SSS WEEK 5
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Give me 4 resp causes of nail clubbing
TB
lung cancer
interstitial lung disease
sarcoidosis
Give 4 cardio causes of nail clubbing
CHD
tetralogy of fallot
subacute bacterial endocarditis
AA
Characteristics of nail clubbing
loss of small diamond window when index fingers are brought together
thickening of fingers
softening of nail beds
increased nail convexity
4 GI causes of nail clubbing
Crohns and UC
hepatocellular
Celiac disease
Liver cirrhosis
Treatment of nail clubbing
Treat underlying disease
Alopecia areata
Discrete annular areas of hair loss anywhere on body
sudden onset of hair loss, increasing area will have a smooth surface, completely devoid of hair or with scattered ‘exclamation mark’ hairs
Trichotillomania (+ddx)
condition where patients compulsively pull out their hair
can be a sign of stress relief habit, impulse control disorder, depression
DDx
alopecia areata
tinea capitis
NORMAL HAIR GROWTH IN THE BALDING AREAS
Telogen effluvium
when anagen stops prematurely and hair then enters telogen phase. anagen then recommences and telogen hairs are released from follicles after the shock
THIS OcCURS DUE TO A SHOCK OF THE SYSTEM
like acute telogen effluvium occurs folllowing childbirth or stopping OCP, any acute illness or major surgery and severe dieting
chronic may be primary and idiopathic or secondary to hypo/hyperthyroidism, malnutrition, cancer, TB, or iron deficiency anemia
CONFIRM by examining lost hair which is mostly in telogen stage (white bulb or club-shaped tip)
Anagen effluvium
drugs, toxins or inflammation cause interruption of active or anagen hair growth
Hypertrichosis vs hirsutism
widespread overgrowth of non–androgen-dependent hair, occasionally
seen with drugs such as cyclosporin and phenytoin.
• In hypertrichosis, areas like the forehead and forearms have increased hair growth— rather than the lower face and midline of the trunk that are preferentially affected by androgens
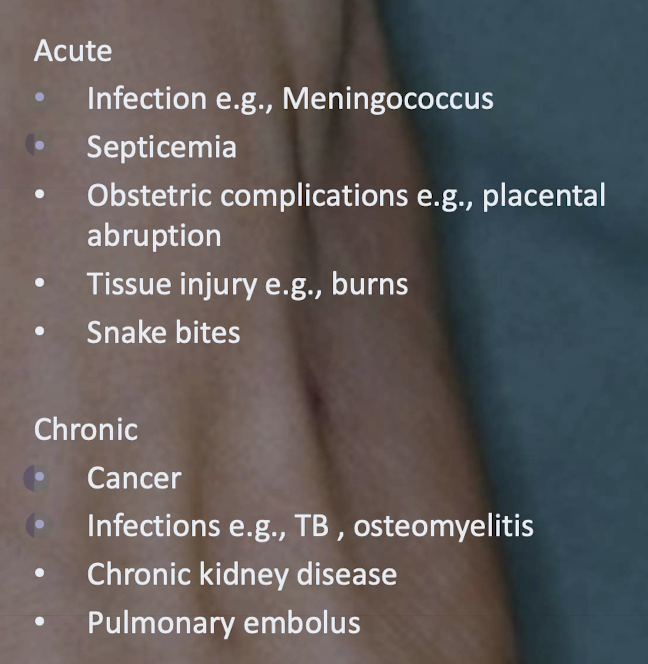
Acute vs chronic clinical features of DIC
Acute
• Ecchymoses (bruises)
• Mucous membrane involvement
• Internal hemorrhage
• Malaise and high fever purpuric rash affecting the extremities
• Petechiae and purpura
Chronic
• Thromboembolism
• Deep vein thrombosis
Acute vs chronic causes of DIC
General signs
peripheral and central cyanosis
finger clubbing
swelling of ankle
elevated JVP
Skin manifestations of sarcoidosis and clinical features
Sarcoidosis - non-caseating granulomas
multisystem granulomatous disorder
presents with one or more of the following abnormalities
bilateral hilar adenopathy (hilar - lungs)
pulmonary reticular opacities (a net-like pattern of fine lines seen on a chest X-ray or CT scan, indicating a problem in the lung's interstitium)
skin joint and/or eye lesions
lupus pernio
violaceous or erythematous indurated papules, plaques or nodules
distributed on nose, cheeks, chin and ears
erythema nodosum
a type of panniculitis
painful nodules that are most common on anterior surface of lower extremities
Skin manifestations of diabetes
necrobiosis lipoidica
starts as violaceous but atrophy and become brown-red or slightly yellow
blood vessels VISIBLE
apear on front of shins (like erythema nodosum)
diabetic dermopathy
brownish scars on skin, mostly on shins too!
granuloma annulare
skin coloured or slightly pink annular lesions over knuckles composed of dermal nodules fused into a rough circle
candida infections
staph infections
eruptive xanthomas - crops of yellow papules with erythematous base
neuropathic foot ulcers
acrochordons (skin tags)
acanthosis nigricans - hyperpigmented, velvety thickening of skin folds
Signs of hyperthyroidism (graves) + specific manifestations
skin: hyperhidrosis, facial flushing, hyperpigmentation
hair: alopecia
nails: yellow nail syndrome
Specific manifestations
ophthalmopathy
pretibial myxedema
acropachy (triad - digital clubbing, soft tissue swelling of hands and feet, periosteal reaction in long bones)
pretibial myxoedema
Hypothyroidism signs
loss of outer third of eyebrows
cold insensitivity
bruising and purpura
weight gain
puffiness of eyes, face and hands
General descriptions of adrena hyperfunction vs insufficiency
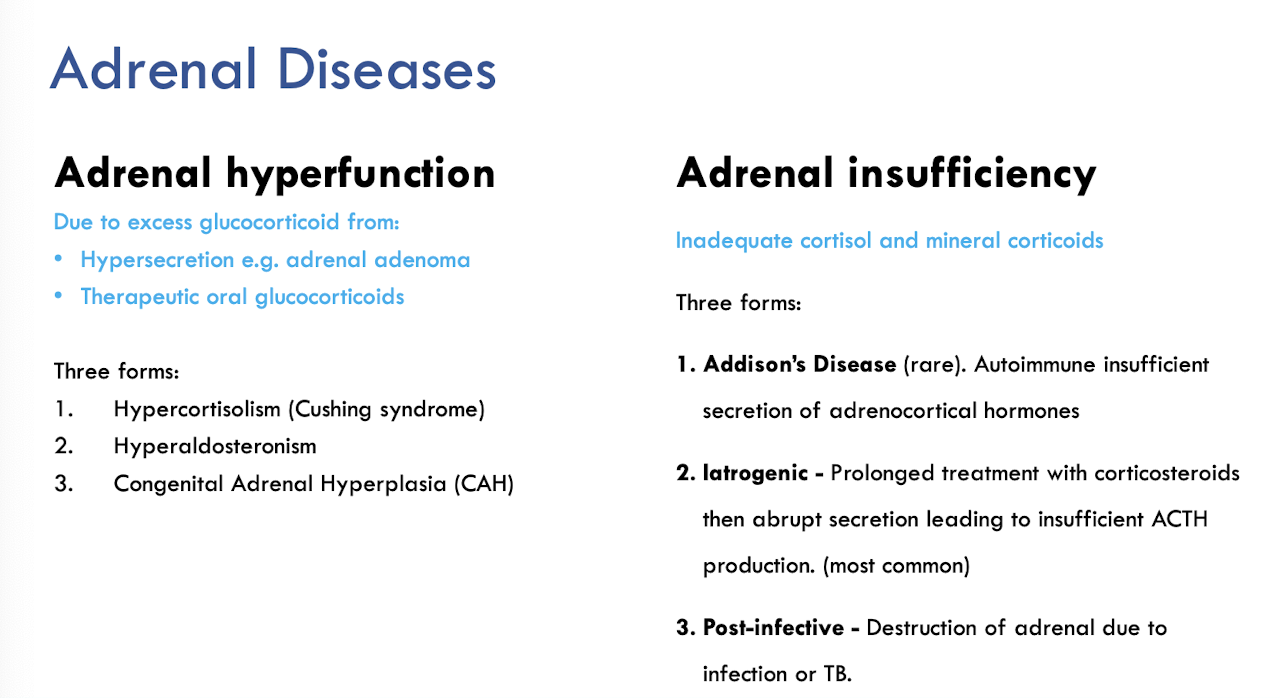
Skin signs of cushings
acne
telangiectasia
facial roundness
buffalo hump
central adiposity
bruising
excess facial and body hair
striae
Adrenal insufficiency skin signs
hyperpigmentation of skin, buccal surfaces and knees, elbows and genitals
loss of body hair
vitiligo
Skin manifestations of hepatic disease
pruritis (most common) - worse at night, hands and feet
jaundice
palmer and facial erythema
spider naevi
nails - half and half nails
bruising
feminisation
photosensitivity, skin erosions and mucosal changes due to deficiencies in zinc, vitamin B leading to classic rashes of pellagra
GIT disease skin manifestations
Dermatitis herpetiformis
associated w gluten intolerance
pruritis vesicles, papules and bullae on elbows, knees and lumbosacral areas
need biopsy to confirm IgA
erythema nodosum (also seen in sarcoidosis resp disease)
panniculitis
pyoderma gangrenosum
painful ulcerative disease
associated with
IBD
RA
lupus
begins as papule and breaks down to form rapidly enlarging ulcer
investigate biopsy to differentiate infective and malignant
Clin presentation of chronic cutaneous discoid LE (+ treatment)
chronic rash
well defined red scaly plaques (like plaque psoriasis lol)
secondary changes: hyper/hypopigmentation and atrophic scarring
treatment
sun protection
topical corticosteroids
systemic agents eg. methotrexate (like psoriasis), hydroxychloroquine
Autoimmune - Scleroderma


Autoimmune - bullous pemphigoid
may present as non-specific dermatitis or urticarial rash
investigations
skin autoantibodies
skin biopsy and direct immunofluorescence
treatment
potent topical steroids or oral steroids
long term alternatives
antibiotics: doxy as a steroid sparing
nicotinamide as steroid sparing agentList 5 causes of pruritis
liver disease
intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
lymphoma and leukemia
multiple myeloma
iron deficinecy anemia
Presentation of dermatomyositis
periorbital macular violaceous erythema (heliotrope rash)
scaly, reddish papules over dorsum of IPJs of hands (Gottons papules)
so if u get a case saying heliotrope rash, gottons papules immediately think dermatomyositis and immediately think internal malignancy
Skin manifestations of internal malignancy
acanthosis nigricans GI malignancy adenocarcinoma
pyoderma gangrenosum
dermatomyositis
generalised pruritis
superficial thrombophllebitis
erythroderma
sweets syndrome
Aetiology of chronic leg ulcers

Treatment of chronic leg ulcers
