Unit 1 Psych
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
The Brain

Medulla (brain stem)
regulates rhythm, blood flow, breathing rate, digestion, and vomitting
Pons (brain stem)
involved in regulating sleep and arousal
generate bursts of action potentials to the forebrain — activiation
Cerebellum
controls movement, posture, and equilibrium
Basal ganglia
regulates initiation of movements, balance, eye movements, and posture, and functions in processing of implicit memories.
Thalamus
relays visual,auditory, taste, and somatosensory info to/from appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus ( also a part of the endocrine system
controls multiple behaviors, activation of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, and secretion of hormones of the pituitary.It is involved in regulating homeostasis, including temperature, hunger, thirst, and circadian rhythms.
reticular formation
a network of neurons in the brainstem that regulates sleep, wakefulness, and alertness, playing a crucial role in arousal and attention.
pituitary gland
a small gland located at the base of the brain that produces and releases hormones regulating various body functions, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
amygdala
a key brain structure involved in processing emotions, particularly fear and pleasure: fight or flight reaction
corpus callosum
a thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain, facilitating communication between them.
Hippocampus
enables formation of long-term memories
Cerebral Cortex
center for higher-order processes such as thinking, planning, judgment; receives and processes sensory info and directs movement
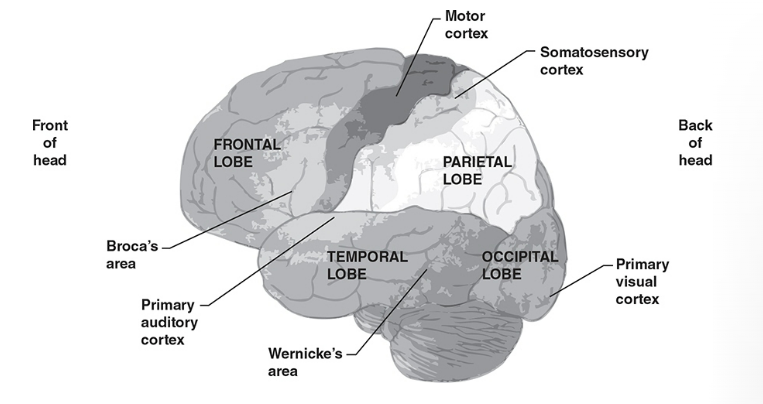
Frontal Lobe
region of the cerebral cortex associated with reasoning, problem-solving, and planning; involved in controlling voluntary movements.
Motor Cortex
area of the cerebral cortex involved in planning, controlling, and executing voluntary movements.
somatosensory cortex
region of the cerebral cortex responsible for processing sensory information from the body, including touch, temperature, and pain.
parietal lobe
region of the cerebral cortex that processes sensory information such as touch and spatial awareness, and integrates information related to body orientation.
occipital lobe
the region of the cerebral cortex responsible for processing visual information.
temporal lobe
plays a crucial role in processing auditory information, language comprehension, memory formation, and visual recognition.
Broca’s Area
Left Frontal Lobe — ability to speak — deterioration causes expressive aphasia
Wernicke’s area
Left Temporal Lobe — ability to comprehend language
Lesions
precise destruction of brain tissue
plasiticity
the brain’s ability to reorganize and take over a function if a certain region is damaged

Nervous System
—
Central Nervous System
brain + spine
Peripheral Nervous System
midline portion of nervous system — carries sensory information to and motor information away from your CNS via spinal and cranial nerves
divides into the somatic and autonomic parts
Somatic Nervous System
motor neurons that stimulate skeletal (voluntary) muscle
Autonomic Nervous System
motor neurons that stimulate smooth (involuntary) and heart muscle
divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems
Sympathetic Nervous System/ Responses
stimulates your body in response to stress to help deal with it — dilation of pupils, secretion of adrenaline, acceleration of breathing rate.
Parasympathetic Nervous System/ Responses
calms your body following sympathetic stimulation — restores digestive processes (salivation, peristalsis, enzyme secretion), returning pupils to normal pupil size, stimulating tear glands, and restoring normal bladder contractions.
The Neuron
—
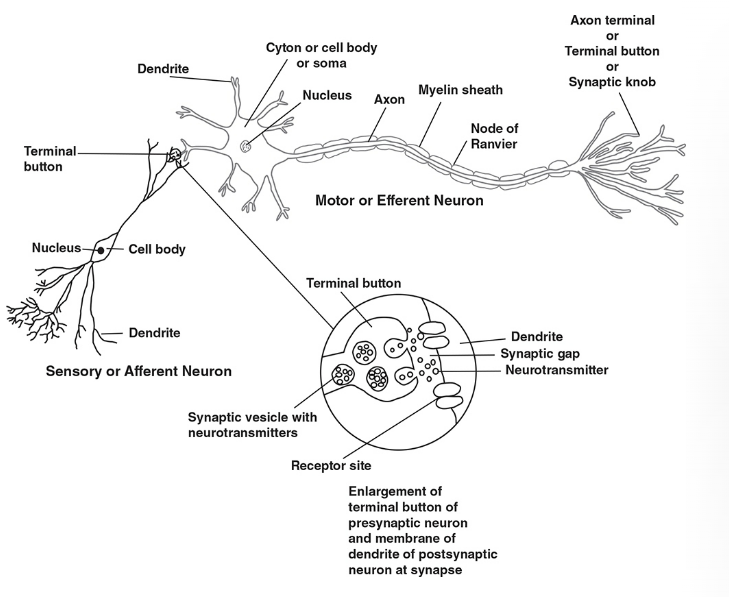
dendrites
branching tubular processes capable of receiving information
axon
a single conducting fiber(longer than a dendrite) that branches and ends at the axon terminals
myelin sheath
a fatty, protective coating that insulates the axons of neurons
Neurogenesis
growth of new neurons
action potential
after reaching the threshold, the rapid change in potential across the membrane
all-or-one principle
a neuron will only fire if it receives the full action potential and reaches the threshold, if not it won’t
glial cells
guide the growth of developing neurons, help provide nutrition for and get rid of wastes of neurons, and form an insulating sheath around neurons that speeds conduction.
sensory (afferent) neurons
transmits impulses from your sensory receptors to the spinal cord or brain
interneurons
located w/in brain and spinal cord — help with sensory + motor neurons
motor (efferent) neurons
transmit impulses from sensory/interneurons to muscles cells
Neurotransmitters
chemicals stored in structures of the terminal buttons called synaptic vesicles
Dopamine
reward- stimulates hypothalamus to synthesize hormones — affects alertness and movement
Glutamate
the ultimate excitatory neurotransmitter — info processing and memory formation
Serotonin
mood regulator — sexual activity, concentration, attention, moods, and emotions
Gaba
major inhibitory neurotransmitter
Norepinephrine
noradrenaline or adrenaline — attentiveness, sleeping, dreaming, and learning
Agonists
mimic neurotransmitters and bind to its receptor sites to produce the effect of said neurotransmitter
antagonists
block a receptor sites, inhibiting the effect of the neurotransmitter or agonist
endocrine system
system that consists of glands secreting hormones into the blood
Pineal Gland
produces melatonin and regulates circadian rhythms and is associated with S.A.D
Pituitary Gland
produces stimulating hormones promoting secretion by other glands
Thyroid Gland
gland in beck that produces thyrozine — stimulates and maintains metabolic activities
Parathyroids
endocrine glands in neck that produce parathyroid hormone, which helps maintain calcium ion level in blood necessary for normal functioning of neurons.
Adrenal glands
above lungs — produces cortisol and adrenaline
pancreas
secretes insulin and glucagon, regulating blood sugar, fueling all behavioral processes
ovaries and testes
gonads in females and males, respectively, that produce hormones necessary for reproduction and development of secondary sex characteristics.
Behavioral Geneticists
study the role played by our genes and our environment in mental ability, emotional stability, temperament, personality, interests, and so forth; they look at the causes of our individual differences.
identical twins
two individuals who share all of the same genes/heredity because they develop from the same fertilized egg or zygote; they are monozygotic twins.
Fraternal Twins
siblings that share about half of the same genes because they develop from two different fertilized eggs or zygotes; they are dizygotic twins.
Heritability
the proportion of variation among individuals in a population that is due to genetic causes
Levels of Consciousness
Preconscious — the level of consciousness that is outside of awareness but contains feelings and memories that you can easily bring into conscious awareness
nonconscious —level of consciousness devoted to processes completely inaccessible to conscious awareness, such as blood flow, filtering of blood by kidneys, secretion of hormones etc
unconscious — the level of consciousness that includes often unacceptable feelings, wishes, and thoughts not directly available to conscious awareness.
dual processing— processing information on conscious and unconscious levels at the same time.
unconsciousness — haracterized by loss of responsiveness to the environment, resulting from disease, trauma, or anesthesia.
Sleep and Dreams
Computerized axial tomography (CAT or CT)
Structure — a computerized image using X-rays passed through various angles of the brain showing two-dimensional “slices” that can be arranged to show the extent of a lesion.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Structure — a magnetic field and pulses of radio waves cause the emission of faint radio frequency signals that depend on the density of the tissue
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
an amplified tracing of brain activity produced when electrodes positioned over the scalp transmit signals about the brain’s electrical activity (“brain waves”) to an electroencephalograph machine.
Positron Emission Tomography ( PET)
produces color computer graphics that depend on the amount of metabolic activity in the imaged brain region.
Functional MRI (fMRI)
hows the brain at work at higher resolution than the PET scanner.
Changes in oxygen in the blood of an active brain area alters its magnetic qualities, which is recorded by the fMRI scanner.
Sleep
complex combination of states of consciousness, each with its own level of consciousness, awareness, responsiveness, and physiological arousal.
Circadian Rhythm
natural,internal process that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours — your body’s internal clock— influenced by light and darkness and influences when you sleep and wake up
sleep spindles
high frequency bursts of brain activity occuring during NREM-2
EEGs in sleep
theta waves = high amp low freq. — meditation , daydreaming, deep relaxation
alpha waves = high frew low amp — relaxed wakefulness
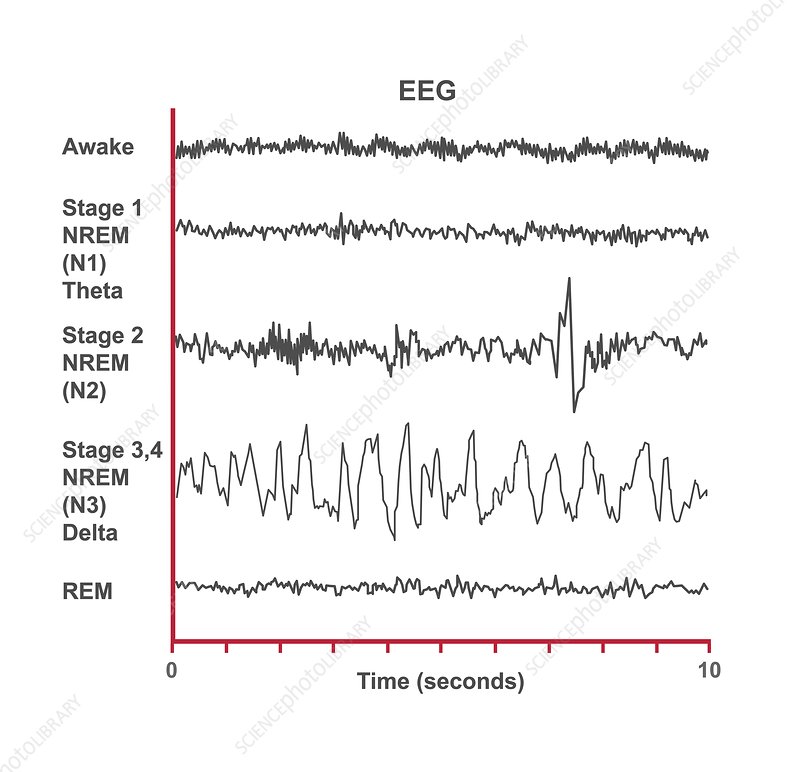
Stages of sleep
—
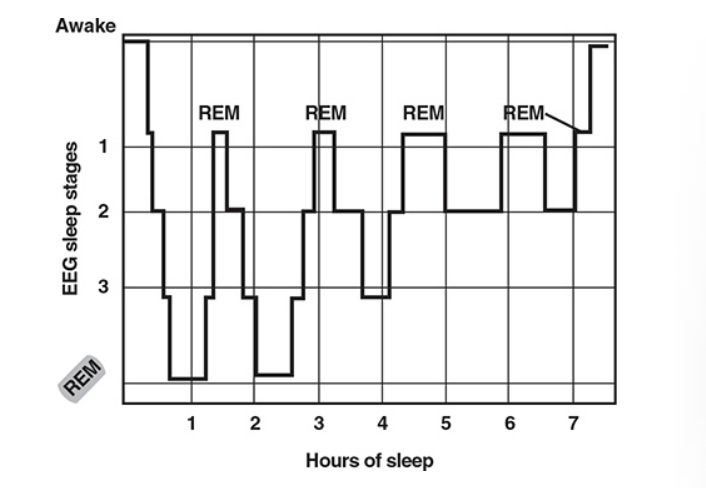
NREM- 1
theta waves
hypnagogic state — relaxed and fail to respond to outside stimuli
NREM-2
sleep spindles occur here and k complexes
NREM-3
delta waves
REM sleep
Rapid Eye Movement sleep — happens 90 min after falling asleep
nightmares occur during this stage
manifest content
the remembered story line of a dream
latent content
the underlying meaning of a dream
activation-synthesis theory
dreams are result of the brain’s attempts to make sense of random neural a
sleep disorders
—
insomnia
the inability to fall asleep and/or stay asleep
nacolepsy
condition in which an awake person suddenly and uncontrollably falls asleep, often directly into REM sleep
sleep apnea
temporary cessations of breathing that awaken the sufferer repeatedly throughout the night
night terrors
most likely childhood sleep disruptions during the deepest stage (NREM-3)— characterized by trips out of bed or carrying on complex activities
sleepwalking
characterized by trips out of bed or carrying on complex activivies
dissociation theory
hypnotized individuals experience two or more streams of consciousness cut off from each other
Psychoactive drugs
chemicals that can pass through the blood-brain barrier into the brain to alter perception, thinking, behavior, and mood, producing a wide range of effects from mild relaxation or increased alertness to vivid hallucinations.
psychological dependence
develops when a person has an intense desire to achieve a drugged state despite adverse effects
tolerance
decreasing responsibility to a drug
physiological dependence/addiction
changes in brain chemistry from taking the drug necessitate taking the drug again to prevent withdrawal symptoms
depressants
psychoactive drugs that reduce the activity of the CNS and induce relaxation
includes sedatives like barbiturates, tranquilizers, and alcohol
narcotics
pain reducers that work by depressing the CNS
can also depress the respiratory system
stimulants
psychoactive drugs that activate motivational centers and reduce activity in inhibitory centers of the central nervous system by increasing activity of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine neurotransmitter systems.
hallucinogens
also called psychedelics, are a diverse group of psychoactive drugs that alter moods, distort perceptions, and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input.
Substance P
a neuropeptide involved in various physiological processes, including pain transmission, inflammation, and immune regulation
Actecholine
endorphins
body’s natural painkiller & mood boosters
leptin
regulation of appetite and fat storage
ghrelin
stimulates hunger
melatonin
causes sleepiness