Ear Examinations
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
anatomy of the outer ear
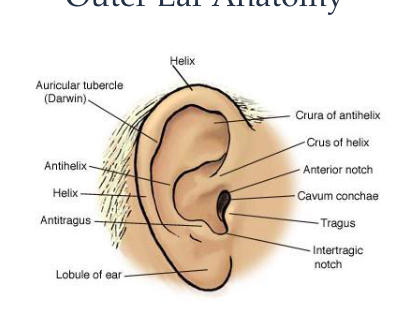
pinna
external auditory meatus
lateral surface of tympanic membrane
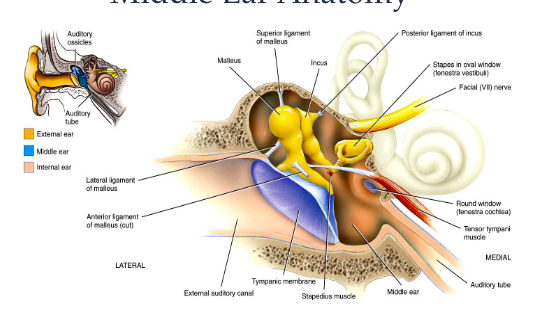
anatomy of the middle ear
medial surface of tympanic membrane
tympanic cavity
mastoid air cells
eustachian tube
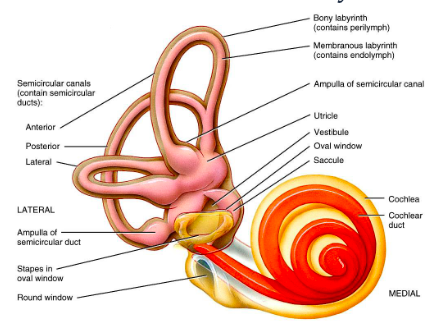
inner ear anatomy
history taking - 5 questions
pain
discharge
infections
surgery - operations
perforations
otoscopy - method before examinations
wash hands
instruct patient clearly as to what the procedure involves and will happen
consent
brief history
method - during examination
correct size speculum
left ear left hand and vice versa
pink finger touching face
pull pinna gently back and up to open and straighten ear canal
guide speculum into ear approx 1cm should be in ear-canal
observe tympanic membrane
dispose of used speculum and wash hands
what should a normal eardrum look like
pearly grey appearance
handle of malleus sometimes flushed
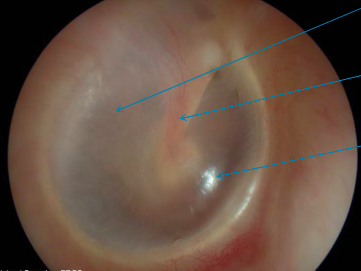
possible sights and conditions
wax
foreign bodies
infection
discharge
blood
swelling
boils, polyps
perforations
mastoid cavity
grommets
otitis externa
affects ear canal and eardrum
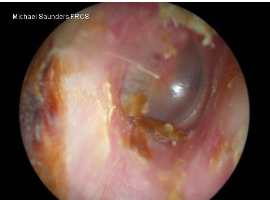
fungal aspergillus niger
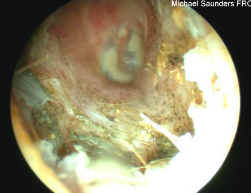
otitis media
occurs behind the eardrum
fluid (bubbles and lines) behind retracted semi-opaque ear drums
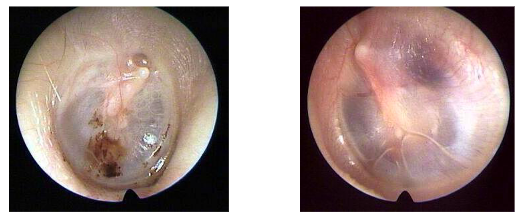
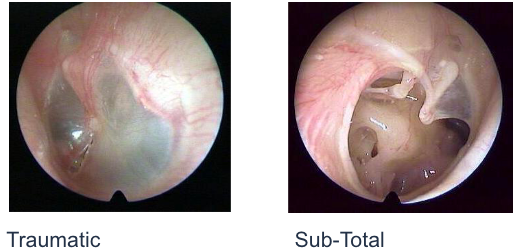
perforations
two types
traumatic and sub total
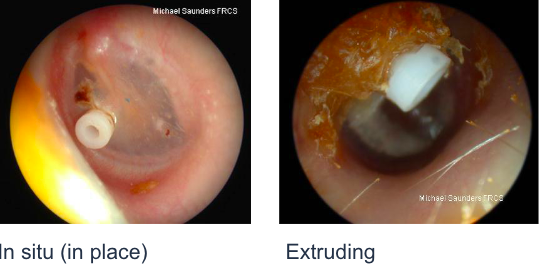
grommets (ventilation tube)
In situ and extruding