Conservation Biology Chapter 8
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
LC
least concern- widespread and abundant
NT
near threatened-likely to qualify for a threatened category in the future
VU
vulnerable- facing a high risk of extinction in wild
EN
Endangered- facing high risk of extinction
CR
critically endangered- extreme high risk of extinction
EW
extinct in the wild
EX
Extinct
DD
data deficient
NE
not evaluated
IUCN Red List Assessment Advantages
Uses clear taxonomy, Standardize assessment process, Formal Listing and review process, A place to keep all of the records
IUCN Assessment Process
Collectives of experts in government agencies, universities, wildlife preserves, zoos, botanical gardens, and museums assess the populations
IUCN Red List of Ecosystems
The goal is to place organisms into categories that describe risk of collapse → characteristic native biota will no longer be sustained.
Threatened Species
Of the 96,951 species assessed, 26,840 are listed as Threatened
Endangered Species Act
Made government HAVE to protect these species
Biodiversity Regulations
Regulated by a balance of speciation and extinction
Extinction rates
E/MSY=E/S10^6/t; Number of species expected to go extinct in 1 million years per the number of species that exist
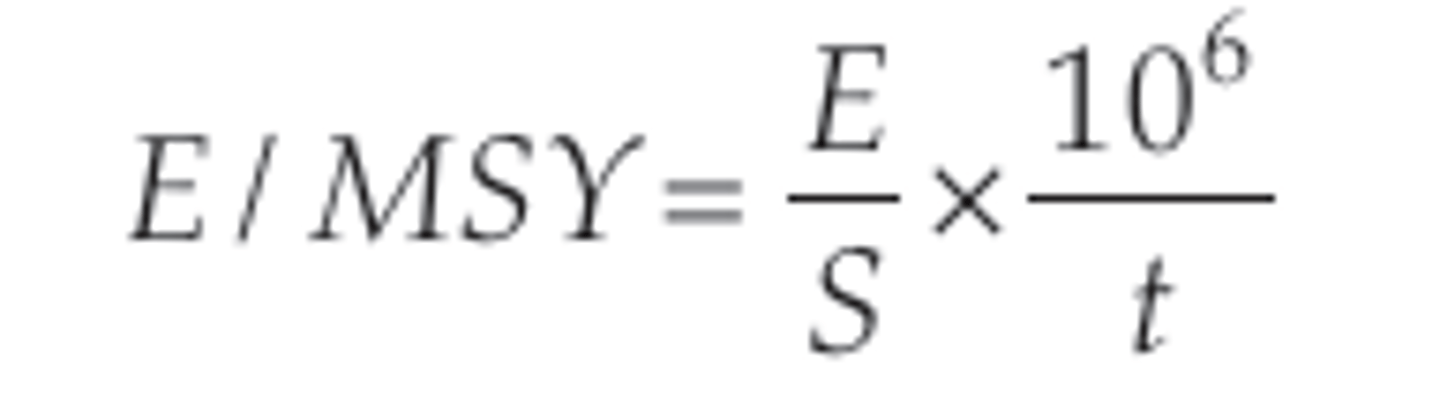
Expected Extinction Rate
Should expect 0.1 to 1.0 species to go extinct out of a million per year
Current Extinction Rate
Currently 100-10,000 times faster
Drivers of Extinction
I = P ✕ A ✕ T; Impacts on biodiversity = human population size ✕ Affluence ✕ Technologies
HIPPO + C
Habitat loss, invasive species, population growth, pollution, overexploitation, and (new one) Climate Change
Habitat loss
Habitat loss, degradation, and fragmentation is the biggest cause of loss of biodiversity
Local Changes to Biodiversity
Balance between local extirpations and introduction of new species due to migration or reintroduction
Species-Area relationships
Species richness increases with area but will level off
Longterm Monitoring
Repeatedly testing and sampling biodiversity at the same location over a long period of time
Controls of Extinction Risk
Population size (rarity), Specialists, Trophic Level→ carnivores, Large body size, Limited range, Population density, Endemism, Isolation
Allee effects
Set of phenomena in biology where population density influences the fitness of individuals.
Endemism
A species found only in one geographical location.
Neoendemics
Species that occupy small areas because they have only recently evolved from closely related species
Paleoendemics
Ancient species whose close relatives have all gone extinct.