Histo 12 | Respiratory System
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What is the main function of the respiratory system?
To supply oxygen to the blood and eliminate carbon dioxide.
How large is the surface area of the respiratory system?
Around 80 m².
What are the two main divisions of the respiratory system?
Conducting portion: Air passageways that move and condition air.
Respiratory portion: Where gas exchange occurs.
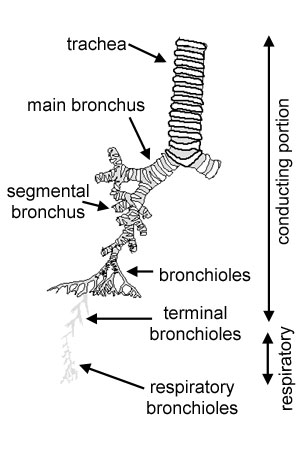
What is the main function of the conducting portion?
To admit a maximum volume of air through a narrow inlet while keeping passageways minimal.
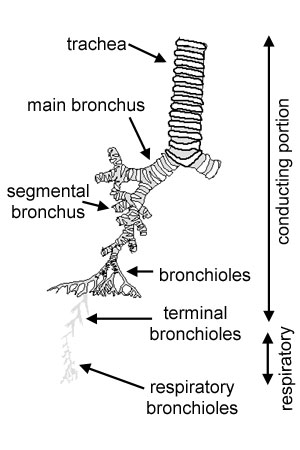
What are the minor functions of the conducting portion?
Filtering particulate material from the air.
Adjusting temperature and moisture content of incoming air.
Facilitating phonation (voice production).
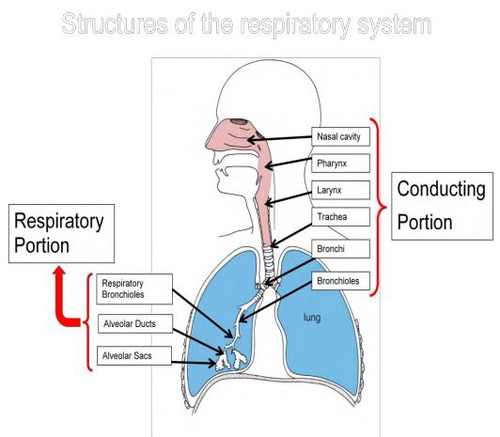
What structures make up the conducting portion?
Nasal cavities & paranasal sinuses
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Terminal bronchioles.
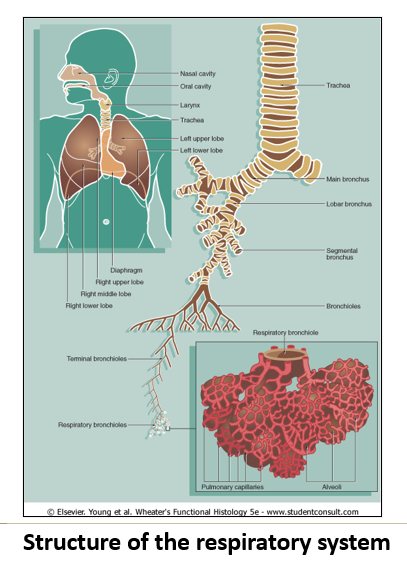
What is the general histological structure of the conducting portion?
Layered tubes with:
Conducting mucosa (epithelium + lamina propria).
Submucosa.
Muscularis mucosa (smooth muscle layer, not always present).
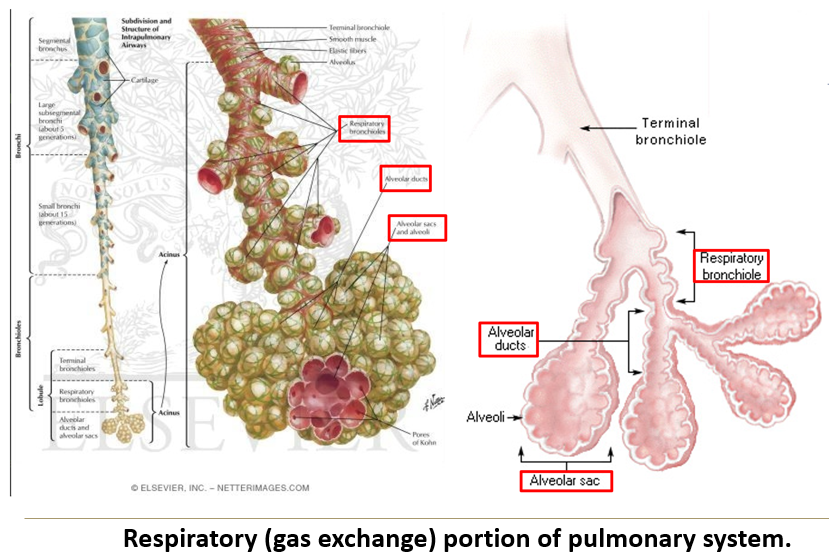
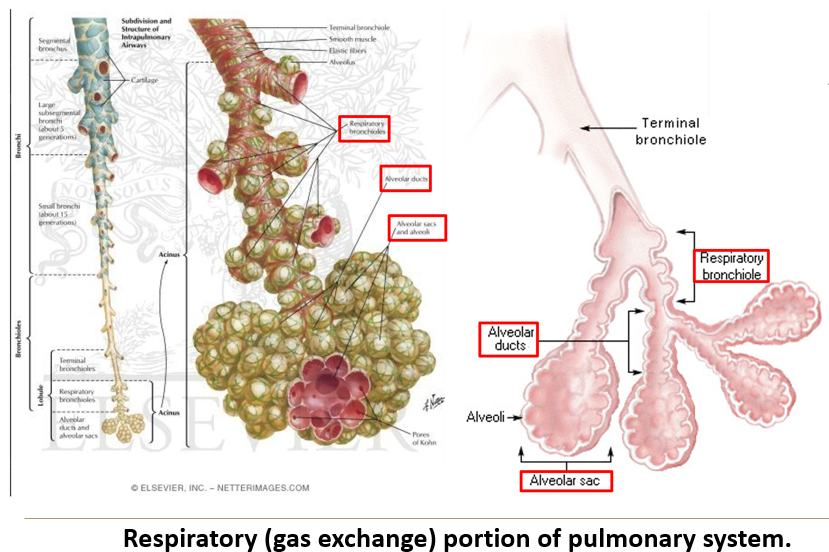
What are the components of the respiratory portion of the respiratory system?
Respiratory bronchioles → Alveolar ducts → Alveolar sacs → Alveoli.
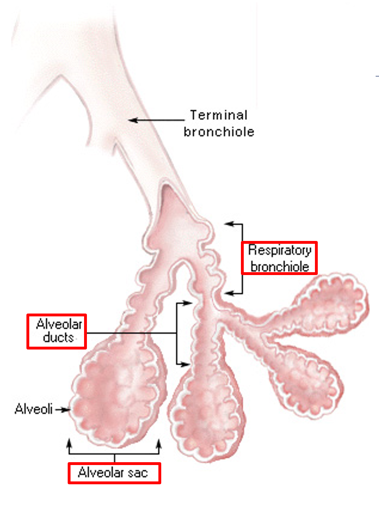
How many branching generations are needed to reach the alveoli?
Approximately 25 generations of branching.
What type of epithelium lines the nasal passages?
It begins as stratified squamous epithelium and transitions to pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells.
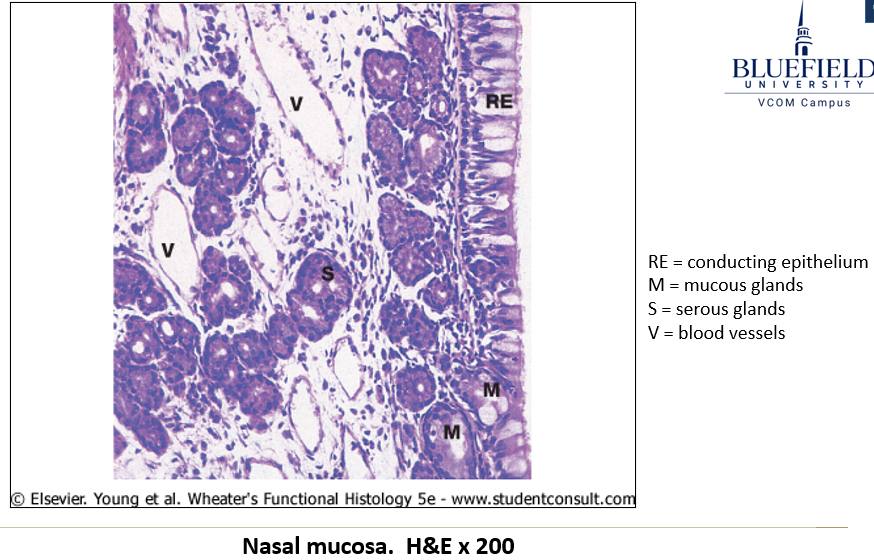
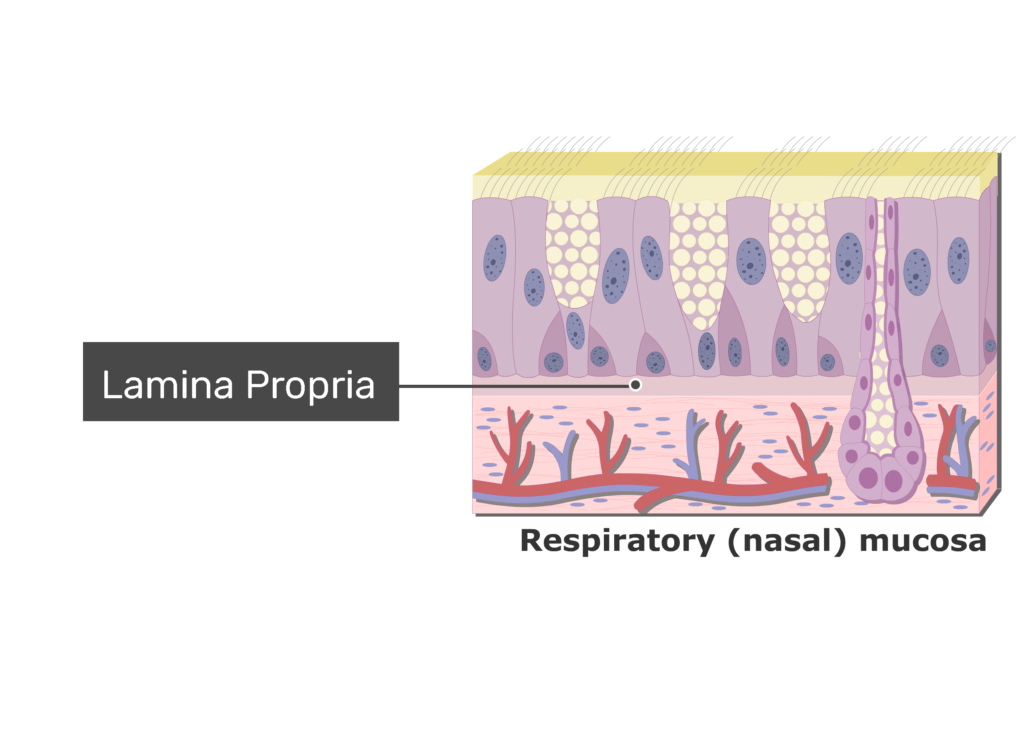
What is the function of the lamina propria in the nasal passages?
Contains serous and mucous glands.
Houses aggregates of lymphoid nodules.
Supports thin-walled blood vessels (cavernous or erectile tissue) that alternate engorgement to allow breathing through one side at a time.
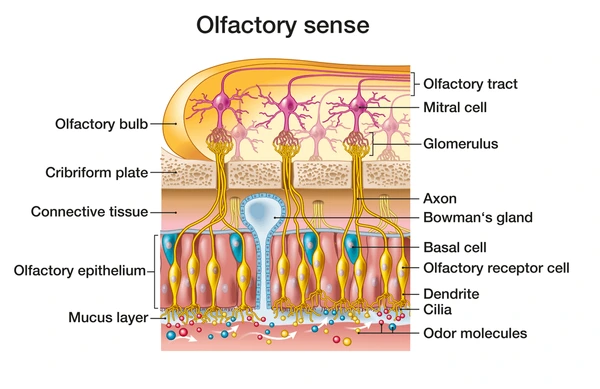
Where is the olfactory mucosa located?
In the roof of the nasal cavity.
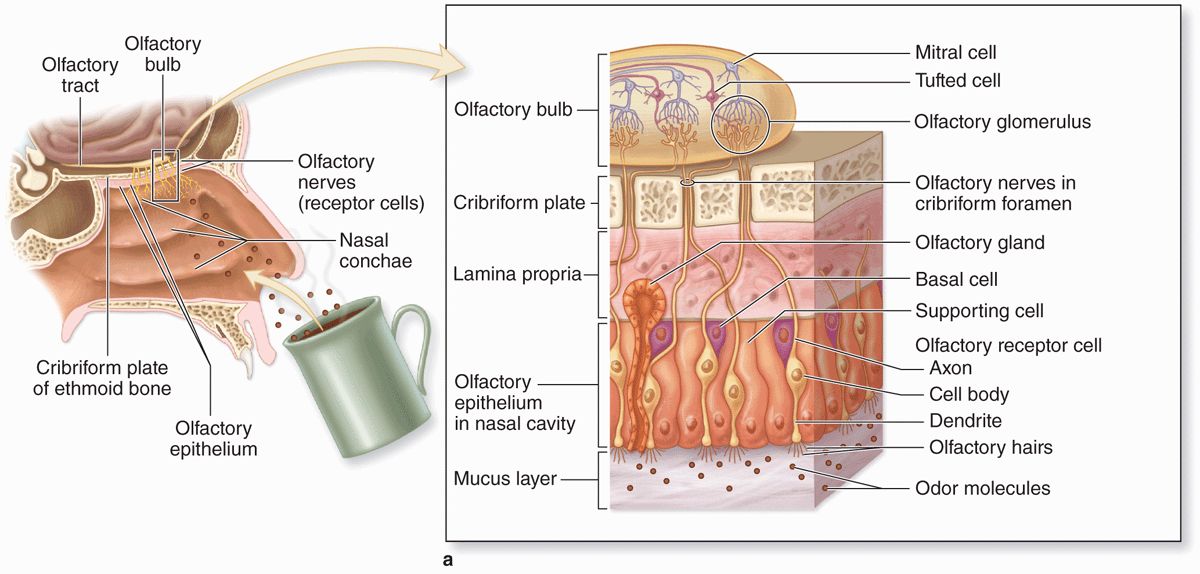
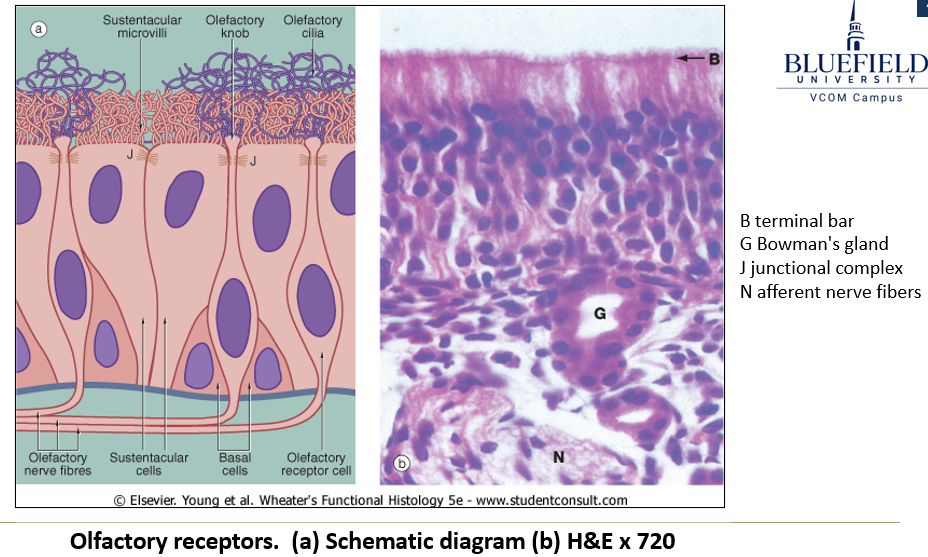
What are the three cell types of the olfactory mucosa?
Basal cells: Stem cells for olfactory neurons.
Olfactory receptor cells: Bipolar neurons that detect odor molecules.
Sustentacular cells: Tall ciliated columnar cells that support olfactory neurons. Provides “sustenance”.
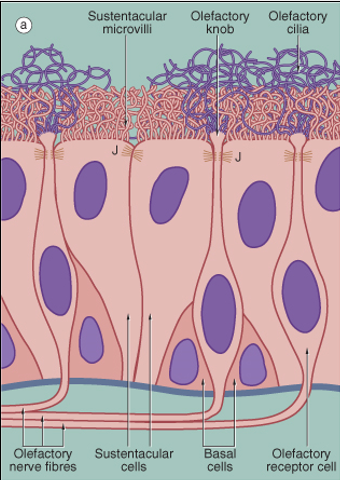
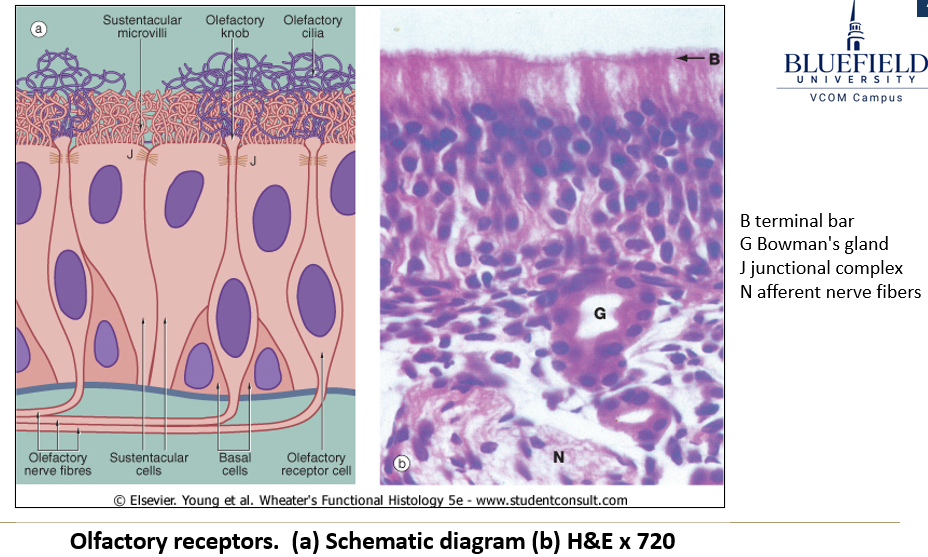
What is the function of Bowman’s glands in the olfactory mucosa?
They secrete serous fluid to dissolve odorous molecules.
What type of epithelium lines the larynx?
Mostly pseudostratified epithelium, but some areas (e.g., true vocal cords) may be stratified squamous epithelium.
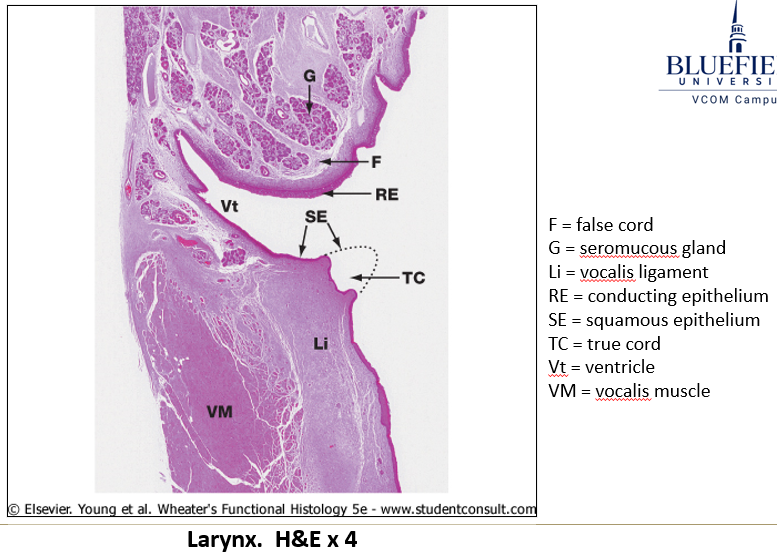
What is the composition of laryngeal cartilage?
It contains hyaline and elastic cartilage, which may calcify with age.
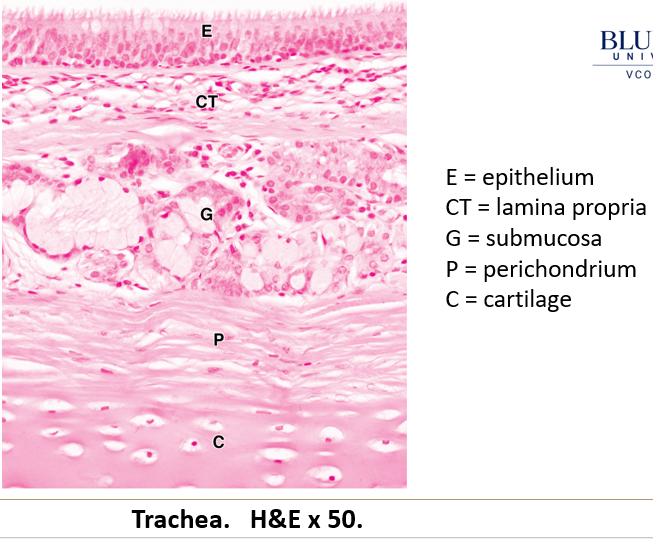
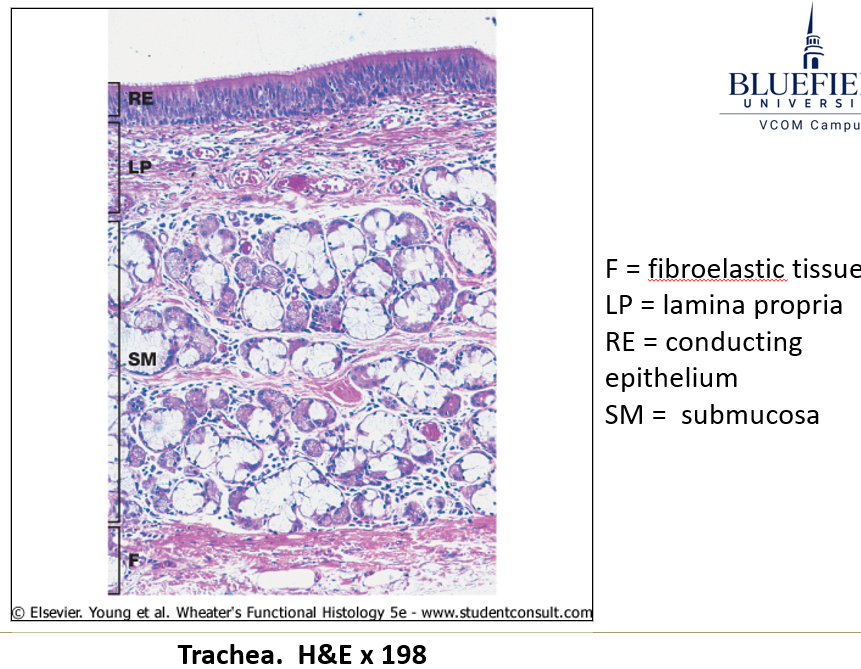
What type of epithelium lines the trachea and bronchi?
Pseudostratified epithelium containing:
Goblet cells – Secrete mucus.
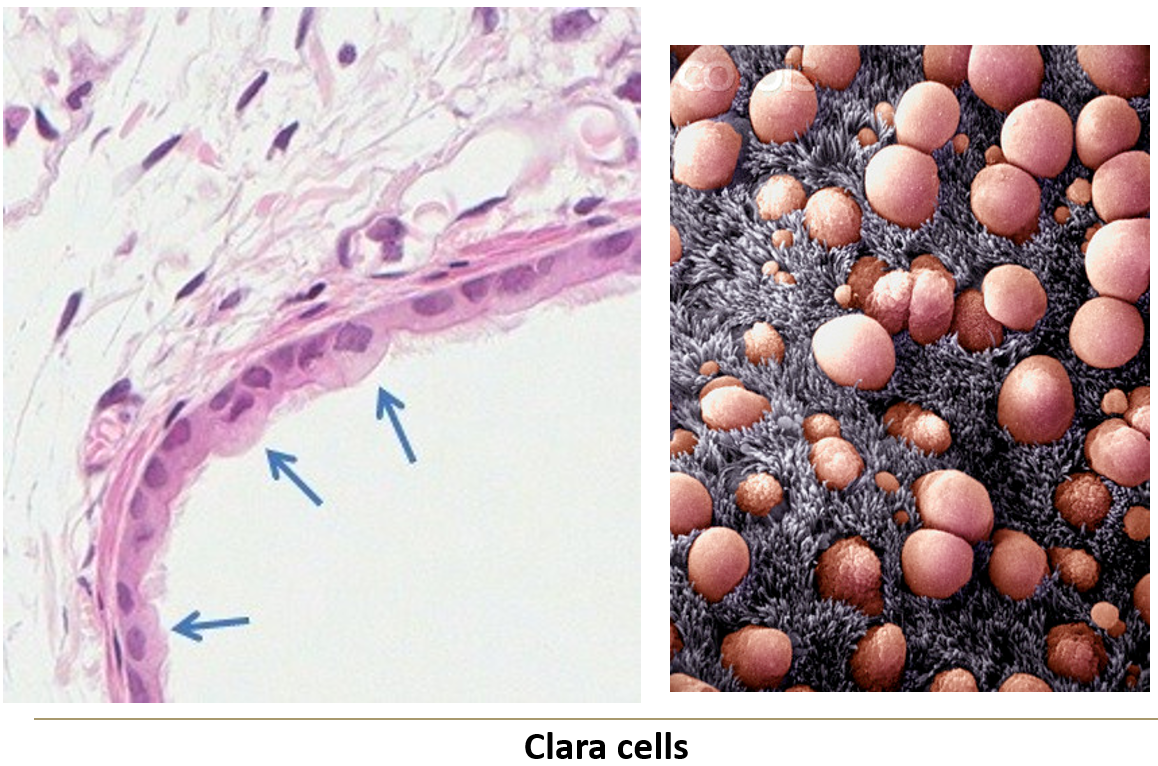
Clara cells – Secrete surfactant-like substances.
Enteroendocrine cells – Secrete bioactive amines and peptides into blood vessels.
What are key structural components of the trachea and bronchi?
Extremely thick basement membrane.
Lamina propria rich in immune cells (macrophages, plasma cells, lymphocytes, mast cells).
Submucosa with glandular epithelial invaginations.
Muscularis mucosa (smooth muscle layer) increases in bronchi.
Hyaline cartilage for support.
How does cartilage structure differ between the trachea and bronchi?
Trachea – C-shaped rings connected by smooth muscle.
Bronchi – Irregular cartilage plates that decrease in size distally.
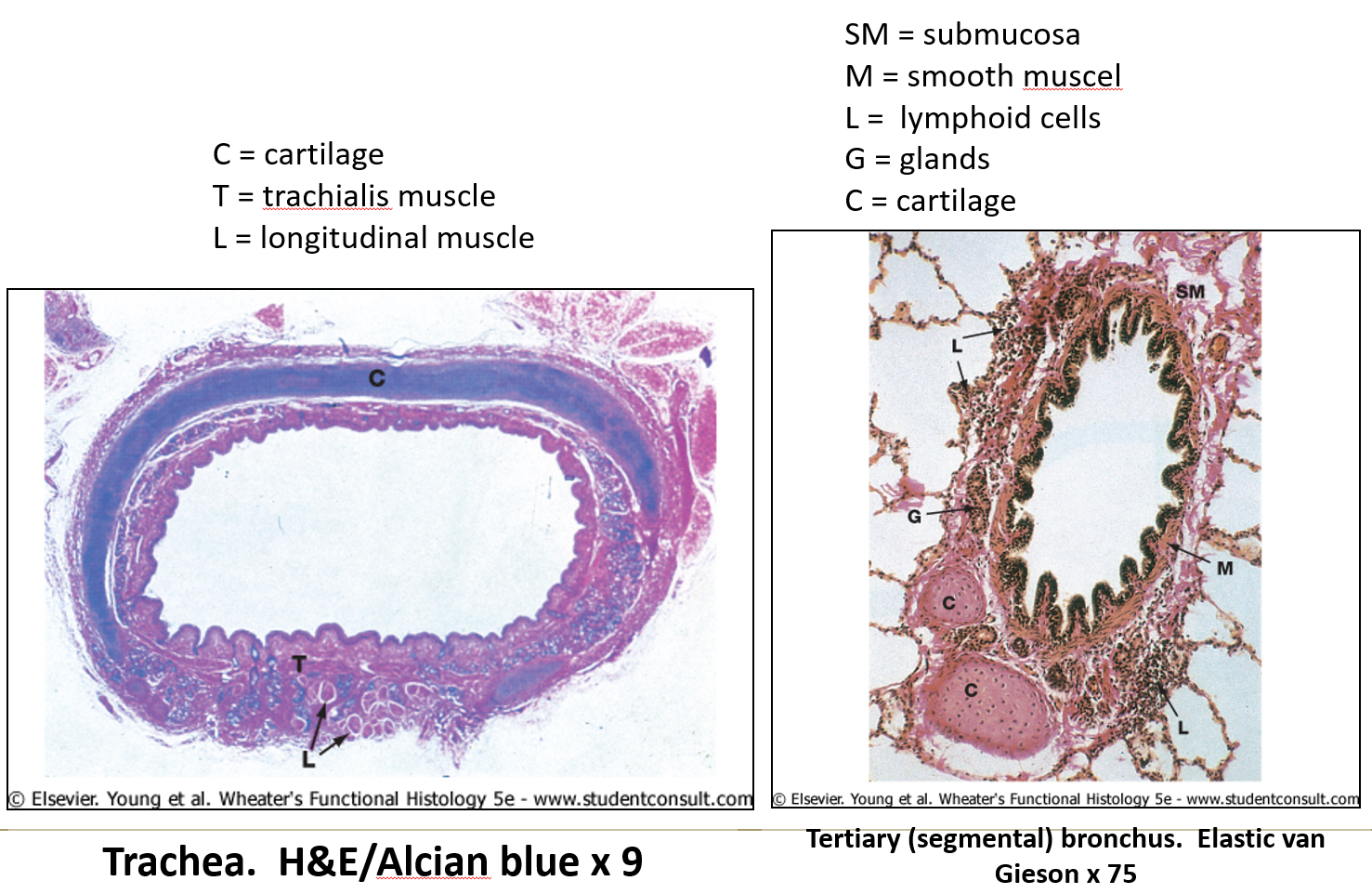
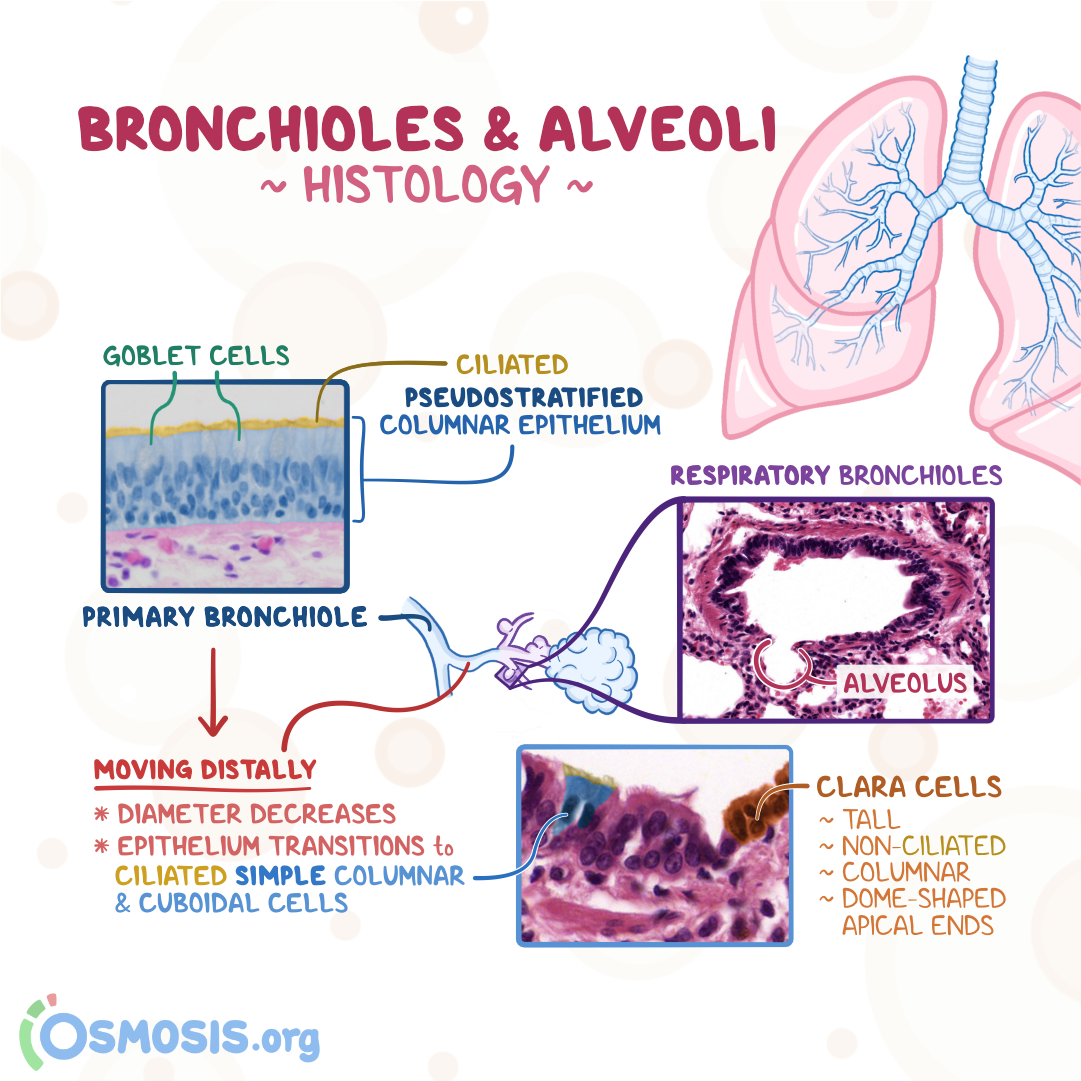
How are bronchioles different from bronchi?
They lack cartilage surrounding.
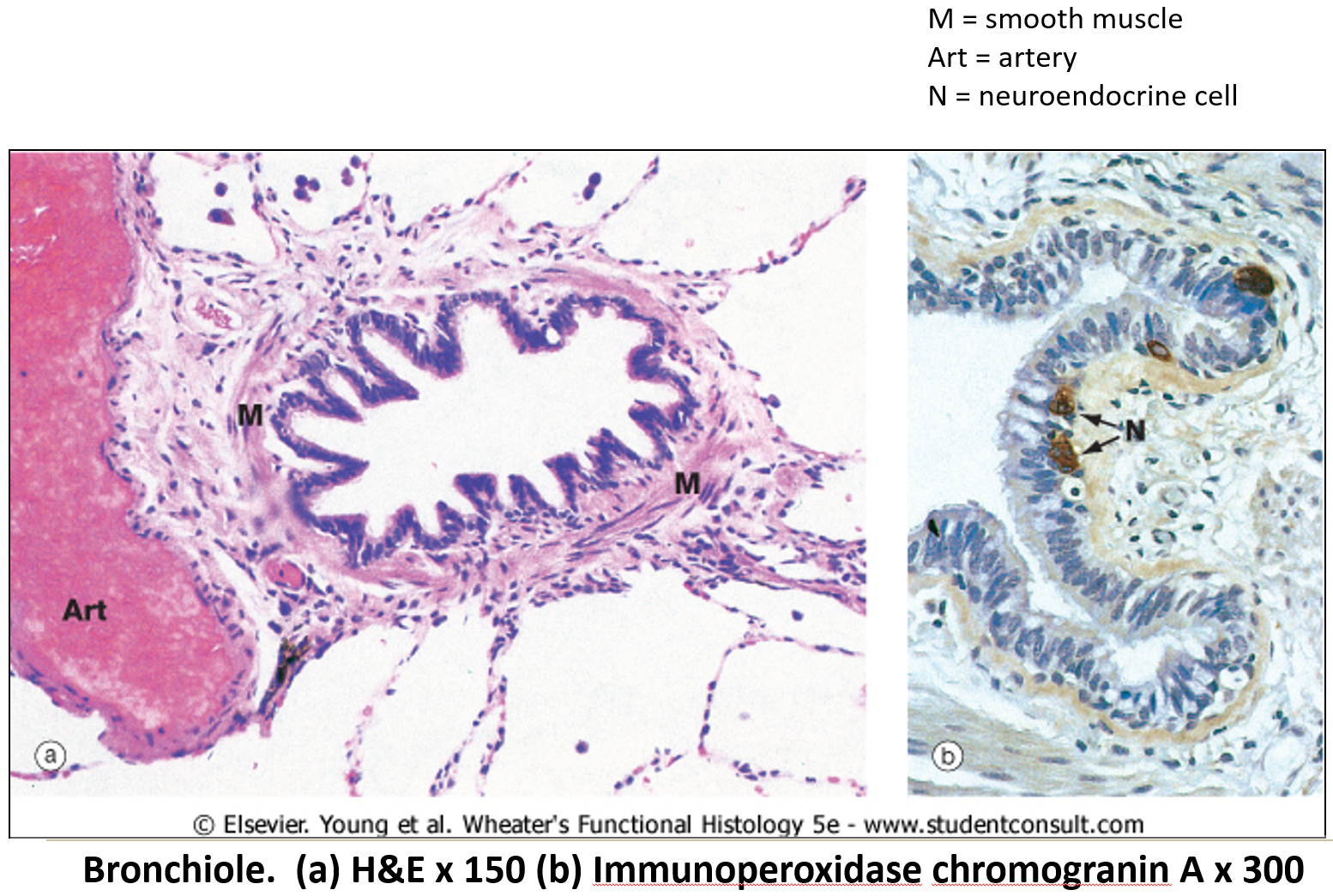
How does epithelium change as airways become smaller?
Starts as pseudostratified epithelium.
Quickly transitions to simple columnar and then simple cuboidal epithelium.
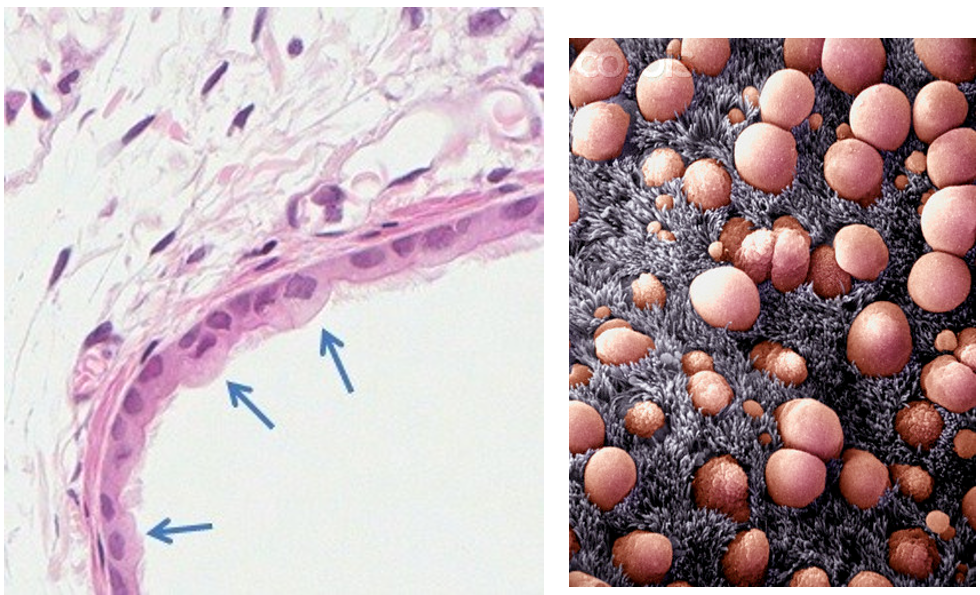
What happens to clara cells and submucosal glands in bronchioles?
Clara cells (Secrete surfactant-like substances) increase in number, while submucosal glands disappear distally.
What type of epithelium lines the respiratory portion?
Simple squamous epithelium with a rich capillary network.
What makes respiratory bronchioles unique?
They have alternating conducting and respiratory linings.
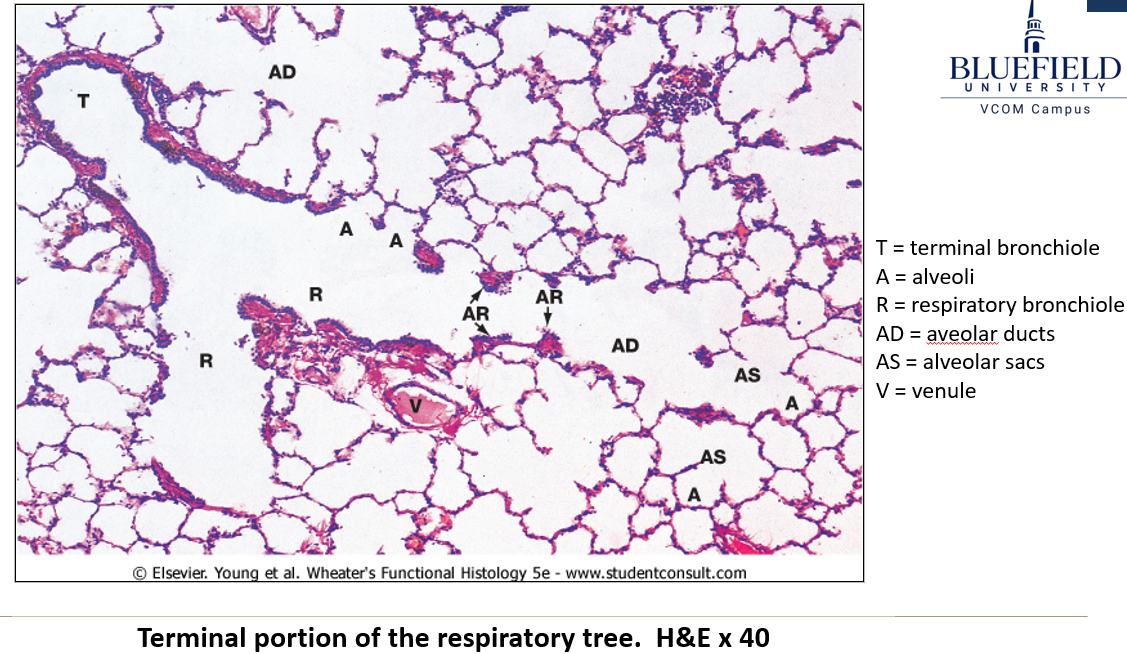
What are the features of respiratory bronchioles?
Short passageways
Three generations of branching.
Simple cuboidal epithelium (ciliated and non-ciliated).
Openings to alveolar ducts and alveoli.
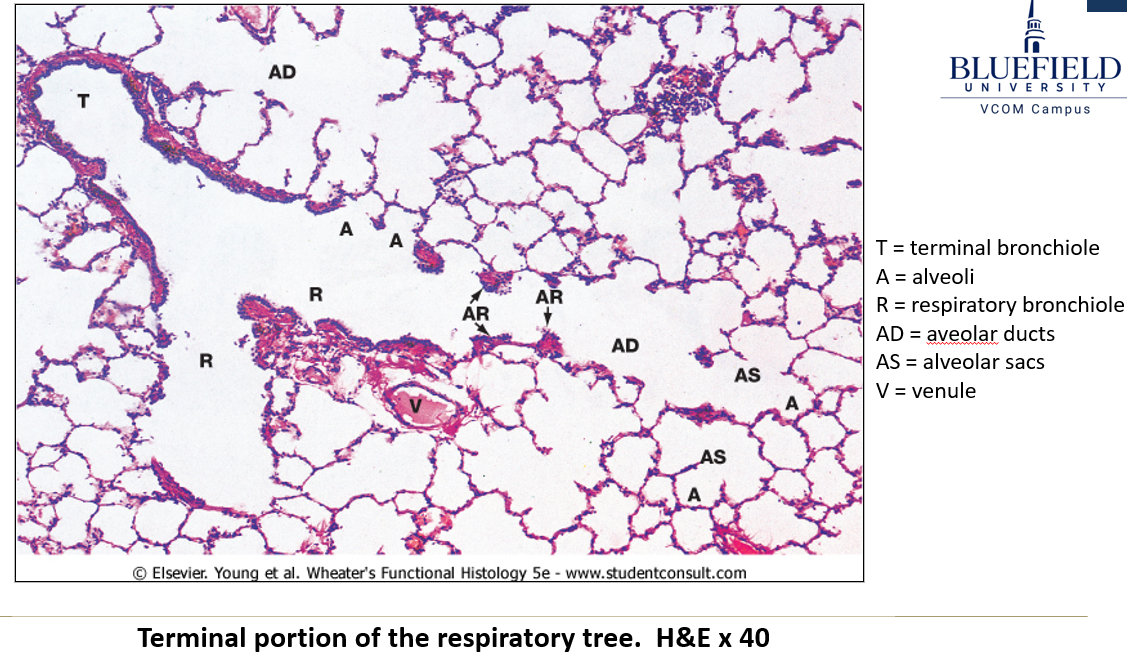
How do alveolar ducts lead to alveoli?
Alveolar ducts branch 2-3 times, forming alveolar sacs, with 5-6 alveoli per sac.
What are alveoli?
The terminal ends of respiratory passageways where gas exchange occurs.
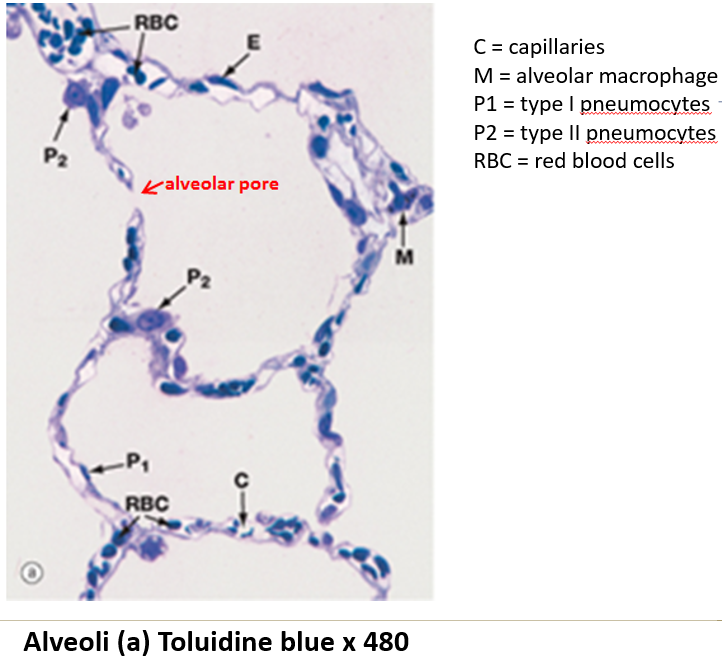
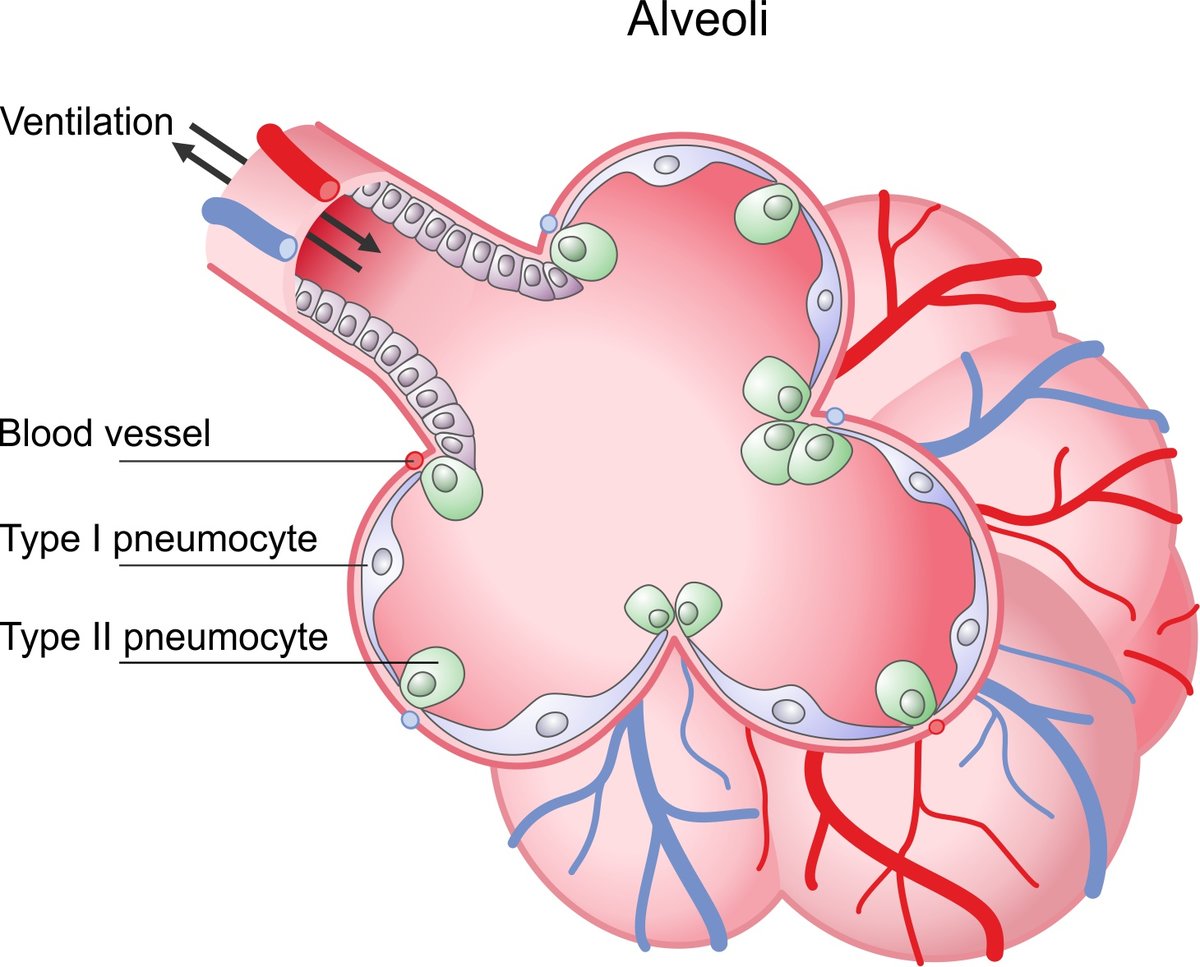
What are the two types of alveolar cells?
Type I alveolar cells: Thin simple squamous epithelial cells.
Type II alveolar cells: Rounded cells (4% of lining) that produce surfactant.
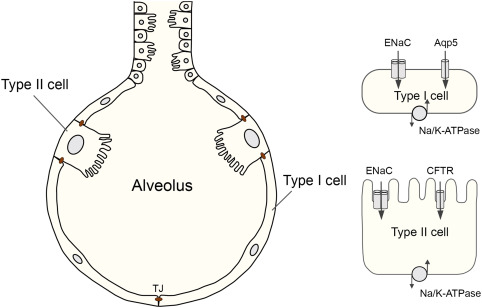
What is the role of surfactant?
It reduces surface tension, preventing alveolar collapse.
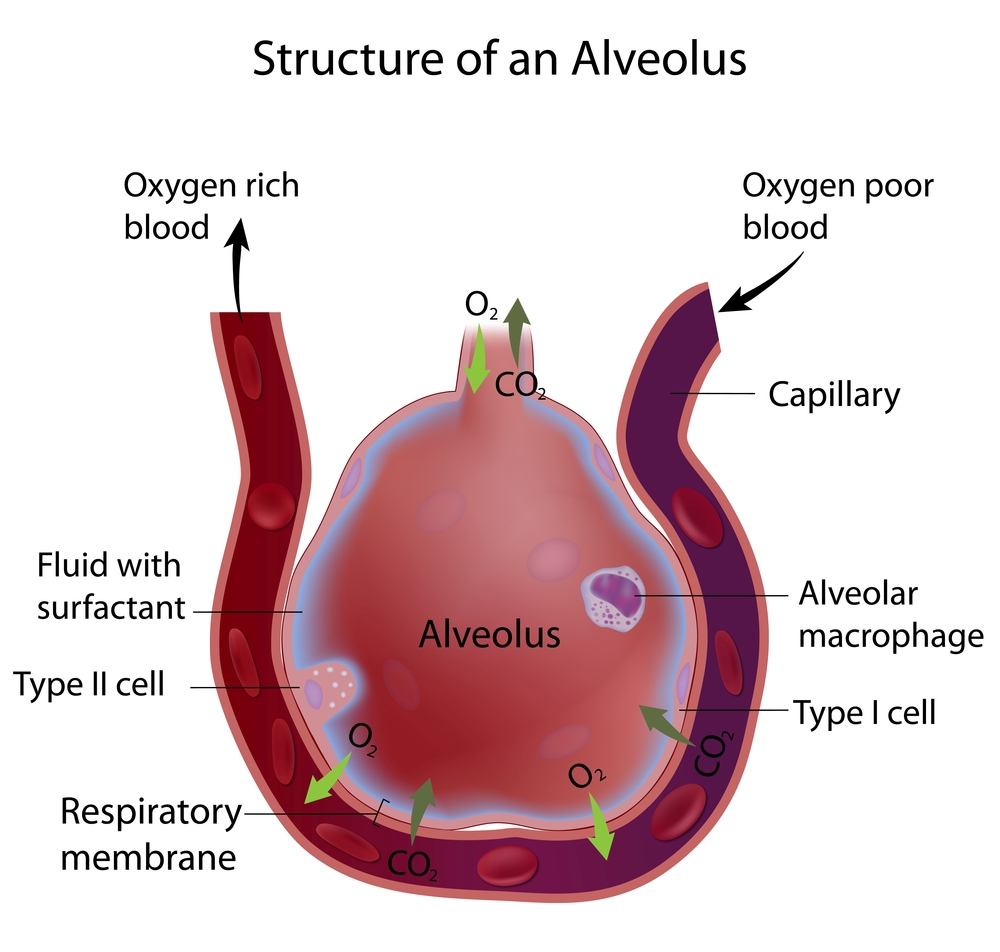
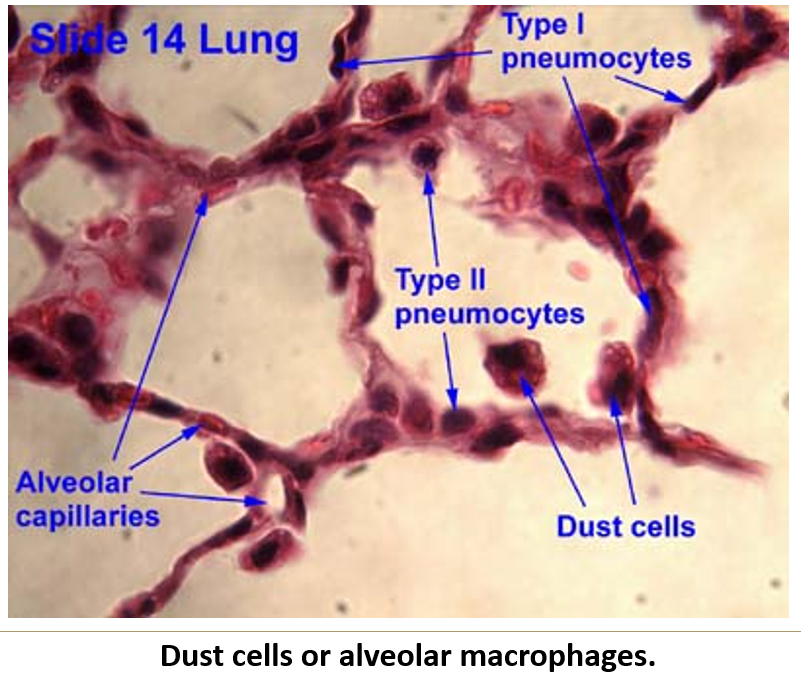
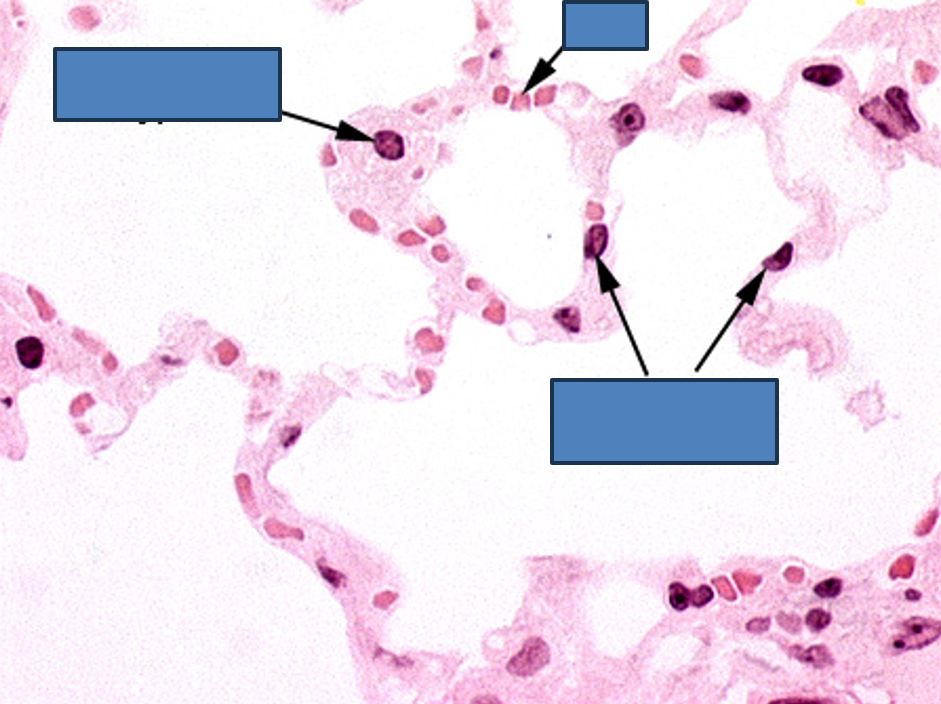
What are alveolar macrophages (dust cells)?
Monocyte-derived cells that phagocytize debris.
Move up the mucociliary escalator.
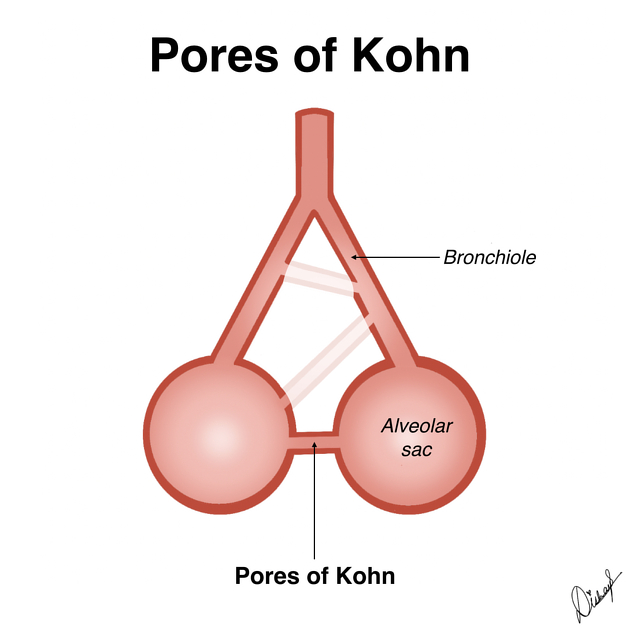
What is the function of alveolar pores?
They connect adjacent alveoli, providing alternate pathways for air circulation.
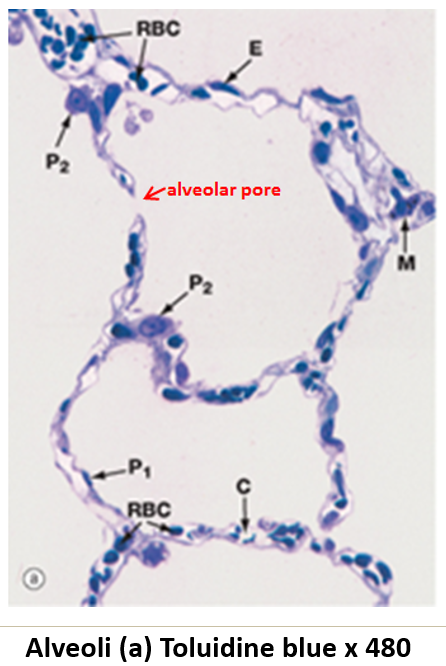
What structural support is present in alveolar walls?
Elastic fibers, which allow expansion and recoil.
What are the two layers of pleura?
Visceral pleura: Covers the lungs.
Parietal pleura: Lines the chest cavity.
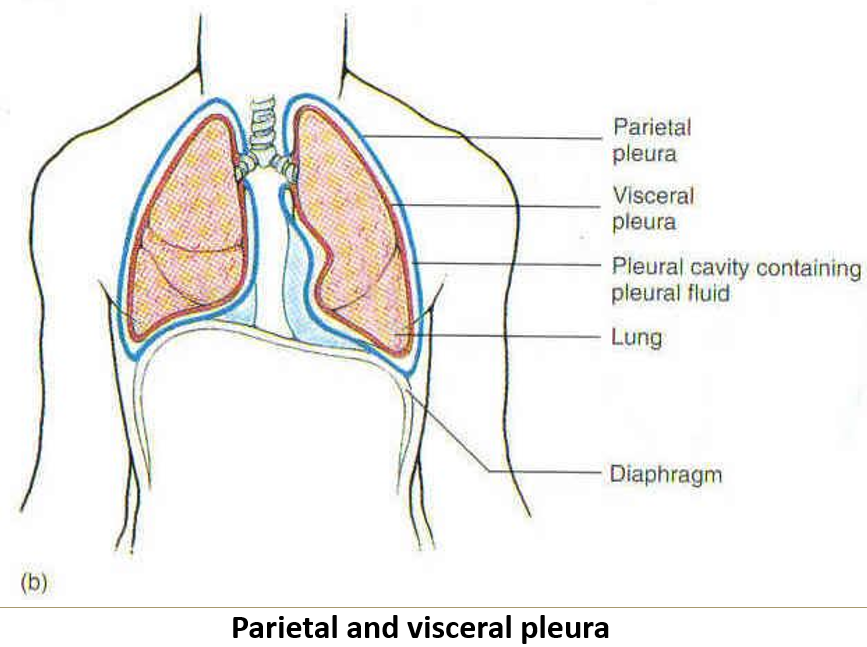
What is the histological structure of the pleura (visceral/parietal)?
Mesothelium (simple squamous epithelium).
Collagen and elastic fibers in supporting connective tissue.
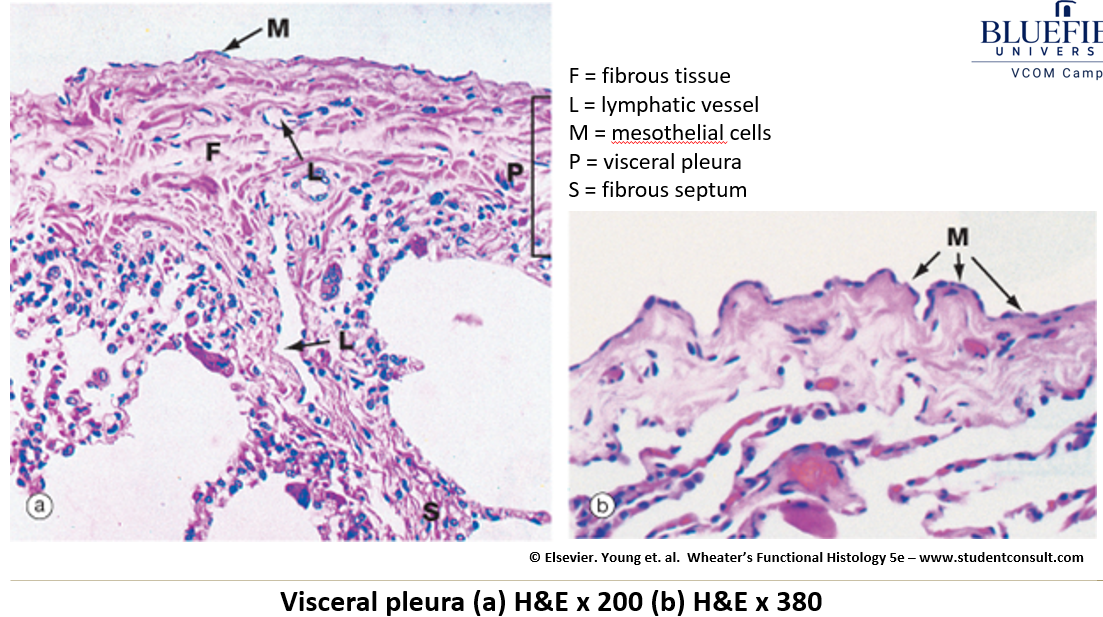
What is the function of pleural fluid?
It lubricates the lungs, allowing smooth movement against the chest wall.
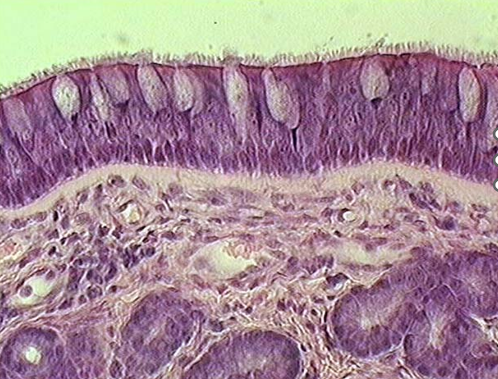
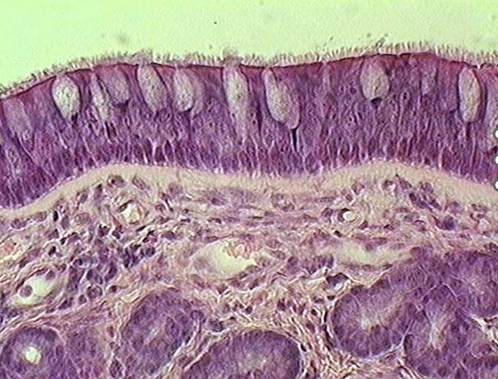
Identify this structure
Nasal cavity
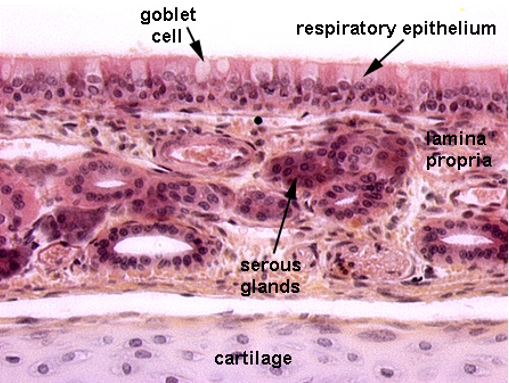
Identify the type of epithelium, the cilia, cartilage, the lamina propria and serous glands
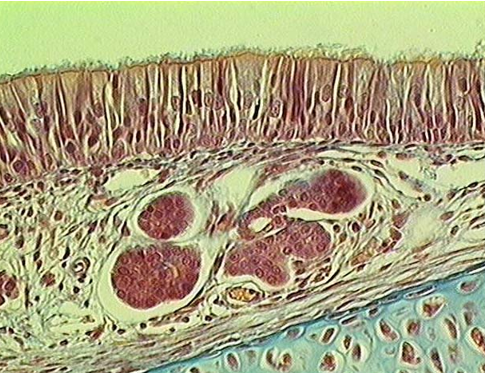
Nasal cavity
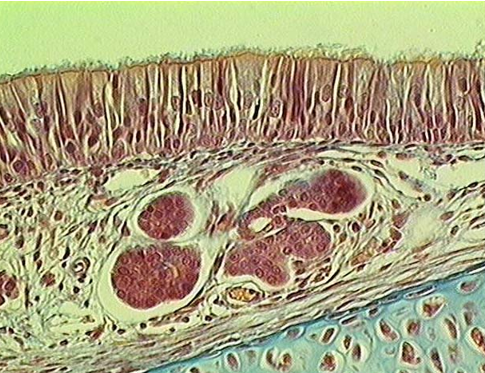
Identify the type of epithelium, cilia, mucous cells, lamina propria, submucosa and serous glands.
Nasal cavity
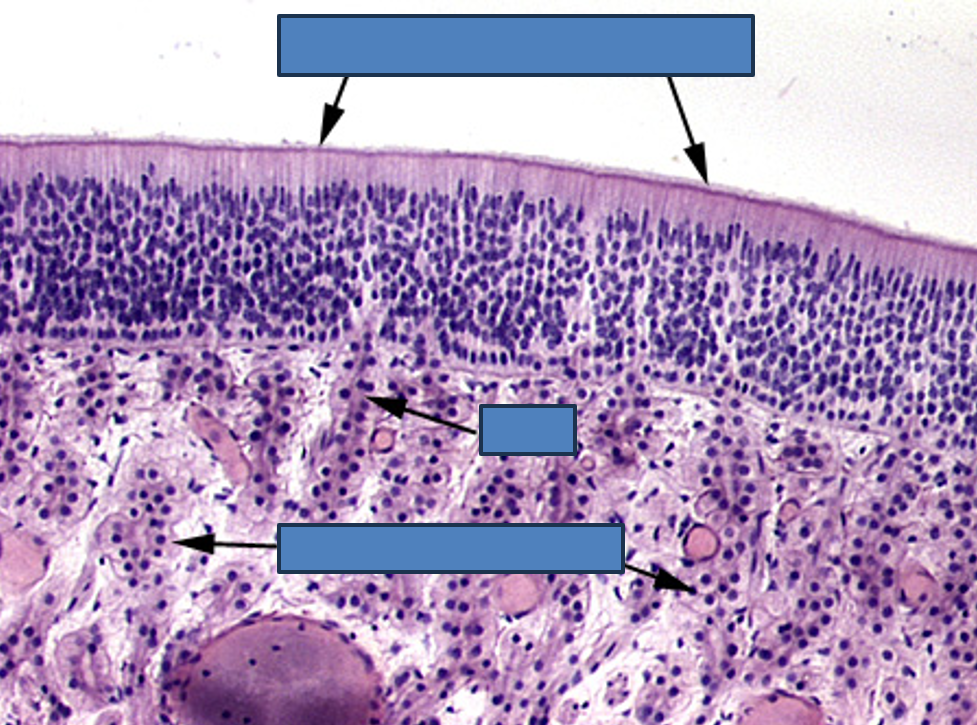
Identify this structure/organ
Olfactory epithelium
Stereocilia (longer than true cilia) observable and many many layers of pseudostratified nuclei
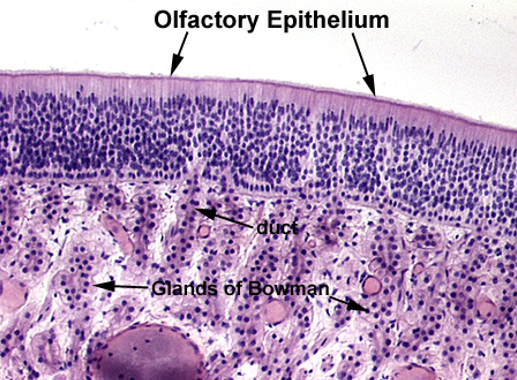
Identify the organ, the type of epithelium, the lamina propria and Boman’s glands.
Olfactory epithelium
Stereocilia (longer than true cilia) and Bowman’s gland observable and many many layers of pseudostratified nuclei
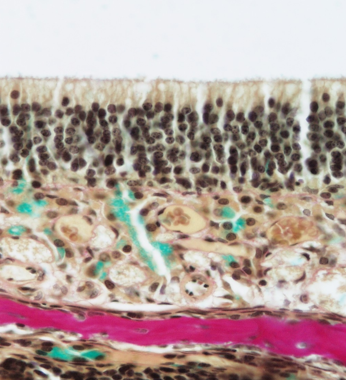
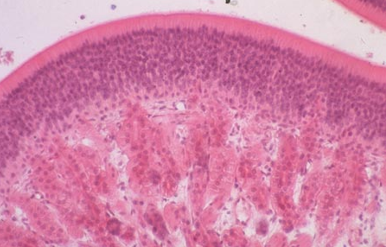
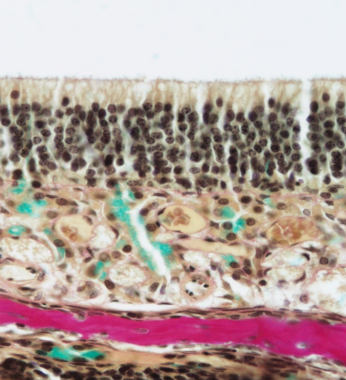
Identify this structure
Olfactory epithelium
Stereocilia (longer than true cilia) observable and many many layers of pseudostratified nuclei
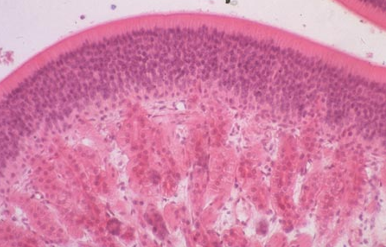
Identify this structure
Trachea
C-shaped cartilage ring obsverable
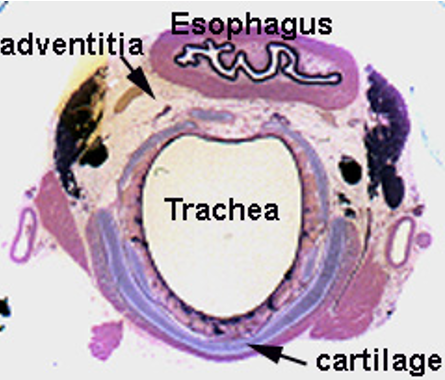
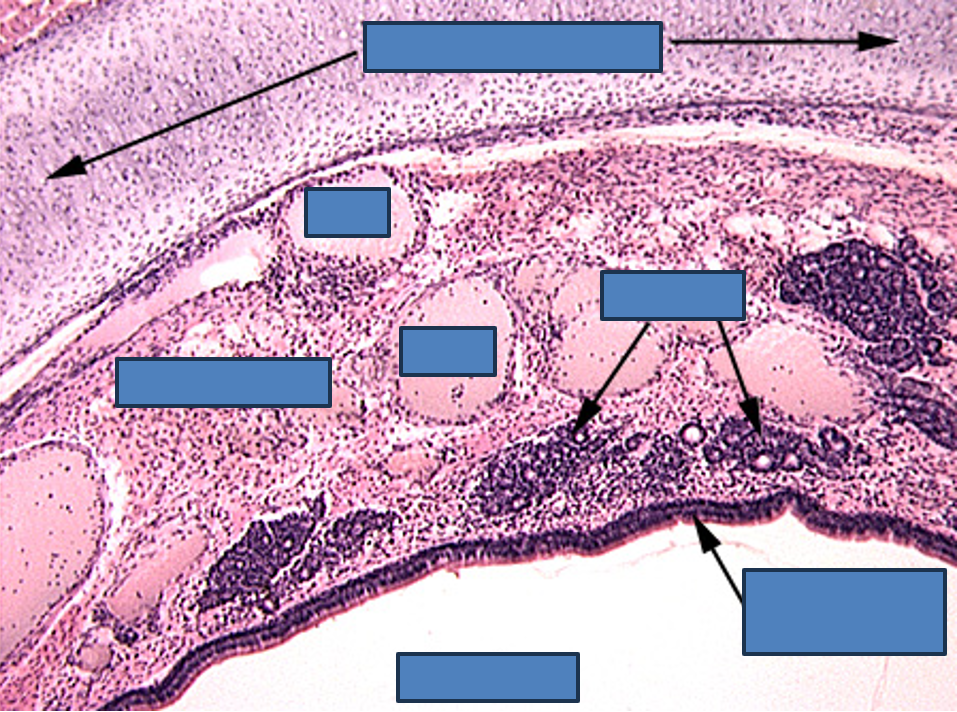
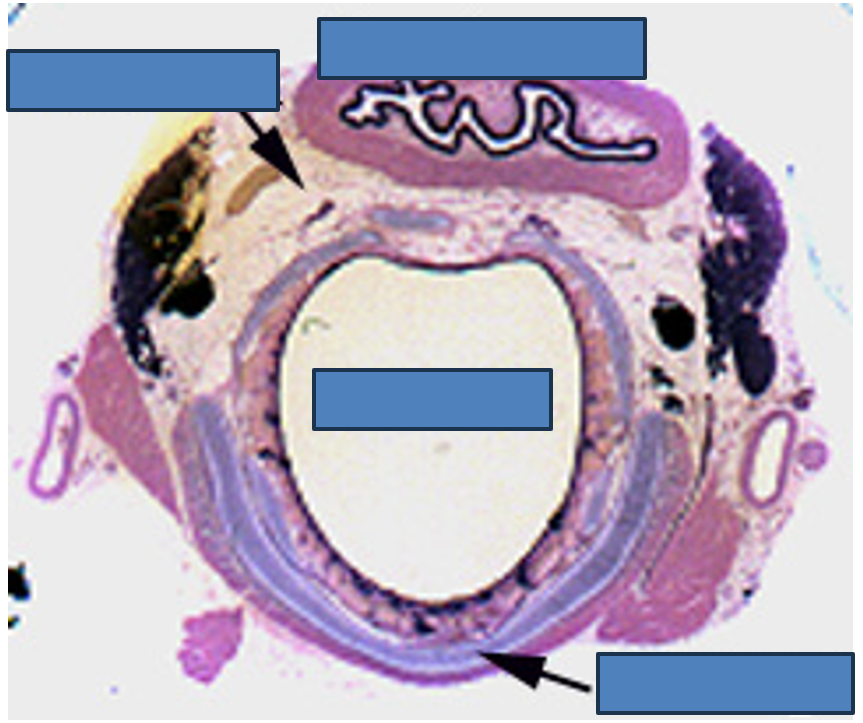
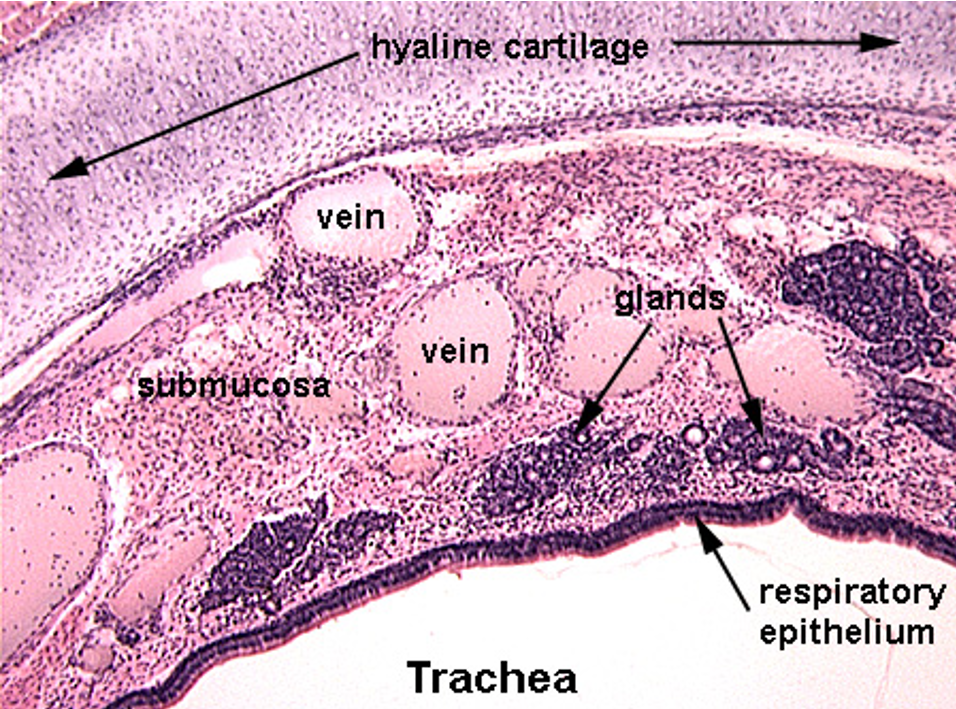
Identify this structure
Trachea
Thick conducting epithelium and hyaline cartilage observable
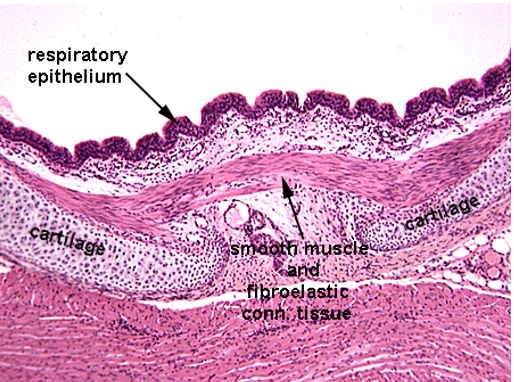
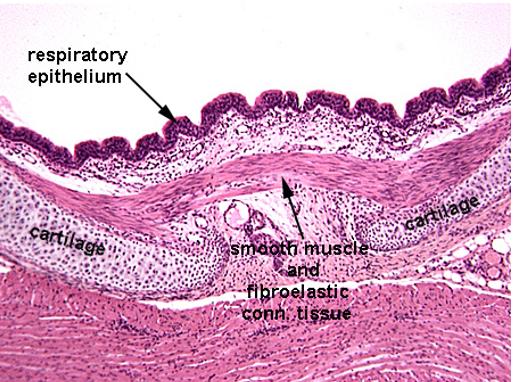
Identify this structure
Trachea
C-shaped cartilage ring obsverable. Smooth muscle observable
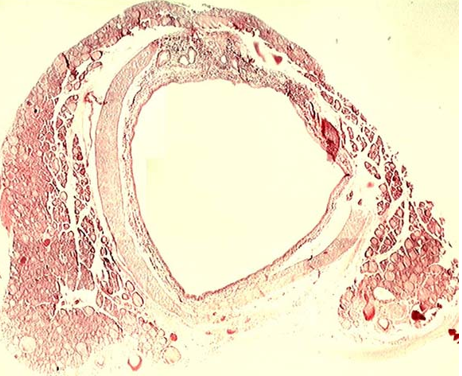
Identify this structure
Trachea due to the c-shaped cartilage ring
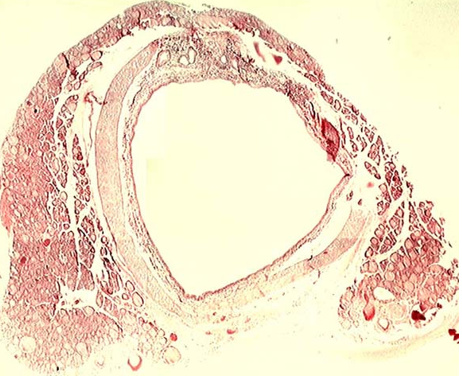
Identify this structure
Bronchi
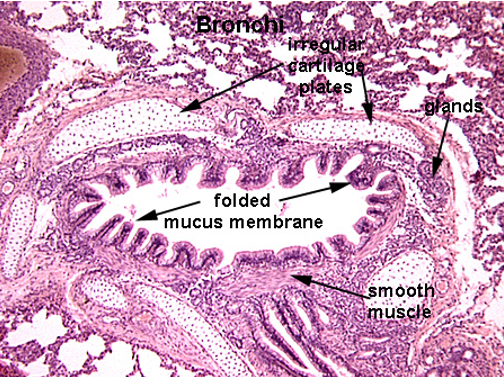
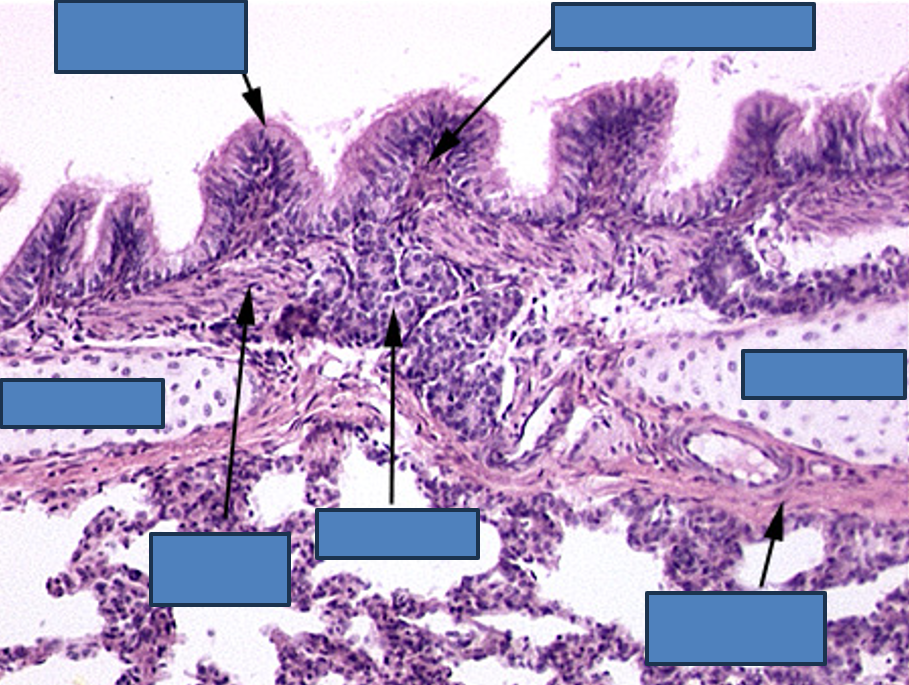
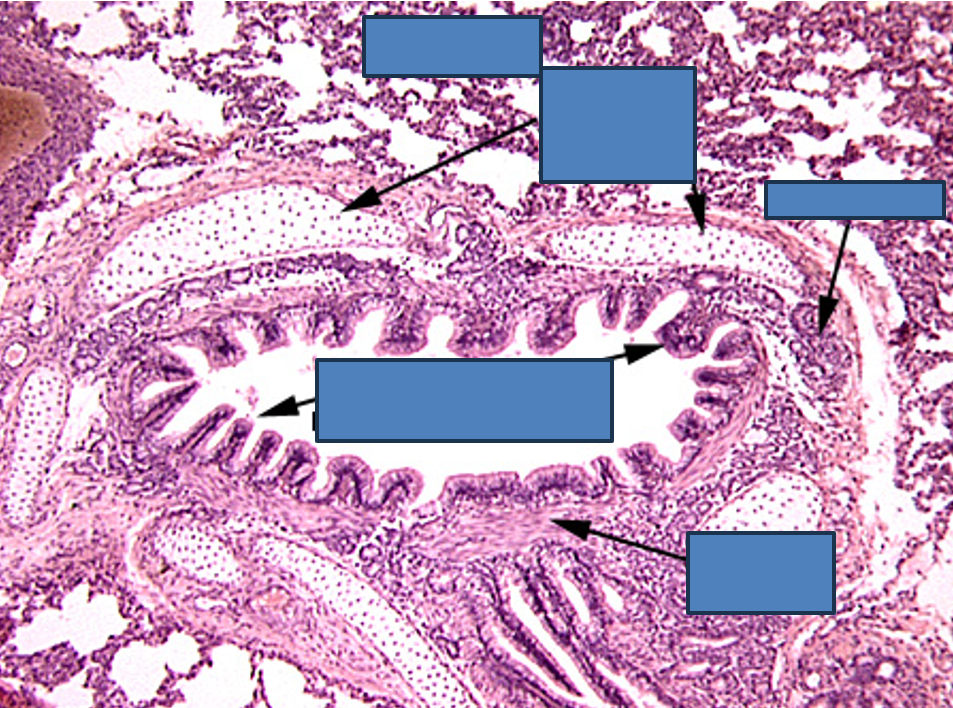
Identify this structure
Bronchus
Has cartilage. Bronchioles will not have cartilage
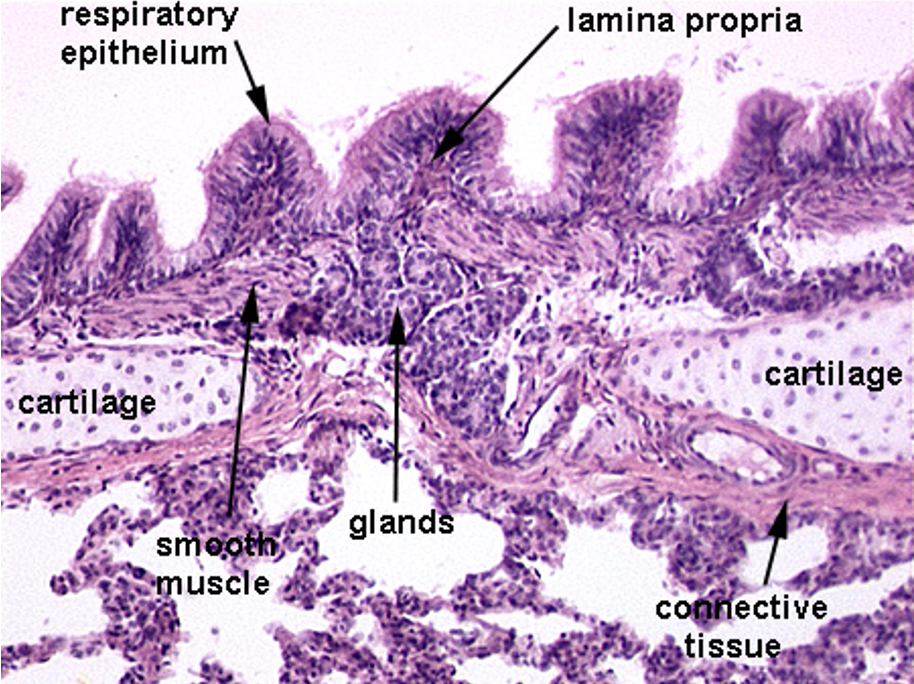
Identify this structure
Bronchus
Has cartilage. Bronchioles will not have cartilage
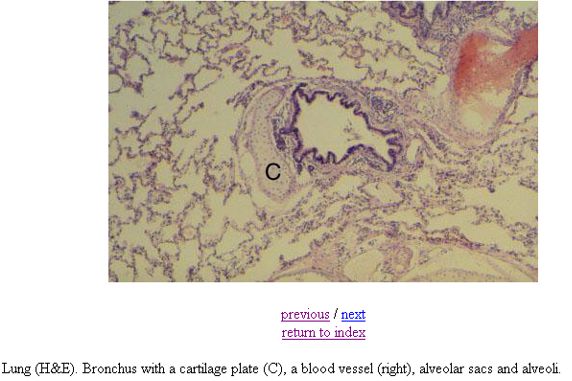
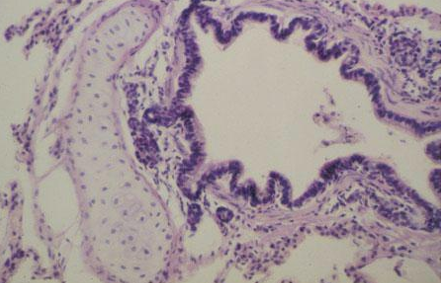
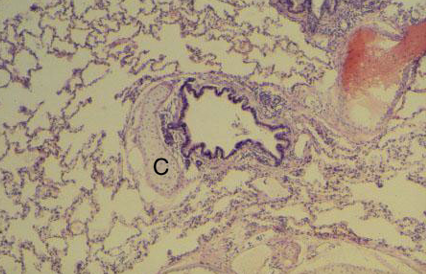
Identify this structure
Bronchus
Has cartilage. Bronchioles will not have cartilage
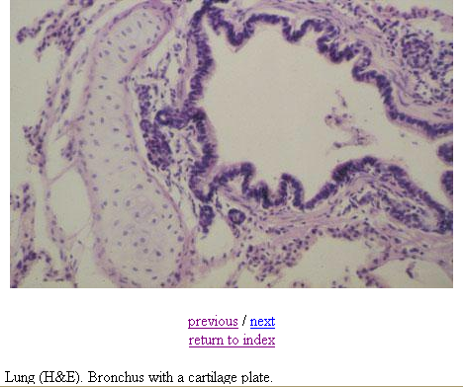
Identify this structure
Alveolar duct/sac
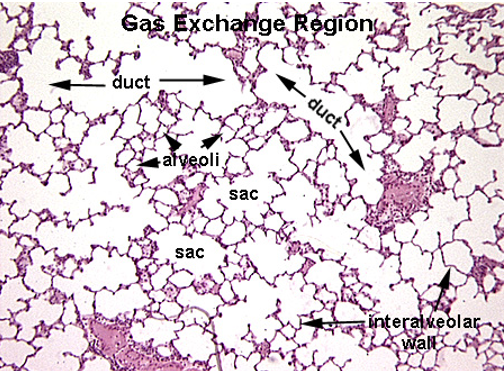
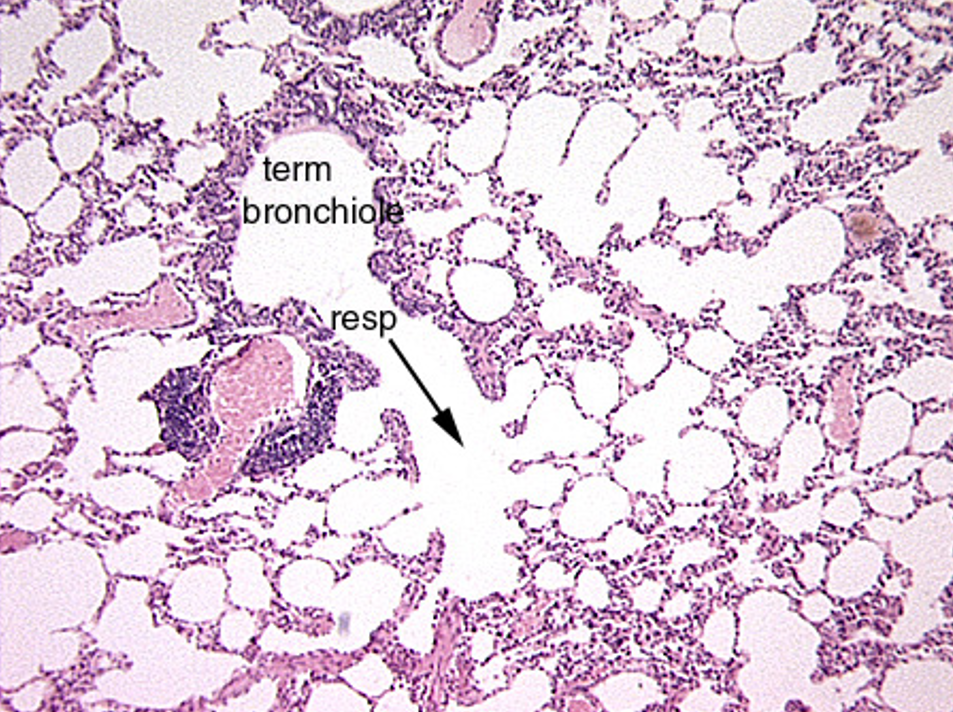
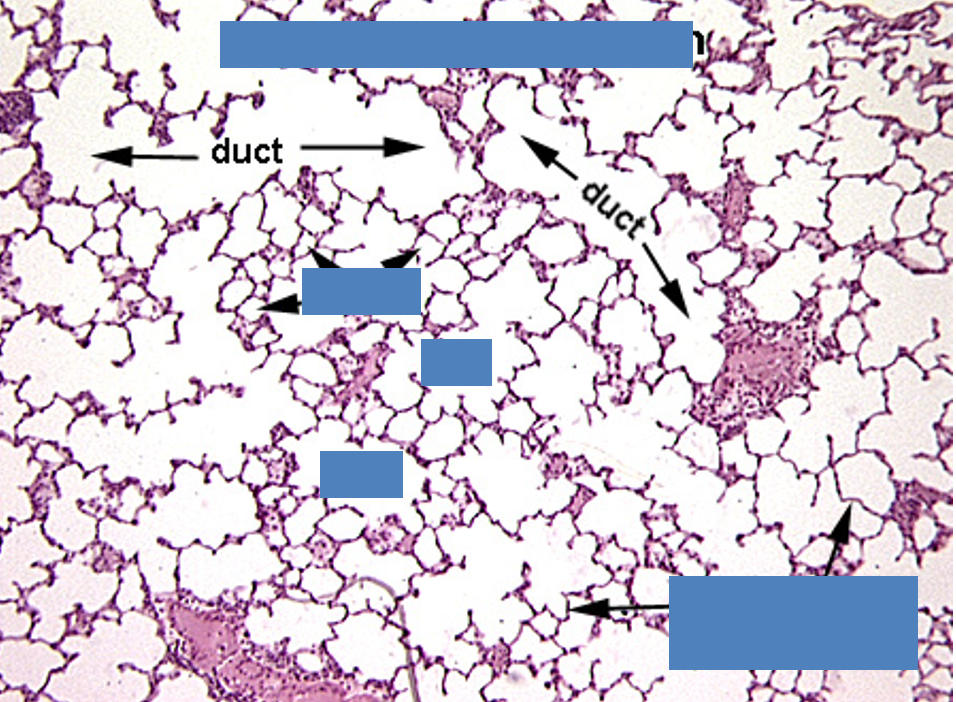
Identify the terminole bronchiole, respiratory bronchiole, aveolar duct, alveolar sac and alveoli.
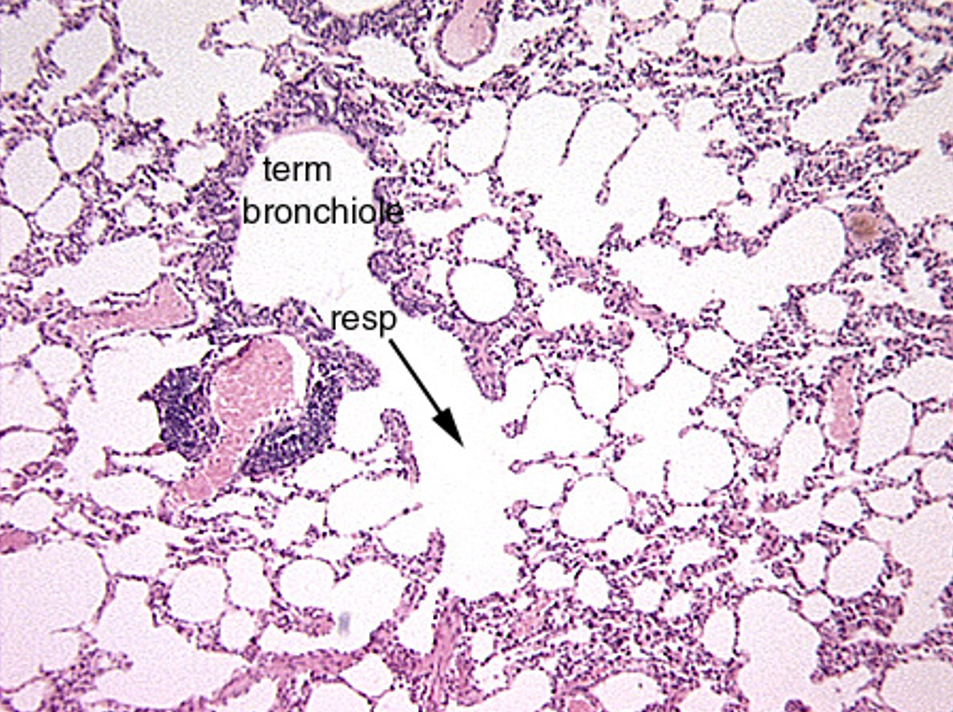
Identify this structure
Bronchioles, alveolar sacs and alveoli
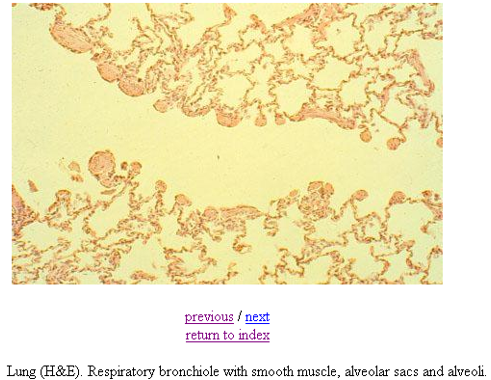
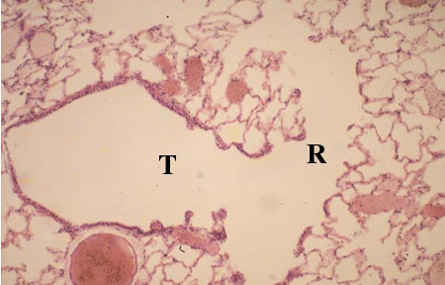
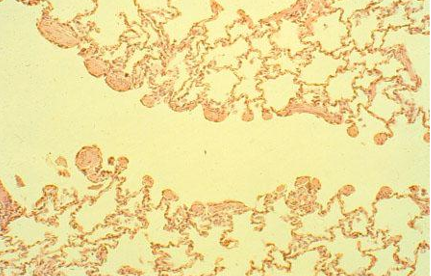
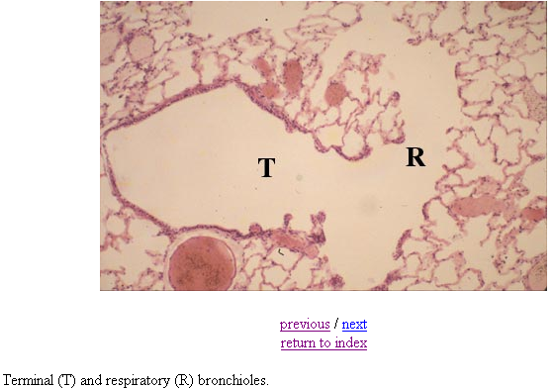
Identify this structure
Bronchioles
Terminal bronchioles has continuous thick epithelium, respiratory has alternating thick, thin, thick epithelium.
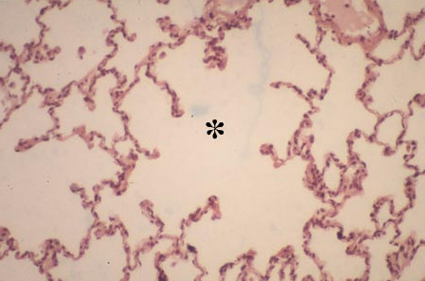
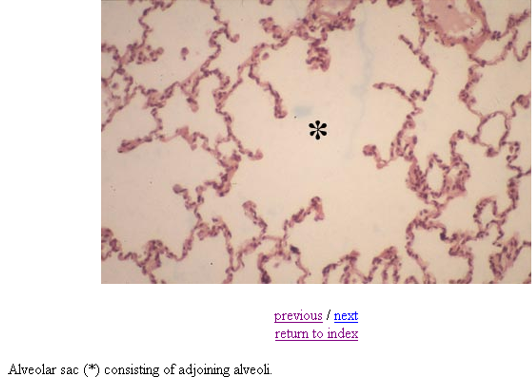
Identify this structure
Alveolar sac
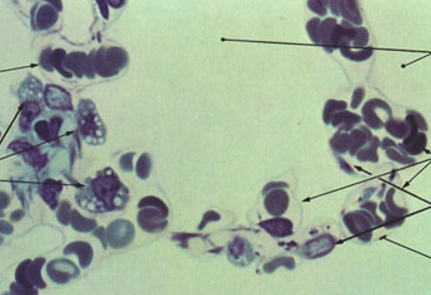
Identify this structure
Alveoli
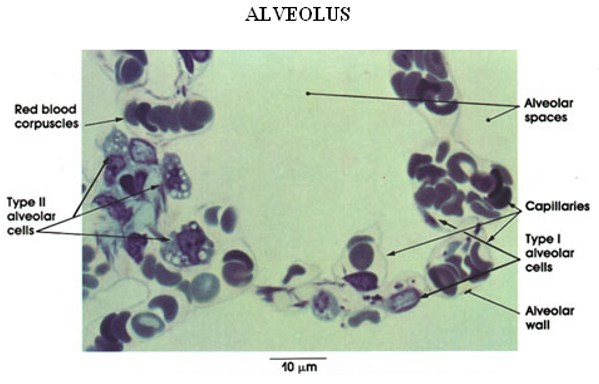
Identify this structure
Alveoli
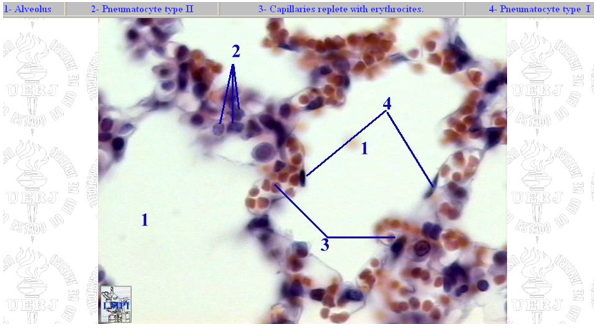
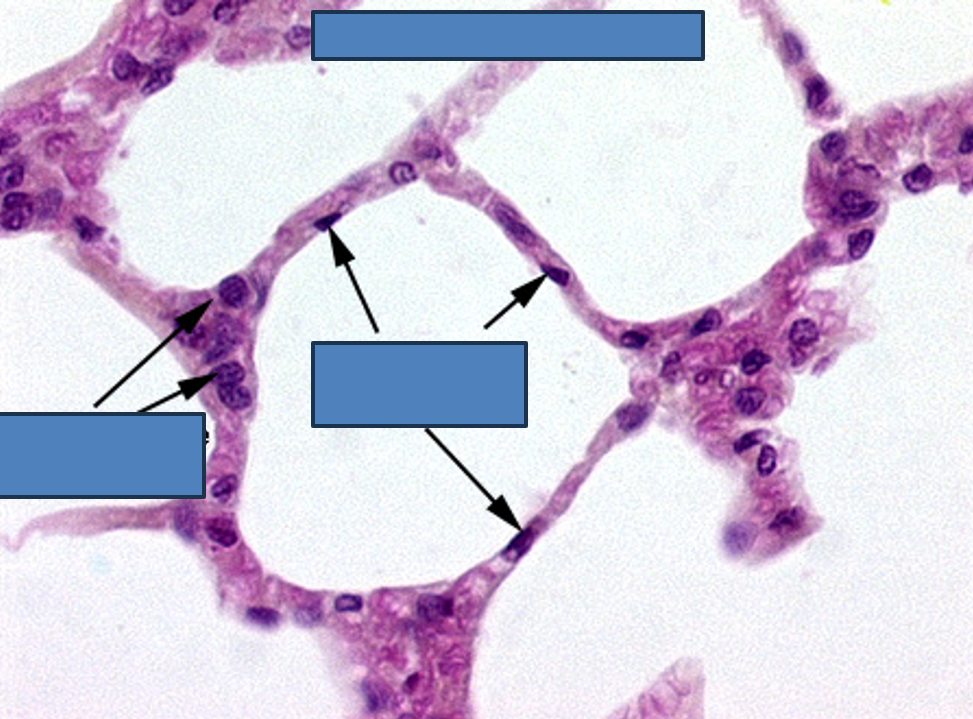
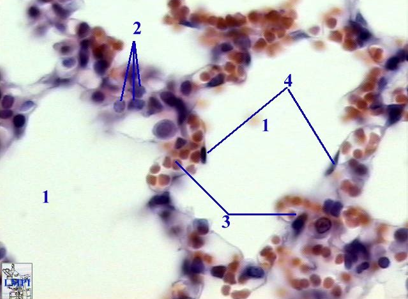
Identify this structure
Alveoli
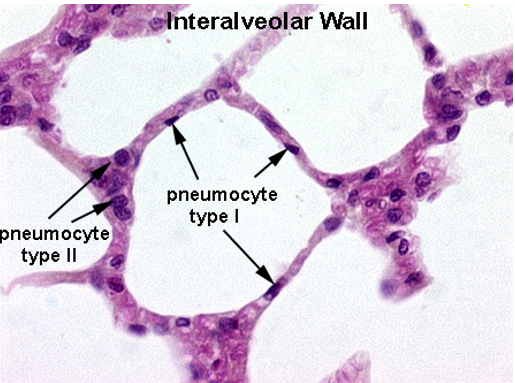
Identify this structure
Alveoli
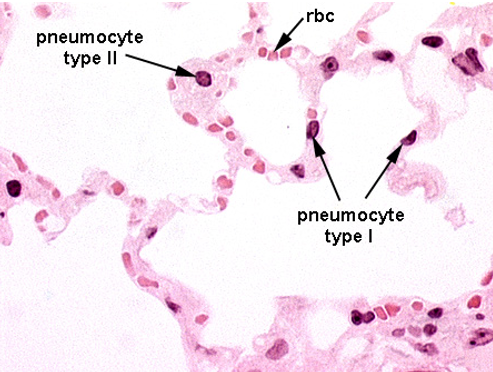
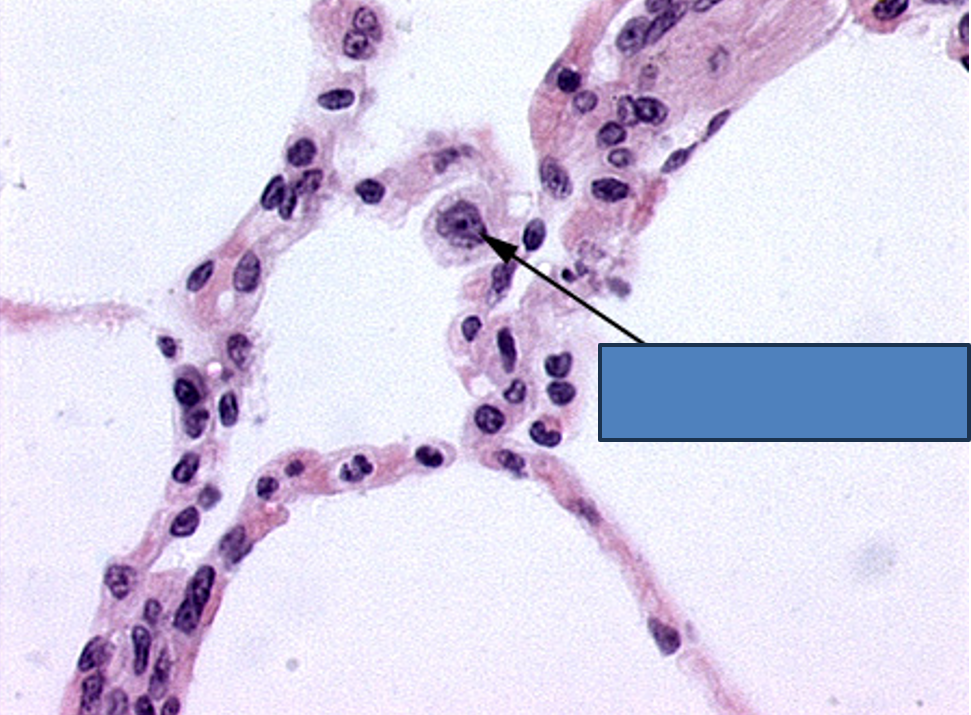
Identify this structure
Alveoli
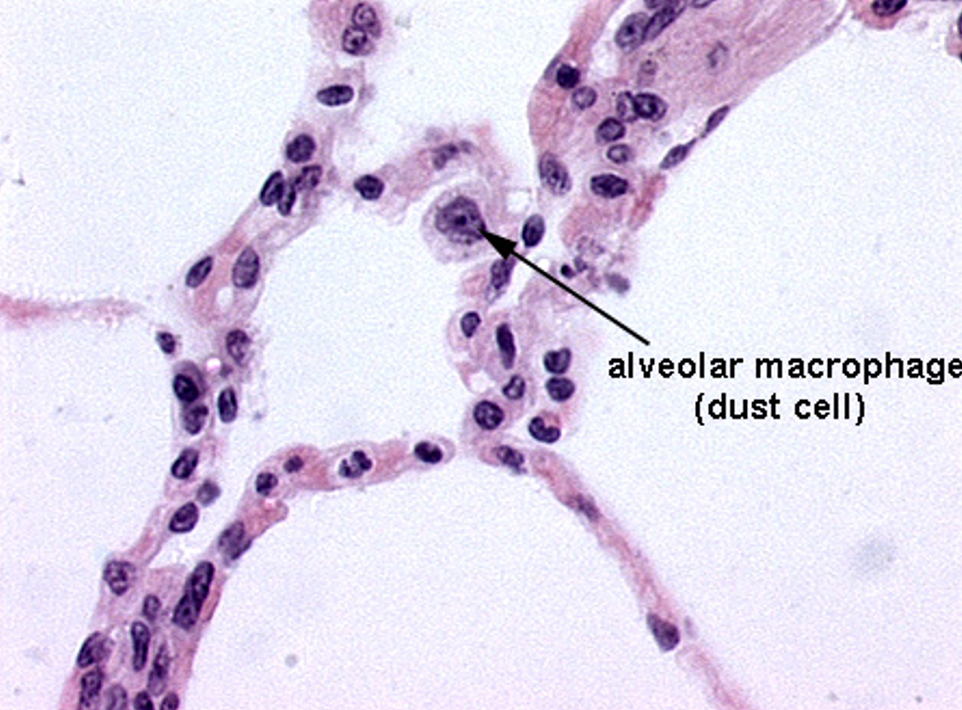
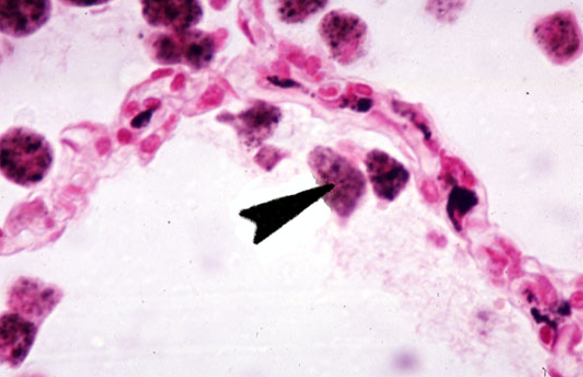
Identify the numerous dust cells in this image.
Alveoli
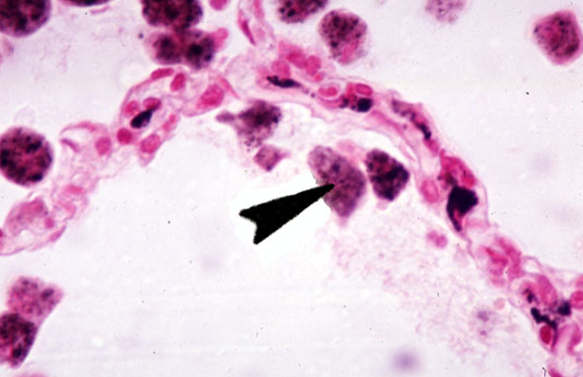
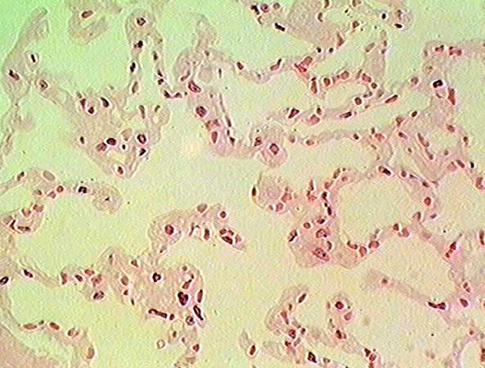
Identify this structure
Alveoli