Clinical Skills Exam 3 ( focused)
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
What are the different categories of physical agents?
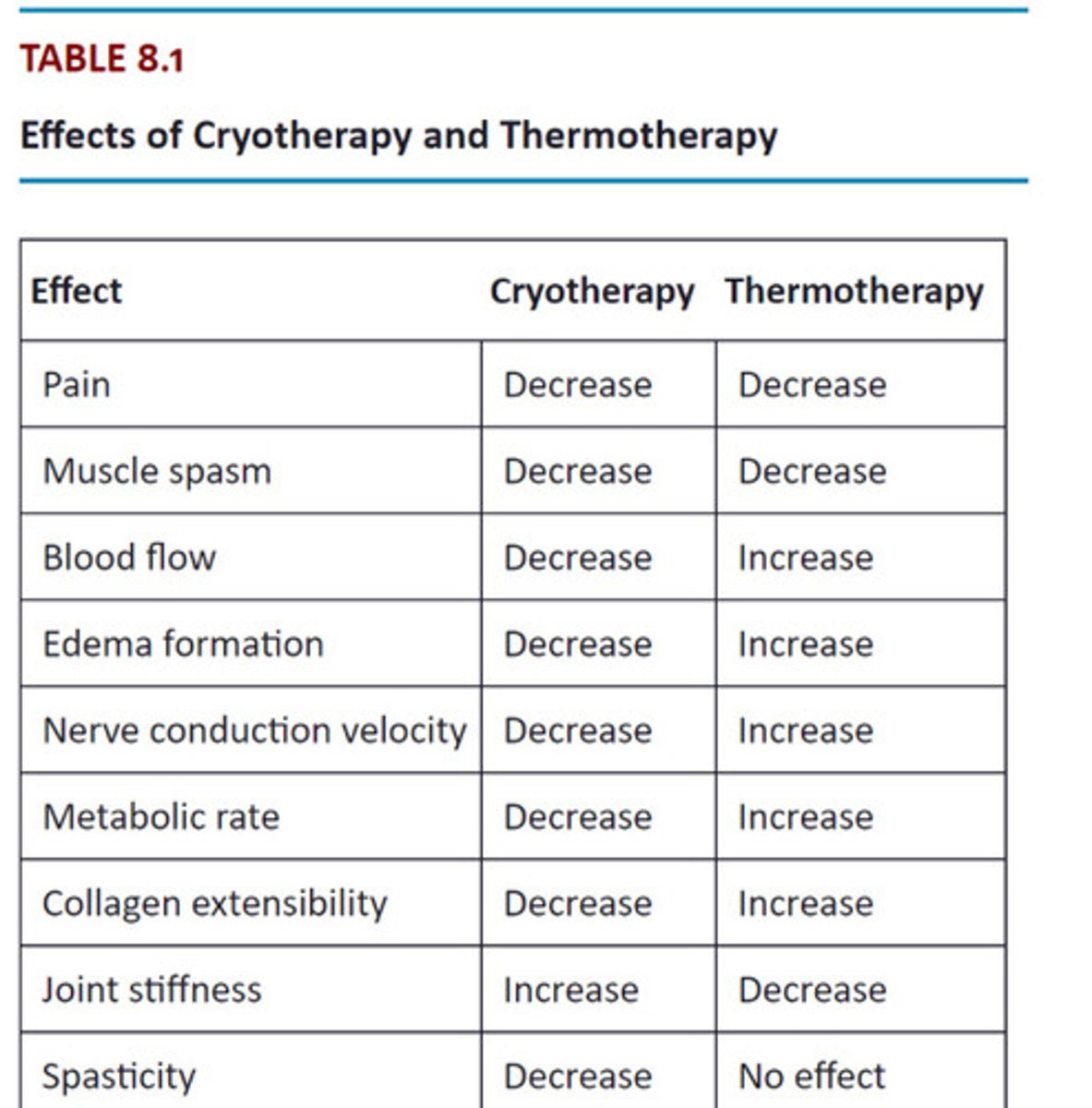
Thermal such as deep heating agents, superficial agents and cooling agents
Ultrasound, diathermy, Hot pack, Ice pack
Mechanical such as Traction, compression, water, and sound
Mechanical traction, Elastic bandage/stockings, Whirlpool, Ultrasound
Electromagnetic such as electromagnetic fields, and electrical currents
Ultraviolet/laser, TENS
Effects of physical agents: What does I Play Cool Tunes stand for?
Effects of Physical Agents
-I
Does the patient have Inflammation (decreases inflammation)
-P
Does the Patient have Pain (can decrease pain)
-C
Is the collagen tight Type III muscle fibers vs Type I (Collagen Extensibility)
-T
Tone (Modify Muscle Tone)
Inflammation Phase of Healing
Reduces circulation, reduces pain, reduces enzyme activity rate, controlling mtion, and promoting progression to the proliferation phase
Proliferation phase of healing
Increases circulation and enzyme activity rate by promoting collagen deposition and progression to the remodeling phase of healing
Maturation phase of healing
Alters balance of collagen deposition and resorption and improves the alignment of new collagen fibers.
Pain relief can do what for pts? When should physical agents be discontinued?
Relieving pain can help participate more fully in ADLS, however physical agents are to be discontinued once no longer needed.
Use of Physical Agents in combination **
To progress toward the goals of intervention, a number of physical agents may be used simultaneously and sequentially, many agents are often applies in conjunction.
Ex:
E-Stim & Heat pack
Contraindications for general physical agents?

Pregnant Malik Paces Impatiently irritated PMPII
What to know about APTA statements
“don't use (superficial or deep) heat to obtain clinically important, long-term outcomes in musculoskeletal conditions.”
Looking at this statement carefully, it does imply that heat can be used to facilitate an active treatment program, as recommended in this book
“don't use whirlpools for wound management.”
Based on the evidence and this recommendation, the use of whirlpools for wound management has been deleted from this book, and details on directed wound irrigation and pulsed lavage with suction are provided.
In other words, the APTA believes that the use of physical agents alone does not constitute physical therapy and that physical agents should be applied in conjunction with other skilled therapeutic or educational interventions. AKA its a tool (Like Chris J) not the whole treatment.
What are the 5 ways energy can be transferred?
Conduction, Convection, Conversion, Radiation, evaporation
Know def for each as the question will be a fill in the blank style
Conduction**
Heating by conduction is the result of energy exchange by direct collision between the molecules of two materials at different temperatures.
Hot pack or warm paraffin
Convection**
Heat transfer by convection occurs as the result of direct contact between a circulating medium and another material of a different temperature. This contrasts with heating by conduction, in which contact between a stationary thermal agent and the patient is constant.
"Fluidotherapy and Whirlpool do convection"
Conversion**
-Heat transfer by conversion involves the conversion of a nonthermal form of energy such as mechanical, electrical, or chemical energy into heat.
"Ultrasound causes molecules in the tissue to vibrate; the friction between them generates heat, resulting in an increase in tissue temperature"
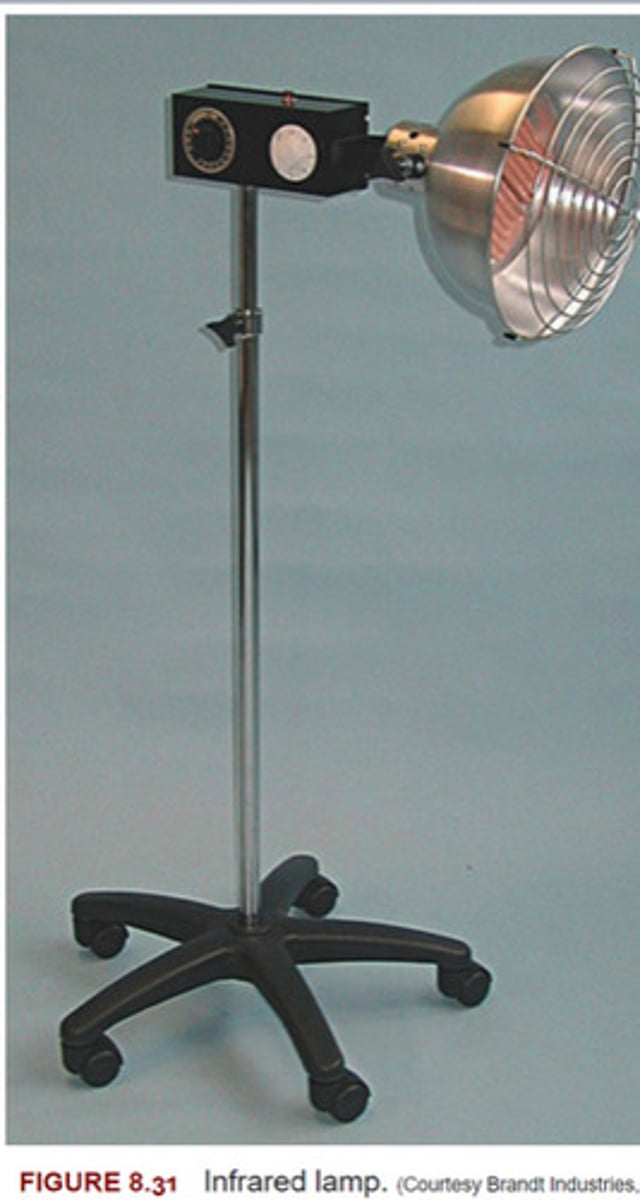
Radiation**
-Radiation Heating by radiation involves the transfer of energy from a material with a higher temperature to one with a lower temperature without an intervening medium or contact.
" This contrasts with heat transfer by conversion, in which the medium and the patient may be at the same temperature, and from heat transfer by conduction or convection, which require the thermal agent to contact the tissue being heated."
Infrared lamp (UV rays)
Evaporation**
-A material must absorb energy to evaporate or change from a liquid to a gas (or vapor). This energy is absorbed in the form of heat derived from the material itself or an adjoining material, decreasing its temperature.
A vapocoolant spray evaporates at an even lower temperature than water. When heated by the warm skin of the body, the spray very quickly changes from its liquid form to a vapor and cools the skin.
Vapocoolant spray
Cryotherapy
Therapeutic use of Cold
Hemodynamic effects of Cryotherapy**"huntings response"
-Initial Decrease in Blood Flow
Cryotherapy causes vasoconstriction, which reduces local blood flow
-Later Increase in Blood Flow
Lewis reported that when an individual's fingers were immersed in an ice bath, their temperature initially decreased; however, after 15 minutes, their temperature cyclically increased and decreased (Fig. 8.3). Lewis correlated this temperature cycling with alternating vasoconstriction and vasodilation and called this the hunting response
Contraindications for cryotherapy **

Captian Colds Cyo Pistol Rips Open Ober CCCPROO
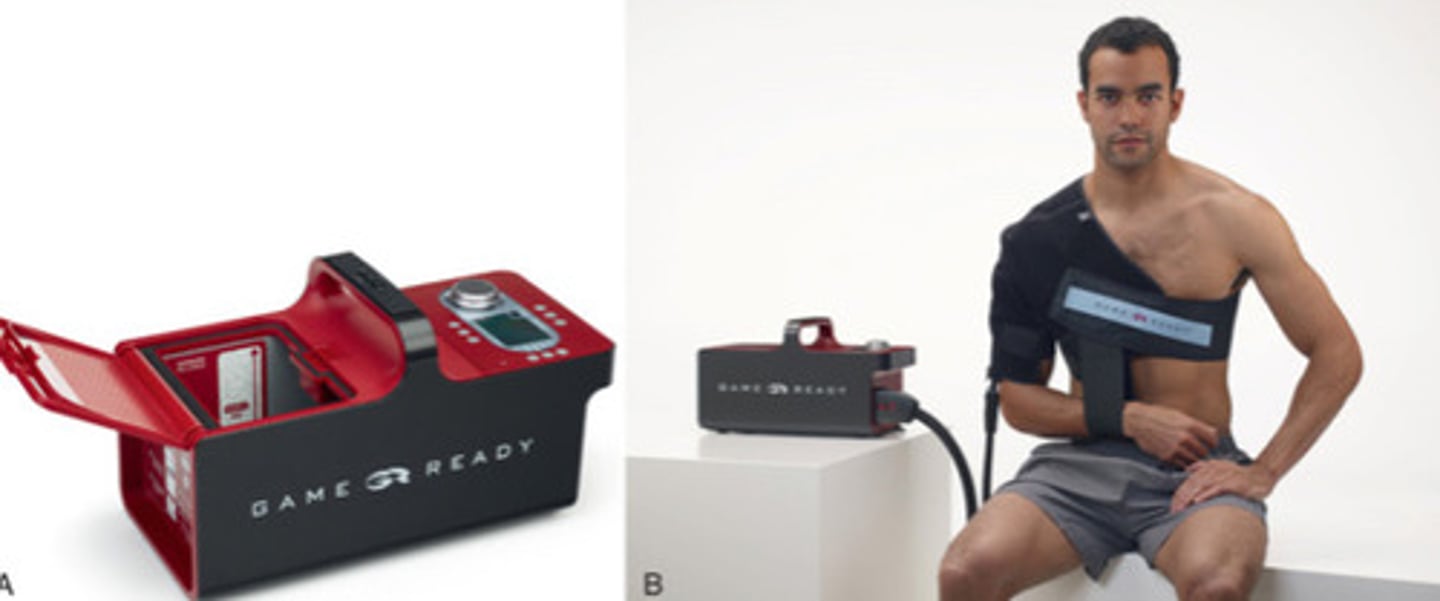
Game Ready**
This is a motor with a cuff that pumps water through it , essentially keeps the area at a constant temperature unlike a normal ice pack.
(Don't do more than 15 minutes)

Cryocuff**
(Non-electric)
Pumps water through but ice melts meaning the temperature with this one changes (decreases)
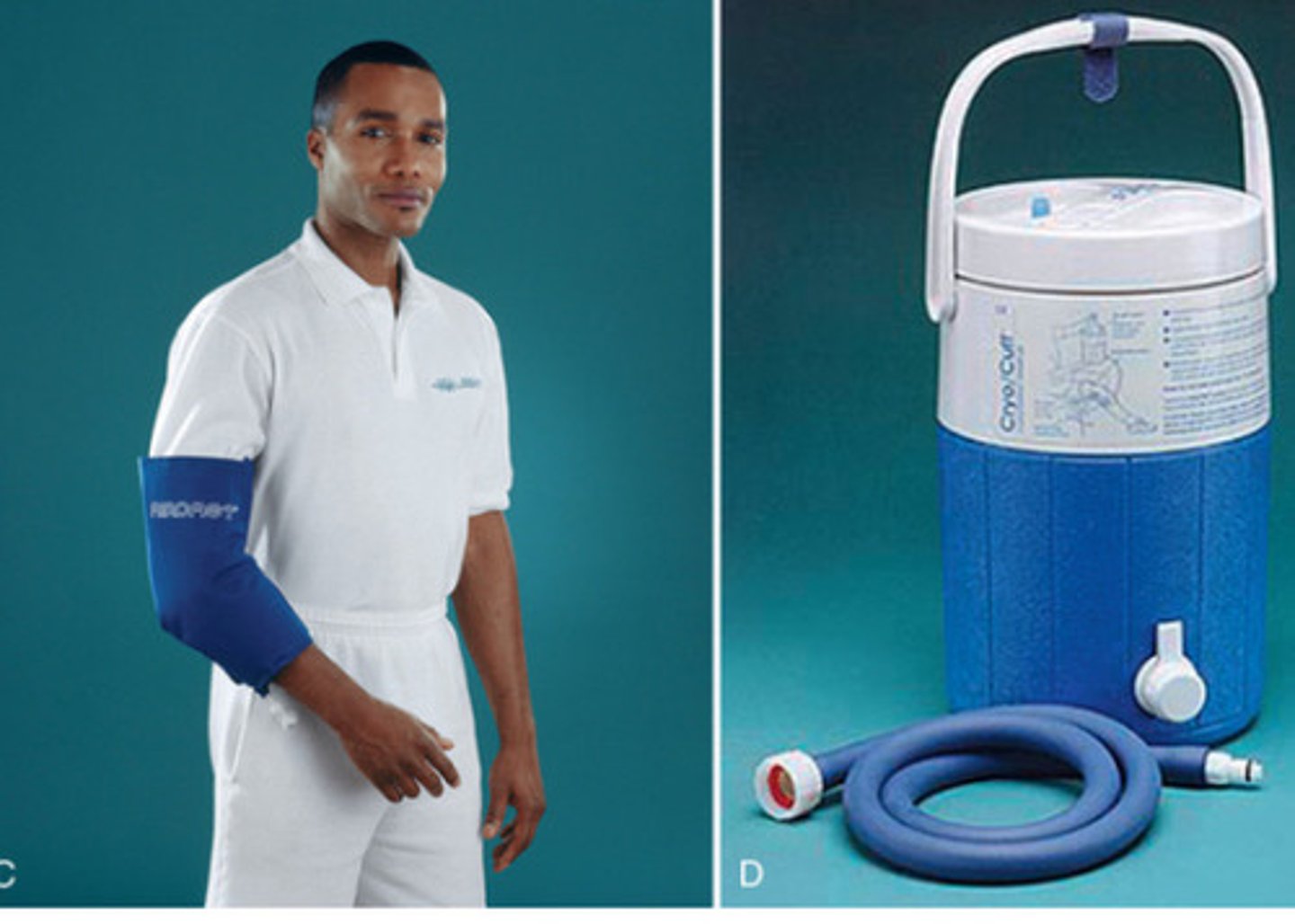
Vapocoolant is used to treat?
"Stretch is the Action spray is the distraction"
Used to treat Trigger Points

Ice Massage **
Can use a cup of crushed ice, ice is directly on skin and being moved to cause a similar effect to an icepack
Contraindications of Thermotherapy
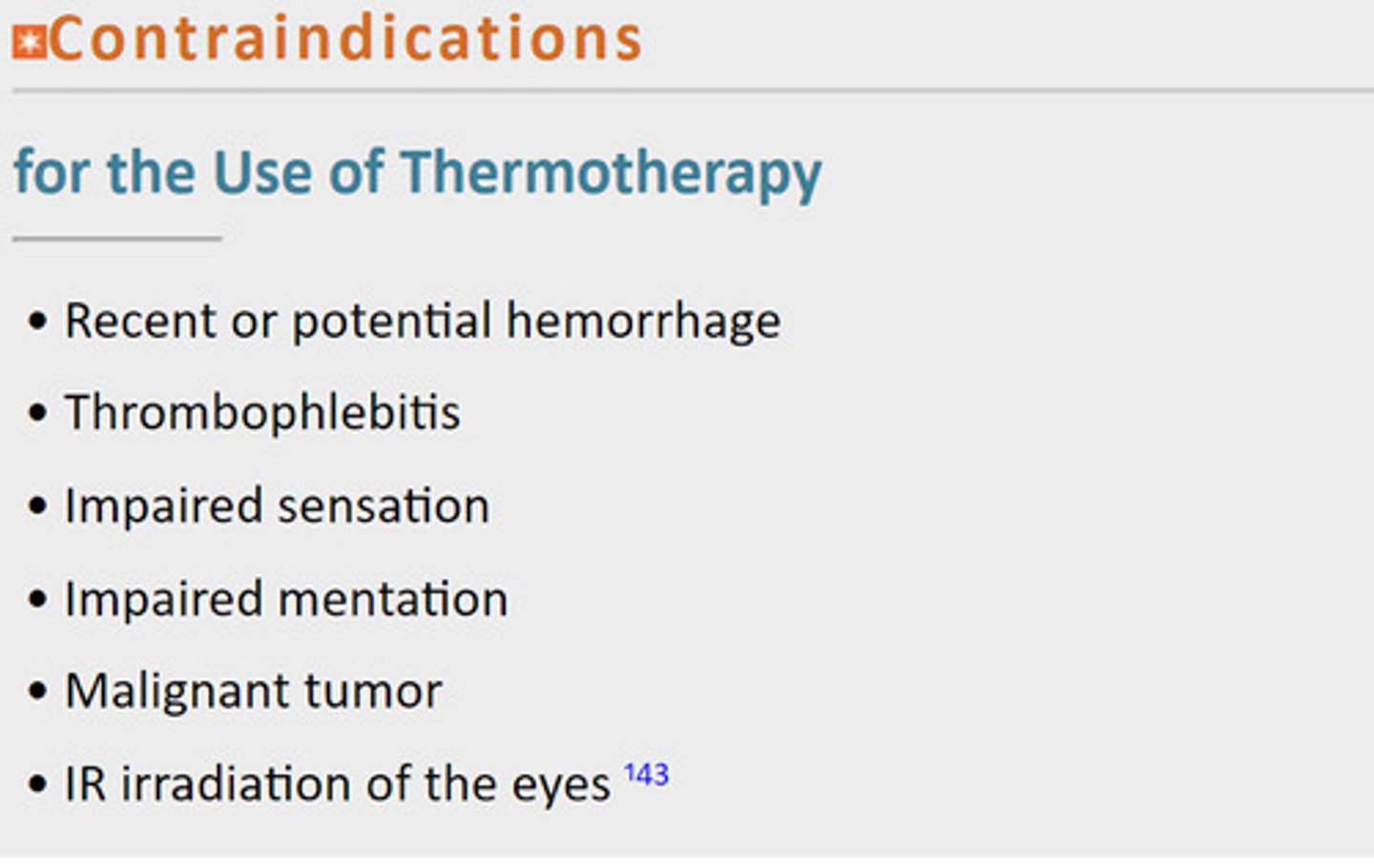
Helen threw impala Imps mad irregularly HTIIMI
Adverse Effects of Thermotherapy
Burns
Fainting
Bleeding
Skin and Eye Damage From Infrared Radiation
For hot packs how long to heat before use and between uses?
How many layers of towel for a hot pack? What about with hot pack covers?
Heat hot packs for at least 2 hours before initial use and for 30 minutes between uses.
Wrap the hot pack in six (initially and on top of pt) to eight layers (pt lying on top hot pack) of dry towels. Hot pack covers, which come in various sizes to match the hot packs, can substitute for two to three layers of towels.
Paraffin
Wax meant to insulate hand and warm instead of hot pack. Usually wrap in plastic and mitts to help keep the heat in.

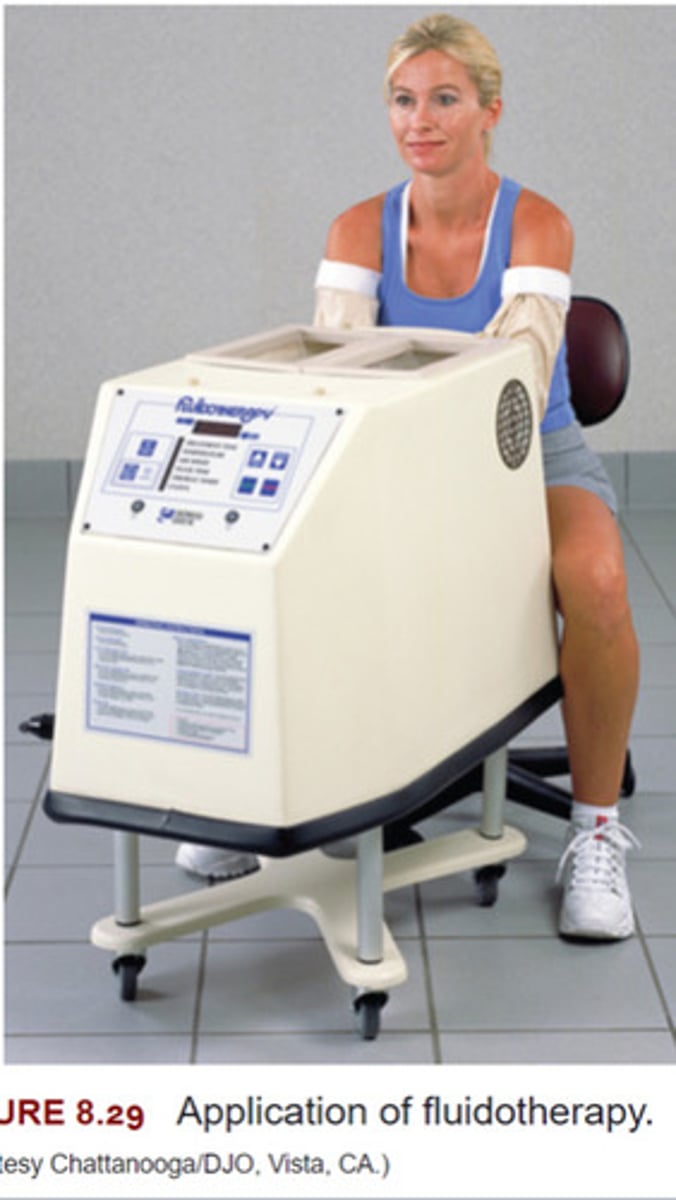
Fluidotherapy
Dry heating agent that transfers heat through convection (Air)
Infrared Lamp

Contrast Bath is used for what benefits while avoiding what?
-Hydrotherapy used to achieve the benefits of heat including decreased pain and increased flexibility while avoiding increase edema.
-The Varying sensory stimulus is thought to promote pain relief and desensitization

Table Cryotherapy vs Thermotherapy
Cryo = vasocontriction
Thermo = vasodialation
Ultrasound is most effective on what tissue?
Ultrasound is a type of sound and like all forms of sound, consists of waves that transmit energy by alternately _____ and _____ material
-Ultrasound most effectively heats deep tissue with a high collagen content such as tendons, ligaments, joint capsules, and fascia.
-Ultrasound is a type of sound and like all forms of sound, consists of waves that transmit energy by alternately compressing and rarefying material.
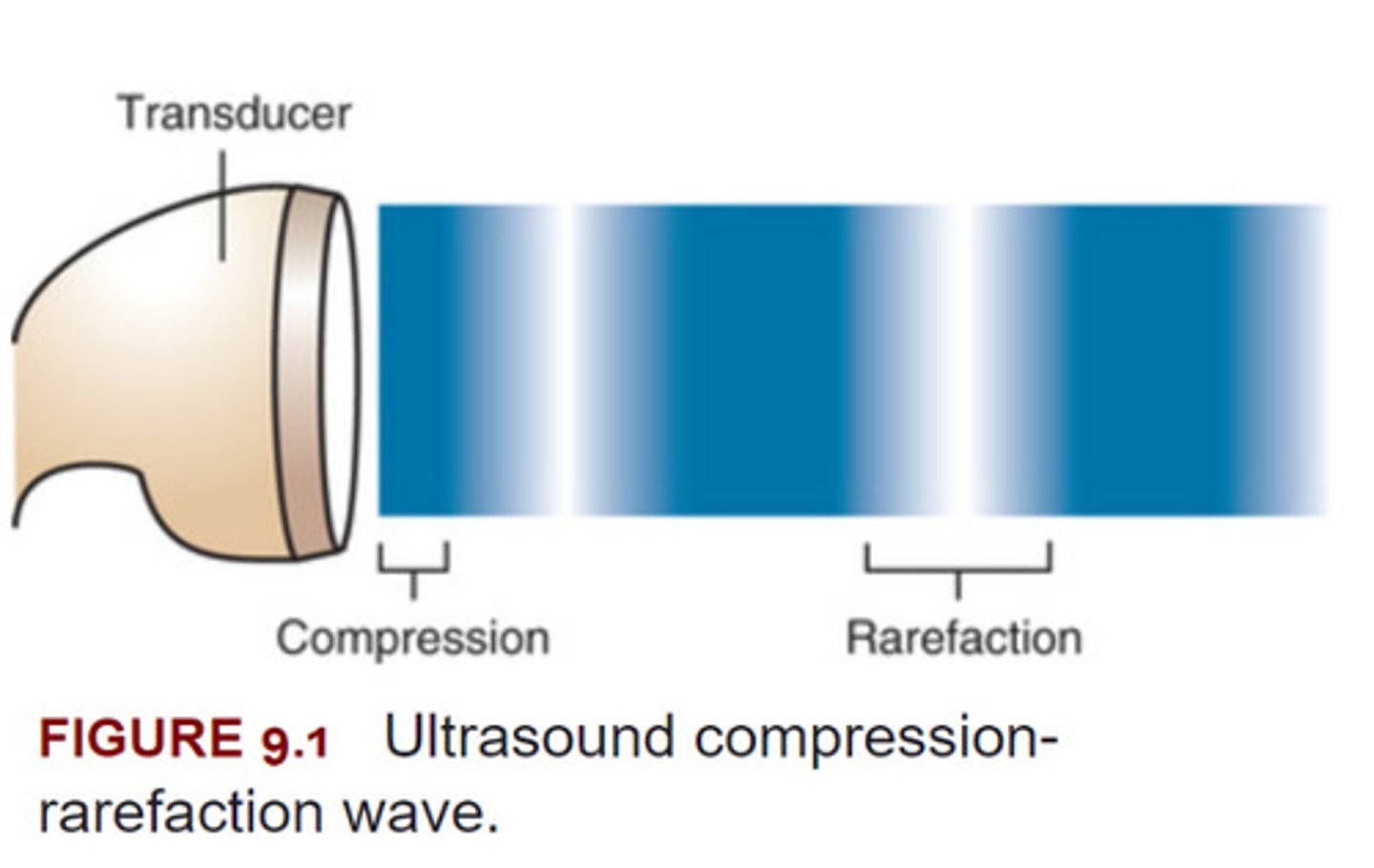
What is phonophoresis
Phonophoresis (also known as sonophoresis) is the application of ultrasound in conjunction with a topical drug preparation as the ultrasound transmission medium.
-The ultrasound is intended to enhance delivery of the drug through the skin, thereby delivering the drug for local or systemic effects
Contraindications for Ultrasound
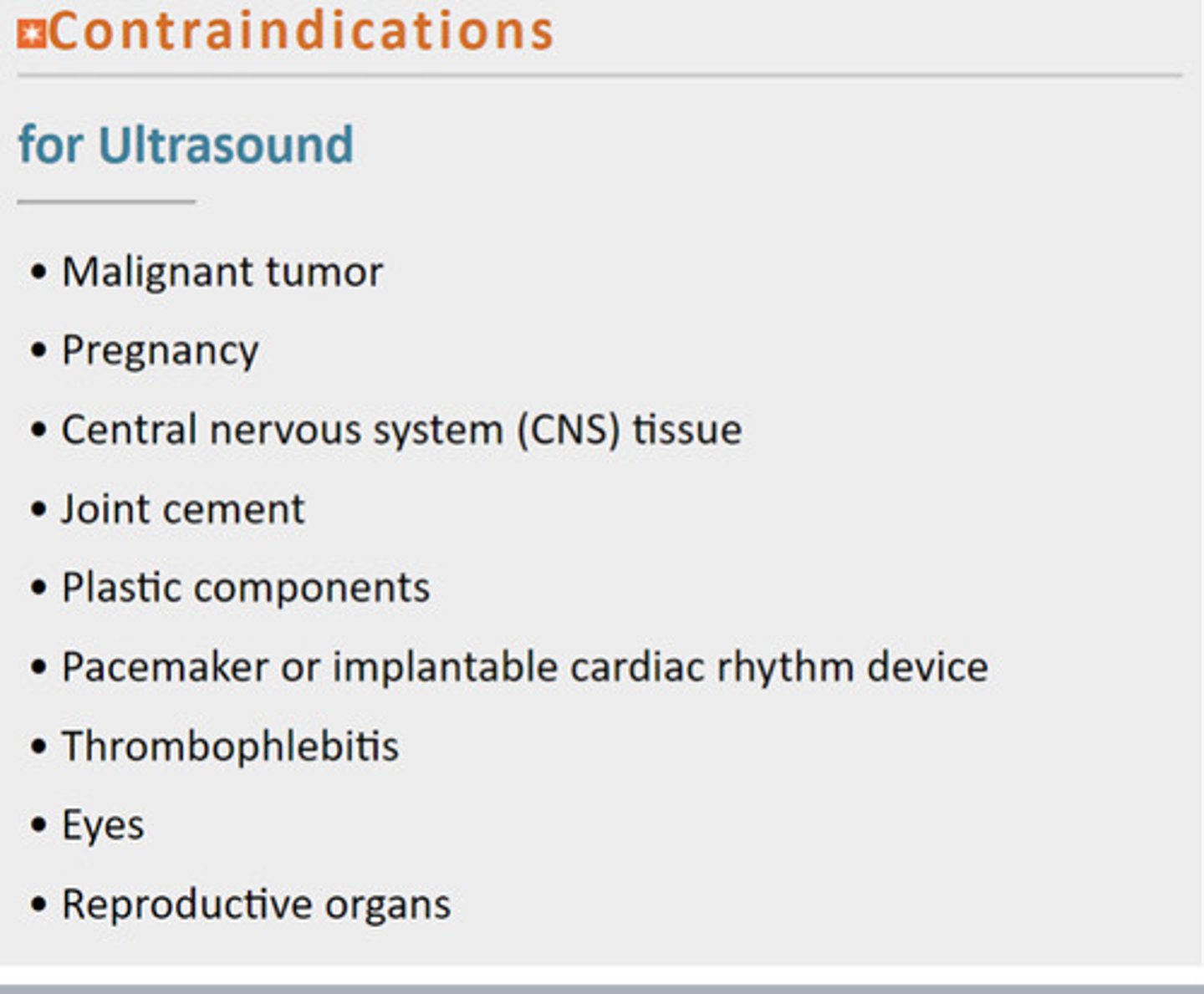
Mail Pregnant central joins plastic peace through every reproduction MPCJPPTER
Frequency for US is for?
When is 1 MHz used VS 3 MH
The frequency is selected according to the depth of tissue to be treated.
For tissue up to 5 cm (2 inches) deep, 1 MHz is used; for tissue 1 to 2 cm (1 inch) deep, 3 MHz is used
Duty Cycle for US is used for?
100% is used for VS 20% and below?
The duty cycle is selected according to the treatment goal.
When the goal is to increase tissue temperature, a 100% (continuous) duty cycle should be used.
When ultrasound is applied where only the nonthermal effects without tissue heating are desired, pulsed ultrasound with a 20% or lower duty cycle should be used.
What is Intensity for US? When do you use 1.5 - 2.0 W/cm² and 0.5 W/cm²
Values for acute subacute and chronic?
If doing superficial thermal, what value?
What and when should the patient feel if US is used to increase tissue temp?
Intensity is selected according to the treatment goal.
When 1 MHz frequency ultrasound is used, an intensity of 1.5 to 2.0 W/cm2 generally produces this effect.
When 3 MHz frequency is used, an intensity of approximately 0.5 W/cm2 is generally sufficient.
(A lower intensity is effective at the higher frequency because energy is absorbed in a smaller, more superficial volume of tissue, resulting in a greater temperature increase with the same ultrasound intensity)
0.5 W/cm² for as non thermal as possible (Acute) and moving it up to 1 for subacute and chronic would be 1.5 - 2.0
If you do anything thermal superficial you have to keep intensity low at 0.5 all the time to avoid burns
When the goal is to increase tissue temperature, the patient should feel some warmth within 2 to 3 minutes of initiating ultrasound application and should not feel increased discomfort at any time during the treatment.
Duration and how to preform?
5-10 minutes. 8 to charge
Small concentrc circles that are 2x the area of tranducer
Area to treat
twice the size of the transponder
Number and Frequency of Treatments (Thermal and non thermal)
Ultrasound Thermal Stage (Sub, chronic) :
When treatment three times a week is recommended
ultrasound at nonthermal (acute)
May be applied at earlier stages, when treatment may be daily
sequence of treatment for US
If US is used to heat, when should it not be applied?
When should it be applied to increase collagen extensibility to maximize increase in length produced by stretching?
In most cases, ultrasound may be applied before or after other interventions.
however, when ultrasound is used to heat tissue, it should not be applied after any intervention that may impair sensation, such as ice.
Also, when thermal level ultrasound is used to increase collagen extensibility to maximize the increase in length produced by stretching, the ultrasound must be applied directly before and, if possible, during application of the stretching force.
Moving the Ultrasound Head should be how many inches per second?
1-2 inches per second
Diathermy is essentially?
Difference between it and US and Hot pack?
Essentially large Static Ultrasound. main difference is diathermy covers a larger area than US while also being able to penetrate deep tissue unlike hot packs.
Application of shortwave appxt 1.8-30MHz Frequency and 3-200m wavelength.
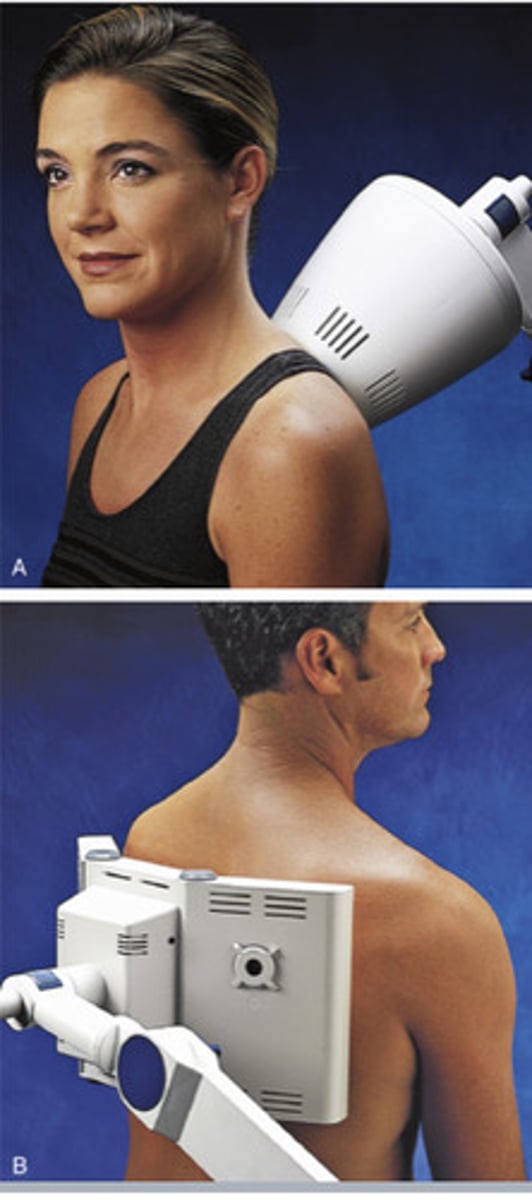
Effects of Diathermy
Diathermy is specifically used to heat large, deep areas of tissue. Diathermy produces thermal effects in both superficial and deep tissues; for example, it increases circulation in the skin, subcutaneous tissues, and muscles, 18 , 22 , 24 , 25 and it increases deep tissue extensibility. 26 , 27 This is in contrast to superficial heating agents, as described in Chapter 8, which increase the temperature of only the outer few millimeters of tissue, and in contrast to ultrasound, 28 which heats small but deep areas of tissue (discussed in Chapter 9).
Nonthermal Effects
Altered Cell Membrane Function and Cellular Activity
Increased Microvascular Perfusion
Contraindications for Diathermy

Contraindications for Thermal-Level Diathermy

Contraindications for Nonthermal Shortwave Therapy

Inflammation Stage
Prepares the wound for healing
Proliferation phase
Rebuilds damaged structured and strengthens the wound
Maturation Phase
Modifies Scar into its mature form
Stages of Healing
Cardinal Signs of Inflammation
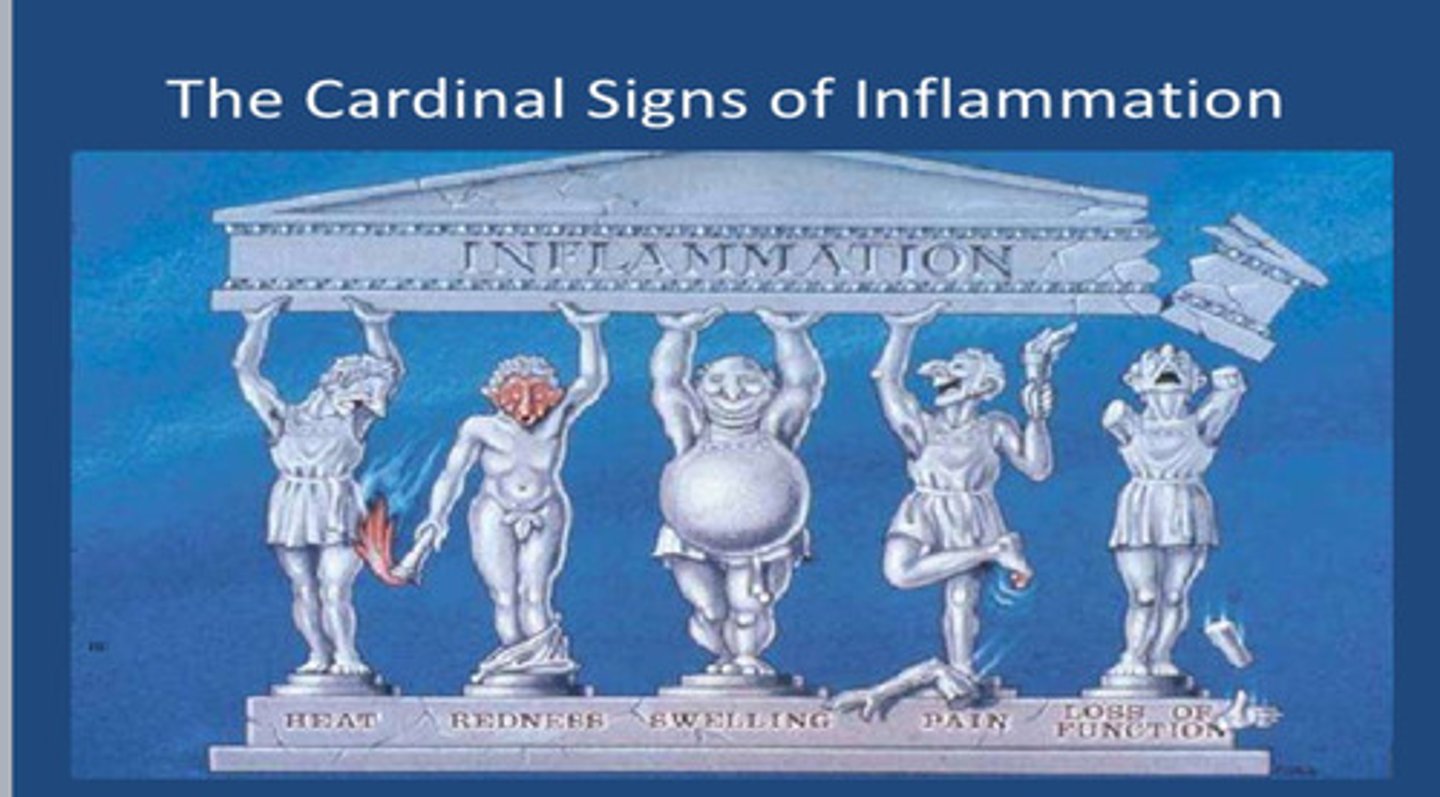
Acute Stage
Inflammation, pain, swelling. Everything is trying to heal the area.
Subacute Stage. The tissue is what collagen type?
By what day does it get replaced and what does it get replaced by?
how many weeks after an injury does a wound healing regain 80% of its strength?
Proliferation Phase (becoming more organized)
Initially fibroblasts lay down a weak collagen in an unorganized orientation (Type III)
By day 12 Immature Type III Fiber starts getting replaced with type I collagen
6 weeks afte injury when a wound is healing well it will have 80% of its strength.
Chronic Stage
During the maturation phase (chronic stage), the collagen synthesized and deposited is predominantly type I.
Chronic Inflammation: what two ways can it arise?
Chronic inflammation is the simultaneous progression of active inflammation, tissue destruction, and healing.
* Chronic inflammation can arise in one of two ways.:
- The first follows acute inflammation and can be a result of the persistence of the injurious agent (e.g., cumulative trauma) or some other interference with the normal healing process.
- The second may be the result of an immune response to an altered host tissue or a foreign material (e.g., an implant or a suture), or it may be the result of an autoimmune disease (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis).
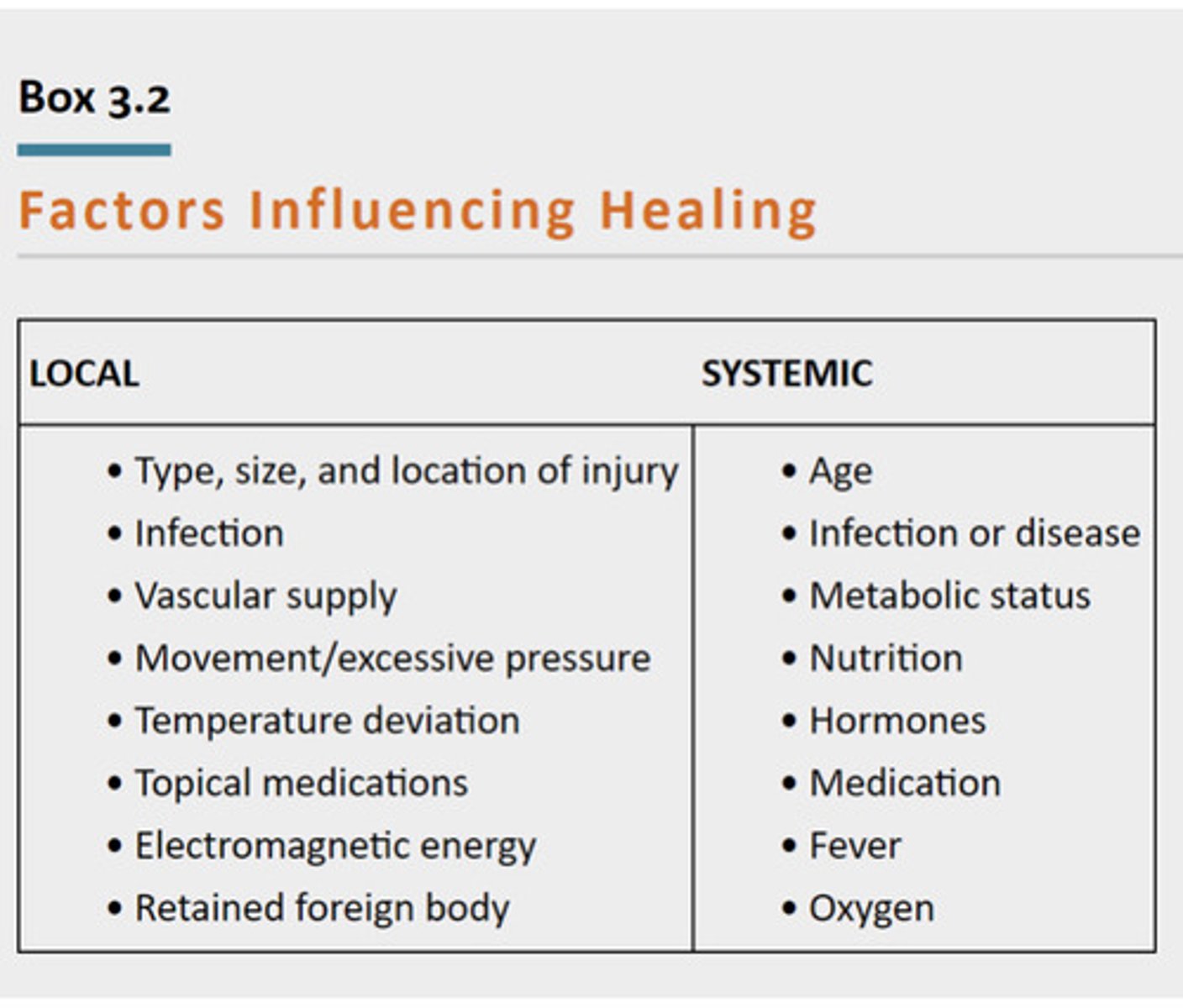
Factors Influencing Healing (Local and systemic)
****
What is Pain?
Pain is not the same as nociception. Pain is an output of the brain triggered as part of the process of converting afferent action potentials into conscious awareness.
Pain is defined as
"an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage"
Types of Afferent Nuerons
C fibers
A-delta fibers
A-beta fibers
C Fibers
Large but Unmyelinated
Long pain (Second pain, is not immediate more throbbing than sharp)
Also known as group IV afferents, are small unmyelinated nerve fibers that transmit action potentials relatively slowly—at 1.0 to 4.0 m/second. 10
A-Delta Fibers
-Small but Myelinated
-Immediate/Sharp Pain
Also known as group III afferents, are small-diameter myelinated fibers that transmit action potentials faster than C fibers—at approximately 30 m/second.
A-beta fibers
Big and Myelinated (Nonnociceptor)
"Makes everything A Beta"
Light touch
transmit nonnociceptive sensations related to vibration, stretching of skin, and mechanoreception. A-beta fibers have their own specialized nerve endings located in the skin, bones, and joints and relatively large myelinated axons that allow them to conduct impulses more quickly than A-delta or C fibers
Endogenous Opiod Theory and Gate control theory
EOT: Bearable Pain causes our body to release opioids. Motor stimulation to get pain relief to hormonal release (Endorphins) Example is doing long distance running and eventually body releases endorphins
body's natural pain relief system. production of endorphins = decreased pain. during stress, pain or high intensity exercise the body releases these opioids which bind to receptors releasing NT'S leads to reduced pain perception
Bearable levels of painful stimulation such as topical preparations that cause the sensation of burning or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) that causes the sensation of pricking or burning have been shown to reduce the intensity of less bearable preexisting pain in the area of application and in other areas.
GCT: Exploit A beta non-nociceptors and use its sensory benefits
Many physical agents as well as other interventions are thought to control pain in part by supplying no nociceptive input to the sensory nerves, thereby inhibiting activation of nociceptive interneurons and blocking the transmission of nociception at the spinal cord
suggests that inhibition of nociceptive signals has opposite effect. so when BOTH type of fibers (C, A delta AND A beta) are activated it "closes the gate" inhibiting transmission of pain signals to the brain.
central sensitization
Central sensitization can cause pain that does not fit a typical anatomical or neurological distribution
Pain Management approaches: What type of agent should be used first before another? Can they both be used at the same time?
Use physical agents before pharmacological agents, many can be used in conjunction however
Muscle Tone
When it tone bad?
Tone will be higher right before a run compared to relaxing on the beach with alcohol, which would be a lower tone
High tone and low tone are only a problem if they cant function (To low or to high)
Tone Abnormalities
Quantitative and qualitative measure for tone?
Hypotonicity, or low tone, means that the muscle has decreased resistance to stretch (Down syndrome ad poliomyelitis)
Hypertonicity, or high tone, means that the muscle has increased resistance to stretch. Rigid or spastic
Quan: When a voluntary contraction is measured, a patient is asked to “push against the device with all your strength.” When muscle tone is measured, a patient is asked to “relax and let me move you.”
Qual: The clinician obtains an impression of the muscle tone relative to normal by passively moving the patient at varying speeds. When muscle tone is normal, movement is light and easy. When muscle tone is decreased, movement is still easy or unrestricted, but the limbs are heavy, as if they are dead weight, and the joints may be hypermobile. When tone is increased for a particular muscle, the movement that mechanically stretches that muscle is stiff or unyielding.
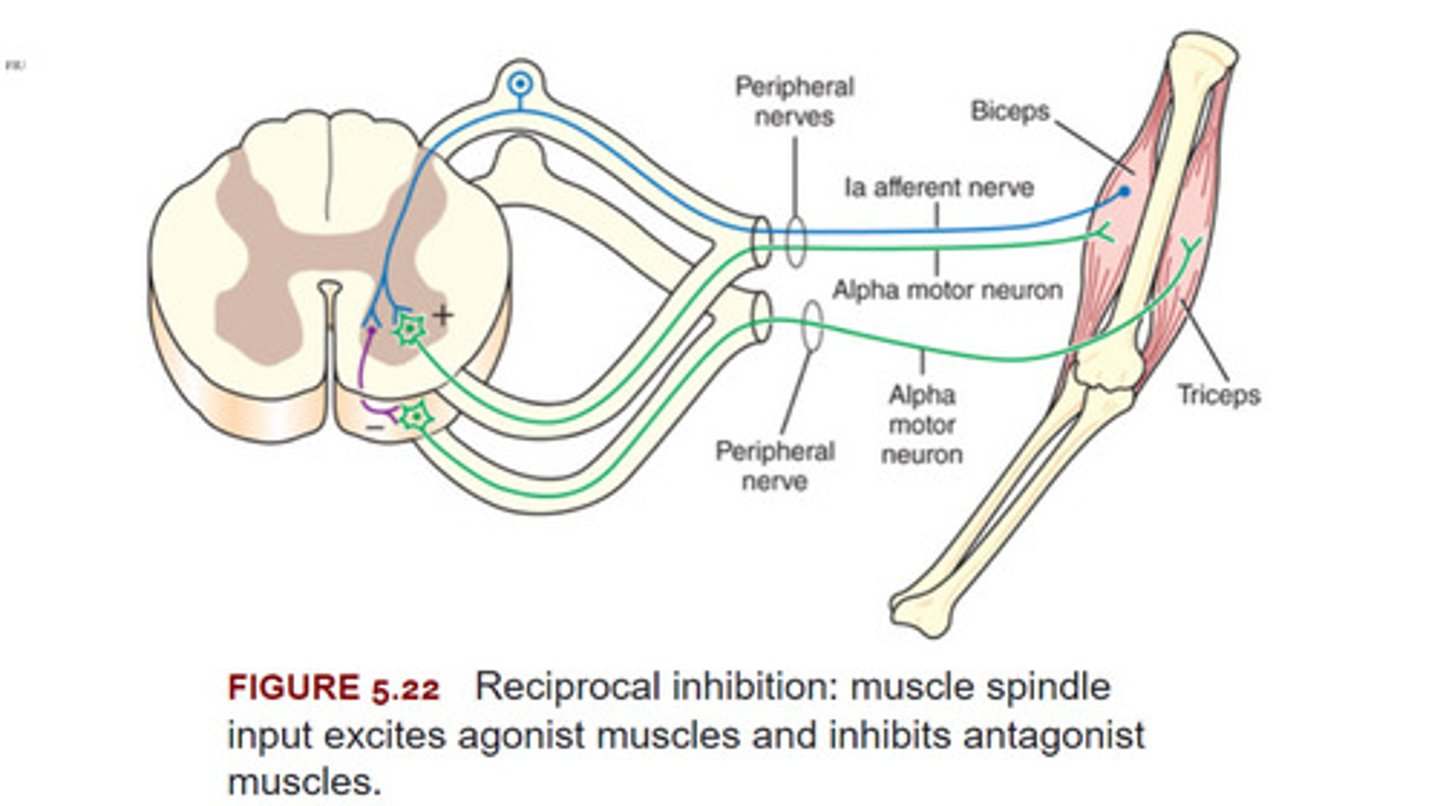
Reciprocal Inhibition
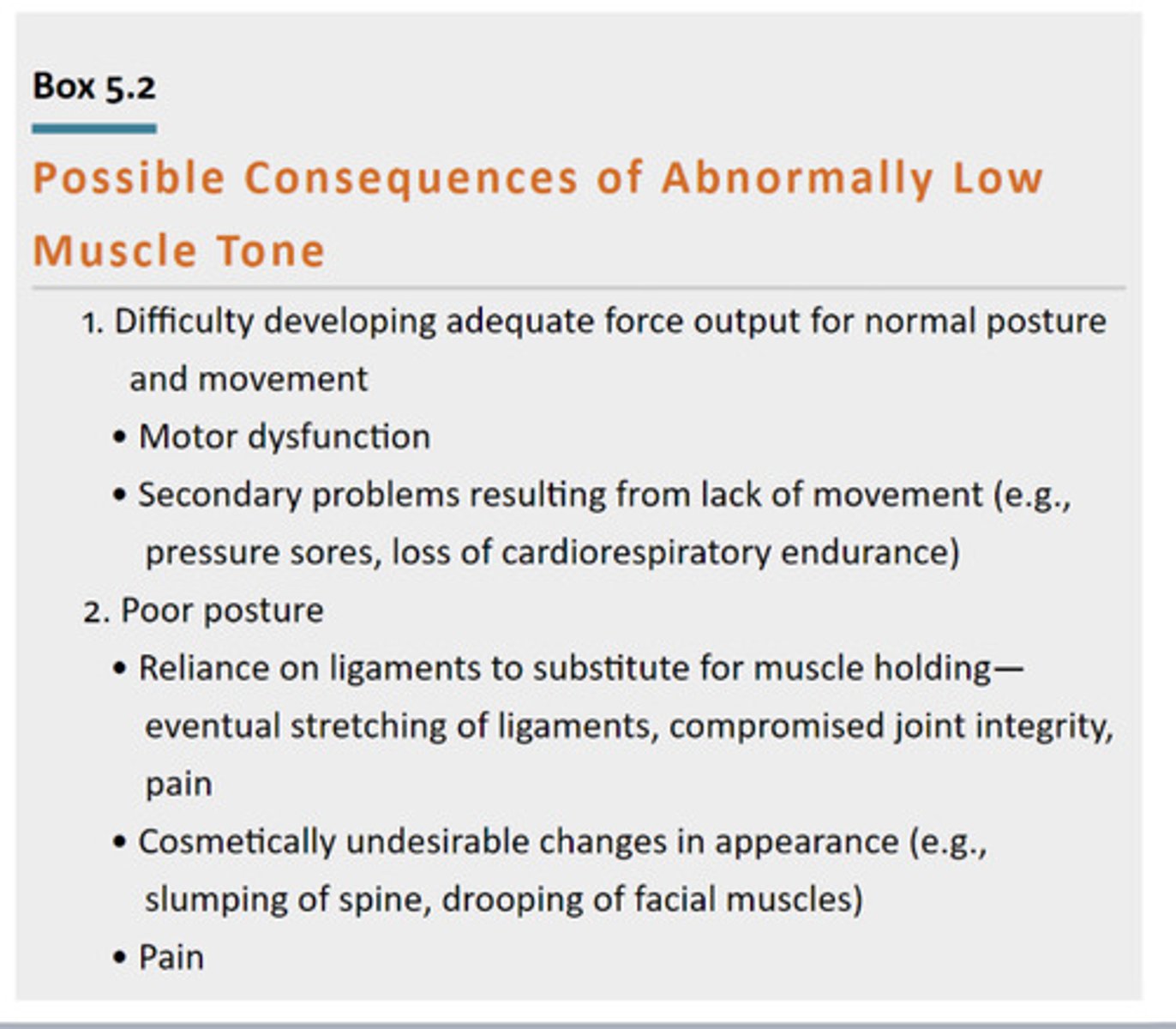
Consequences of Abnormally Low Tone
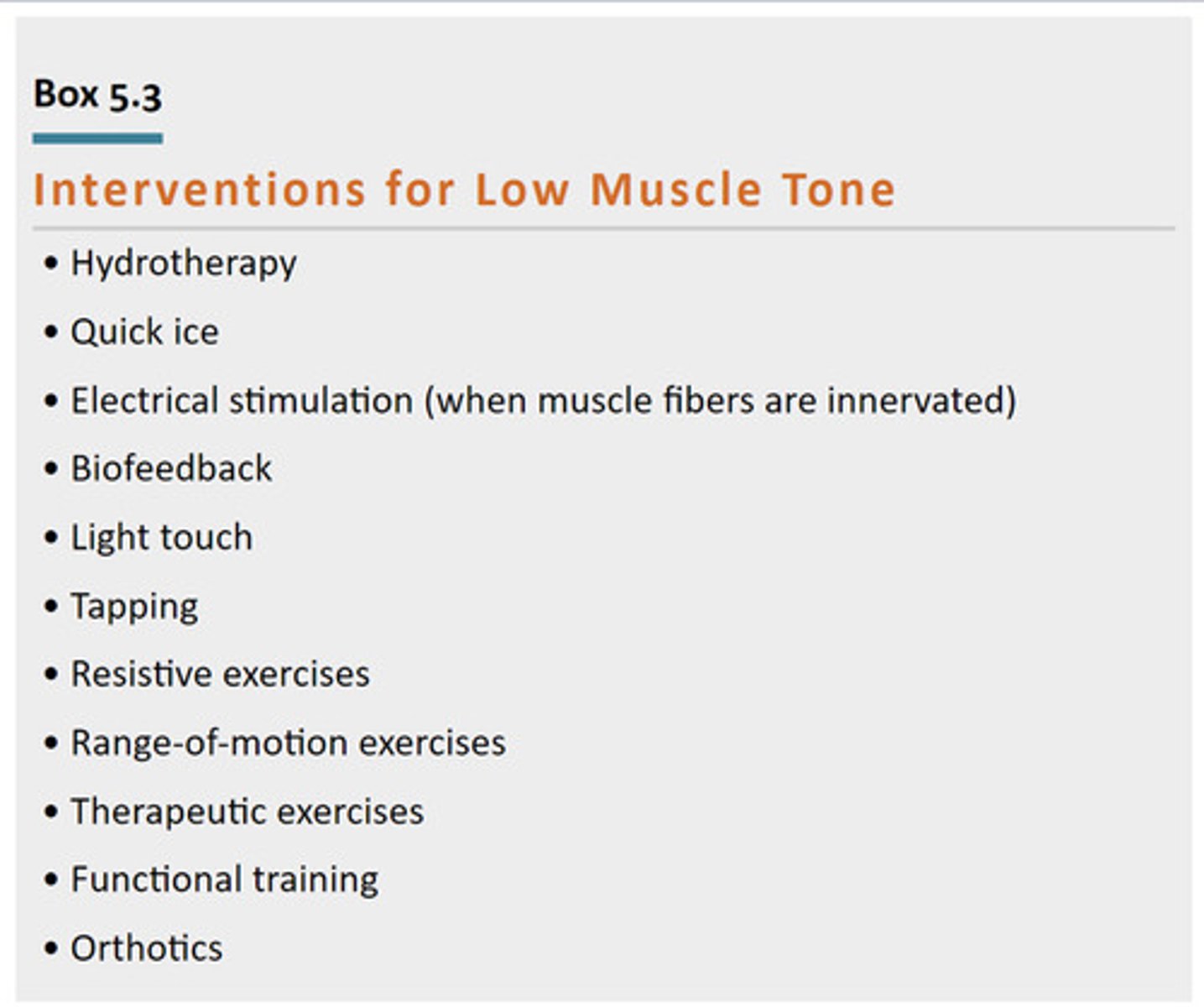
Interventions for Low Muscle Tone
Ways to activate or fire it
Abnormally High Muscle Tone

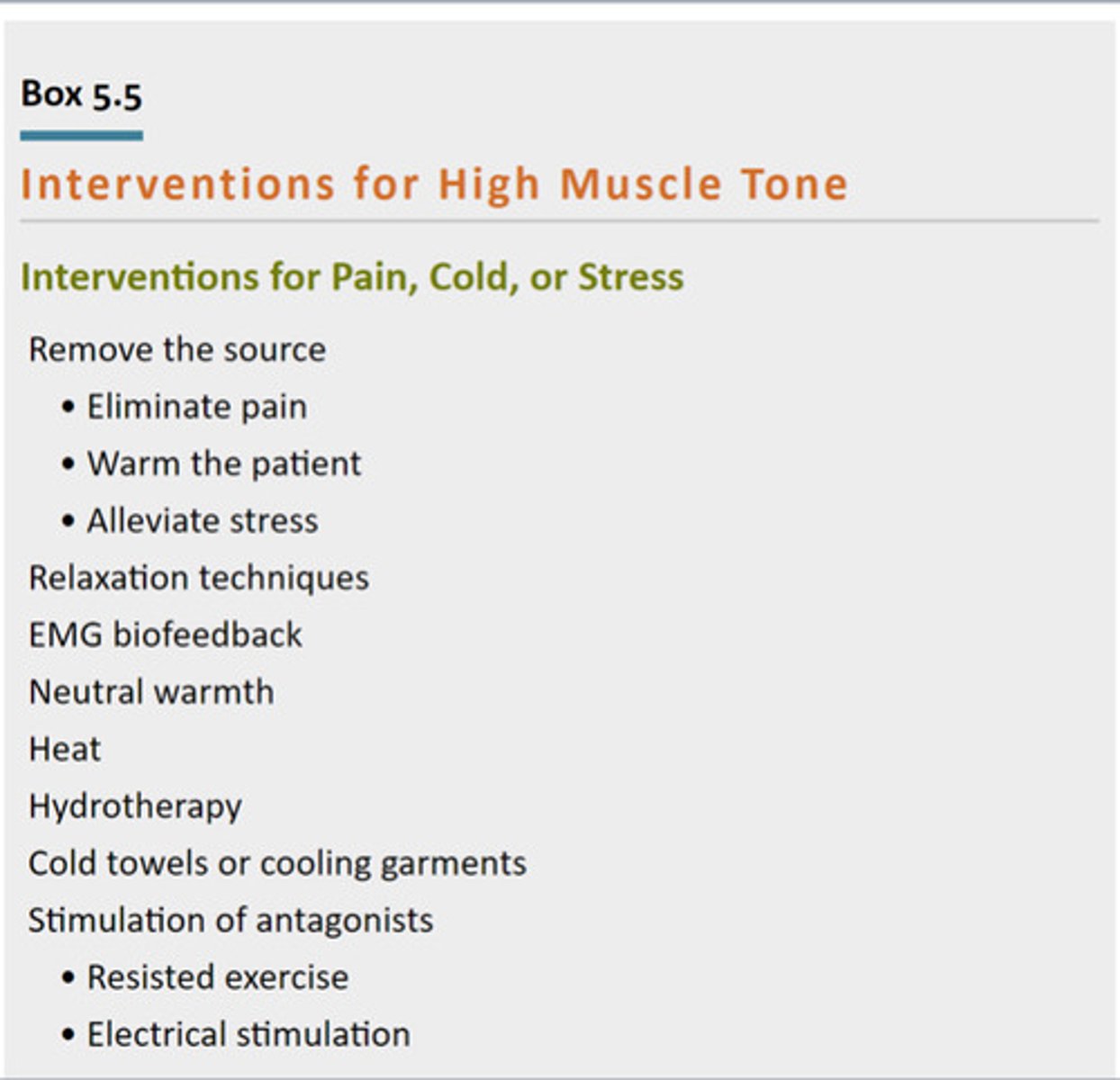
Interventions for High Muscle Tone
Ways to relax it
Motion Assessment Chart
KNOW FOR EXAM ****
Spinal alpha neurons
Weak leg, cant fire very well, firing the other leg will have cross over benefits.
Supraspinal alpha motor neurons
From brain down.
Crespo is coming at you to give you a hug
You stumble every time he hugs you
So your brain tells you to tense up your muscles before he gets to you so you don’t fall
Peripheral stimulation on muscle (Peripheral alpha neurons)
Which way do they move?
Away from CNS
Ahole Friend sees you Relaxing at the beach, pours ice cold water on your back Periphery Reacts cuz of cold sensation causes muscle to tense.
"SAME" Afferent vs Efferent
Sensory - Afferent
Motor - Efferent
Ultrasounds (nonthermal) "MAC"
With heat? What will the patient feel?
M-(Microstreaming) cell Membrane permeability
A- (acoustic streaming) Alleviates Pain
C- (Cavitation)
Brings nutrients to the area (Inflammatory process)
These MAC effect still occur with heat (100%), as all it does it just add heat to it. They will feel slight warmth.
Ultrasound Thermal
Same effects as nonthermal but now with heat.
Verbal cues should be "at most patient should feel a slight warmth"
Hot pack is resting on pt
6 towels to start (6 if on top of patient, 8 if they are supine on one)
(Remember hot pack covers count as 2 towels. So if they are used then 4 towels + hot pack cover on top and 6 + hot pack cover if supine on one. )
Pt is resting on hotpack
8 towels to start
Process pt experiences when putting on a cold pack (proper order of events, know order)
Intense cold, Burn, aching, and finally numbness & analgesia
What can we do before stretching to improve mobility
Some form of Ultrasound
Thermal vs Nonthermal
Ultrasound Depths
3MHz- Superficial 2cm, just under an inch
1MHz - Deep 5cm almost 2 inches
Ultrasound vs Diathermy vs Hot packs
Ultrasound
Deep and surface level heat (covers smaller area)
Diathermy
Deep and surface level heat (Larger areas)
Massage therapy/modalities are ____ of a therapeutic program
Tool (Something used to get to one point to another, not the whole therapy)
What can help with healing and the inflammatory process?
Proper nutrition.
L arginine (Meats poultry and dairy)
Glutamine (Animals or plants)
Omega 3 (Oily fish, beans, seeds, avocados)
Which tissue heals fastest?
Two that are slower?
One that is the most slow?
Which type of tissue doesnt have a good capability to heal at all?
Muscle
Tendon and ligaments
Bone
Articular cartilage
Evelio drops a brick on your foot. What is the initial pain receptor and type of receptor?
What is the dull pain after that lingers after and type of receptors?
Rubbing done to make yourself feel better is and type of receptors?
A Delta (nociceptors)
C receptors (nociceptors)
A beta (Non-nociceptors)
To manage pain as a whole what is the best approach?
Single modality, just behavioral management, medication?
TEAM APPROACH/ COMPRENSIVE APPROACH using multiple methods. So larger pain management team approach is always preferred.
Types of dyskinesia
of abnormal movement that is involuntary and has no purpose is dyskinesia
choreiform movement or chorea (dance-like, sharp, jerky movements), ballismus (ballistic or large throwing-type movements), tremor (low-amplitude, high-frequency oscillating movements), and athetoid movement (worm-like writhing motions).
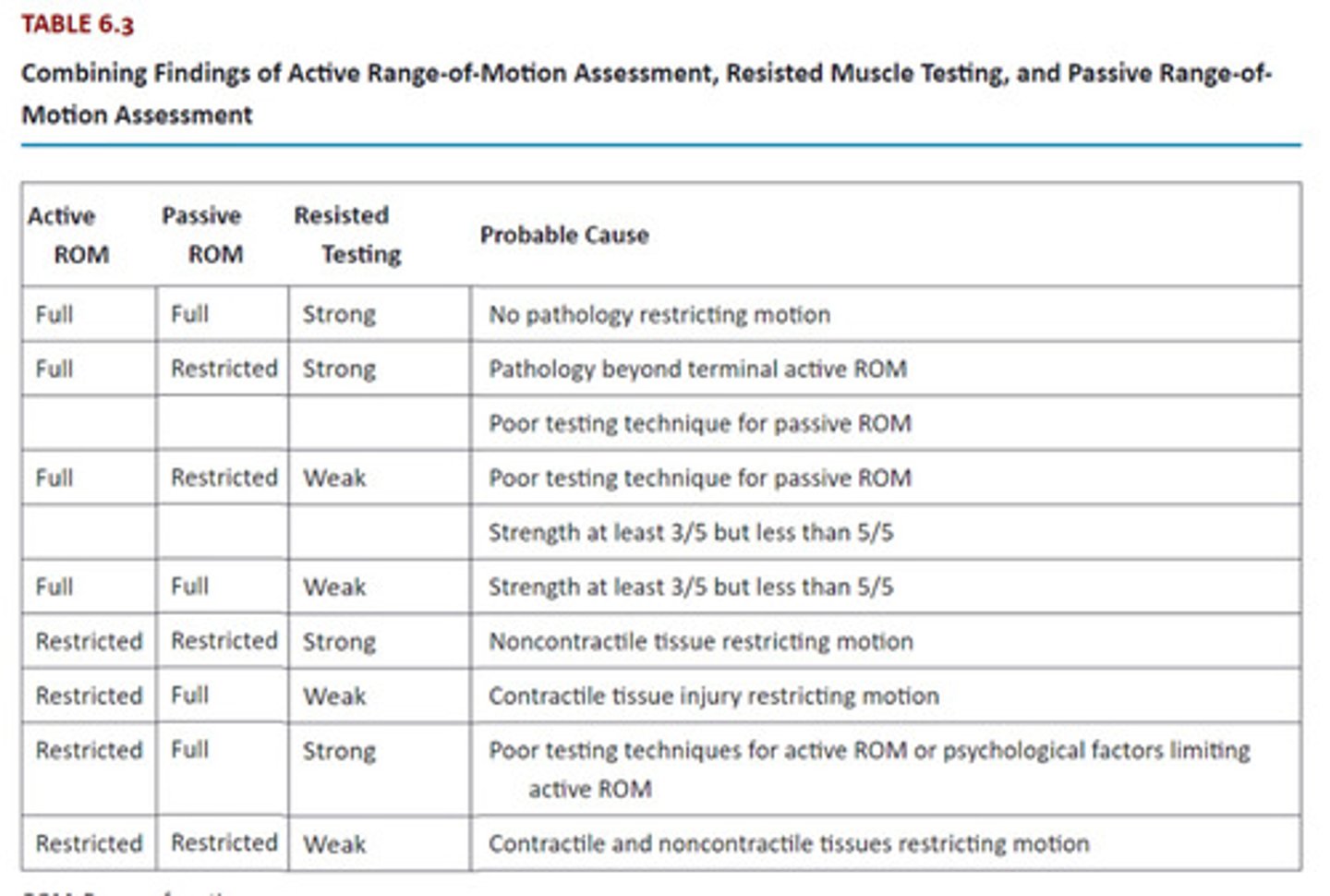
Motion restriction treatments?
AROM, PROM, AAROM
Stretching dynamic static and PNF
MUA manipulation under anesthesia
Prior to doing anything to help a patients ROM, what should you do before you stretch them?
Warm them up, Thermal things not cold (obvious but he did mention it)