comp 2 part 2
1/246
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
247 Terms
What does the “E” in E-M-P-A-T-H-Y stand for?
Eye contact
Ras is a part of the
MAP pathway
Akt is associated with the
mTOR pathway
Germinal centers are the sight of
B. Cell proliferation
Type 2 epitheliorecticular cells are in the
In the cortex of the thymus
Function of spleen
Decrease clearance of encapsulated bacteria from the blood
White pulp deals with
Lymphoid tissue with T and B cells from immune response
Red pulp is involved in
Old red blood cells and pathogens
Benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and alcohol act on
GABA
Gq activates
Phospholipase
How do Botox injections work
Prevents acetylcholine release from the presynaptic nerve terminals
Which of the following mechanisms is primarily responsible for terminating the calcium signal in the cytoplasm?
Na⁺/Ca²⁺ exchange and Ca²⁺-ATPase–mediated reuptake
IP3 degradation prevents
further Ca2+ release
What terminates cAMP signaling?
Phosphodiesterase
Which pathway generates IP3 and DAG
Gq pathway
cAMP is associated with the
Gs pathway
Lipoxygenase enzyme catalyzes the formation of
Leukotrienes and HETE compounds which cause inflammation
GABA and chlorine are associated with
Ligand-gated ion channels
TNF-alpha causes
Fever and hypotension
C5a is associated with
Neutrophil chemotaxis
Mycobacteria is identified with
Autamine/rhodamine
Legionella pneumophila Is diagnosed by
Buffered charcoal yeast extract
“Catalase and coagulase positive”
Staph aureus
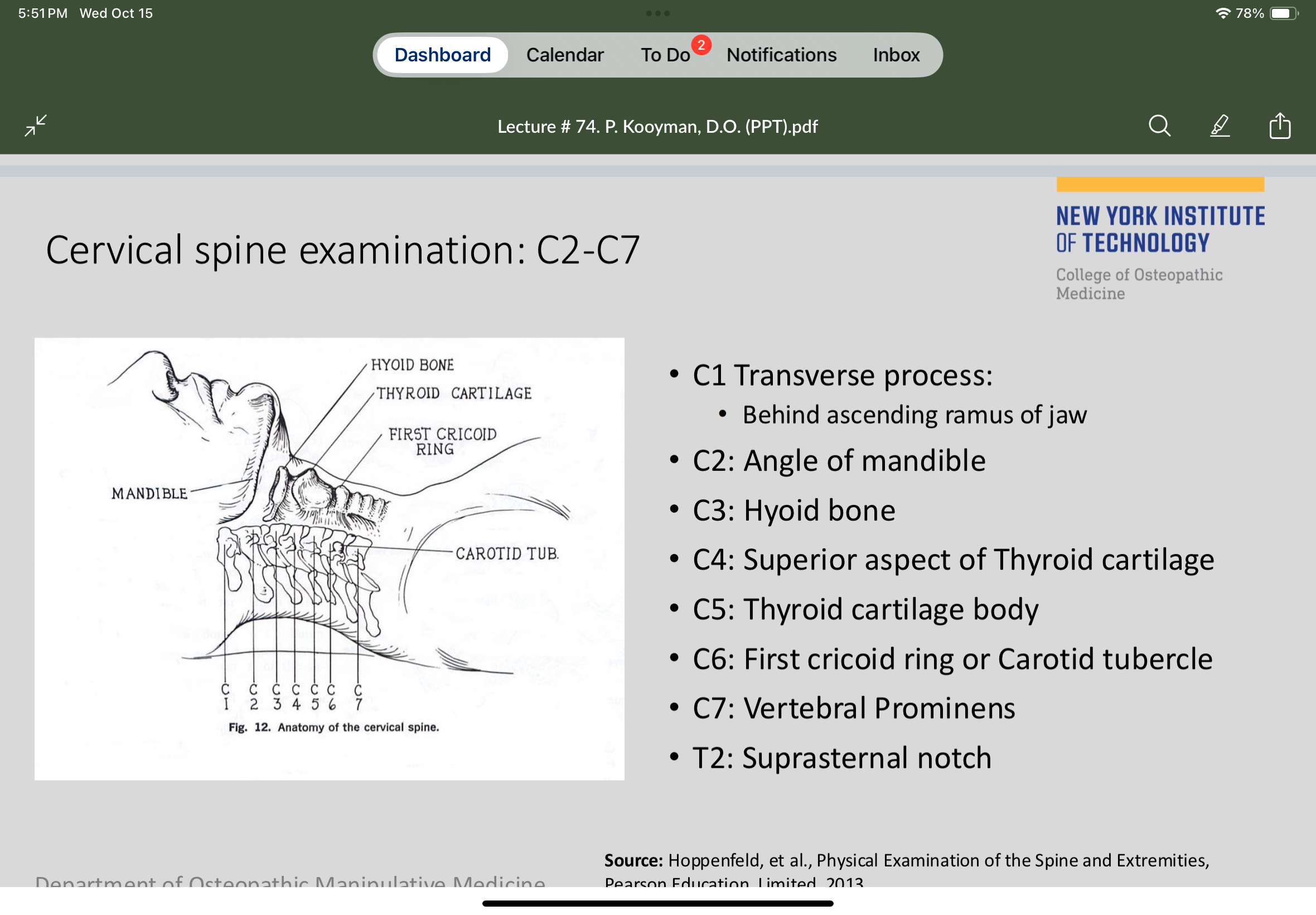
C2 is at the
Angle of the mandible
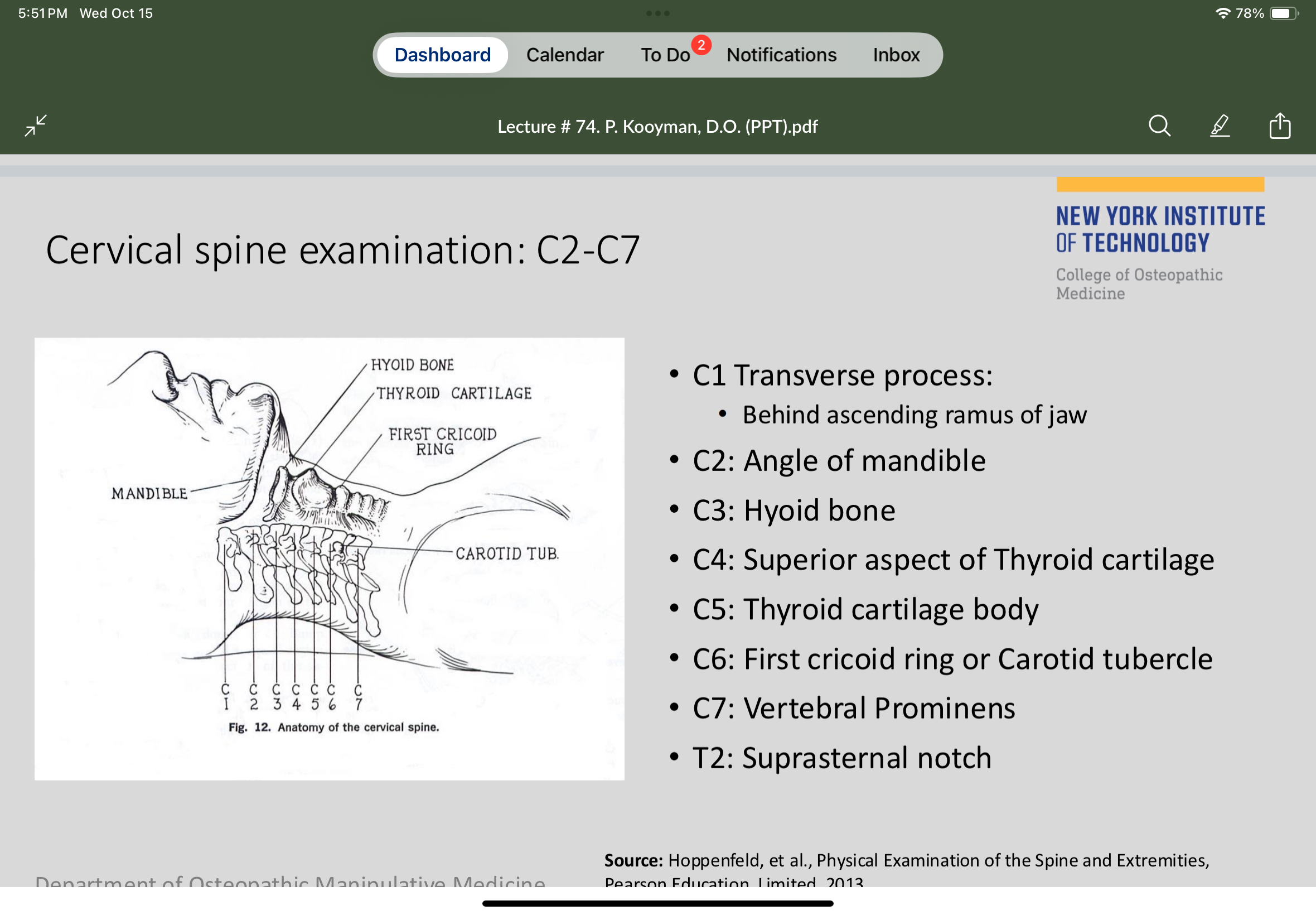
C6 is at the
First cricoid ring
C7 is at the
Vertebral prominens
“oRotation and Side-bending are in the same direction“
Type 2-like mechanics of C2-7
“T helper”
CD4+
“T-cytotoxic”
CD8+
the wright-giemsa stain, is used on
Plasmodia
Spore stain is mostly used on
Bacillus and clostridia
Nonselective agars
Blood agar, chocolate agar, and sabouraud dextrose sugar
buffered charcoal yeast extract is used for
Legionella pneumophilia
“Complete absence of dystrophin protein”
DMD
“Reduced or abnormal dystrophin protein”
Becker muscular dystrophy
Spatial summation
Recruiting more motor units to increase muscle force
Active tension is caused by
Cross bridge formation and contraction after stimulation
Type 2 muscle spindles controls the
Degree of stretch of the muscle
Endospores are
Metabolically dormant
Infectivity
How often an infection is transmitted
Pathogenicity
The number of persons who develop disease divide by the total number infected
Virulence
The number of fatal or severe cases divided by the total number of cases
Incidence
the number of new cases of a disease within a
specified period, and also the number of new cases divided by the
size of the population under surveillance.
Prevalence
The total number of cases existing in a given
population at risk at a given point in time or during a defined period
(cases per 100,000).
“By cross-bridge formation and contraction after stimulation”
Active tension
Lymphatic vessels path
Collect lymph (originate from
plasma) → lymph nodes
• Efferent lymphatic vessel →lymphatic trunk or thoracic duct → subclavian vein →superior vena cava
The germinal center and mantel zone and corona is in which layer of lymphatic tissue
Secondary nodule
Small lymphocytes are in
Small lymphocytes
“Display Ag/Ab complexes for years”
Follicular DC
“Important for memory B-cells & affinity maturation”
Follicular DC
“Fc receptors/no MHC class II”
Follicular DC
C5 is located at the
Thyroid cartilage body
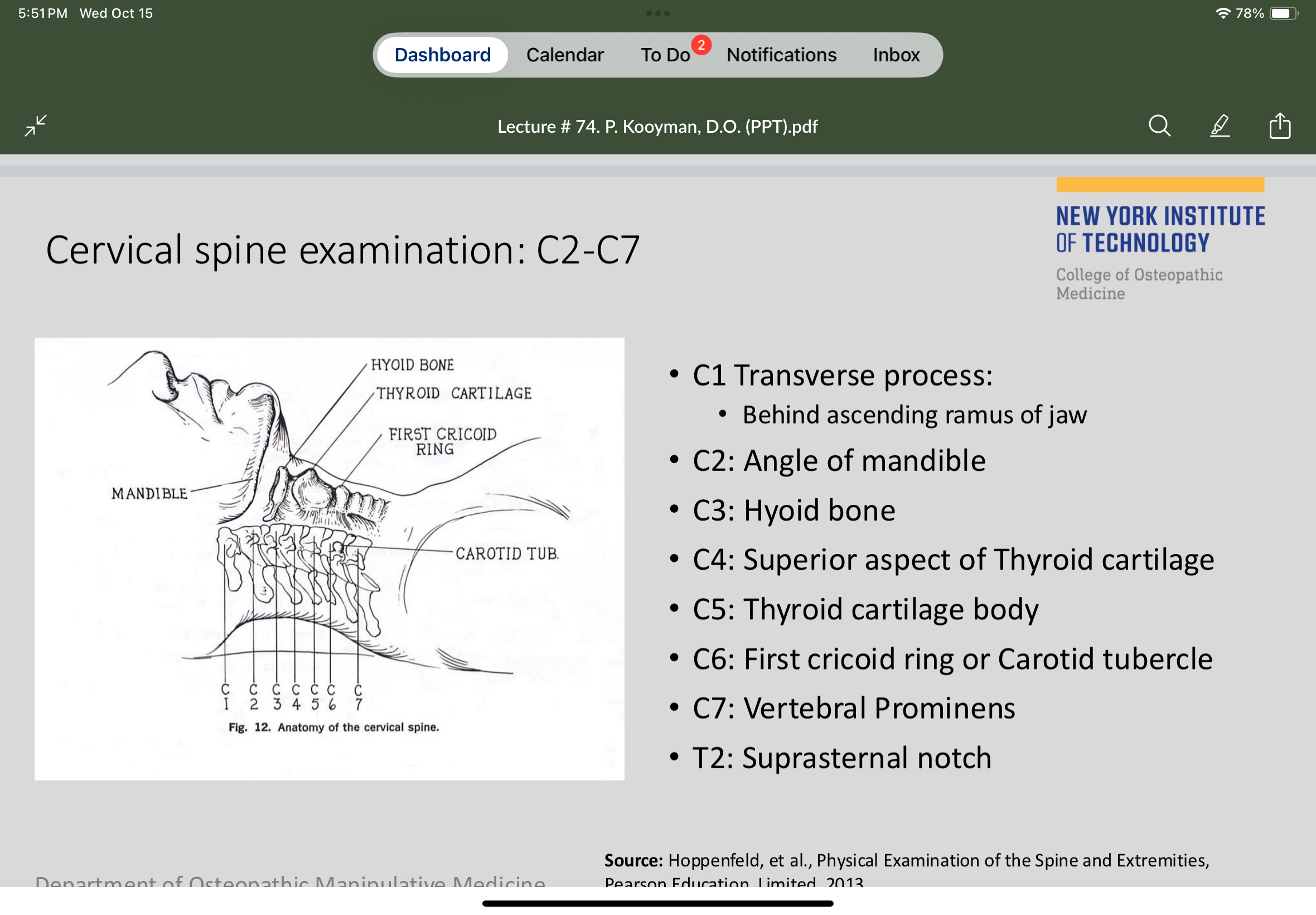
C4 is located at the
Superior aspect of the thyroid cartilage
_____ measures the severity of a disease—specifically, the proportion of severe or fatal cases among those who develop illness.
Virulence
If γ-motor neurons are damaged, spindles become slack when the muscle shortens →
reduced ability to detect stretch or maintain tone
Name two Gram-positive genera that form endospores.
Bacillus and Clostridium.
Describe conjugation.
DNA transfer through a pilus between two bacterial cells.
Describe conjugation.
DNA transfer through a pilus between two bacterial cells.
What forms membrane attack complex (MAC)?
Complement proteins C5b–C9 → 10 nm pore kills bacteria.
H and E does not stain ____ well
Elastin well
“Forms reticular fibers in soft tissue stroma, not arteries.”
Type III collagen
M1 subtype =
tissue injury
M2 subtype =
repair
“Phagocytic cells containing lysosomes”
“Surface receptors for pathogens”
“Derived from circulating monocytes”
“Antigen-presenting cells”
“Fuse to form multinucleated giant cells in chronic inflammation”
Macrophages
Reticular CT
Type III collagen mesh in lymphoid organs; not in umbilical cord.
Sabouraud (potato) agar” →
Standard fungal medium
ergosterol is in
Fungal membrane
Tubular branching filaments / hyphae” →
Mold
Terbinafine (Lamisil) inhibits ergosterol synthesis” →
Great for dermatophytes/onchomycosis
Flucytosine serves as a
Pyrimidine analogue to block DNA/RNA synthesis block
Griseofulvin disrupts ____
Microtubles
Azoles inhibit
Ergosterol synthesis
Echinocandins inhibit
Beta glucagon synthesis which affects caspofungin so the cell wall is inhibited
Non-septate hyphae with right-angle (≈90°) branching →
Mucor and Rhizopus
Aspergillus fumigatus –
septate hyphae, acute-angle (~45°) branching, not 90°.
What triggers cross-bridge formation?
Rise in intracellular Ca²⁺ levels
Which training leads to hypertrophy and IIa → IIb/IIx conversion?
Resistance (strength) training
Difference between disuse and denervation atrophy?
Disuse = immobilization; Denervation = motor nerve damage
Define isotonic contraction.
Length changes, tension constant
Type Ib afferent neuron role?
From Golgi tendon organ, signals force
What neurons control skeletal muscle contraction?
α motor neurons (from spinal cord
Force-velocity relationship depends on?
Afterload; lighter load = faster contraction
Treatment set up for AC1 anterior and mandible
Rotate Away
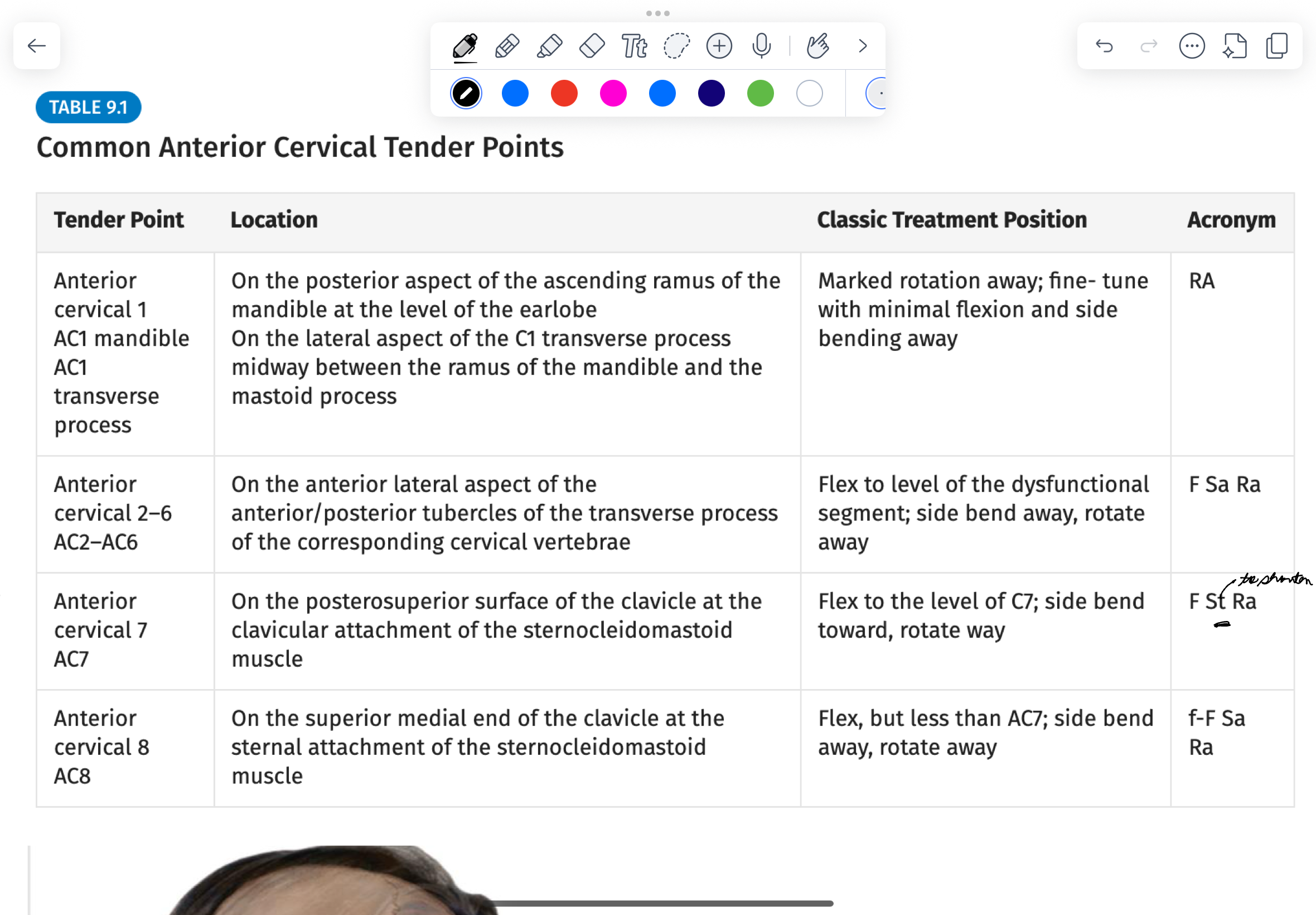
Anterior Cervical Set up for 2-6
F Sa Ra
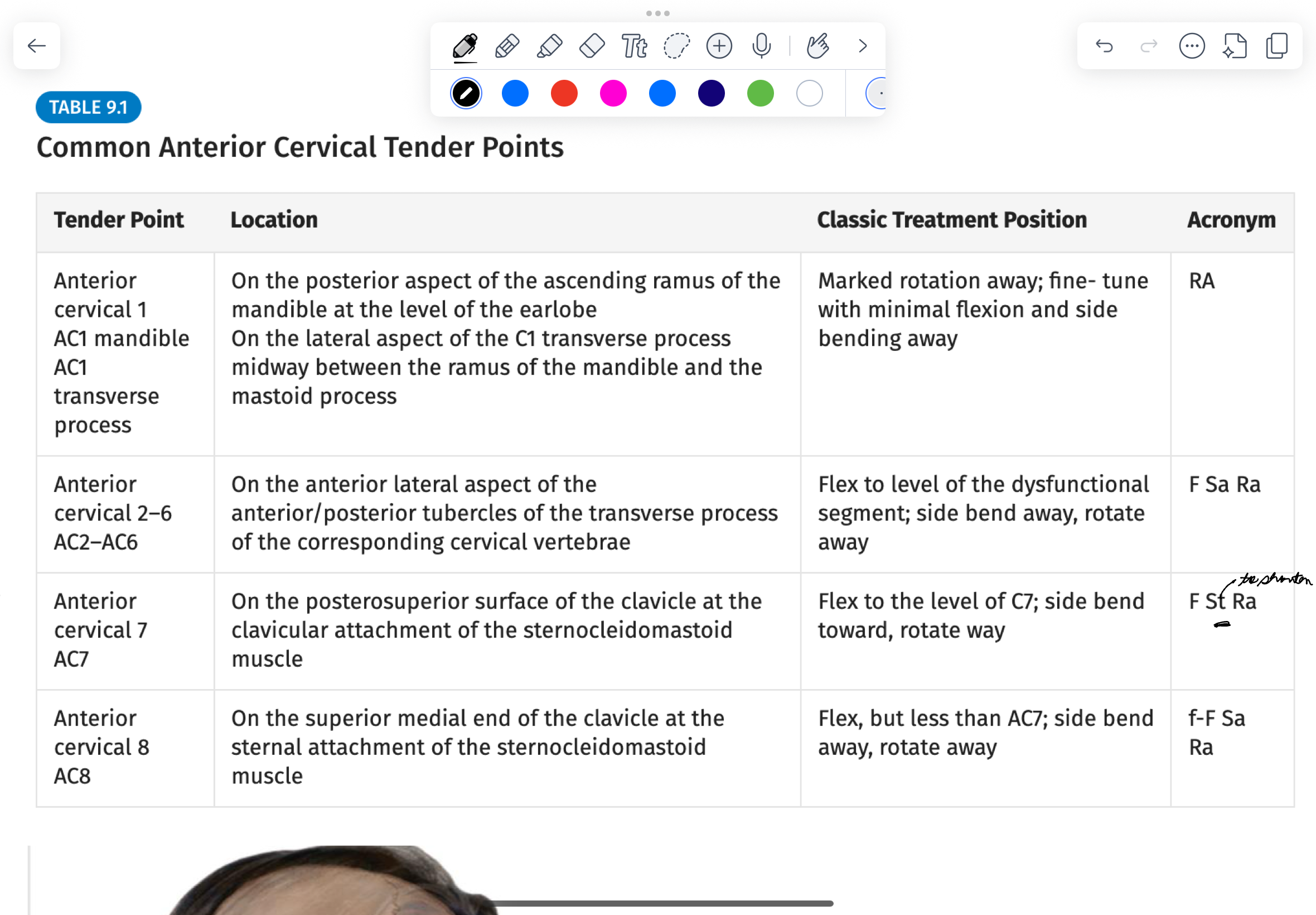
Counterstrain Set Up for AC 7
F stra (the only one on the cervical spine that’s like this)
Why is the set up for AC 7 F Staw
To shorten to SCM
CS set up for AC 8
F Sara
You can use the “sidebending head on a pike” method for the
OA
“Shallow sulcus in the OA region on the left”
Side bent to the left because the atlas is in a bowl
To diagnose the AA you must
Be standing
What zone of the lymph node is T-cell-rich?
The paracortex
What are the three main types of lymphocytes?
T-cells, B-cells, and NK (natural killer) cells.
Two hormones, A and B, have similar structures. Hormone A normally binds its own receptor, but at high concentrations, it also activates receptor B’s pathway, producing some of hormone B’s effects.
Which of the following mechanisms best explains this phenomenon?
Hormone spillover
intracellular receptors (like steroid or thyroid hormone receptors) act
Slowly
Thyroxine is
Lipid-soluable