Attitude and Stereotypes - Allport
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Attitude
An evaluation a person makes about of an event, object, group or issue. They are learned ideas we hold about ourselves, others and experiences. They are not innate. It is a judgement which can be based on either experience or observational learning.
How can we form Attitudes
Social activity, media like magazines, tv
Implicit attitude
An involuntary evaluation that occurs without consciousness, we may not know we hold them yet it will still be influential. Our behaviours can reveal them
Explicit attitude
Voluntary and conscious evaluation of an idea, object, person or place. A response based on conscious judgement and can be measured directly by self report.
What does the Tri-Partite Model of Attitude propose?
There are three elements that contribute to attitude formation and provides a framework to unpack an attitude
Three components of Tri-partite model
Affective: feelings or emotions towards an object or person
Behavioural: actions towards various people, objects or institution
Cognitive: the belief about an object or person
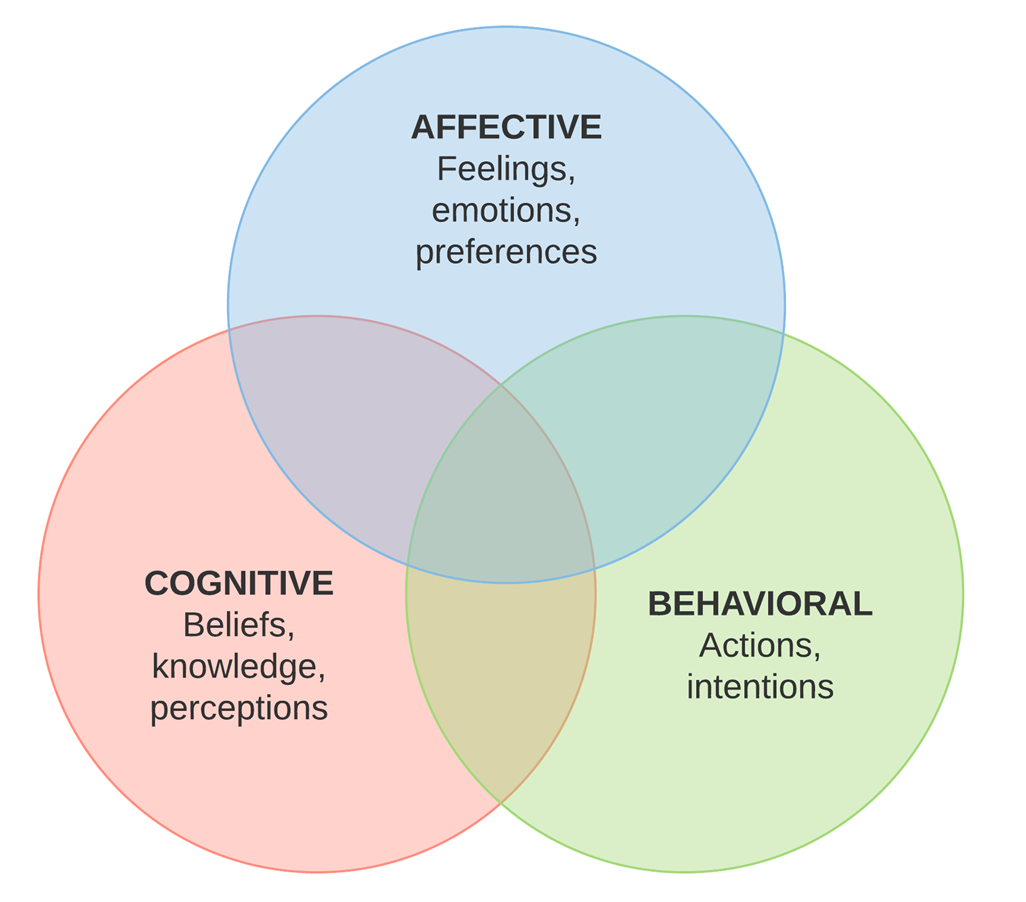
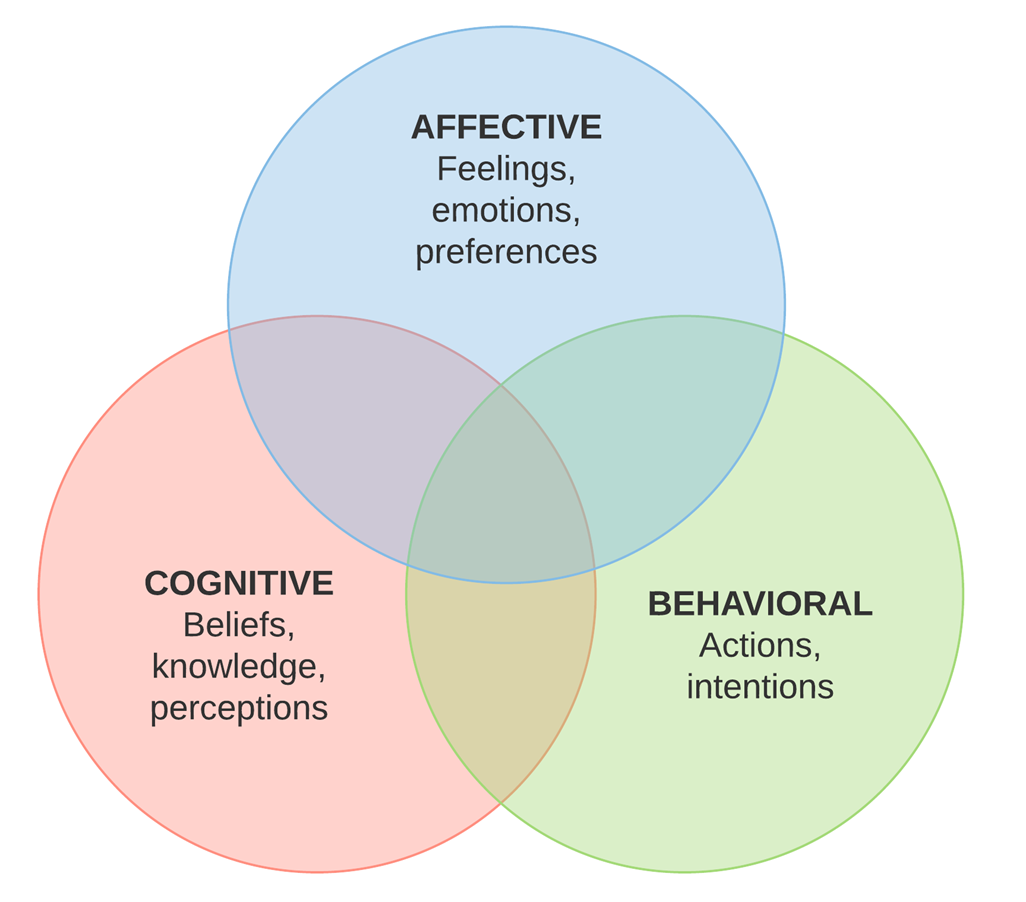
Limitations of tripartite model
Does not indicate strength of an attitude, only direction
Strong attitudes are resistant to change, dont change over time and have a big impact on behaviour
Accessibility of attitude, how often and quickly it comes to mind
Inconsistencies can occur between what a person thinks and feels and their behaviour
Doesnt include ambivalent attitudes
Cognitive dissonance
Social comparison
We take on board other peoples attitudes , attitudes can be changed or challenged, no social interaction-if youre apart of it because you share similar attitudes
How can we view attitudes
Indirectly, observational learning, collective attitudes, communicating
Social learning of attitudes
Direct experience and observation other → attitude → behaviour as evidence of thoughts and feelings
What factors influence whether you adopt someone else’s attitude or ignore it?
Your intelligence and self-esteem influence whether you adopt or ignore someone else’s attitude.
How does intelligence and self-esteem affect how likely someone is to be persuaded by a one-sided message?
Intelligent people, whether they have high or low self-esteem, are less likely to change their attitude based on a one-sided message than less intelligent people with moderate self-esteem.
Attitudes can be dangerous..
If they are negative and will lead to prejudice, stereotypes and discrimination
Why study attitudes?
Every choice made is affected by attitudes, allow the prediction of human behaviour for a given situation, information abt attitudes needs to assessed in line with persoanlity and other psychological characteristics
What is behaviour affected by
Cognitions and affect
What are cognitions and affect affected by?
Attitudes
Most influential?
affect and cognition
Strong attitudes….
predict better than weak attitudes, cause by personal expereince
How aware are we of attitudes?
We are influenced more by attitudes we can express and those that come to mind quickly
Culture
Shared rules can define behaviour, defines identity, learned attitudes, beliefs, values and traditions
Attitudes and values can change
They are learned and respond to influences
Conformity, self-interest or lack of strength of our own culture?
We learn to accept different ways of doing business or meeting people, as to ignore the values and attitudes of other cultures could be considered rude
What is a stereotype?
An oversimplified belief about an outgroup pertaining to either positive or negative thoughts about its members
How can children learn stereotypes?
Children as young as five can develop racial stereotypes by picking up cues from parents, friends, teachers, group labels, derogatory jokes, or other behaviour, even if they are not explicitly taught.
How can stereotypes form when we first meet someone?
Our initial impressions of a person from an identifiable group can form the basis of a stereotype.
What role does the media play in stereotypes?
The media can form or strengthen stereotypes by repeatedly presenting certain ideas or images about groups of people.
Can a person’s behaviour activate existing stereotypes?
Yes, the behaviour of an individual can trigger or activate stereotypes we already hold.
Are stereotypes always negative?
No, stereotypes can be positive or negative, but they are generally disliked because they prevent people from being seen as individuals