forensics Unit 2
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
DNA is a
nucleic acid
Where is DNA found
in nucleus or mitochondria
How many chromosomes do MOSt human cells have
46 total chromosomes
23 pairs
What is the role of genes
control the traits of the organisms, and therefore can vary between individuals
What shape is a strand of DNA
double helix
What are the components of DNA?
sides of helix= backbone of DNA made up of alternative sugar + phosphate molecules
sugar= deoxyribose
How is the double helix formed?
base pairings of two sugar phosphate backbones bind together
What are the 4 nitrogen bases? what are their pairs?
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine and Cytosine
help code DNA with instructions for cells
A-T and C-G
Whats the role of the genome?
Genome= total amount of DNA in all; codes the blueprint for the human body + hpw it works, tells the body to make proteins + other needed molecules
in both nucleus and the mitochondria
3 billion base pairs
Which Segment contain unique patterns?
polymorphisms, non coded DNA segments, unique patterns of repeated base sequences that are unique to individuals
Variable numbers of tandem vs short tandem?
VNTR: 9-80 base length
STR: 2-5 base length
Exons
encoded DNA with directions to build molecules
Introns
are undcoded DNA, that do not code for production of nucleus
What is the purpose of DNA fingerprinting? In what ways was it used
to distinguish between individuals of the same species by using samples of DNA
links suspects to crimes, identify body of killers
Whats the source of DNA fingerprinting? Examples?
Trace evidence; biological evidence left at crime scenes
ex: saliva, blood, semen, skin,hair roots, body tissue, cells, urine.
Steps to DNA fingerprinting?
extraction of DNA
cutting the DNA into restriction fragments
RFLPs, Restriction Fragment Length POlymorphisms
Amplifications (making copies of those fragments)
use PCR
Electrophoresis: a process that separates RFLPs accurately to their length creating a DNA fingerprint.
How is DNA separated and purified?
Cells broken down to release DNA
if only small DNA, can go to amplify with PCR
DNA cut fragments with restriction enzymes, cut DNA at base pair sequences
many different sizes
Fragments separated on the side using gel electrophoresis
injected into wells
Patterns of fragments distributed then analyzed
What is main function of PCR?
make thousands of copies of DNA that investigators want to analyze
What are the 3 steps of PCR?
Denaturation, annealing, elongation
Annealing
spontaneous pairing of complementary DNA or RNA sequences by hydrogen bonding to create a double stranded molecule.
Extension
Using the loosened nucleotides of each base to grow the complementary DNA strand. The end result is two double stranded production of DNA
Restriction Enzymes are used in what step of DNA profiling
Step 2
What do restriction enzymes do? How does this benefit the process?
thet cut DNA out a specific base sequence.
allows for the precise manipulation, cutting, and reassembly of DNA for processes like gene cloning, genetic engineering, and creating DNA fingerprints for forensic analysis.
enables scientists to isolate specific genes, insert them into vectors, and build new DNA molecules with desired traits.
What do restriction enzymes create?
restriction fragments
all different sizes because the base sequence being cut may be far apart (long fragment) or close together (short fragments)
Parts of a tooth
enamel
dentin
gums
bone
pulp
What are the parts of a tooth made of?
Calcium and phosphorus, or enamel and dentin
(Children) - How many primary and permanent teeth
20 primary
32 permanent
Collecting Bite mark evidence
photographed asap while impressions are visible
bite marks swabbed for saliva, could have DNA
different sizes: affects jaw, each unique
individualizing factors include:
Dental work (fillings, crowns, caps)
Damage (chips and cracks)
Coloration
Distances between teeth
Alignment of teeth
Dimensions of each tooth
Arch of the roof of the mouth
crossbite
One or more of the upper teeth biting on the inside of the lower teeth characterizes a crossbite.
occur in the front and/or the sides of the mouth.
Underbite
The lower teeth biting in front of the upper teeth characterizes an underbite.
caused by undergrowth of the upper jaw, overgrowth of the lower jaw, or a combination of the two
or caused by tipped back upper incisors, flared lower incisors, missing upper teeth, or a combination of all.
Open Bite
Inadequate vertical overlap of the front teeth characterizes an open bite.
caused by oral habits such as tongue thrust, digit sucking, or jaws that don’t grow evenly.
Overbite (deep bite)
a measure of the vertical overlap of the upper and lower front teeth.
Excessive overbite may be caused by disproportionate eruption of front teeth or overdevelopment of the bone that supports the teeth.
Where can glass be found in a crime scene?
breaks ins, car shootings, car accidents etc.
primary ingredients
Silicone dioxide (SiO2) or Silica
Types of Glass
Soda Lime Glass: Sodium + calcium oxide (CaO) aka lime.
most common, inexpensive and easy to melt and shape, relatively strong
used for windowpanes, glass containers, drinks
Crystal or Leaded Glass: Calcium Oxide of other glasses is replaced with lead oxide (PbO)
denser which causes sparkle as light passes through
Pyrex: used in ovenware and laboratory glassware; able to withstand wide range of temperatures.
kitchen staple
Properties of glass
distinguish difference with density, each glass has density specific to that glass
to find density, divide mass (g) by volume (mL)
Mass found by using a balance
Volume found by water displacement in a graduated cylinder.
Fractures:
The side where the impact takes place, the glass surface is compressed or squeezed together.
The other side of the glass (side away from the impact) stretches and is under tension and develops fractures.
glass is flexible, but when not able to stretch, it cracks and can break
PROVIDES CLUES: about direction and rate of impact.
How Glass used as evidence
provide clues about direction and rate of impact
glass as evidence:
photograph and identify glass b4 moving
all glass collected bc more than one type could be present and physical matches might be made
Identify and mark inside and outside of the glass
small glass= paper bibles, pill boxes etc
large glass= boxed, separate with cotton
Impressions
objects or materials that have retained the characteristics of other objects through direct contact
created when one object is pressed against another material with enough force to leave an impression of the object
ex: shoeprints, tool marks, tire tracks, bite marks and marks on fired bullet
ex: sole: pattern on bottom footwear
quality of impression depends on object + surface making the impression (how hard +soft material is, like osil mud, dust, concrete, grass, skin etc.)
Types of impressions
Patent, Latent or Plastic
Patent impressions
car travels over a liquid such as paint, blood or tar.
Latent impressions
deposited from the oil used to soften tires
Plastic Impressions
made when vehicle drives on mud, sand or snow
Impression evidence
detectives can gain info about:
the number of people at scene
movement of individuals at crime scene
entrance and exit to the scene
ex: shoemarks, tire marks, tire tracks, bite marks, marks on fired bullet, dental impressions, sole of shoe
What do shoe databases contain?
tread patterns used by different manufacturers, and can often be traced down to retailers which sell the shoe.
how can you highlight 3D impressions
spray pain or spruaing with colored wax spray
Dusting (used to lift latent impressions)
similar for dusting fingerprints
fingerprint powder can visualize print
lifted with adhesive or gelatin
photographed for evidence
materials used to cast plastic impressions 3-D
Dental stone: fills in the print and produces a cast
how do we use forensic photography
oblique, ultraviolet, infrared or other special methods
photographs are taken for later comparison with suspected footwear, therefore they must be very clear
quality photographs taken of impressions if they can’t be transported
to enhance impressions
Electrostatic lifting
a charge is used to lift dry materials from surface to black film to recover impression
normally on tile, wood, etc
lift provides more contrast, on-destructive
photographed for evidence
what chemicals used to enhance shoe prints?
reagents like leuco crystal violet, amido 10 black, or fuchsin acid may be used
What info can we gain from footwear impressions
Identification of Footwear
Elimination of Footwear
Participation of suspect in crime
Location of Impressions
Rebuttal or confirmation of alibis
Determination of shoe brand - FBI Laboratory
Quality photographs should be taken of impressions if they can not be transported
Photographs are taken for later comparison with suspected footwear; therefore they must be very clear
Scale should be used to gauge size of footprint
Gait
the pattern of how you walk
factors affect gait
age, gender, height, size + shape of being components, distribution of mass in body segments, join mobility, muscle strength, type of clothing + footwear, habit, psychological status
tire groove
a depression in the tread of pattern
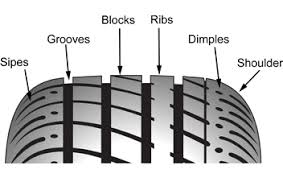
tire rib
ridge running down the tread area around the circumference of the tire
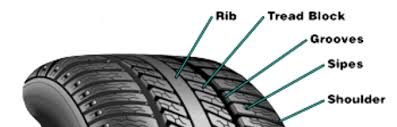
tire ridge
elevated area on the tread pattern (everything thats not groove)
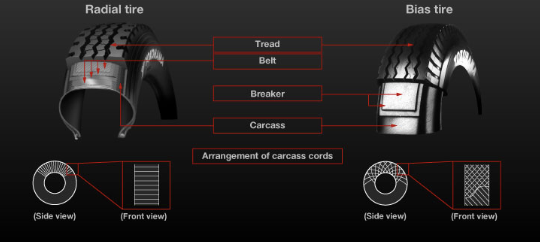
radial vs bias tire
most passenger tires today= radial-ply tires
some bias tires are made and can be found on older vehicles
tires made from various compounds of unvulcanized rubber, steel, and fabric.
tread and sidewall patterns are molded into a green tire
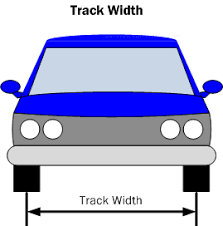
track width
distance from the center of the tread pattern on the left tire ot the center of the read pattern on the corresponding right tire
help identify vehicle + check in database
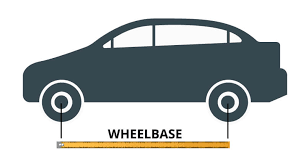
wheel base
distance from the center of the front axle on vehicle to the center of the rear
measurement of the center of hubs of front wheels to center of hubs of rear wheel
normally not present at crime scenes, unless the tracks show evidence of being parked
turning diameter
measure of how tight a circle can be driven by a vehicle
pertains to front wheels only
smaller case= smaller turning diameter
formula for calculating= (B²/A) +A
B= distance between two points (x and x’) on turn circle
A= distance between outer margin and a mid point, between x and x’
skid marks
form when diver slams brakes suddenly
show distance the vehicle traveled after the brakes were applied
help calculate speed of vehicle

yaw marks
sideways skid marks, produced when vehicle turns faster than it can handle
accompanied by smoke and squealing sounds

tire scrubs
damage to tires can show the area of impact

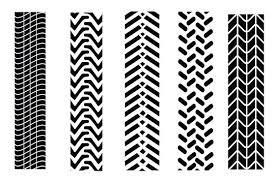
tread pattern
tire treads= ridges and grooves that channel water away from the wheel and provide traction for the vehicle
the unique design of a tires surface
noise treatment
arrangement of design elements used to reduce tire noise