✨ Eye Witness Testimony✨
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Leading Questions, Ronald Cotton, Loftus and Palmer, Long Term Memory, Short Term Memory, Multistore Model of Memory
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Leading Questions
Questions that lead a person to think and respond in a specific manner, altering memory
Ronald Cotton
Previous offender falsely incarcerated when a victim wrongly chose him out of two lineups. This altered her recollection of the event to the point where she could not remember the actual offender, Bobby Poole.
Memory
The process of encoding, storing and retrieving information
Long Term Memory
The proccess of encoding, storing and retrieving information
Short Term Memory
Temporary information holding area, it can store 7±2
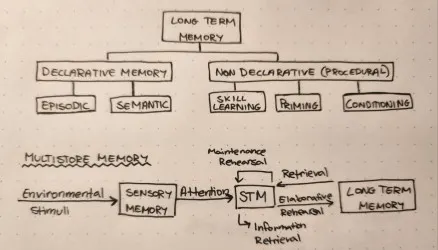
Multistore Model of Memory
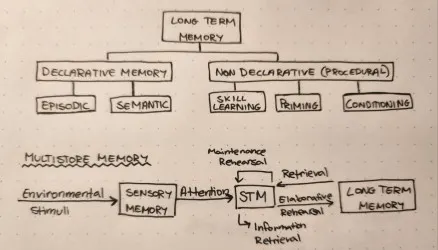
Long term memory structure
Loftus and Palmer aim
To deduce whether leading questions play a role in altering or impacting memory in any manner
Loftus and Palmer method 1
5 groups each with 9 participants
Loftus and Palmer results 1
Smashed - 41mph; collided - 39mph; bumped - 38mph; hit - 34; contacted - 32
Loftus and Palmer method 2
A week after, they were asked if they had seen glass. 3 groups of 50. 1/3 asked hit, 1/3 asked smashed, 1/3 control
Loftus and Palmer results 2
A larger number of those who were asked smashed answered yes than those asked hit or those in the control
Loftus and Palmer conclusion
Questioning techniques can distort memory; our recollection of events is incredibly malleable and unreliable
Declarative memory
A part of long term memory to do with facts
Episodic memory
Part of declarative memory to do with experiences in ones life
Semantic memory
Part of declarative memory to do with facts and general knowledge
Procedural memory
A part of long term memory to do with muscle memory
Priming
Part of procedural memory; a set of things leading a person to think in a certain way
Skill learning
Part of procedural memory; muscle memory
Conditioning
Part of procedural memory; similar to Pavlov’s dogs