The Ensemble Hypothesis - Exam 2
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Emotion
Reflects a motion outward
It is…
inferred, reaction, functional
Purpose…
survival (approach: nourishment and reproduction) (withdrawal: danger/threats)
adaptive (induces motivation)(lowers sensory threshold)
Emotion Brain Regions
Limbic System…
Amygdala, anterior cingulate cortex, anterior insula, autonomic nervous system
Oscillations for Emotions
Delta waves (0.5-4) are elevated in depression
Theta (4-8) are linked to anxiety and regulation
Beta (13-30) are seen in stress and rumination
Rhythmic breathing entrains oscillations in the amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex
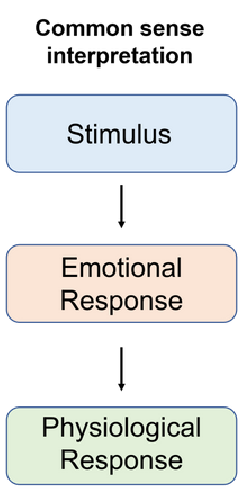
Common Sense Theory
Stimulus → emotional response → physiological response
person sees something scary (lion), then they exhibit the emotional response, then the physiological response
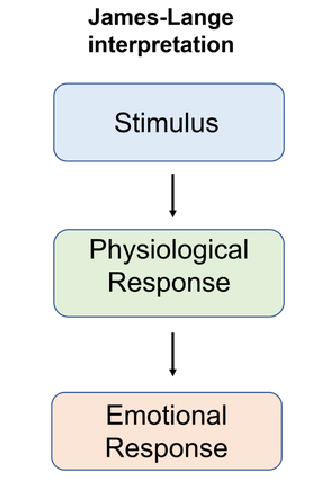
James-Lange Interpretation
Stimulus → physiological response → emotional response
see something arousing (lion), exhibits physiological response, which then creates the emotional response
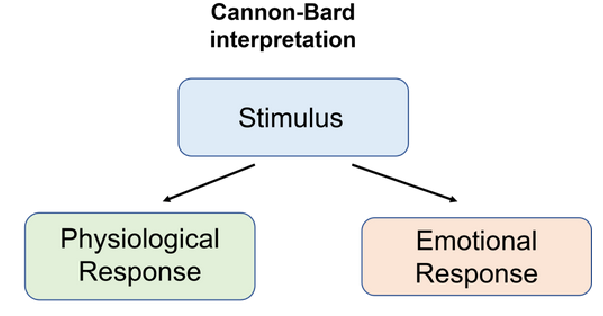
Cannon-Bard Interpretation
Stimulus → Physiological response + emotional response
see something arousing (lion), exhibits the physiological and emotional response simultaneously
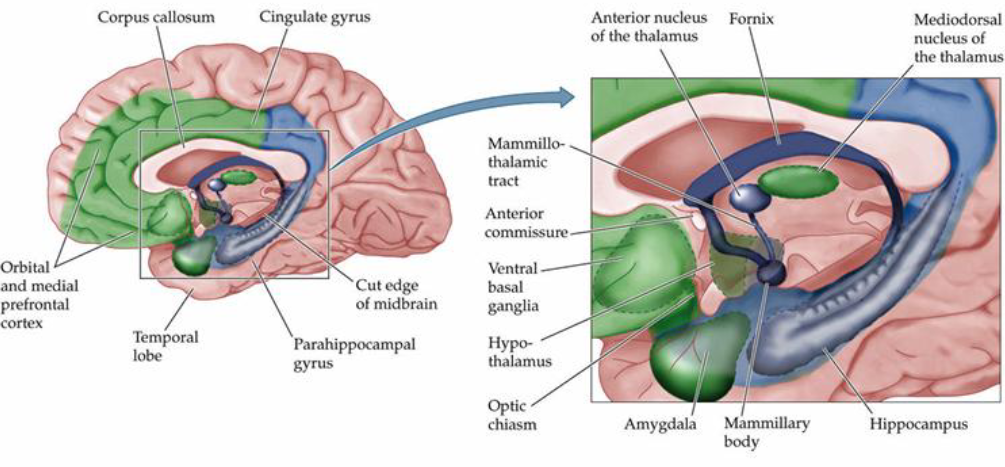
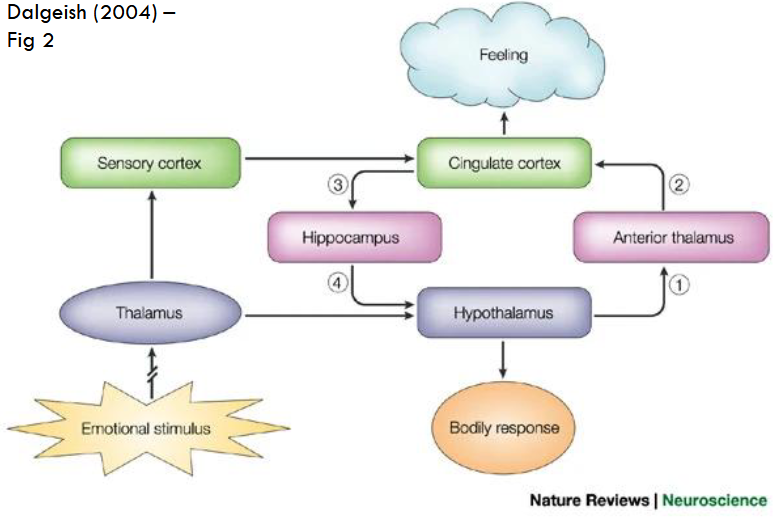
Papez Circuit Theory
Sites the neuroanatomy structures in an emotional response
early neuroanatomical model linking limbic system structures to emotional experiences
Schachter-Singer Theory
Emotion = physiological response + context
emotion is the result of both physiological arousal and cognitive labeling (context) of that arousal
see a snake, label that arousal mentally (i am afraid) and then results the emotion and behavior
Measuring Emotion
Physiological measures…
EEG, FMRI, PET scan
Body Measures
EMG (facial muscles), Heart rate, skin conductance (sweat), stomach activity, hormones
In Skin Conductance & EMG studies: emotional pictures can elicit measurable physiological responses
Reward and Addiction
Reward System…
dopamine in nucleus accumbens drives reinforcement
Addiction: drugs hijack reward pathways; rats self-stimulate dopamine release
Cognitive Appraisal
Interpretation of arousal affect emotional experiences
the difference between sex, combat, and a 200-meter sprint in our minds
Re-appraisal
involves interpreter and executive working memory
facilitates re-framing an emotional experiences
Cultural Evolution of Emotion
Emotions are shaped by both biology and culture
Dual Inheritance Model…
Biology: affective building blocks (arousal, valence)
Culture: labels, norms, expressions (reinforced through language and context)
Emotional Regulation
Re-appraisal - viewing stimuli with detached, analytical mindset
shown to improve emotional stability and regulation
Suppression - inhibiting facial expressions and emotional display
Better working memory (executive) = better emotional regulation abilities