electricity
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
current
rate of the flow of charge
charge equation
Q=IT
how much charge passes in 1 second with an ampere of 1
1 coulomb
voltage equation with energy and charge
V = E/Q
when is the PD across a component 1V
when you do 1 joule of work moving 1 coulomb of charge through the component
Drift velocity
average velocity attained by charged particles in a material due to an electric field
equation to calculate current of a wire made out of a certain material
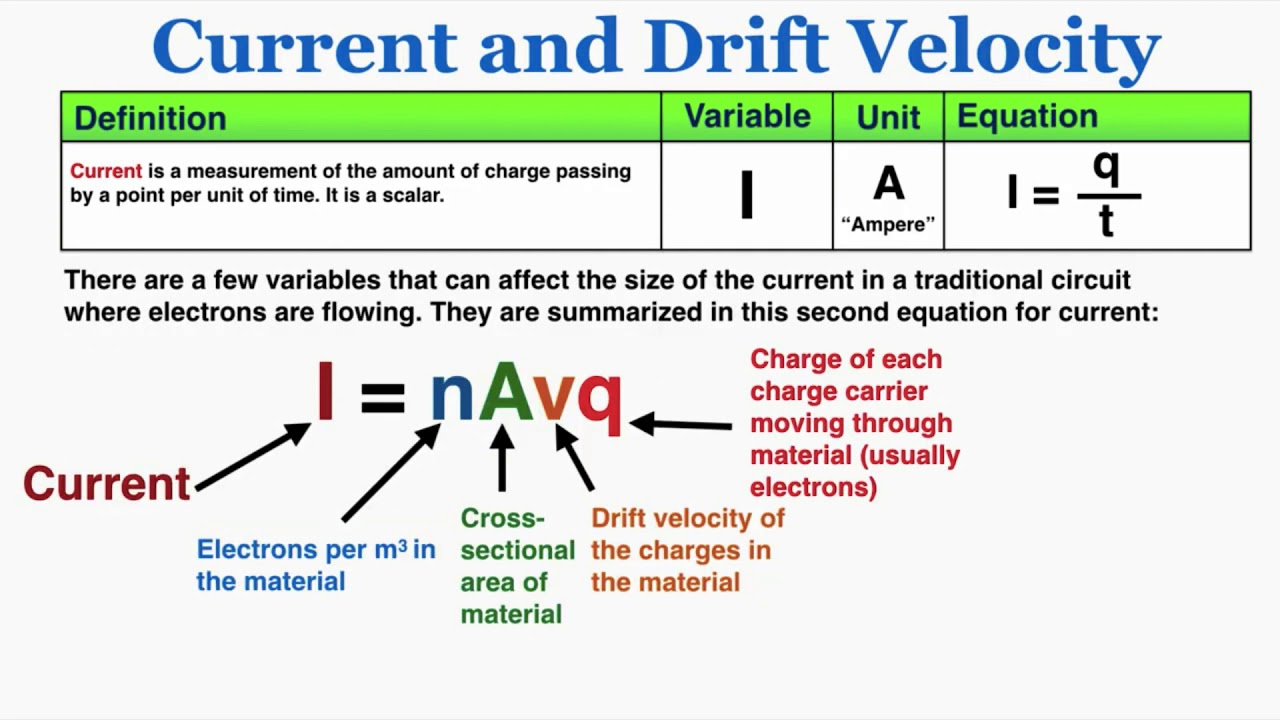
n in the equation for current
number of charge carriers(electrons) per m² of the material
m^-3
q in the equation
amount of charge on each charge carrier
coulombs
V in the equation
drift velocity
ms^-1
A in the equation
cross sectional area
m²
what happens if you double the area of the wire
the current doubles because doubling the area, doubles the amount of paths the charge carriers can flow through making the flow faster therefore
current is directly proportional to area
what happens if you double any one of the values in the equation
the current doubles
what does the resistance of a wire depend on
length of wire
R directly proportional to L
area of wire
R inversely proportional to A
type of material(resistivity of material)
a higher resistivity means it has a lower no of charge carriers
resistivity
a property that describes the extent to which a material opposes the flow of electric current through it
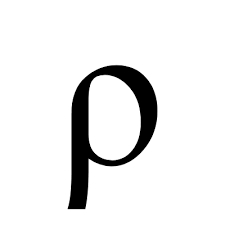
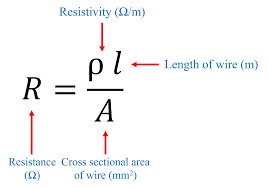
equation for resistivity
why does increasing temp, increase resisitivity
higher the temp of a material, more collisions with atoms due to kinetic energy which increases resistivity
what would a resistance over length graph look like
directly proportional
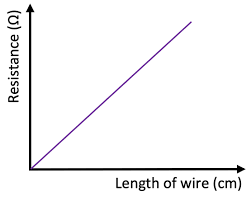
how to calculate resistivity using a resistance over length graph
gradient = R/L
resistivity = gradient x area
resolution
the smallest change in measurement that a insturment can detect
how to work out absolute uncertainty
AU = plus or minus resolution/2
how to work out percentage uncertainty
(AU/measured quantity) x 100
how to reduce percentage uncertainty
measure large quantities or use an instrument with a highr resolution(lower AU)
EMF
energy per charge supplied by the source
V
terminal voltage - energy per charge used in load resistance
v
lost volts - energy per charge wasted in internal resistance
equation for EMF
V + v
or
I(R + r)
internal resistance
the resistance of the power source which causes lost volts
how to measure EMF
voltmeter around the source - extremely high resistance therfore doesnt allow to current to flow so internal resistance doesnt kick in
practical to find EMF and internal resistance
use a voltmeter around source to find EMF
use a voltmeter to find terminal voltage
use ammeter to find current through the circuit
use equation to find internal resistance or plot a terminal voltage against current graph where the gradient is the internal resistance
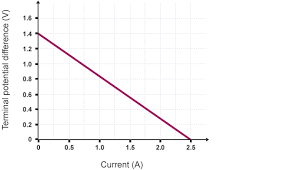
how to find EMF from a terminal voltage over current graph
the y-intercept because current equals 0 therefore no internal resistance
why does current stay the same through the whole circuit
if current is affected in one part of the circuit its affected throughout the whole circuit i.e more resistance means more voltage - I = V/R
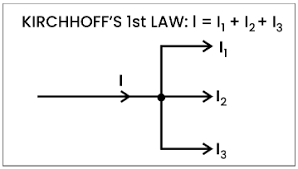
kirchhoff’s first law
conservation of current:
total current entering a junction = total current leaving it
kirchhoff’s second law
when no internal resistance:
the total EMF around a series circuit = the sum of the P.Ds across each component
conservation of energy
resistance in parallel circuits
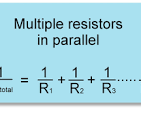
resistance in series

potential dividers
a simple circuit that divides a voltage into smaller, proportional voltages using resistors
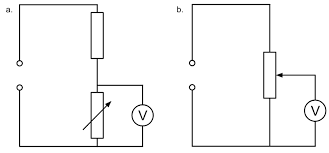
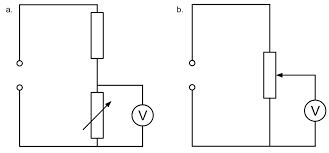
which one of these circuits is more suitable to obtain data?
both circuits are suitable because they allow readings of current and voltage
the min PD for the one on the right is 0V
the min PD for the one of the left is greater than 0V
the max PD for the one on the right is the supply PD
for the one on the left adjusting the resistor changes the circuit resistance - sharing voltage
the one on the left minimum PD depends on the variable resistor
the one on the right is better because it allows for a bigger range
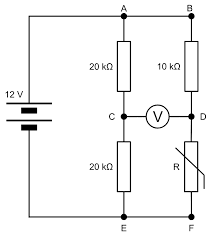
what value would V be
the difference between the voltages of the resistors