Substitution and Elimination
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What makes a good leaving group?
A positive charge or a conjugate base of an acid with pka<0
Typical leaving groups
Br-, Cl-, I-, RSO3-
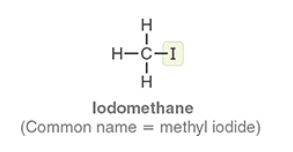
Iodomethane
Common name methyl iodine
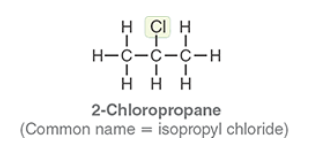
2-Choloropropane
Common name isopropyl chloride
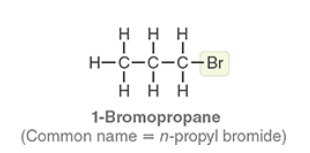
1-Bromopropane
Common name n-propyl bromide
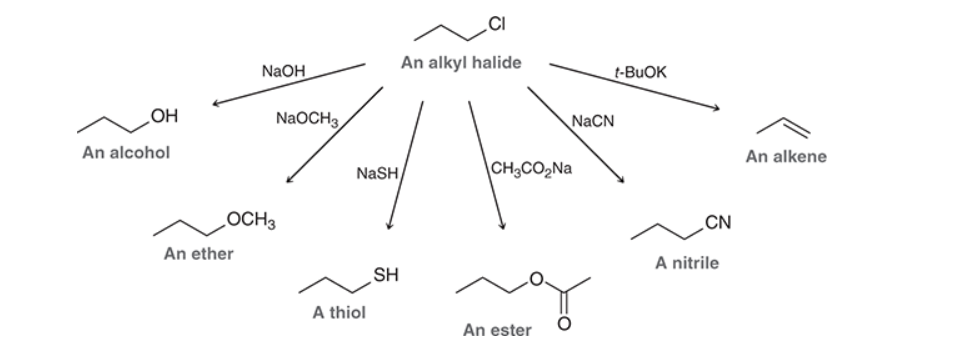
Alkyl halide can be converted to
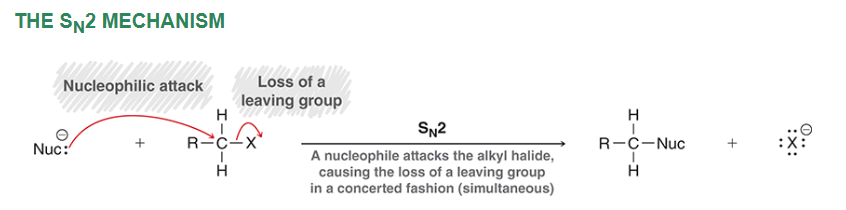
SN2 mechanism
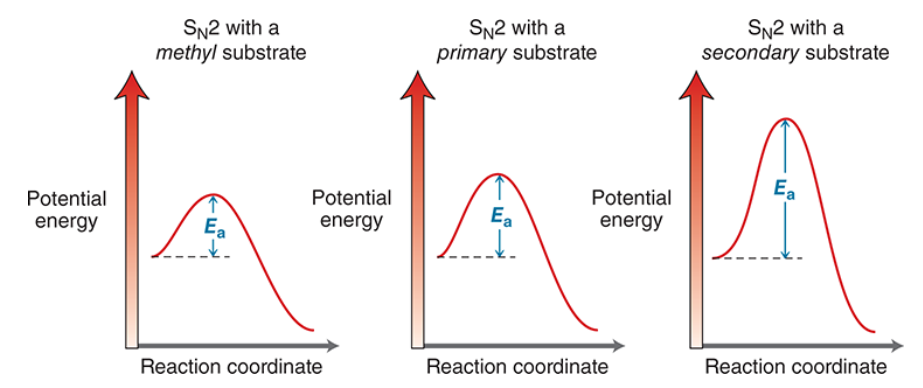
Rate of SN2
Rate decreases as more R groups are added to the alpha carbon
methyl>1*>2*>3*(basically unreactive)
SN2 energy diagram
SN2 nucleophile strength
Needs a fast nucleophile, reaction will not proceed with a slow one
Strong nucleophiles
I- , Br-, Cl-, HS-, RS-, HO-, RO-, N=C-
Weak nucleophiles
H2O, ROH
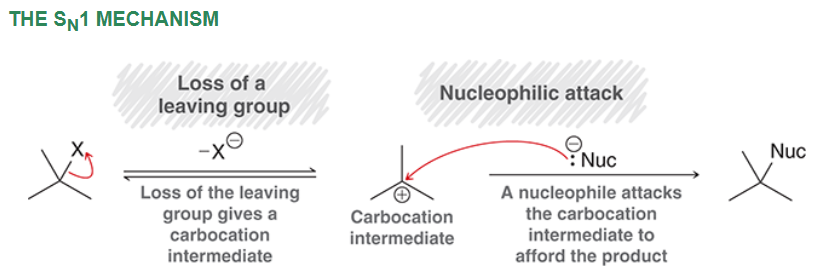
SN1 Mechanism
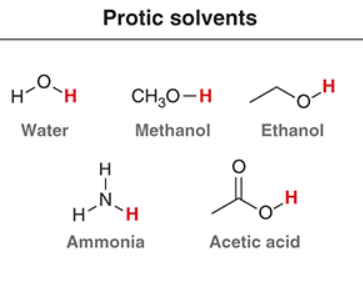
Protic solvents
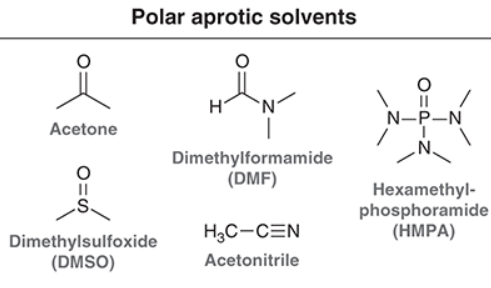
Aprotic solvents
Preferred SN2 solvent
Polar aprotic because they do not bond with the nucleophile and instead raise the energy of the nucleophile, increasing the reaction rate due to smaller Ea
Preferred SN1 solvent
Polar protic because they stabilize the intermediate
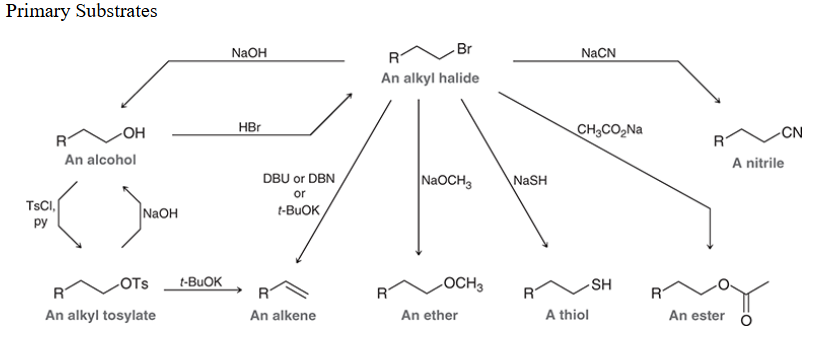
Reactions with primary substrate
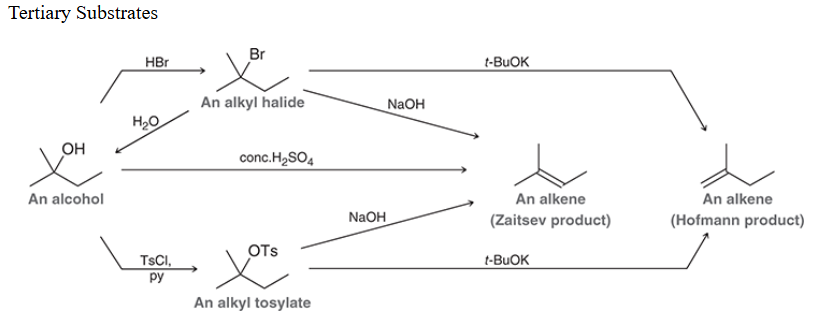
Reactions with tertiary substrate
E2 mechanism
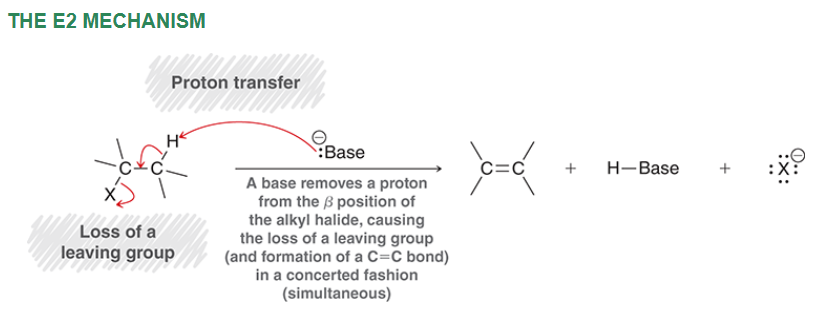
Can E2 proceed with a tertiary substrate?
Yes because it is abstracting a H from a beta carbon, which is not affected as much by steric hindrance
What makes an alkene stable?
Trans will be more stable than cis. Cis has more steric strain, and is less favorable
More substituted means more stable since alkyl groups can also stabilize the neighboring sp2-hybridized carbon atoms of a π bond because of electron cloud delocalization through hyperconjugation
Trans bond in cycloalkenes
Cycloalkenes comprised of fewer than seven carbon atoms cannot accommodate a trans π bond. These rings can only accommodate a π bond in a cis configuration
Bridged bicyclic compounds
A bridgehead carbon cannot have a double bond if the trans bond is being incorporated into a small ring, it is only possible if the bottom ring has at least eight carbons
Regioselectivity of E2
Pi bond will form connecting to all beta positions, but there will be major and minor products, generally the more substituted alkene will be the major product
Zaitsev
More substituted alkene in an E reaction. Major product when a strong, non-bulky base is used.
Hofmann
Less substituted alkene in an E reaction. Major product when a strong, bulky base is used
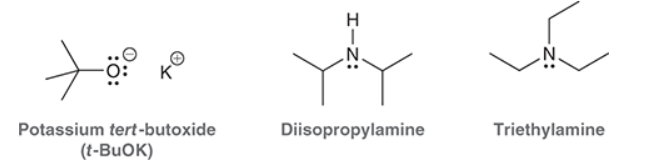
Common sterically hindered bases