Geography
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Yay ig?
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
How much water is fresh water?
2.5% of the total water is fresh
How much of the total water is taken up by oceans?
97.5%
How much of the total water is for plants and animals?
0.8%
How is water distributed across Earth?
not evenly
Why is variation of water uneven?
Because climate change, different rainfall patterns, and changing river levels like in the Darling River.
What are the main rivers in the Murray darling basin?
The Murray and darling river
Why is the Murray-Darling Basin important?
Because it is the main food source and supports many cities and towns
What is liveability?
Describes how good a place is to live in
What are the basic requirements for ALL liveable places?
Fresh water, Food supply, Shelter, Safety, access to services, environment and transport
What is objective?
basic needs to live
What is subjective?
WANTS that make life enjoyable
What factors influenced where early indigenous Australians lived?
Factors like reliable fresh water, abundant food, and natural resources led early Aboriginal Australians to settle along the northern, eastern, and southern coasts, as well as the Murray River.
What factors influenced where modern Australians lived?
Factors like access to suitable housing, essential services, Job opportunities, entertainment, and a preferred climate leads them to the east coast and other coastal areas. But age and interests also influence where they live.
What is the importance of water for life on Earth?
it helps grow food, supports the environment, provides clean water at home, generates power, supports industry, and plays a role in spiritual and cultural life.
How much of Australia’s rainfall is collected in rivers?
12%
What is an Urban place?
Big towns or cities where lots of people live
What are examples of Urban places
Kellyville, Blacktown, Parklea
What is a coastal place?
Places near or along the sea and ocean
What are examples of coastal places
Bondi, Gold coast, Sydney, Melbourne
What is a Remote place?
Far away cities or towns often hard to get to
What is an example of a remote places
Alice springs, Yuendumu,
What is a rural place?
Countryside areas with farms, open land and small towns
What are pros of Urban places?
More jobs & schools, lots of facilities and good transport
What are pros of coastal
Nice weather & beaches, good for tourism & facilites
Pros of remote places
quite & peaceful, Close to nature and tight knight communties
Many people are connected with each other through these water sources
True
What are the 3 main factors that influence where people settle?
Historical and environmental factors, Agriculture factors, Economic factors (trade and transport)
What are canal locks?
used in man-made water ways to connect different water levels
How much of the fresh water used each year goes to agriculture?
70%
How many litres does it take to produce beef?
50000L
What is the irrigation system?
Water is taken from rivers and is delivered to farms through damns, weirs, pipes etc
What is Hydro electricity
electricity generated using moving water
Where was cyclone Yasi located?
Northern Queensland, Australia
Where was cyclone Tracy located?
Darwin, Northern Territory
Where was Eastern Australian floods 2021-2022 located?
East coast of Australia
How does hydro electricity work?
A dam is built across a river creating a large reservoir, this water is then released through turbines causing them to turn then the spinning turbine rotates giant magnets around a huge coil of copper wire to create electricity
What is the largest source of renewable- non-polluting energy in the world?
Hydro electricity
Rice farming in Vietnam what is its titles?
It is the 5th biggest producer, the 2nd largest exporter and the 7th largest consumer of rice
How many people’s daily calorie needs in Vietnam are met by rice?
75%
What is the Mekong Delta?
It is called the rice bowl with more than half of the countries rice produced there. It is also flood prone.
What makes it hard to produce rice in Australia
the dryness, so farmers have to be very efficient in their use of water
How much less water do Australians rice growers use then the worlds average to grow 1kg of rice?
50% less water
What are Australia’s rice growing regions?
Murray Valley (NSW) and Murrumbidgee because they have available water and large areas of flat land
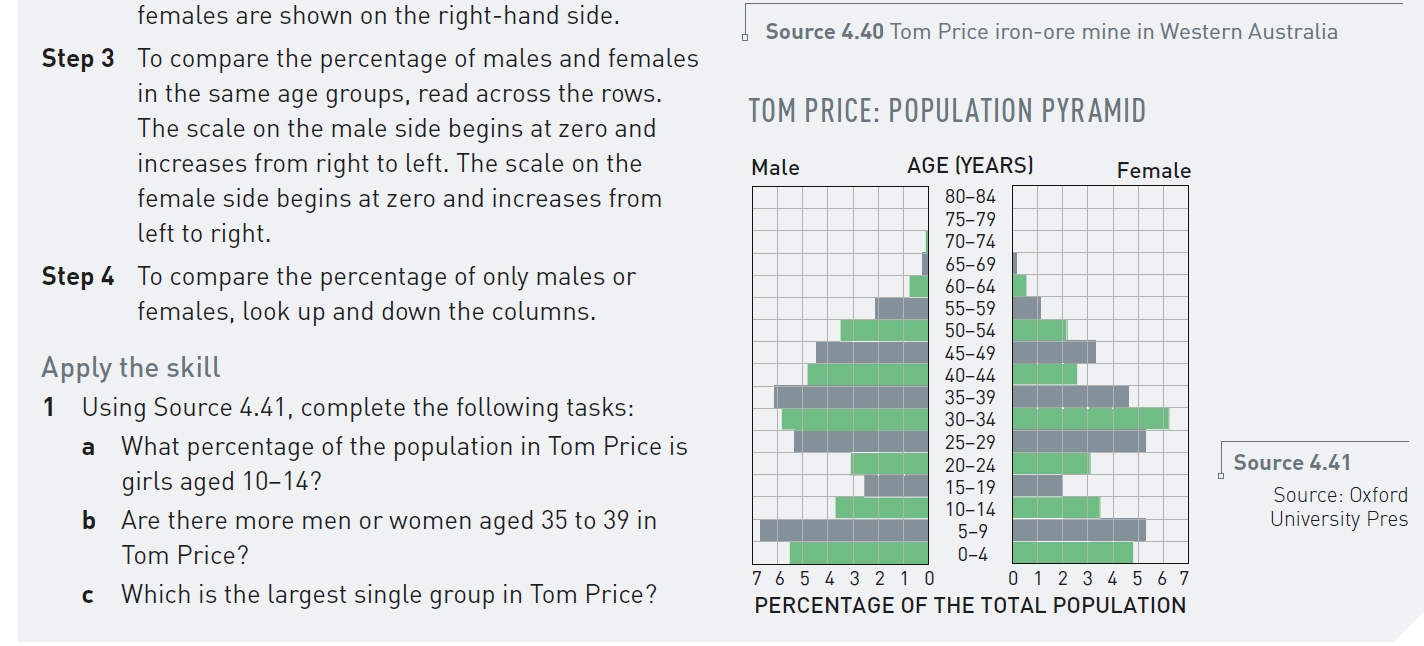
Answer A
3.5%
What are some competition uses of the Murray River water?
irrigation/agriculture, towns and cities, environment/ecosystem, industry etc
What is the largest user of water from the Murray River?
The agriculture sector
What is virtual water?
Hidden water used to produce a product (food, clothing etc)
What is green water?
water that comes from rainfall and is stored in soil
What is an example of green water
wheat grown only using rainwater
What is grey water?
Wastewater that has been used once but is still reuseable for other purposes
What is an example of grey water?
used water from a sink or bath can be reused for gardening
What are renewable resources?
they naturally replace themselves overtime
What are some examples of renewable energy?
Trees and freshwater
What is a non-renewable resource?
cannot be replaced and will run out if we overuse them
What are some examples of non-renewable resources?
Minerals, coal, oil
What is a continuous resource
Can never run out no matter how much we use them
What are some examples of continuous resources
energy from the Sun and Wind
What are some environmental consequences of global warming
Rising sea levels, more extreme weather and loss of biodiversity
What are some human and social consequences of global warming
food shortage and water scarcity
What are some different uses/values of water?
spiritual, domestic, irrigation, environmental, recreational, trade, industry and mining value
what are some causes for floods?
heavy rainfall, overflowing rivers/lakes/dams and cyclones
What is the impact of floods
damage to homes, loss of crops, displacement of people
What are the causes of cyclones?
form over warm ocean water, strong wind +heavy rain and rising warm, moist air forms cloud +thunderstorm
What is the impact of cyclones?
strong winds destroying building, trees, powerlines, damage to ecosystem and disruption to transport
What is the response of communties natural disasters?
communities help clean up damaged homes & streets, they help provide food & clothes for the neighbourhood, sandbags to control water and communities fundraise for affected families
What is water scarcity?
when there isn’t enough clean water available to meet demand
What causes water scarcity in developing countries?
rapid population/growth, low rainfall/droughts, poor water quality and lack of water, infrastructure like pipelines
Why is Australia water poor?
because it is the driest inhabited continent with low rainfall, agriculture demand, drought, warmer temperature (due to climate change and population growth
what are the main water basins?
Murray-Darling Basin, Lake Eyre Basin, Burdekin Basin and Great Artesian basin(underground)
What is a community?
a group of people who share something in common
What are the types of communities (5 p’s)?
Past (similar histories), place (live in same area), Perspective (similar beliefs), Purpose (similar goals) and practice (activities in common).
What is a local scale?
focuses on individual households, farms, businesses and towns
What is a regional scale?
Covers multiple towns, cities or districts
What is a basin scale?
manages water across entire river systems or underground water basins
What factors make a place more liveable?
Life expectancy ,nutrions, literacy and Aid