Chapter 8: Inventory
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
How many inventory accounts does a manufacturing company normally have?
A manufacturing company typically has three inventory accounts:
Raw Materials
Work in Process
Finished Goods
What is used by manufacturing companies to determine cost of goods sold?
Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM) is used to determine the cost of goods sold.
costs of goods sold model
beginning inventory + purchases = cost of goods available for sale - ending inventory = cost of goods sold
definition of inventory
Inventories are assets:
Held for sale in the ordinary course of business;
In the process of production for such sale; or
In the form of materials or supplies to be consumed in the production process or in the rendering of services.”
Inventory is recognized as an asset when
risks and rewards of ownership have been passed by the seller
When are goods in transit included in the seller’s inventory?
If shipped FOB destination (seller keeps title during shipment).
Are goods out on consignment included in the consignor’s (seller’s) or consignee’s inventory?
Goods out on consignment remain in the consignor’s (seller’s) inventory until sold.
Goods sold under buyback agreements belong to who?
Still the seller, because the seller is required/expected to repurchase them.
What happens when goods are sold but have very high, unmeasurable return rates?
They stay in the seller’s inventory because revenue cannot be recognized.
Does title pass to the buyer when a purchase commitment is signed?
No — title does not pass until delivery.
How are non-cancellable purchase commitments reported?
They are not recorded, but material ones are disclosed in the financial statement notes.
When is a loss recognized on a purchase commitment?
When it becomes onerous — meaning the unavoidable costs to fulfill it exceed the expected benefits.
What is the journal entry when contract price is $640,000 and market value drops to $500,000?
Loss on Purchase Contracts ............... 140,000
Liability for Onerous Contracts .......... 140,000
Company signs a contract to purchase goods for $640,000. Goods finally delivered. Market value = $460,000. What is the entry?
Inventory .......................................... 460,000
Liability for Onerous Contracts ..…... 180,000
Accounts Payable .........................……....... 640,000
If ending inventory is undercounted, what happens to inventory on the balance sheet?
Inventory is understated.
If ending inventory is undercounted, what happens to COGS?
COGS is overstated.
If ending inventory is undercounted, what happens to net income?
Net income is understated.
If ending inventory is undercounted, what happens to retained earnings?
Retained earnings are understated.
If ending inventory is undercounted, what happens to working capital?
Working capital is understated.
If ending inventory is undercounted, what happens to the current ratio?
Current ratio is understated.
What happens when items are not counted in Purchases and not counted in Inventory?
Both Purchases and Ending Inventory are understated.
If items are missed from inventory count, what happens to Inventory?
Inventory is understated.
If a purchase is not recorded, what happens to Accounts Payable?
Accounts payable is understated.
If both Purchases AND Ending Inventory are understated, what is the effect on COGS and Net Income?
COGS: No effect
Net income: No effect
(They cancel each other out.)
If current assets are understated but current liabilities stay overstated or unchanged, what happens to the current ratio?
Current ratio is overstated.
What does inventory cost include?
“All costs of purchase, costs of conversion, and other costs needed to bring inventory to its present location and condition.”
What are examples of product costs included in inventory?
Invoice price, freight-in, and other direct acquisition costs.
What do conversion costs include?
Direct labour, plus fixed and variable manufacturing overhead.
Are period costs inventoriable?
No — selling, general, and administrative expenses are not included in inventory.
How are volume rebates (bulk purchase discounts) treated?
If the rebate is probable, it is recorded as a reduction to the cost of inventory.
How do you allocate cost in a basket (lump-sum) purchase?
Allocate the total cost based on relative sales value of each item.
How are joint product costs allocated?
Using the relative sales value of each product
When can a vendor rebate be recognized?
When the rebate is probable and can be reasonably estimated.
How do you record a vendor rebate when it’s recognizable?
As a reduction in the cost of purchases, allocated between inventory and COGS.
A company buys 60,000 units this year and expects to buy 50,000 units next year. How many units are expected to qualify for a rebate?
110,000 units (60,000 current + 50,000 expected).
If 110,000 units qualify for a $0.10 rebate per unit, what is the total rebate amount?
The total rebate is $11,000 (110,000 × $0.10).
The company purchased 60,000 of the 110,000 qualifying units this year. What rebate amount should be recognized this year?
The company recognizes $6,000 this year (60,000 ÷ 110,000 × $11,000).
How is a $6,000 vendor rebate allocated between inventory and COGS when 5,000 units remain and 55,000 units were sold?
Inventory receives $500 (5,000 × $0.10) and COGS receives $5,500 (55,000 × $0.10).
A $6,000 vendor rebate must be allocated based on units on hand (5,000) and units sold (55,000).
Rebate = $0.10 per unit.
What is the journal entry?
Rebate Receivable 6,000
Inventory 500
COGS 5,500
What is included in product costs?
Every penny needed to get the product ready for sale.
What are purchase costs in inventory?
The invoice cost, freight-in, and other direct buying costs.
Are restoration or environmental cleanup costs included in inventory?
Yes — they are part of product cost.
Are taxes included in inventory cost?
Yes — applicable taxes are inventoriable costs.
What are conversion costs?
Direct labour + allocated fixed and variable manufacturing overhead.
How are fixed production costs allocated in inventory?
Based on the company’s normal production capacity.
How does IFRS treat interest/borrowing costs for inventory?
Capitalize interest only when inventory takes a long time to produce.
For high-volume repetitive production, IFRS allows a choice to capitalize or expense.
How does ASPE treat interest/borrowing costs for inventory?
They may be capitalized or expensed, but the company must disclose its policy.
Costs not Included in Inventory
Abnormal waste and spoilage (of labor and material)
Abnormal storage costs
Interest expense for items on delayed payment terms
Selling Expense
General and administrative expenses
Why is an accurate inventory system important for availability?
It ensures the company has enough inventory to meet demand.
How does accurate inventory help prevent waste?
It prevents excessive accumulation of inventory items.
What is the effect of just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems?
JIT helps reduce inventory levels by ordering only when needed.
What does a perpetual inventory system do?
It keeps a continuous, real-time record of inventory changes.
how does a periodic inventory system update inventory?
it updates records only at intervals, usually at period-end.
How are purchases and related costs recorded in a perpetual system?
All purchases, freight-in, returns/allowances, and discounts are recorded directly in the Inventory account.
What happens when inventory is sold in a perpetual system?
The system records COGS and reduces Inventory at the time of sale.
How does a perpetual system track inventory and handle differences?
It uses subsidiary ledgers, still requires physical counts, and differences go to Inventory Over and Short (or COGS).
how are inventory purchases recorded in a periodic system?
Purchases are recorded in a Purchases account, not in Inventory. Freight-in, returns/allowances, and discounts go to separate accounts.
When are Inventory and COGS updated in a periodic system?
They are updated only at the end of the period, after a physical inventory count. there is not cogs entry on sale.
Why are physical counts required in a periodic system?
To determine the quantity and cost of inventory on hand, and because of risks like waste, breakage, and theft. (Required annually under both systems.)
IFRS and ASPE recognize three acceptable cost formulas:
Specific identification
First-in, First-out (FIFO)
Weighted average cost
What is the specific identification inventory method?
Each item purchased and sold is individually identified. Used when items are not interchangeable or are made for specific projects.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of specific identification?
Advantages:
Matches actual cost to revenue
Ending inventory shown at actual specific cost
Disadvantages:
Costly to implement
Allows income manipulation
Hard to assign shared costs (e.g., storage, shipping)
What does the weighted average cost formula do?
The weighted average method assigns every unit of inventory a single average cost, which is reasonable because it reflects the overall cost of goods available for sale and generally follows the actual physical flow of most inventory items.
How is most inventory valued?
At the lower of cost and NRV.
(Some special items, like biological assets, use NRV or fair value instead.)
What must be determined to value ending inventory?
You must know:
Which goods belong in inventory
Which costs to include
Which cost formula to use
Whether there is any impairment/loss
What is net realizable value (NRV)?
the estimated selling price minus the costs to complete and sell
Grouping is allowed only for items:
they are closely related in terms of their end use.
they are produced and marketed in the same geographical area
they cannot be evaluated separately form other items in the product line in a practical or reasonable way
What happens to inventory under the Direct Method when NRV is below cost?
Inventory is recorded at net realizable value at year-end.
Where is the loss reported under the Direct Method?
The loss is included in Cost of Goods Sold.
How does the Indirect (Allowance) Method record inventory declines?
Inventory stays at cost, and declines are recorded in an Allowance account with a Loss on the income statement.
How are recoveries handled under the Indirect Method?
Recoveries are recorded, but only up to the original cost—never above it
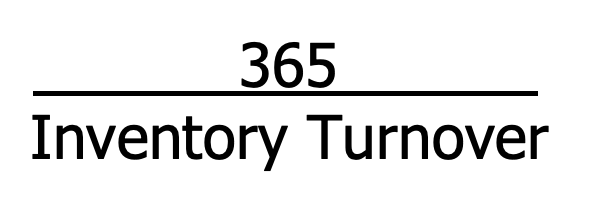
inventory turnover formula
Measures number of times on average inventory was sold during the period

average days to sell inventory formula