chem 1a midterm 2
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
AX2E0
linear, 180
AX3E0
trigonal planar, 120
AX2E1
bent, <120
AX4E0
tetrahedral, 109.5
AX3E1
trigonal pyramidal, 109.5
AX2E2
bent, 109.5
AX5E0
trigonal bipyramidal, 90, 120
AX4E1
seesaw, 90, 120
AX3E2
T-shaped, 90
AX2E3
Linear, 180
AX6E0
octahedral, 90
AX5E1
square pyramidal, 90
AX4E2
square planar, 90
AX3E3
T-shaped, 90, 180
AX2E4
linear, 180
2 in electronic geometry
linear
3 in electronic geometry
trigonal planar
4 in electronic geometry
tetrahedral
5 in electronic geometry
trigonal bipyramidal
Pressure
Force/area
760 torr
1 atm
As volume increases
pressure decreases.
as temp increases
volume increases.
as moles increase
volume increases.
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT
Ideal Gas Conditions
Gas will be most ideal at low pressures and high temperatures.
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures
Ptotal = P1 + P2 + P3 +…
Mole Fraction
X1 mole fraction = n1/ntotal = P1/Ptotal
Kinetic molecular theory
1) Gas molecules are small compared to space between them 2) Particles are in constant motion 3) Neither attract nor repel each other 4) Average kinetic energy: KEavg directly proportional to temp
Average kinetic energy formula
KEavg = 3/2 RT
Root mean squared velocity
√(3RT/M)
Average velocity formula
Mavg = √(8RT/M)
Boltzmann's constant
R/NA
Diffusion
Mixing of gases
Effusion
Gas passes through pinhole
Collision rate
Collisions per second = ZA
Real gases assumptions
1) Gas molecules have no volume 2) Gas molecules are not attracted to each other
Van der Waals equation
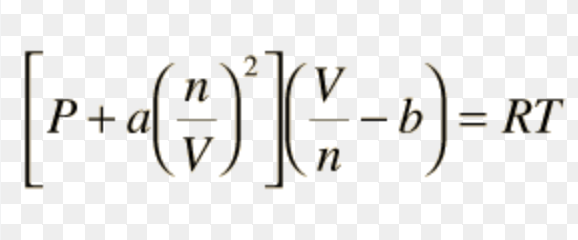
Spectroscopy
Analysis of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by substance
Frequency
Cycles/sec in 1/s or Hertz (Hz)
Wavelength and frequency relationship
Wavelength * frequency = c (speed of light)
Wavelength order
Red wavelength > green > blue
Energy formula
Energy = (h * c)/frequency
Planck's constant (h)
h = 6.626 x 10^-34 J*S
Photoelectric effect
Phenomenon where light can eject electrons from metals.
Kinetic energy of electron (KEe-)
KEe- = Ephoton - Binding
Kinetic energy formula
½ mev^2 = hfrequency - hfrequency0
De Broglie equation
Wavelength = h/mv
X-ray diffraction
Technique used to measure crystal layer spacings.
Constructive interference
Waves add together for increased intensity.
Destructive interference
Trough of one wave meets the peak of another, canceling out.
Emission spectrum
The spectrum of light emitted by a substance.
Bohr Model
Model of the atom with fixed energy levels.
Principal quantum number (n)
Indicates the energy level of an electron.
Ionization energy
Energy required to remove an electron.
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
Cannot simultaneously define position and momentum of an electron.
Orbital energy level order
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s
Electronegativity
Ability of an atom to attract electrons.
Ionic radius
Size of an ion compared to its neutral atom.
Lewis structures
Diagrams showing valence electrons in a molecule or ion.