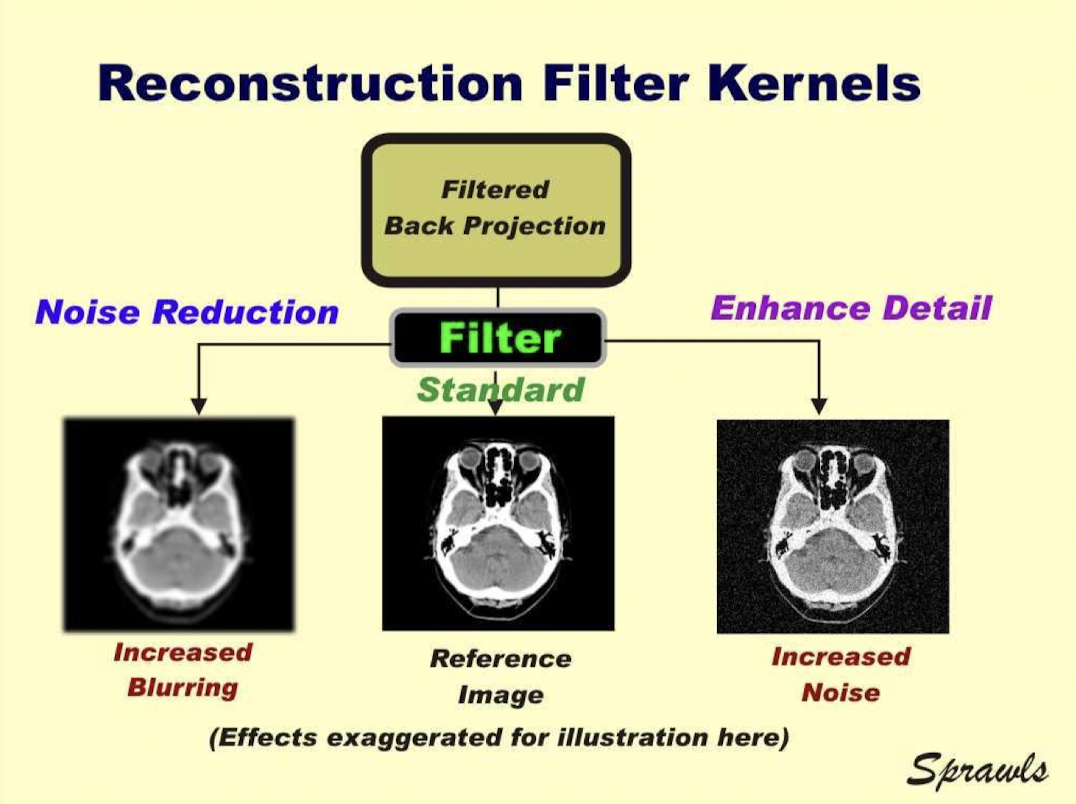
Smoothing recon filter
Dec artifacts but dec spatial resol
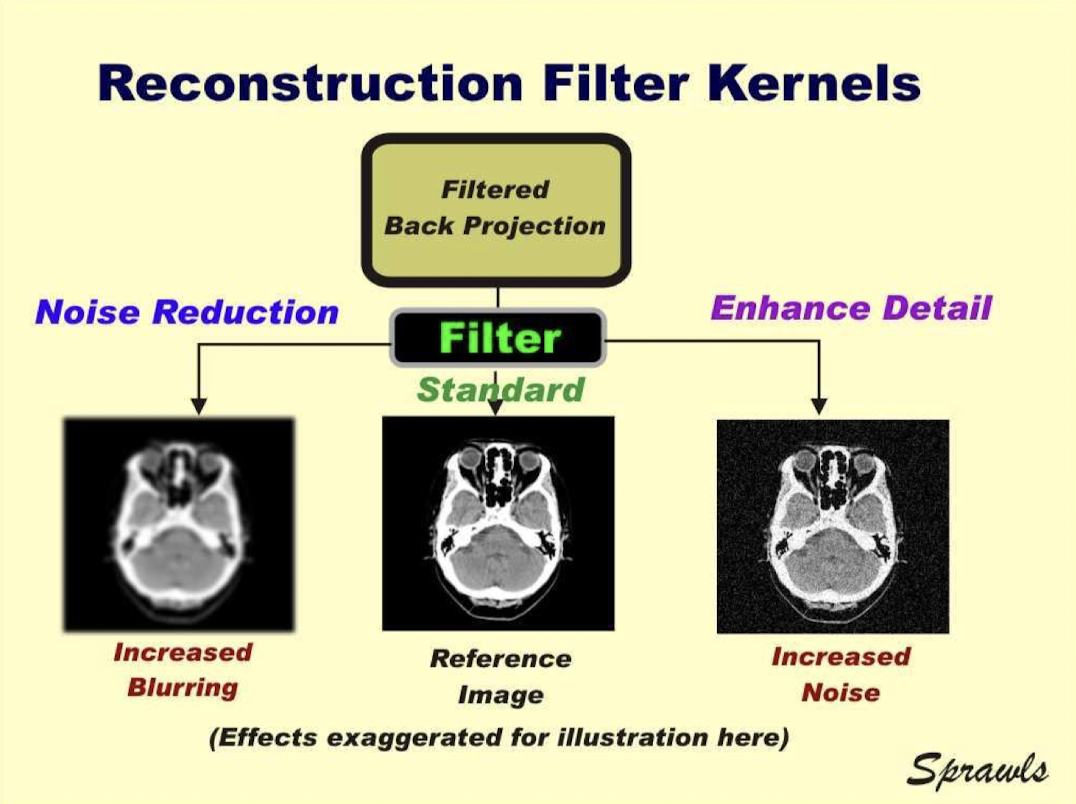
Enhancing recon filter
Inc spatial resol but dec contrast resol
Another word for filters
Kernels
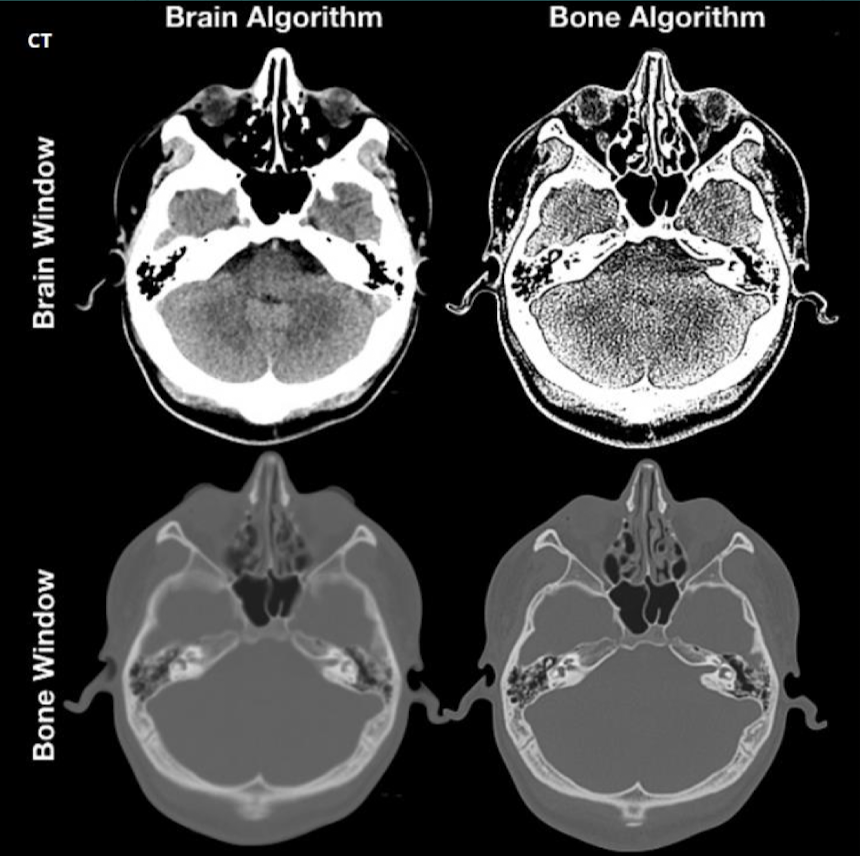
Recon algorithms
Soft
Std
Lung
Detail
Bone
Edge
Bone plus
Soft recon algorithm
Useful for tissues w similar densities w contrast
Std recon algorithm
For routine exams like chest, abdo, pelvis
Lung recon algorithm
Interstitial lung pathology
Detail recon algorithm
For post myelograms, where hybrid tissue density detail and bone edges are impt
Bone recon algorithm
For high resol exams and sharp bone detail
Edge recon algorithm
For small bone work in head, as well as high resol scans
Bone plus recon algorithm
For sub mm detailed head work (e.g internal auditory canal)
Is window and algorithm the same?
No
CT number formula
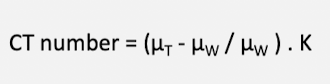
CT number is based on
LAC of H2O
What does a CT number correspond to?
Signal intensity/brightness value
What if the CT numbers are inaccurate?
Misdiagnosis
In an acquired CT image, the CT number of muscle was measured to be 53. What is the LAC for this tissue given an LAC of water is 0.280 at beam energy?
0.295
ROI stands for
Region of interest
What is an ROI?
Provides an averaged measurement of all of the pixels within the ROI
When an ROI is used, the ___ is also displayed
Standard deviation
What does the cursor (+) display?
Measurement of the HU of the pixel that the cursor covers
HU measurements may be affected by
Volume averaging or image noise
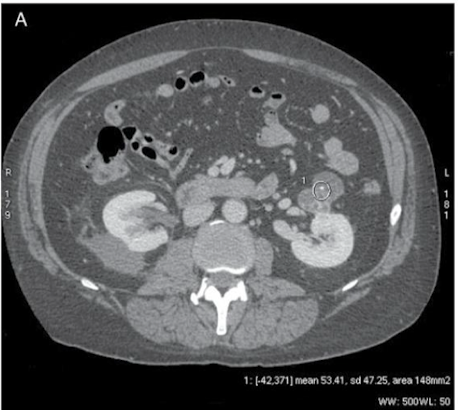
Why is this ROI not appropriate?
Piece of Ca in ROI → SD = 47.25 → make circle smaller so it’s not covering Ca
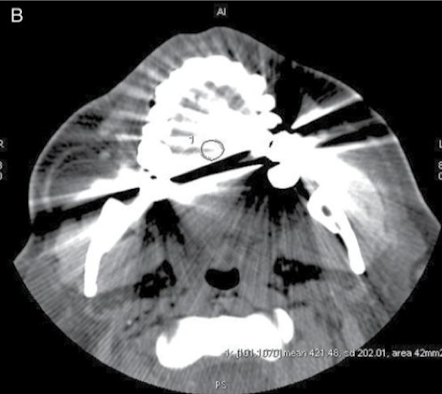
Why is this ROI not appropriate?
Beam hardening incl in ROI → SD = 202.01
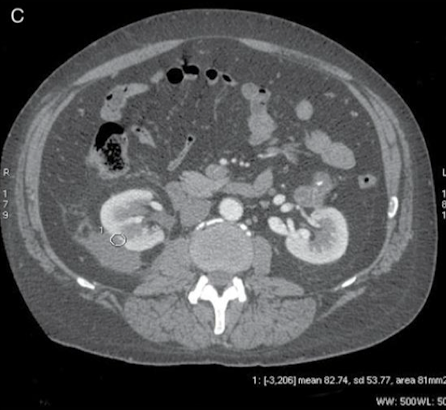
Why is this ROI not appropriate?
Measuring contrast enhanced kidney with non-contrast enhanced tissue → SD = 53.77
When is an ROI used?
Measure HU for contrast running through an area. Monitor ideal peak enhancement to start the scan
Why do we measure the distance in images?
Reporting size of an abnormality
Placement of biopsy needle
Drainage apparatus
Why is it better to use an ROI than the cursor tool when measuring HU?
ROI is less susceptible to variation
How can we measure the distance?
Grid for CT guided procedures
Radio opaque markers that can be seen in images
Scale alongside images
Size reference
Ruler
Magnification vs DFOV
Magnification | DFOV |
No improvement in spatial resolution | Improves spatial resolution |
No change in pixel size | Changes pixel size |
Other display options
Image annotations
Multiple image display
Histogram
MPRs and 3D formatting