Microscopy, Cells, and Diffusion and Osmosis test 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Resolution
The ability of a microscope to distinguish two points as separate.
Contrast
The difference in light intensity between the image and the background.
Parcentered
When an object is in focus on one objective, it will remain centered when switching to another objective.
Parfocal
When an object is in focus on one objective, it will remain nearly in focus when switching to another objective.
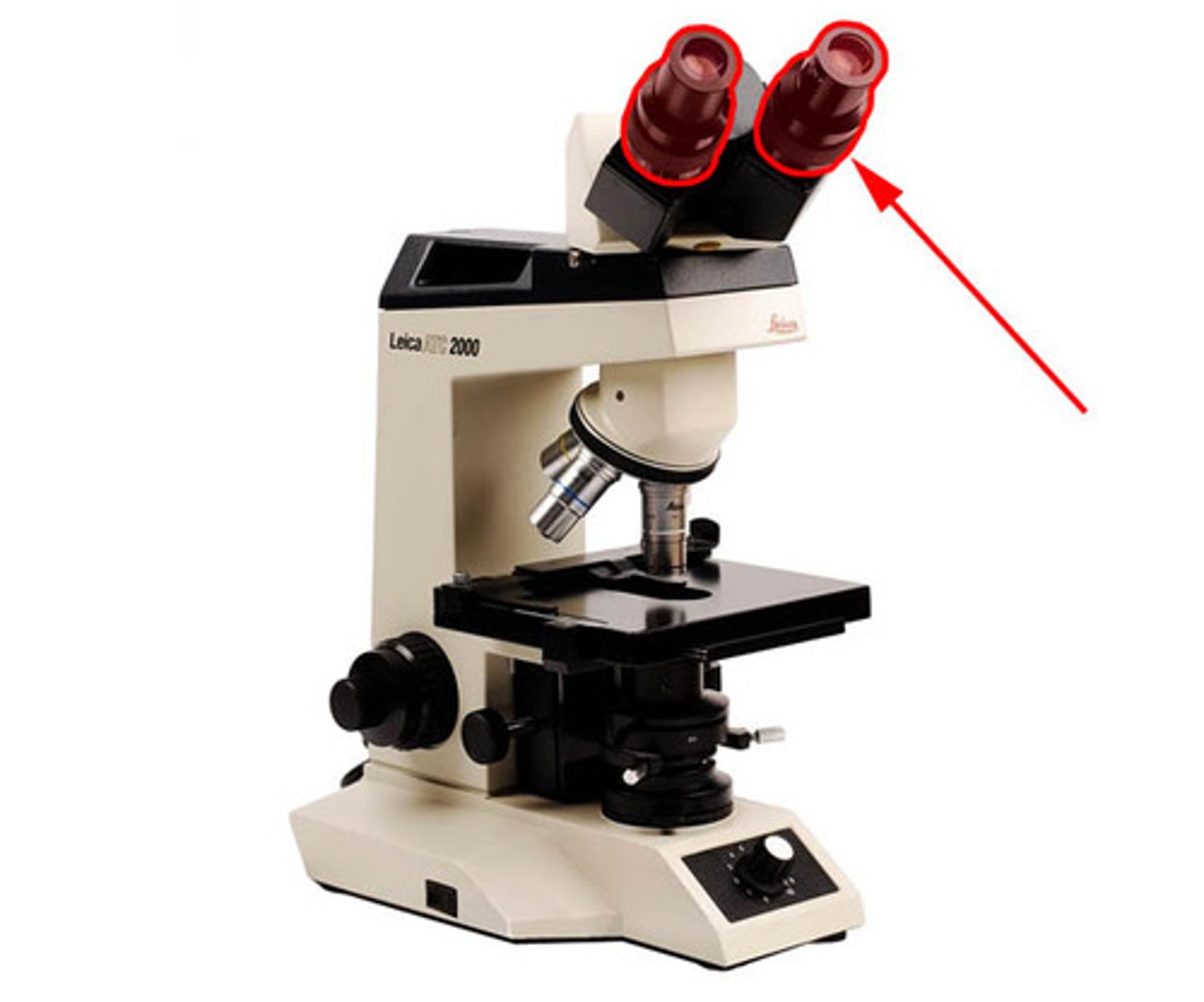
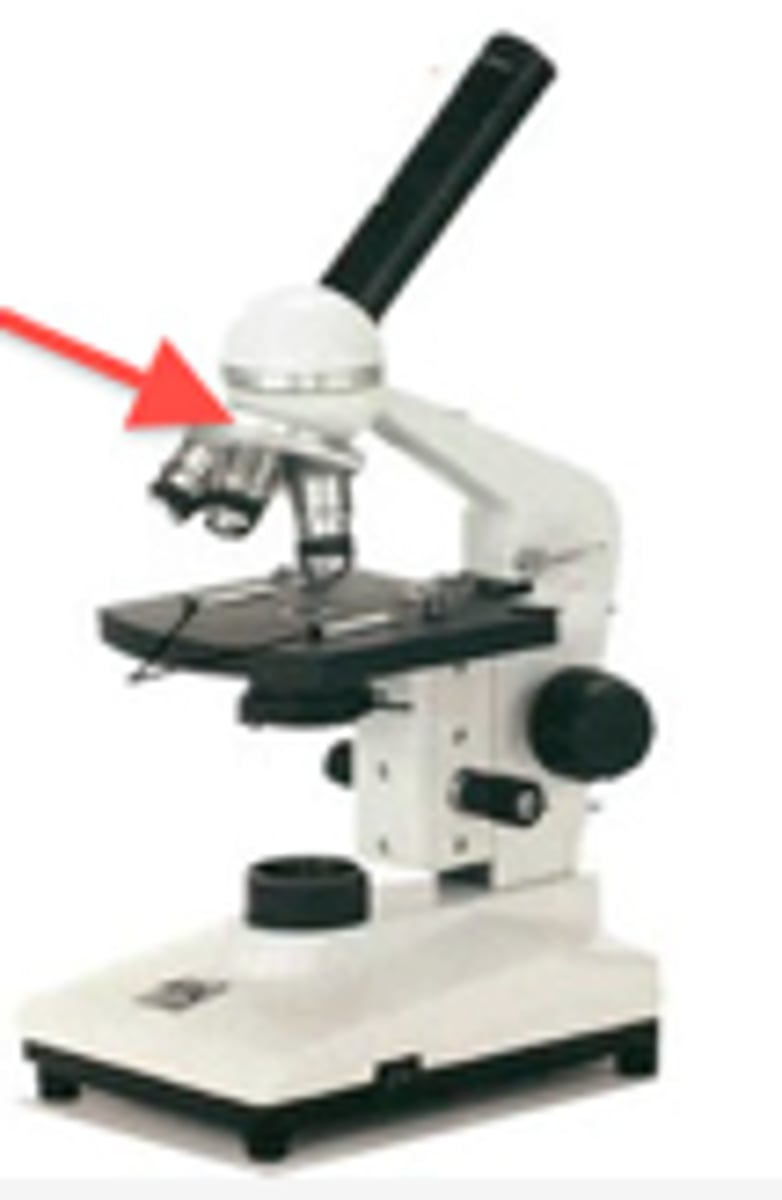
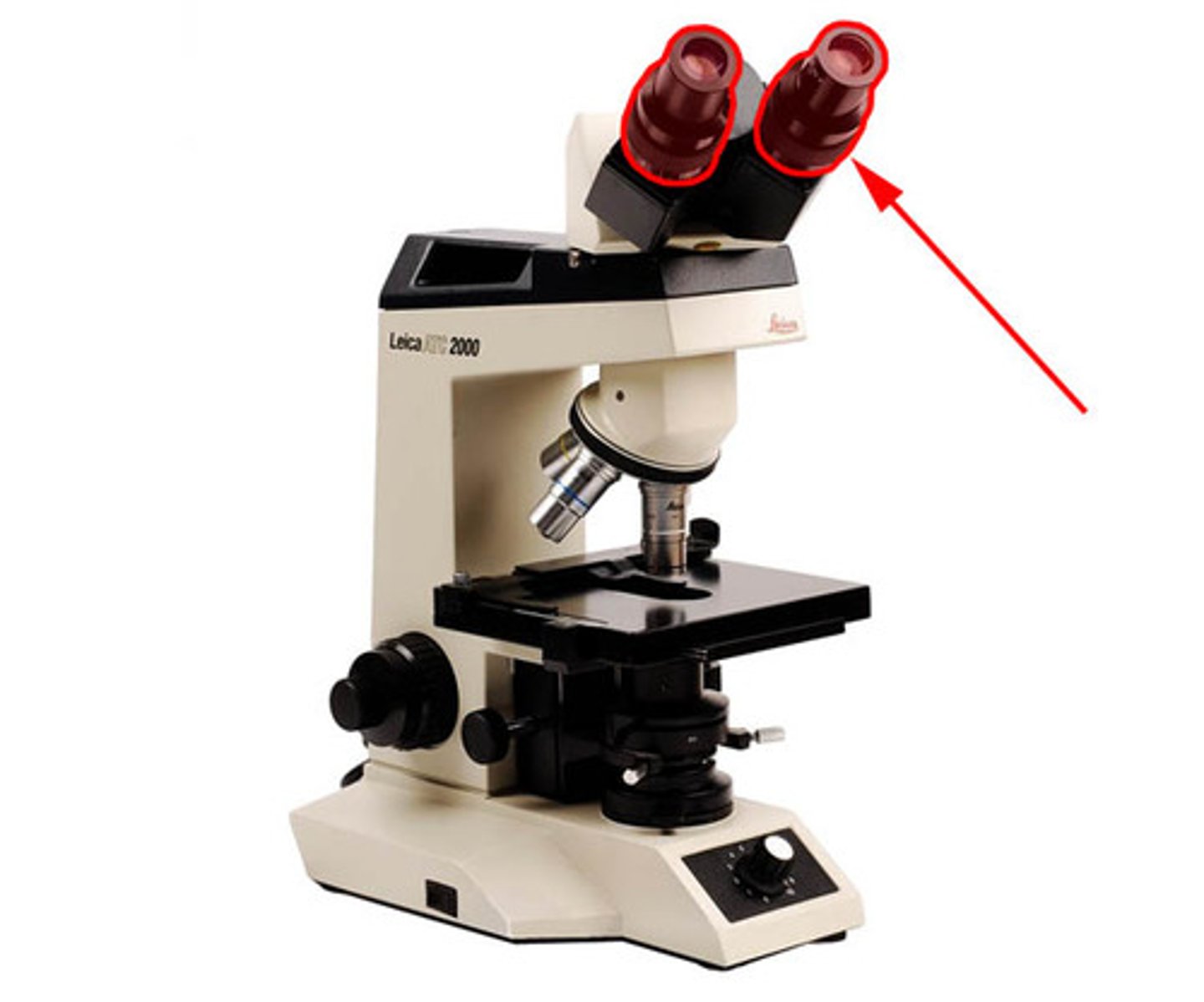
Oculars
Eyepieces where you look through to see the image.
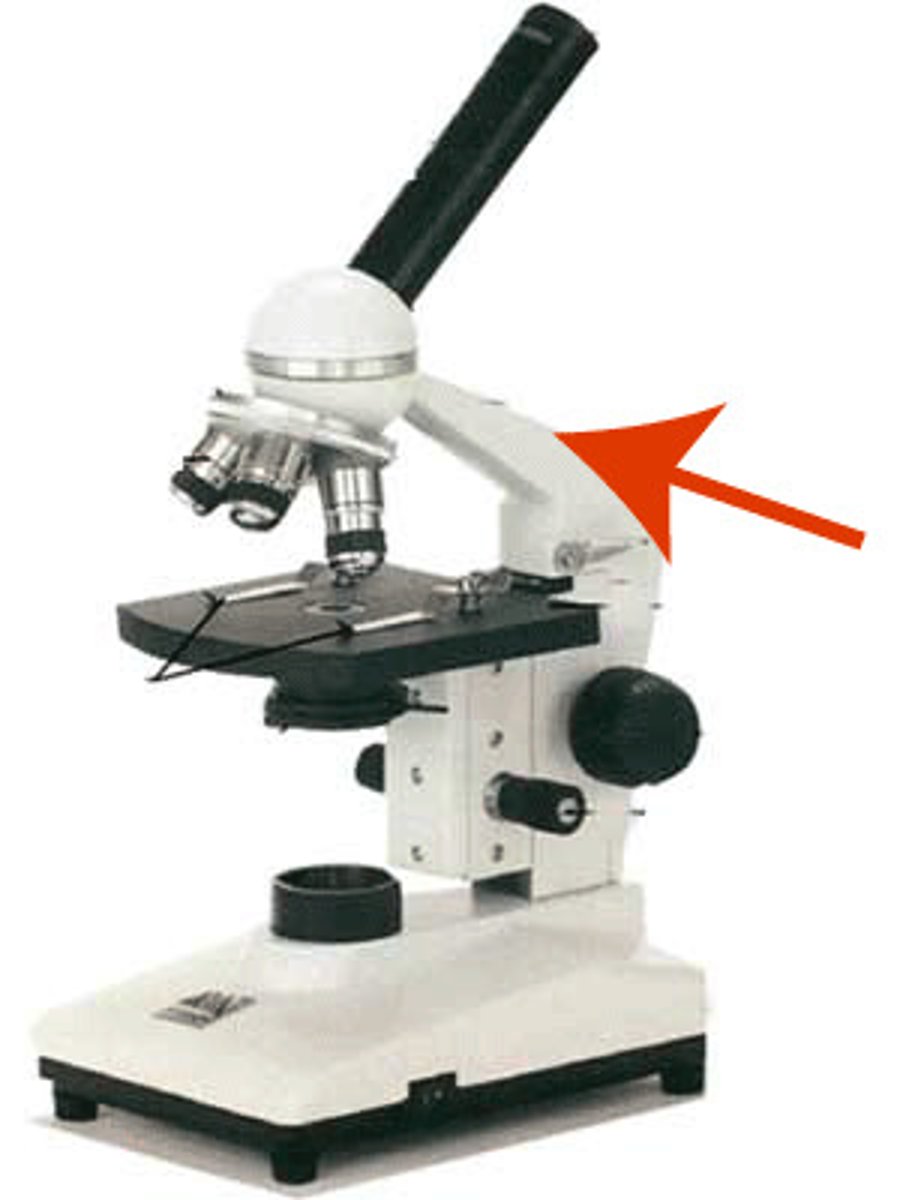
Arm
The part of the microscope you carry it by.
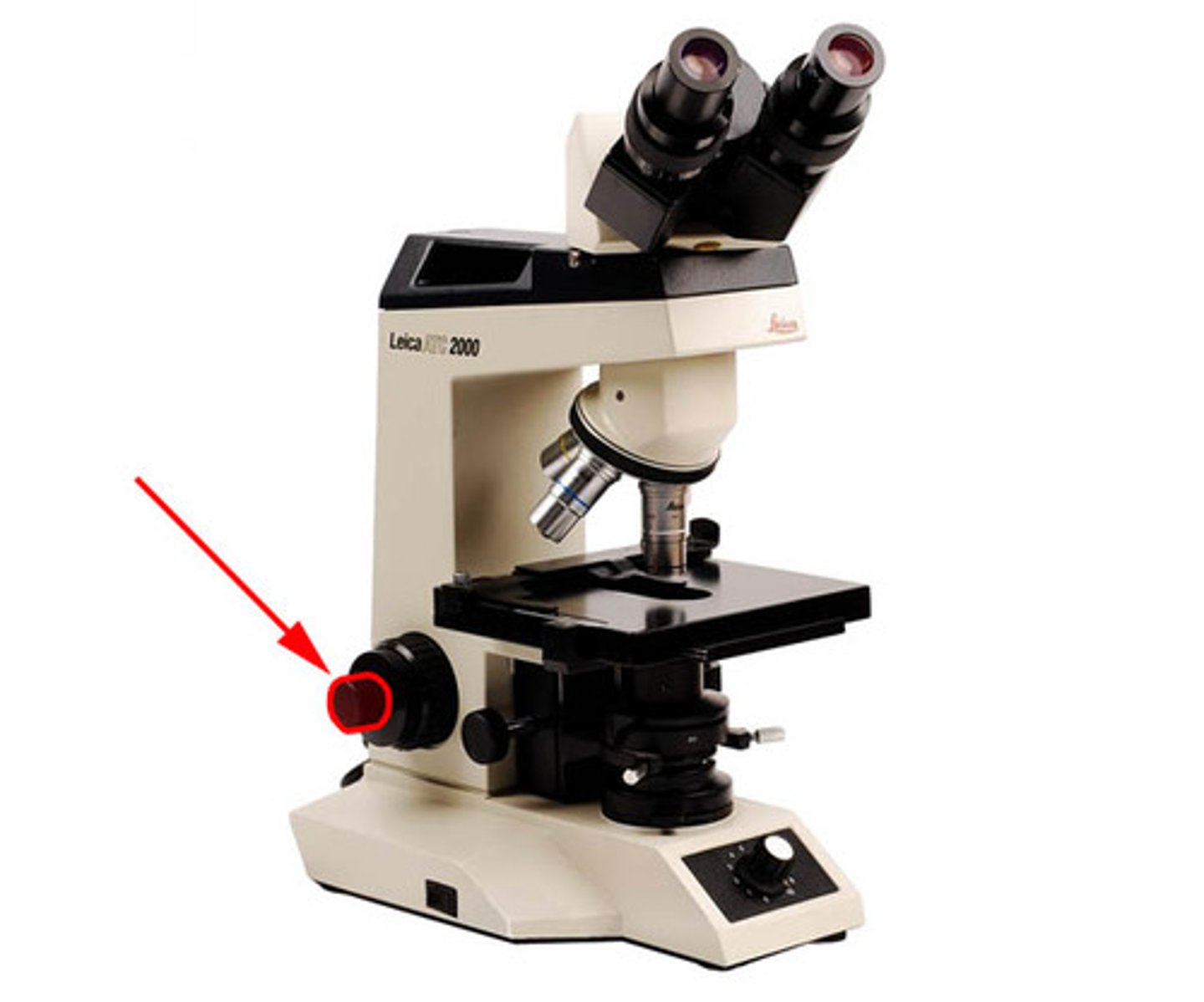
Fine Adjustment
Small focus knob for fine-tuning the image.
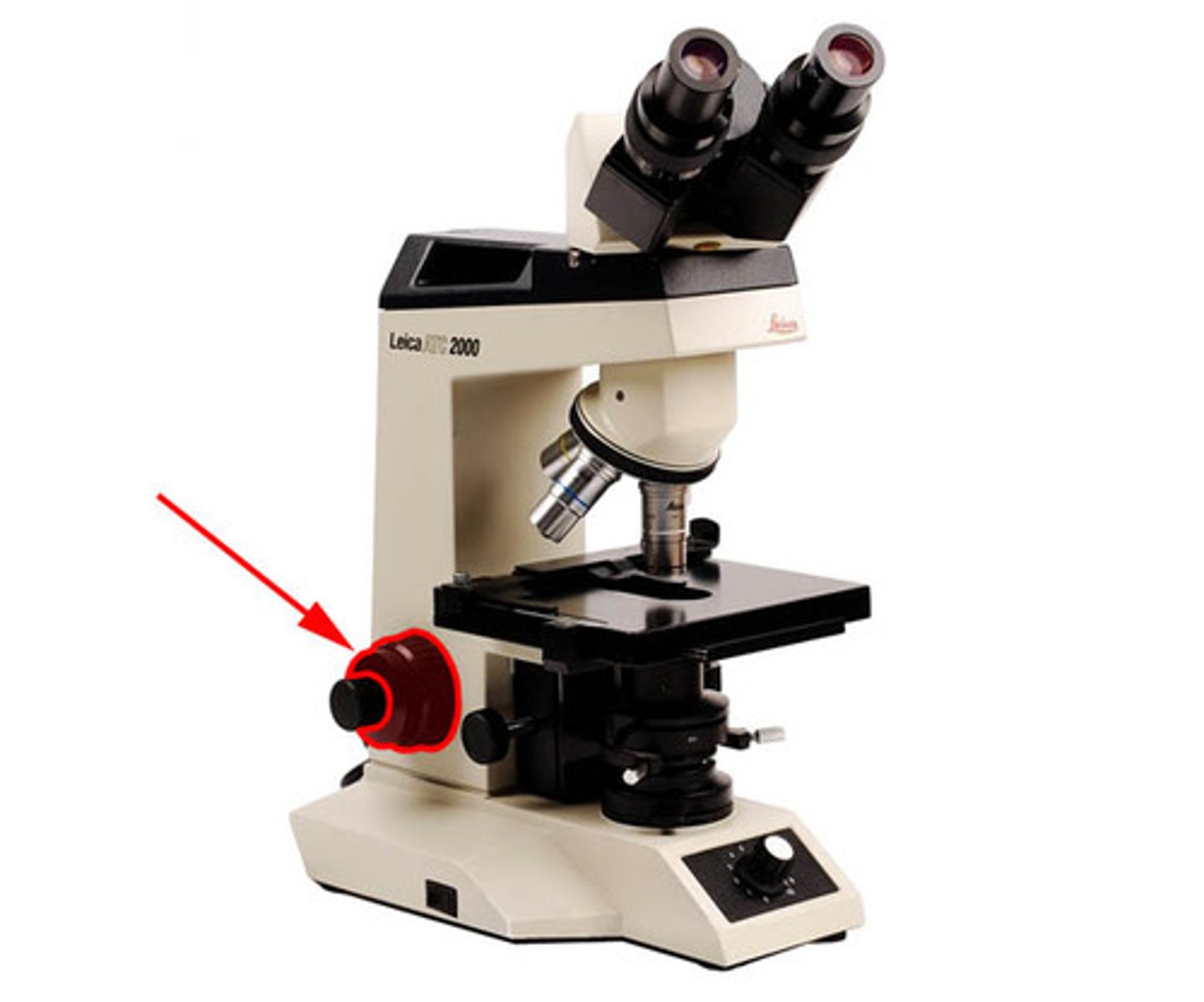
Coarse Adjustment
Larger focus knob for rough focusing.
Stage
Platform where the slide is placed.
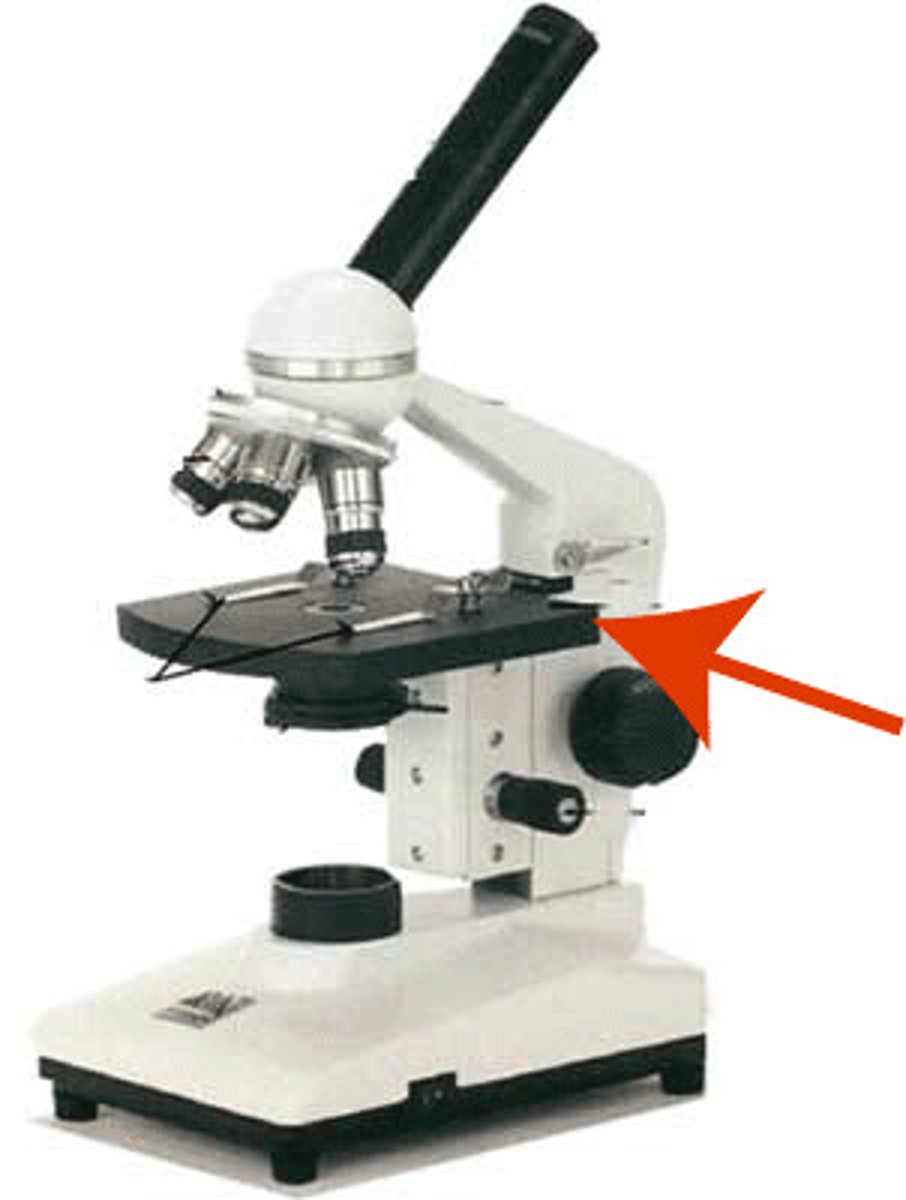
Stage Clip
Clips used to hold the slide in place.
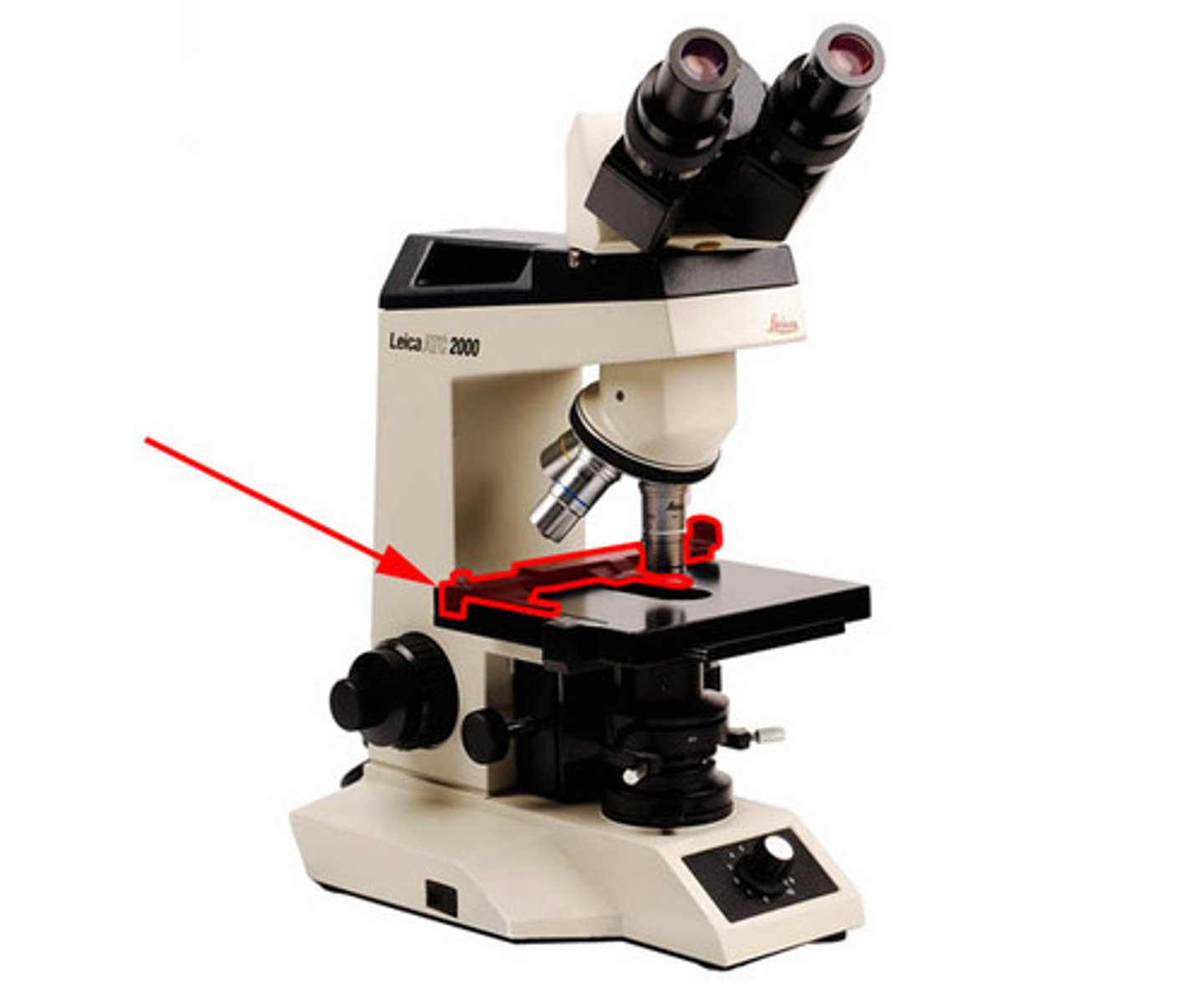
Stage Adjustment Knobs
Controls that move the stage for focusing.
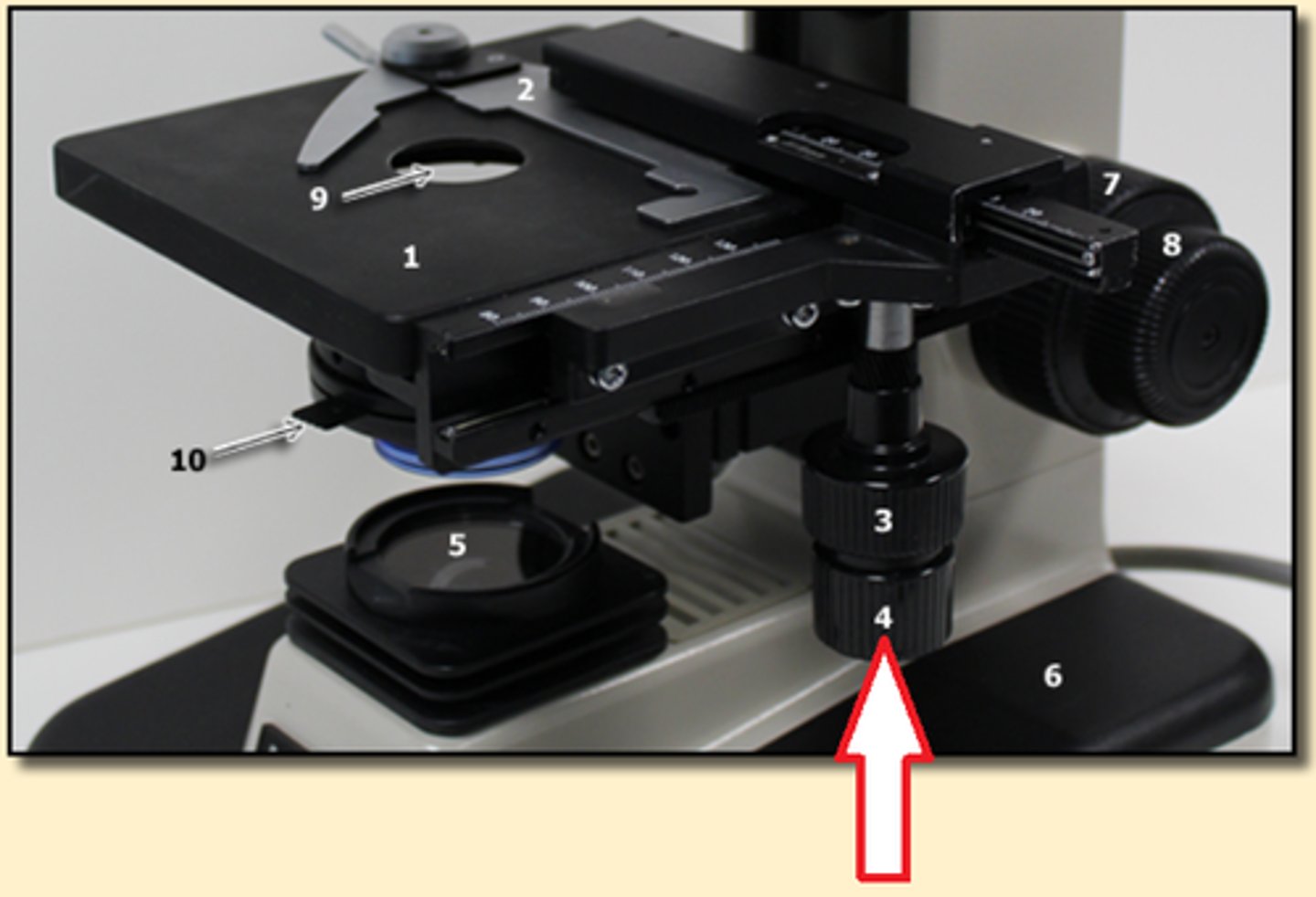
Iris Diaphragm
Controls the amount of light passing through the specimen.
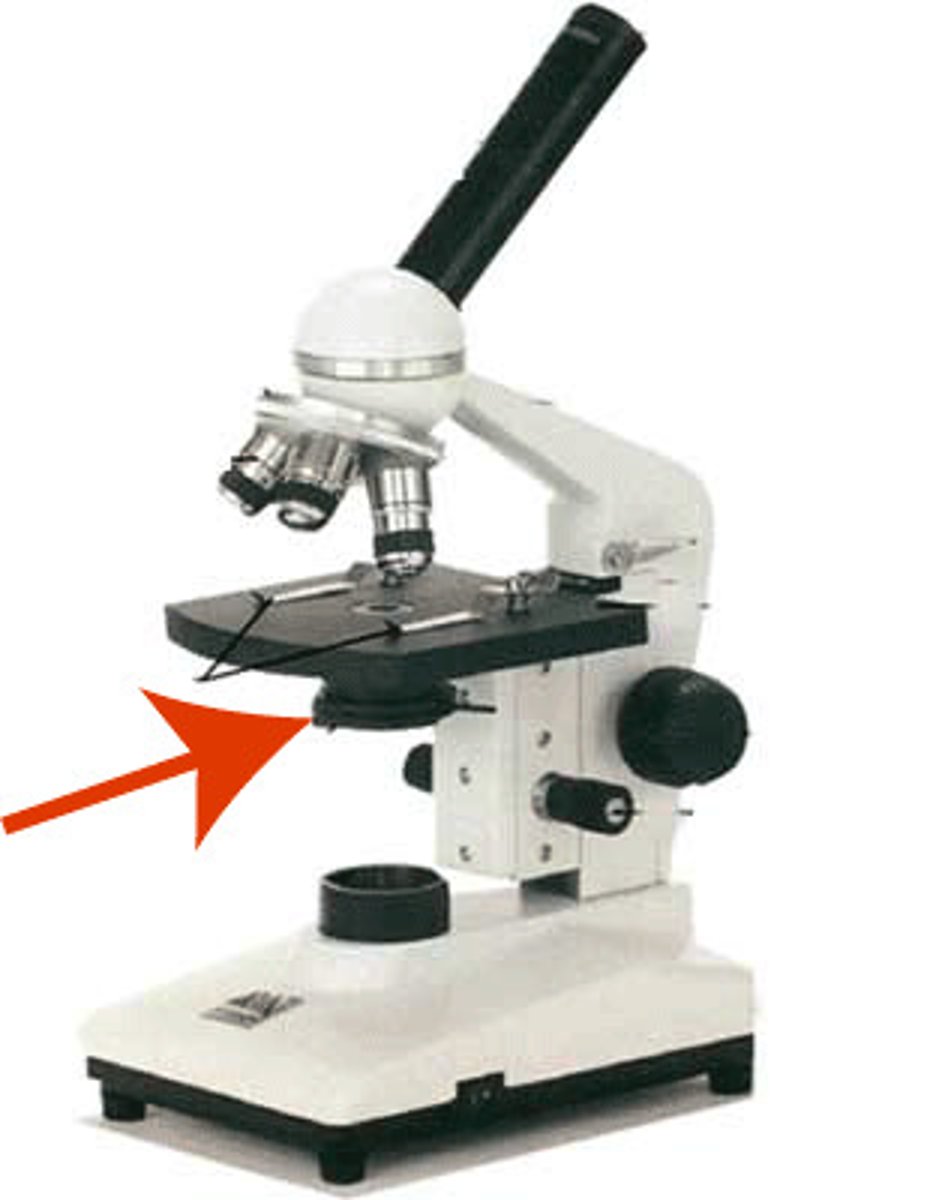
Condenser
Focuses light onto the specimen.
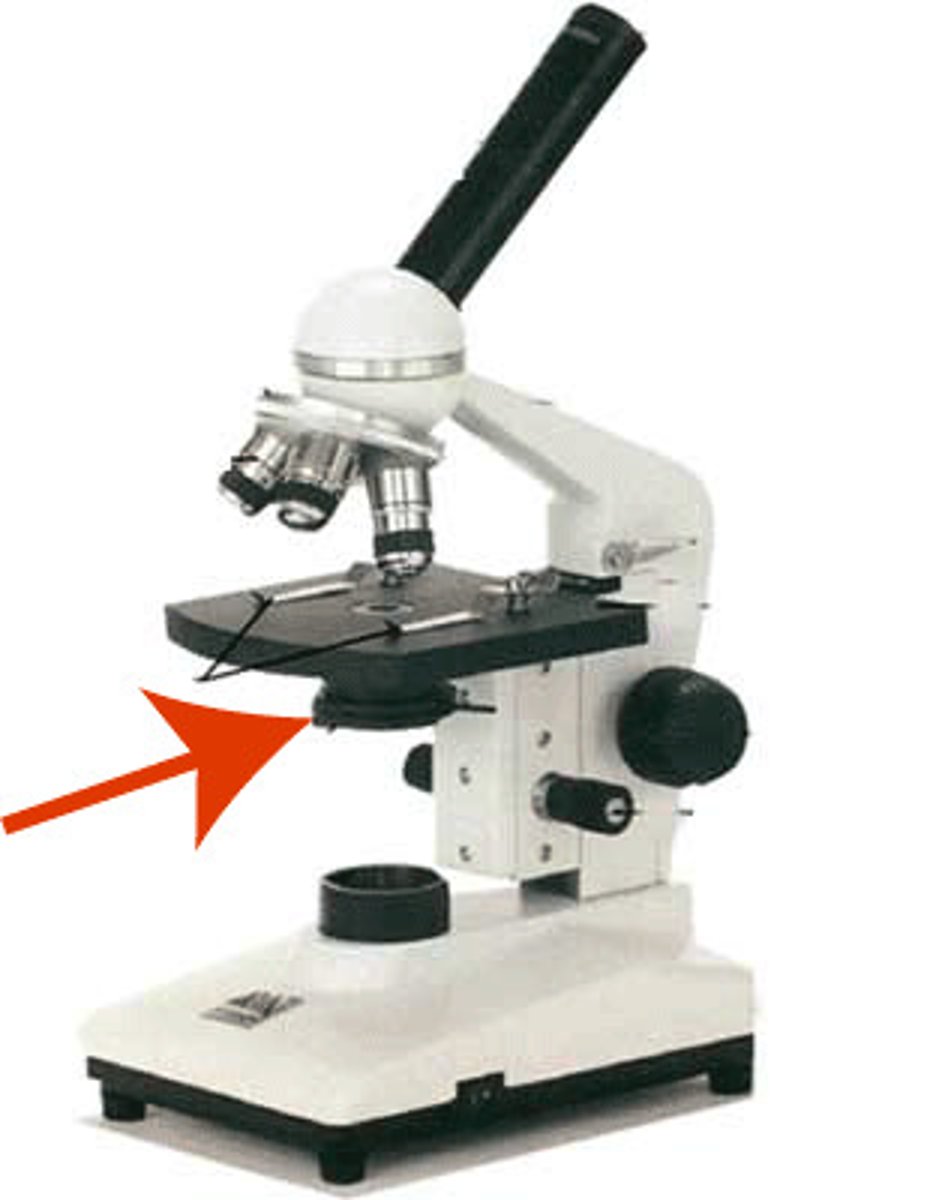
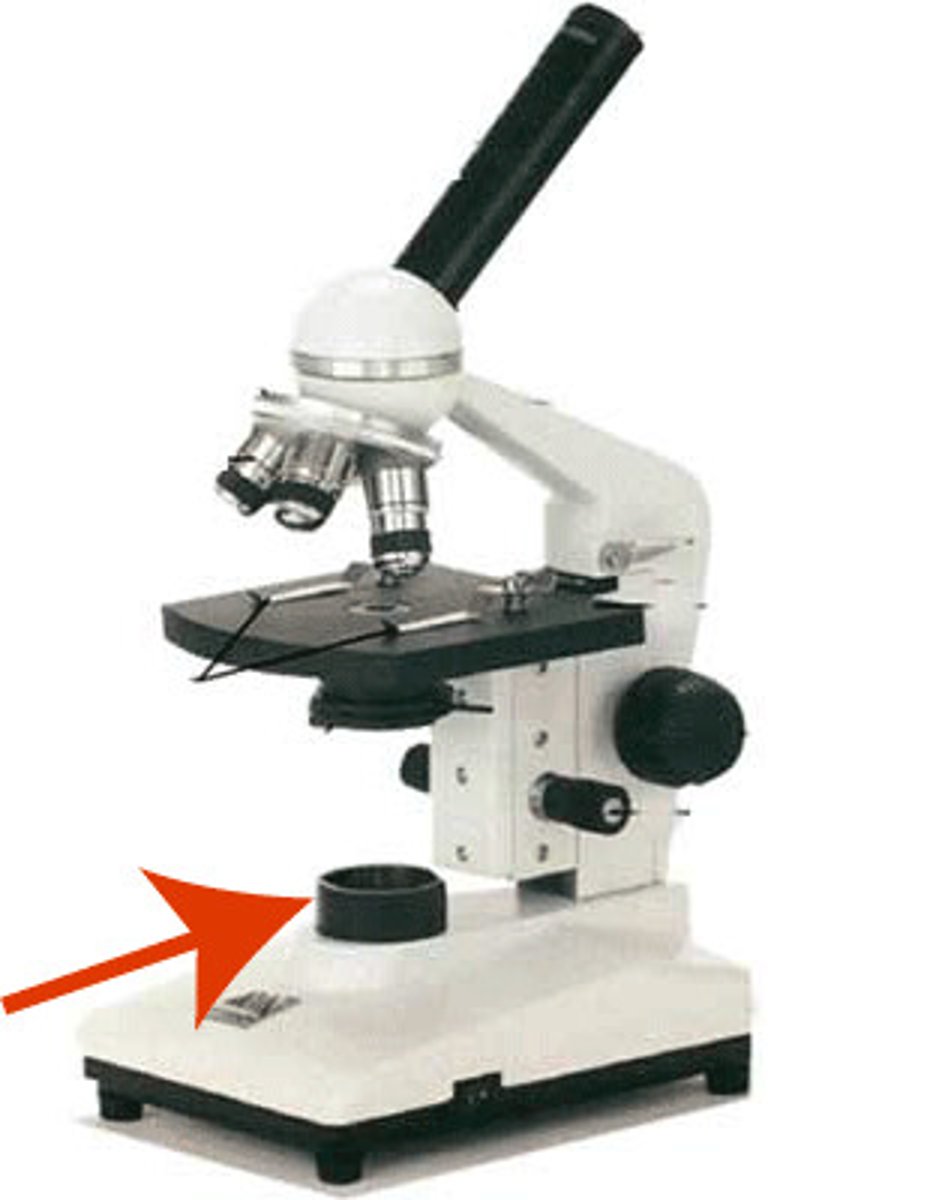
Light Source
Provides light for the specimen.

Nosepiece
Holds the objectives and allows you to rotate them into position.
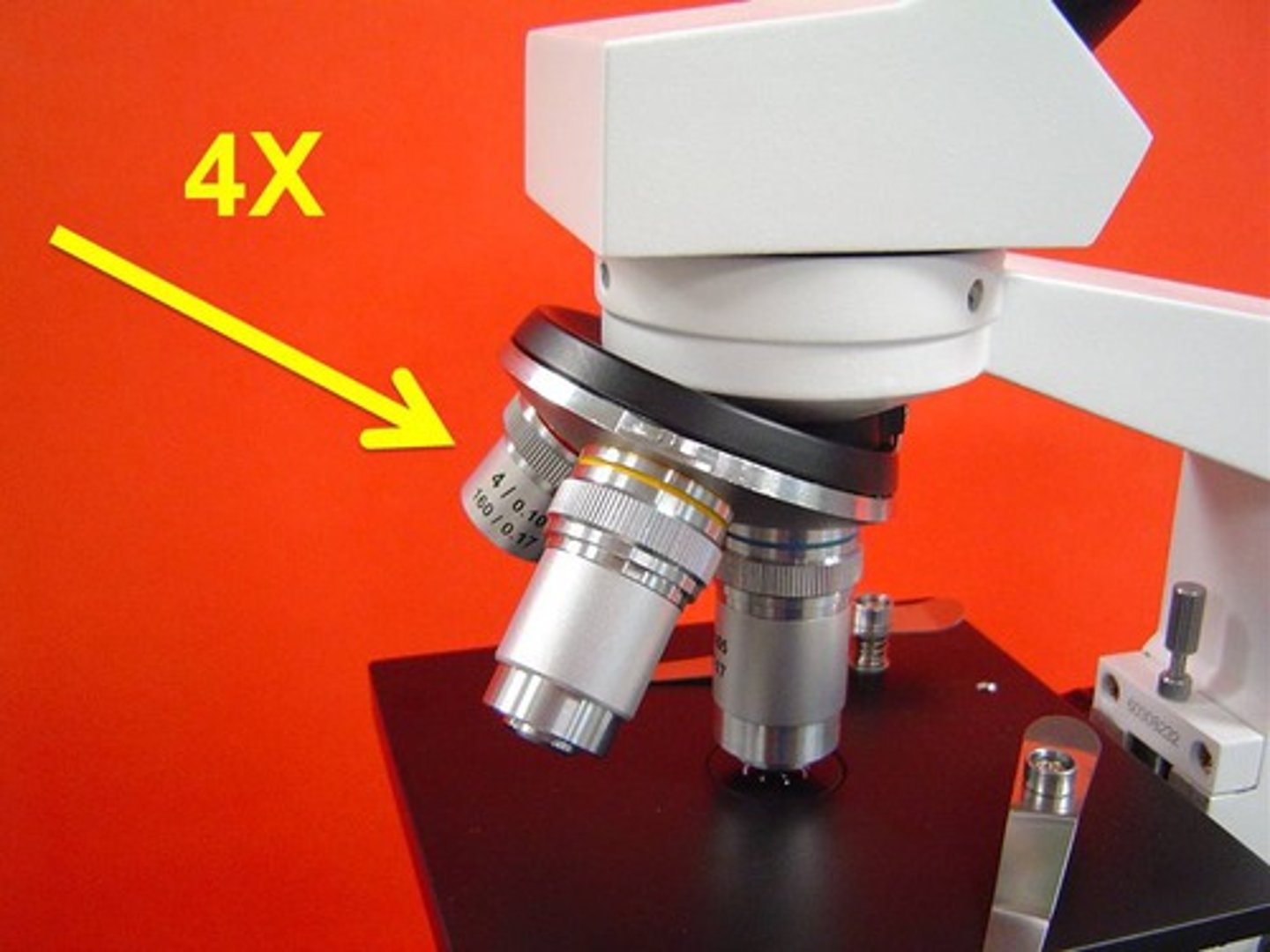
Scanning Objective
4x magnification.
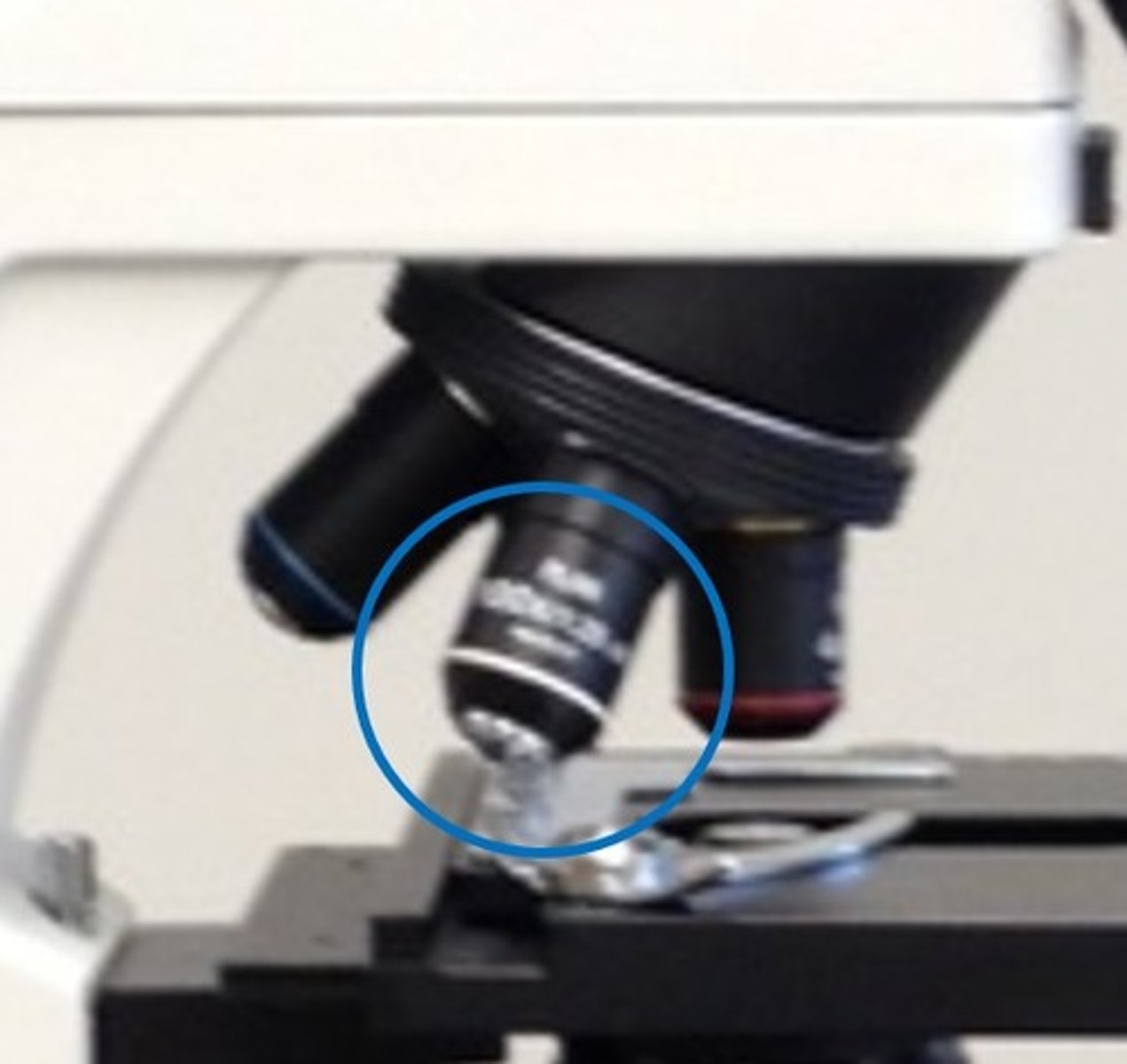
Low Power Objective
10x magnification.
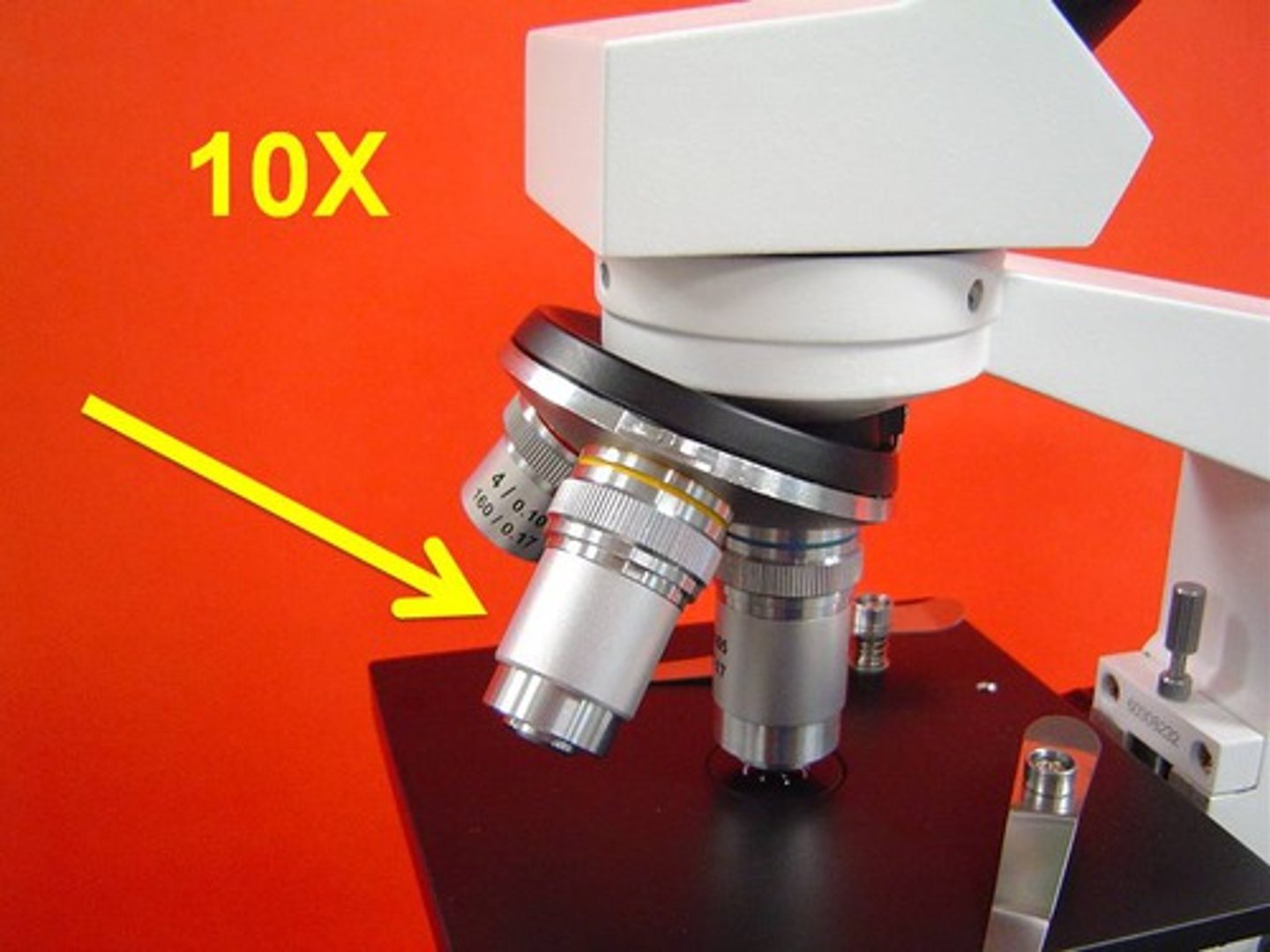

High Power Objective
40x magnification (blue)
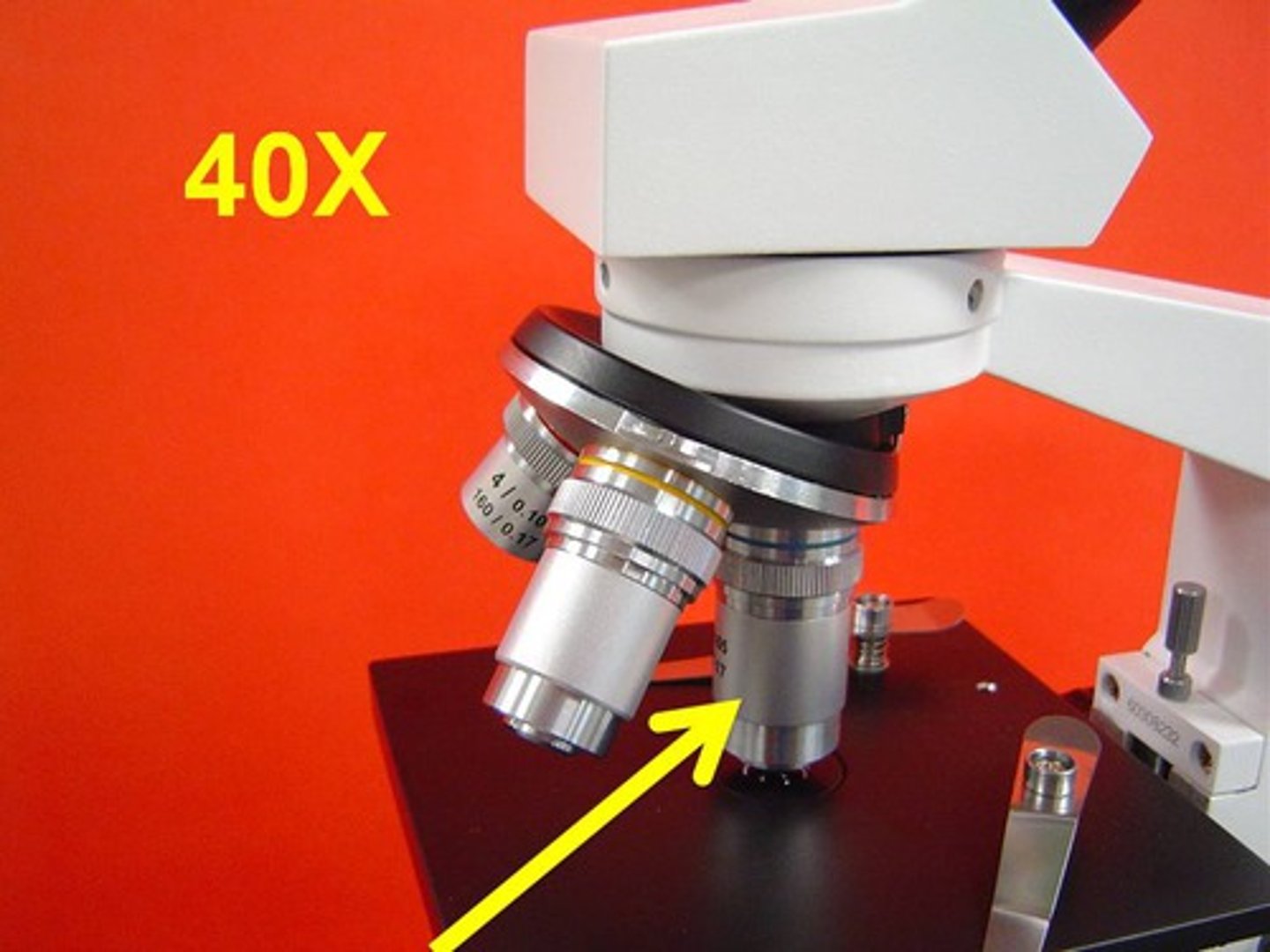

Oil Immersion Lens
100x magnification (requires oil).
Ocular Magnification
Usually 10x.
Objective Magnification
Identified by the label on each objective lens (4x, 10x, 40x, 100x).

Total Magnification
Multiply the ocular magnification by the objective magnification (e.g., 10x ocular and 40x objective = 400x total magnification).
Field of View
The area visible through the microscope.
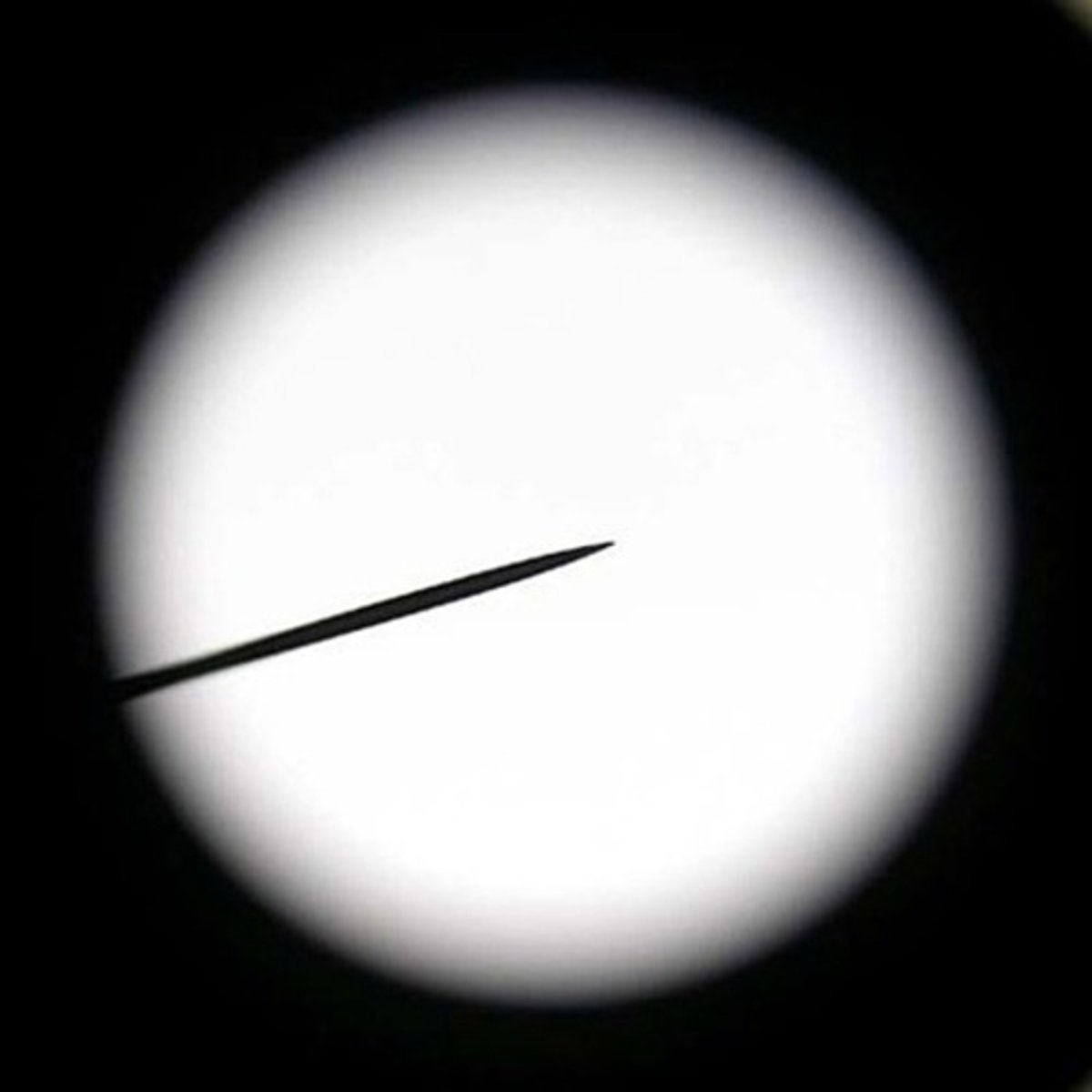
Depth of Field
The thickness of the specimen that can be in focus.

Fixed Slides
Specimens are preserved and mounted on slides.

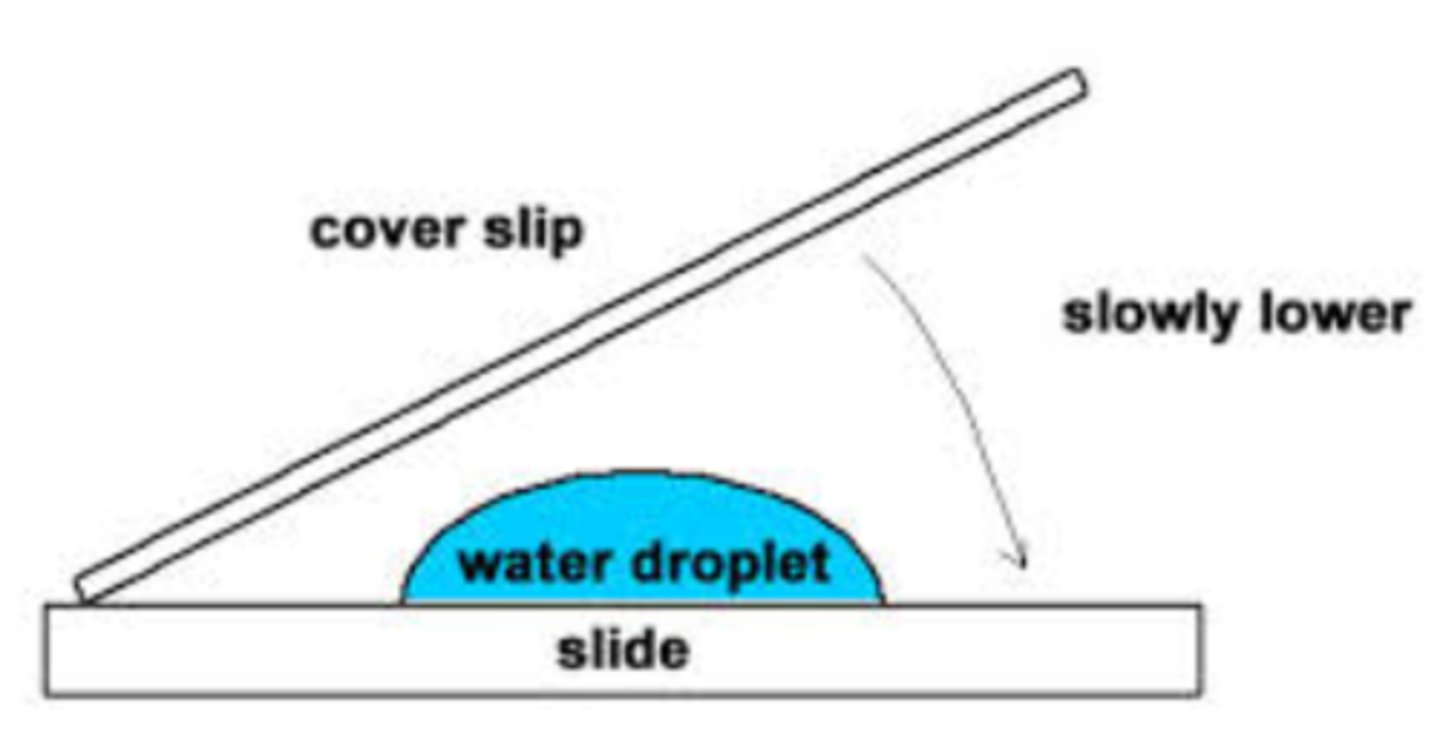
Wet Mount Slides
Specimens are placed in a drop of water and covered with a coverslip.
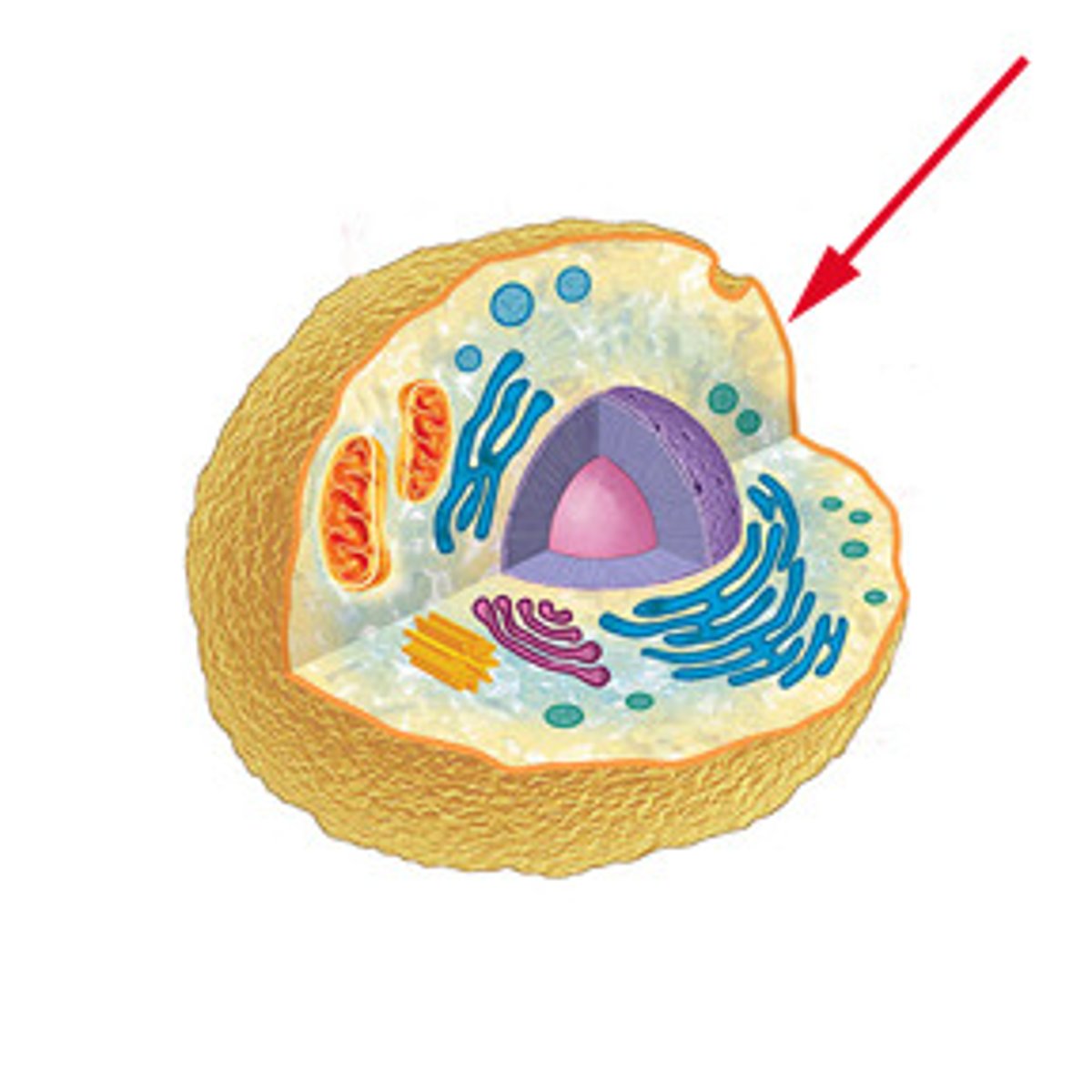
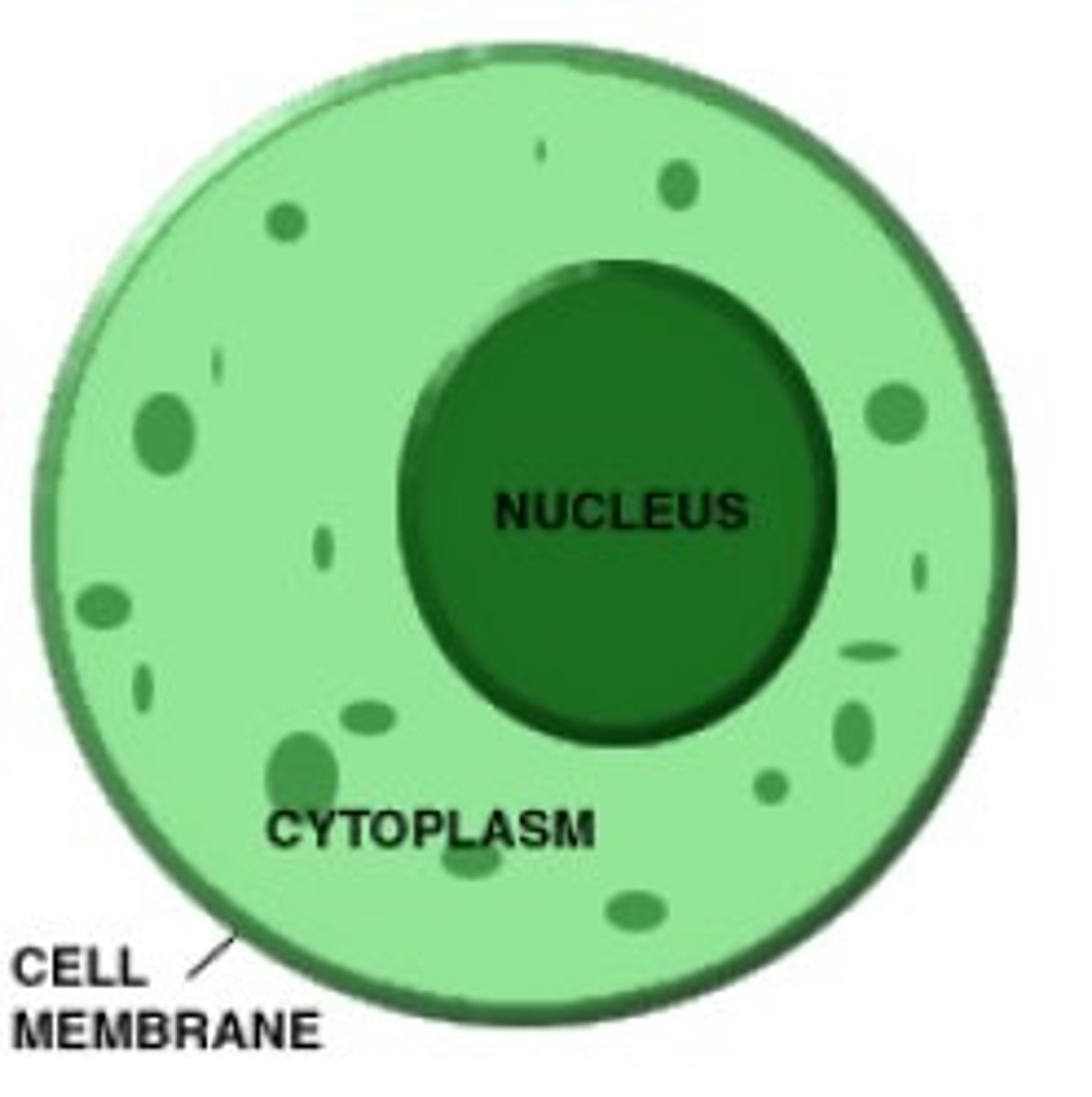
Plasma Membrane
Semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cell.
Cytoplasm
Gel-like substance inside the cell where organelles are suspended.
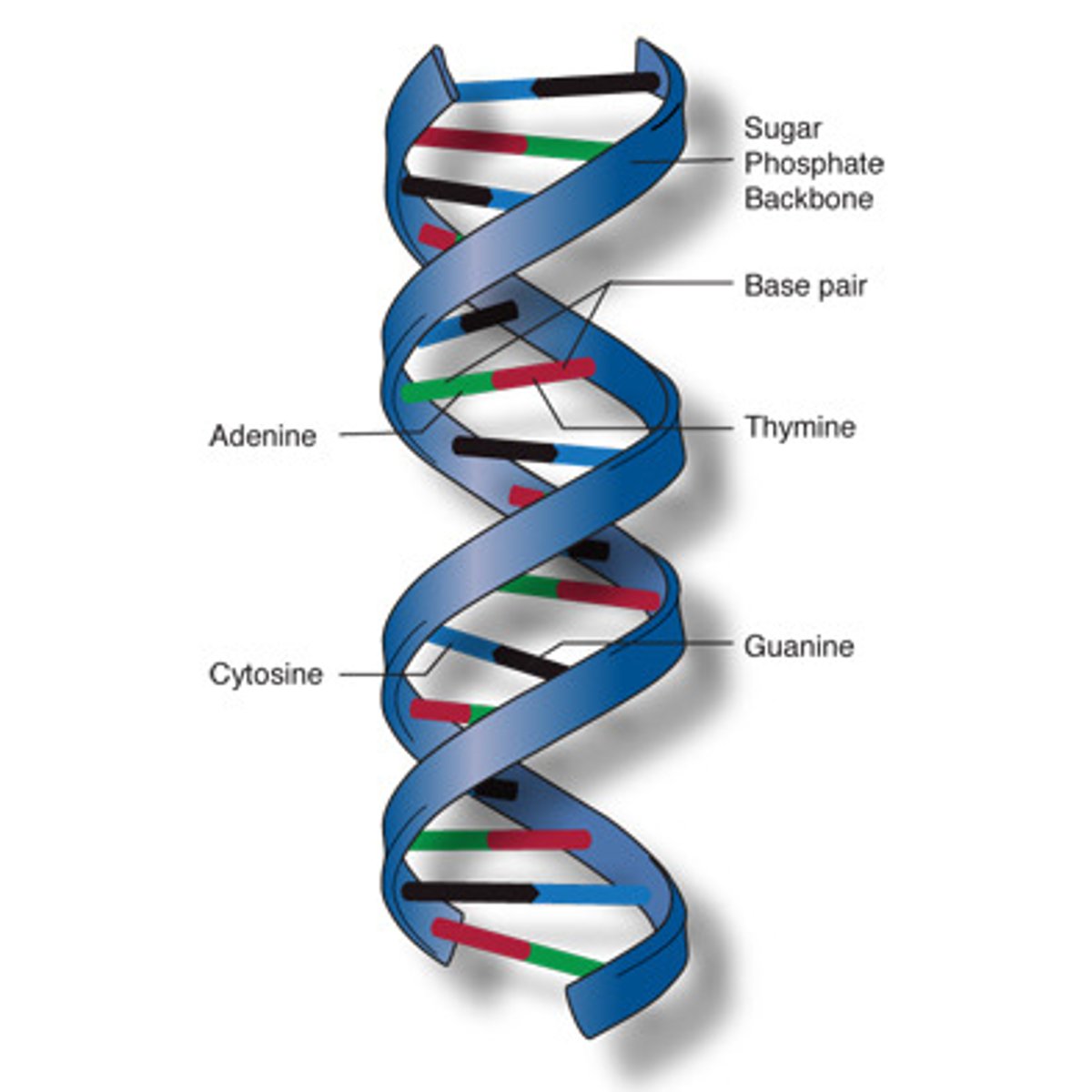
DNA
Genetic material that carries information for cell function.
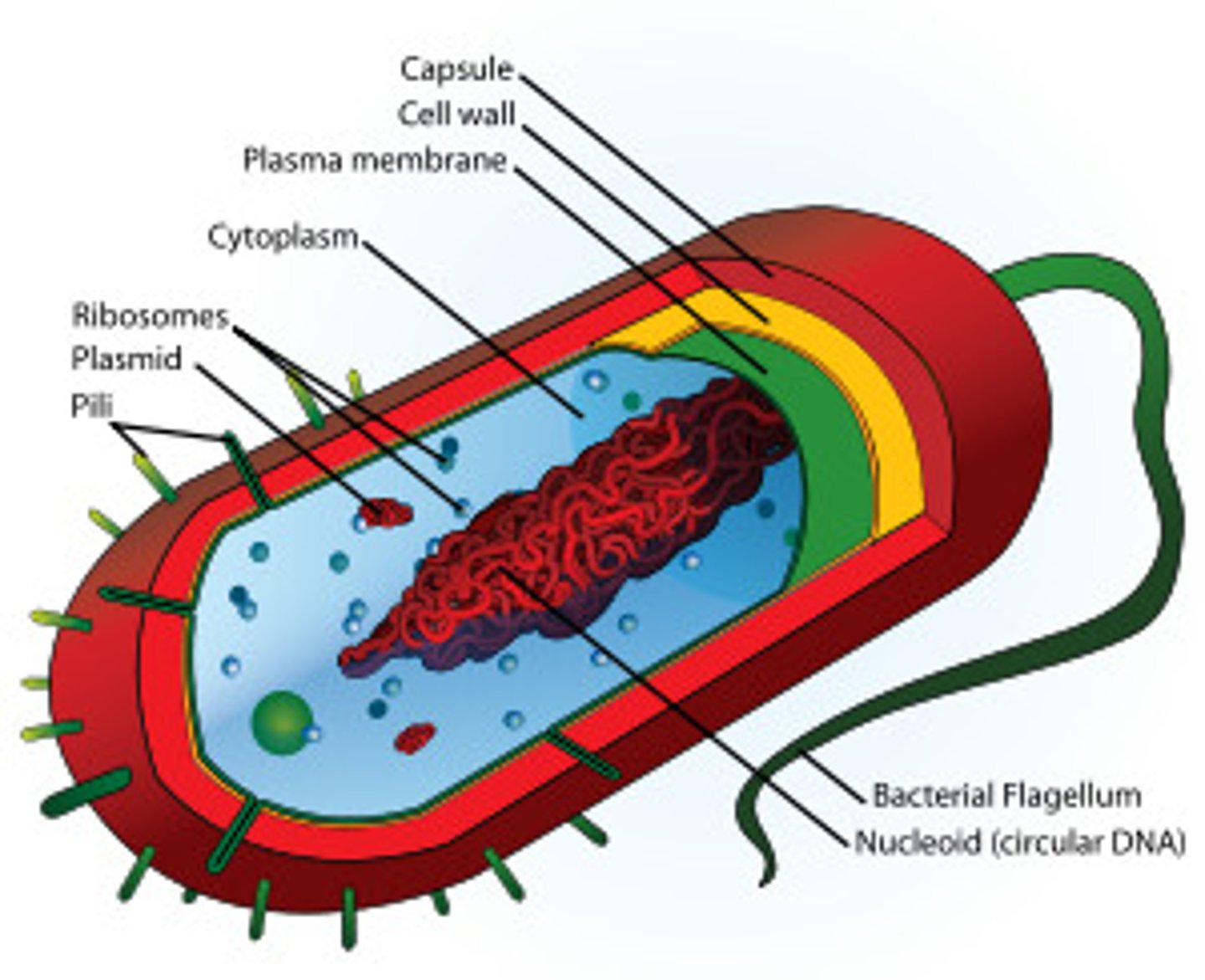
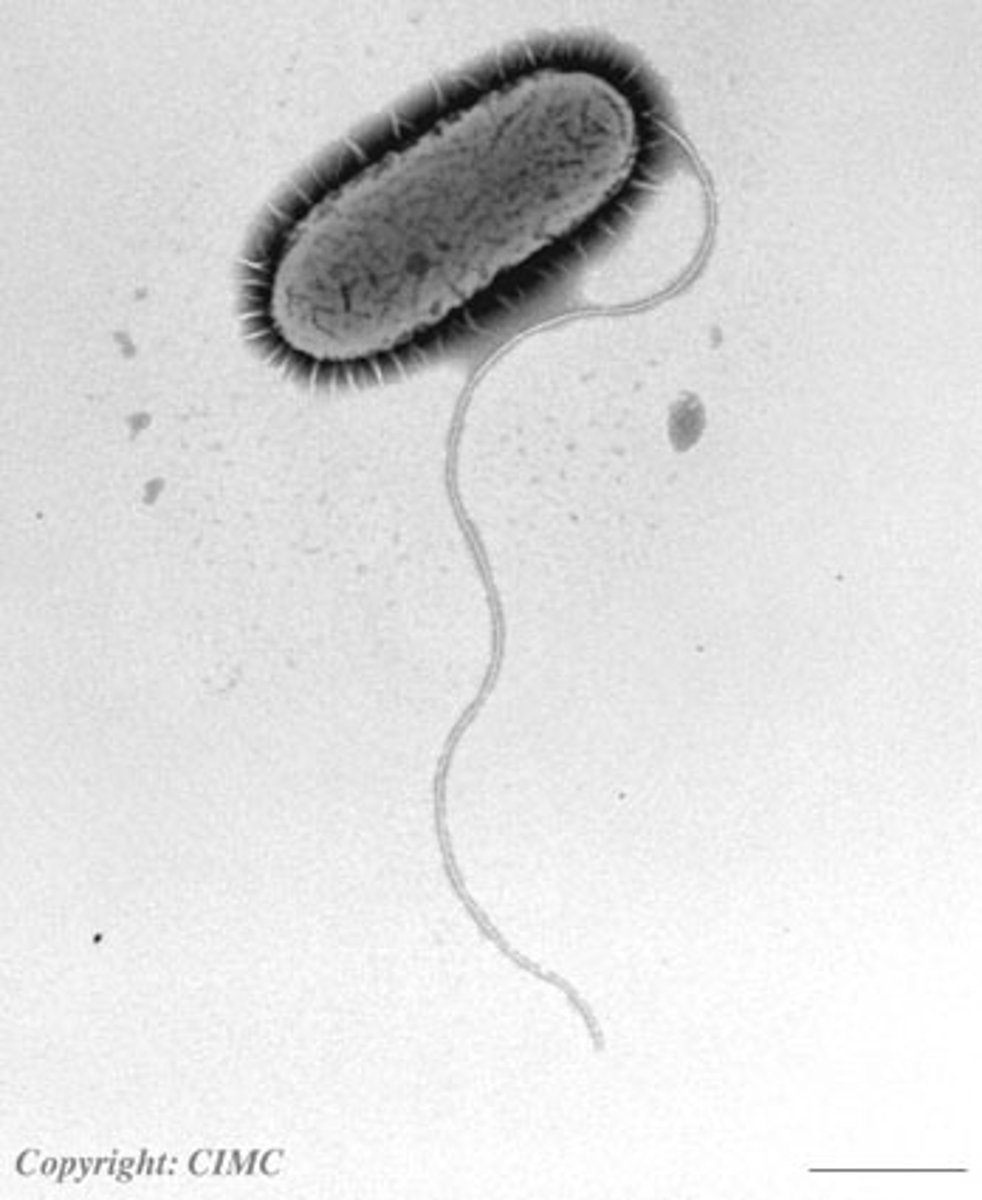
Prokaryotic Cells
Simple, no membrane-bound organelles, smaller. Includes bacteria.
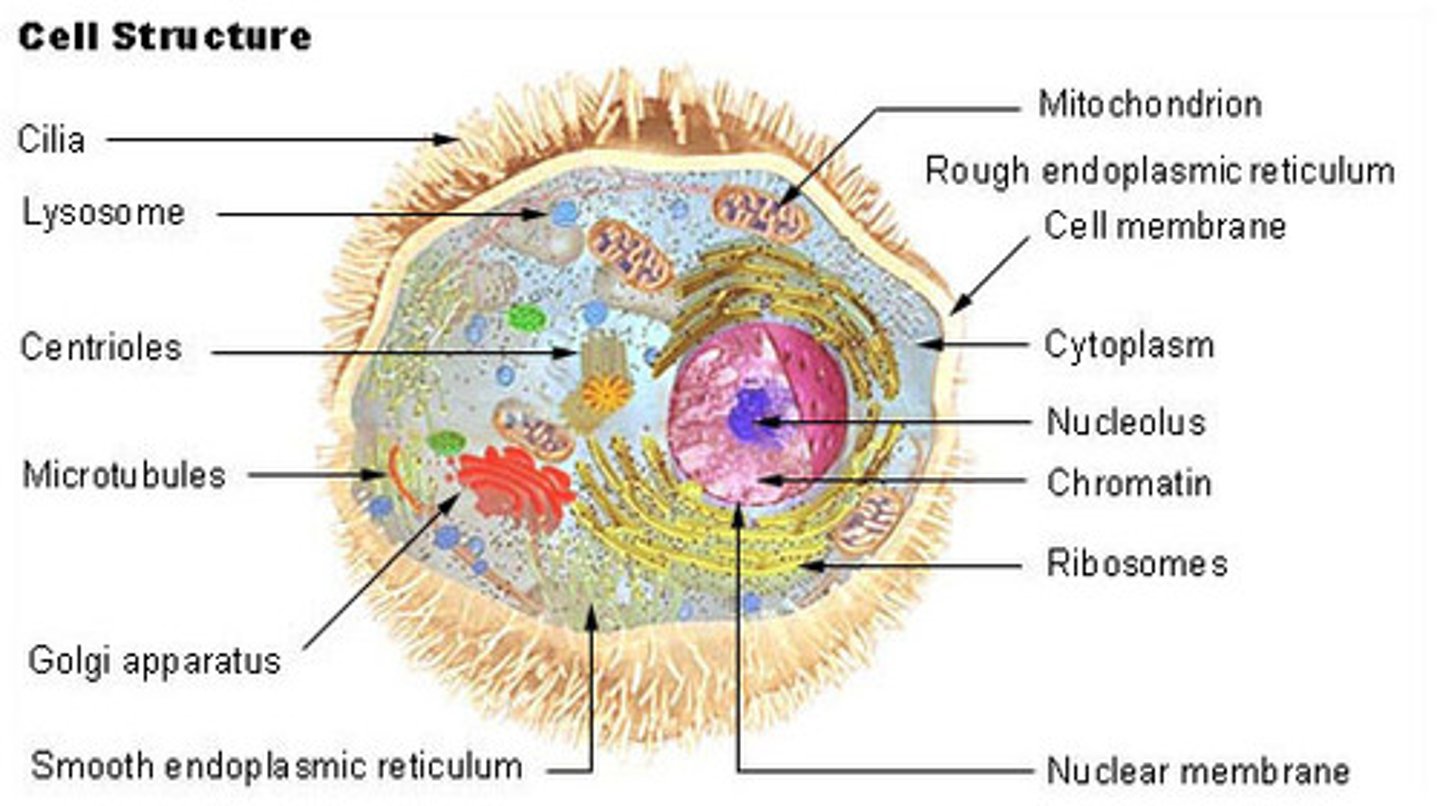
Eukaryotic Cells
Complex, with membrane-bound organelles, larger. Includes plant and animal cells.
Cocci
Spherical shape of prokaryotes.
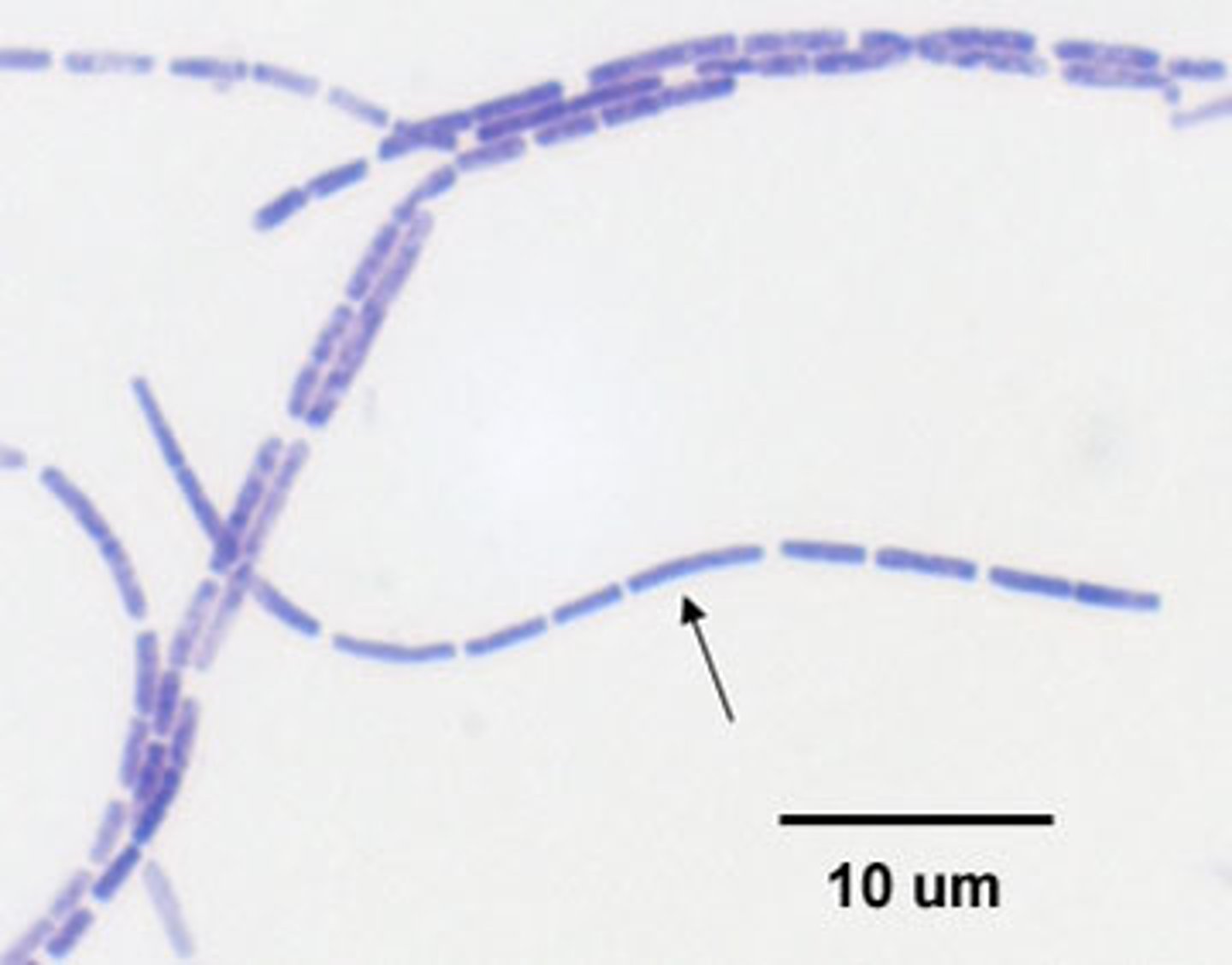
Bacilli
Rod-shaped prokaryotes.
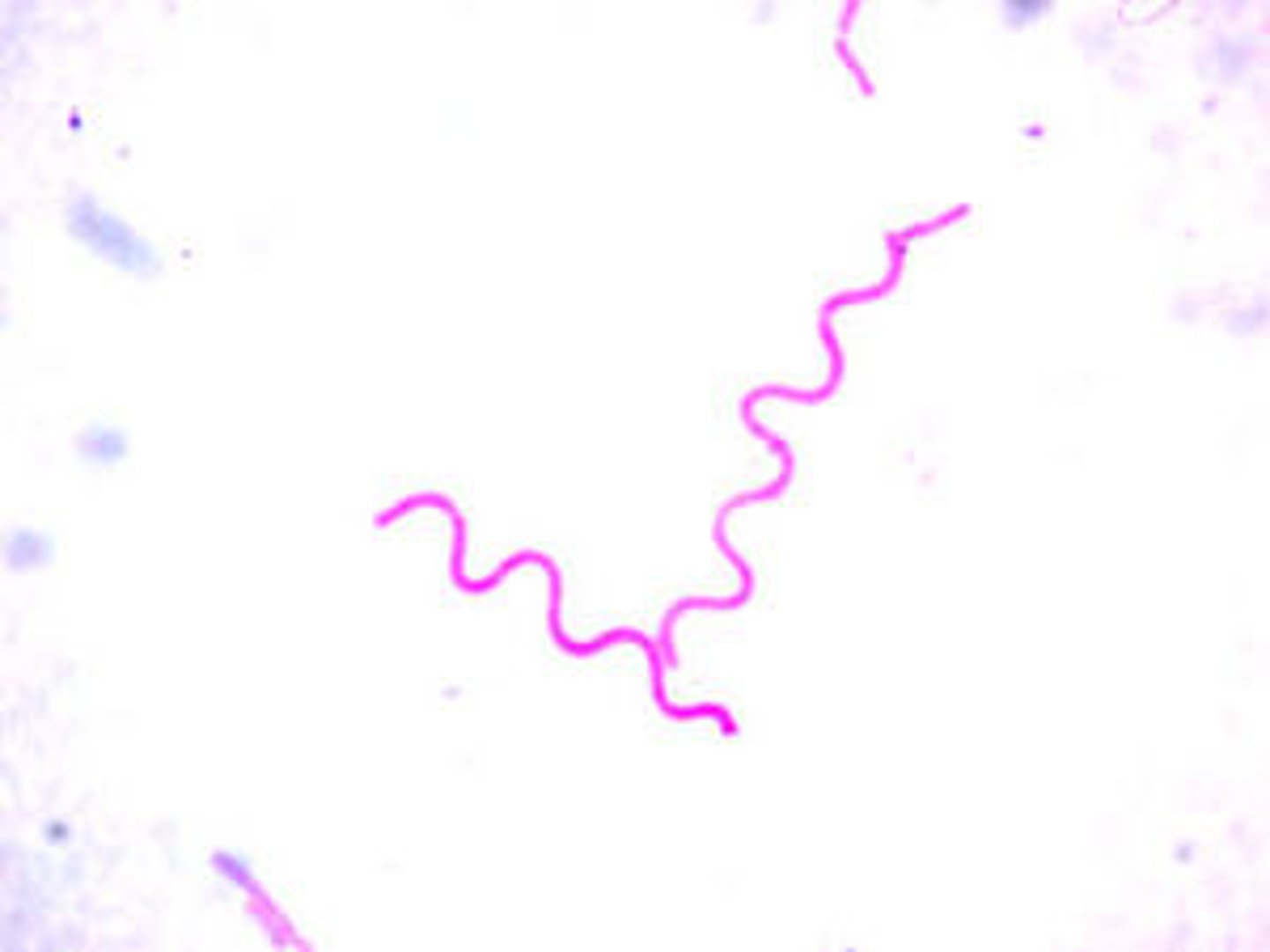
Spirilla
Spiral shape of prokaryotes.
Cyanobacteria
Photosynthetic bacteria that play a key role in oxygen production and ecosystem balance.
Plasma Membrane
A cell part that surrounds the cell.
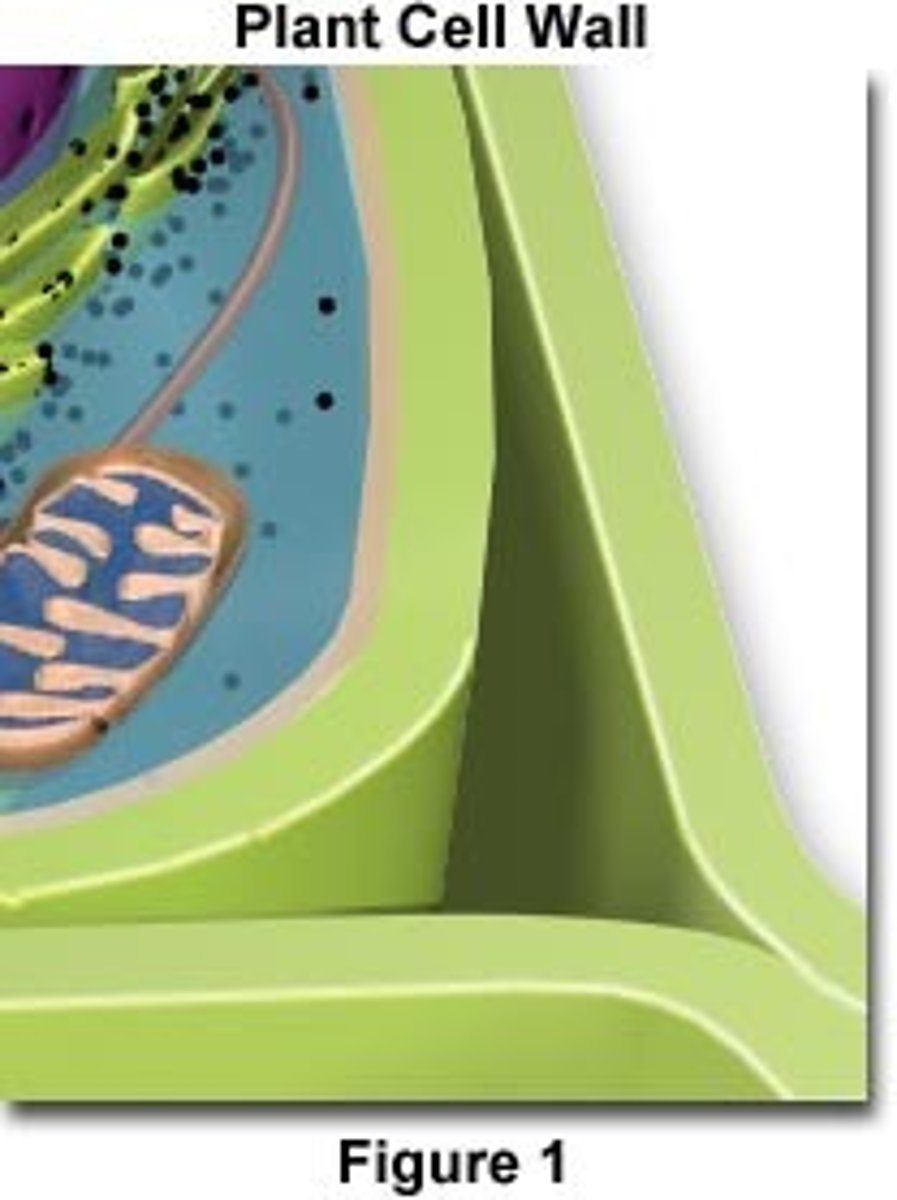
Cell Wall
A rigid outer layer found in plant cells.
Nucleoid Region
Area in prokaryotic cells where DNA is located.
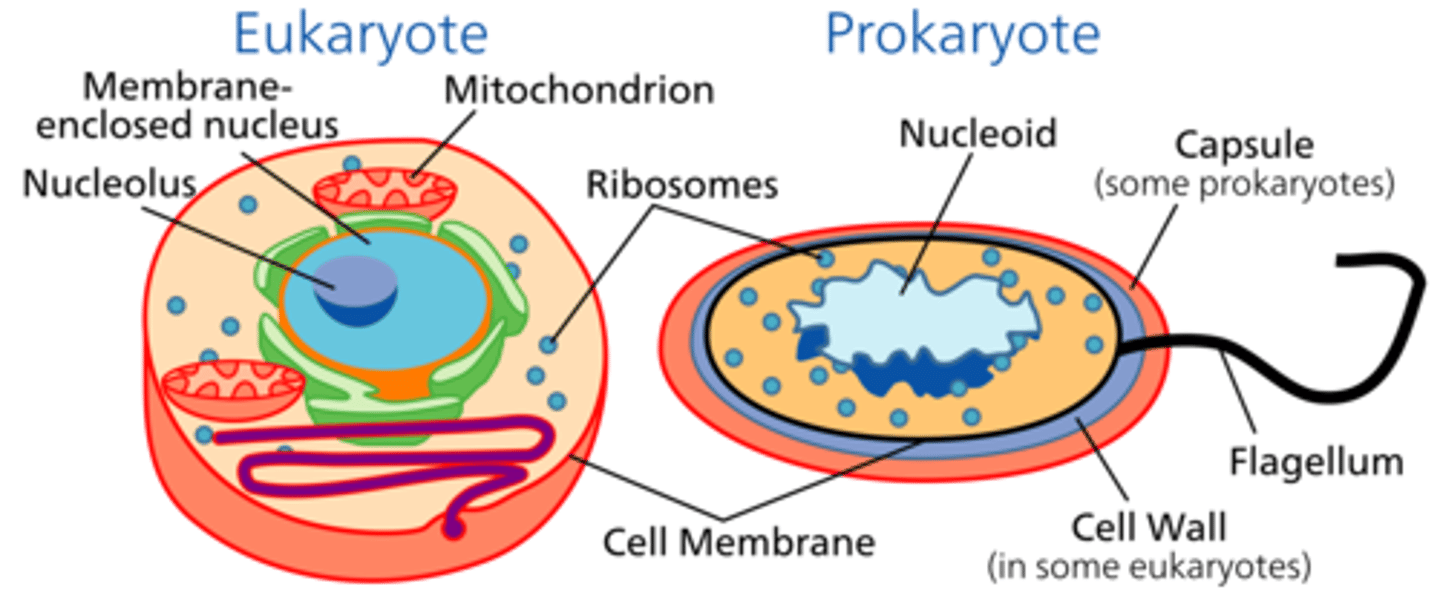
Flagellum
A tail-like structure that helps in cell movement.
Plant Cells
Have cell walls, chloroplasts, and large central vacuoles.
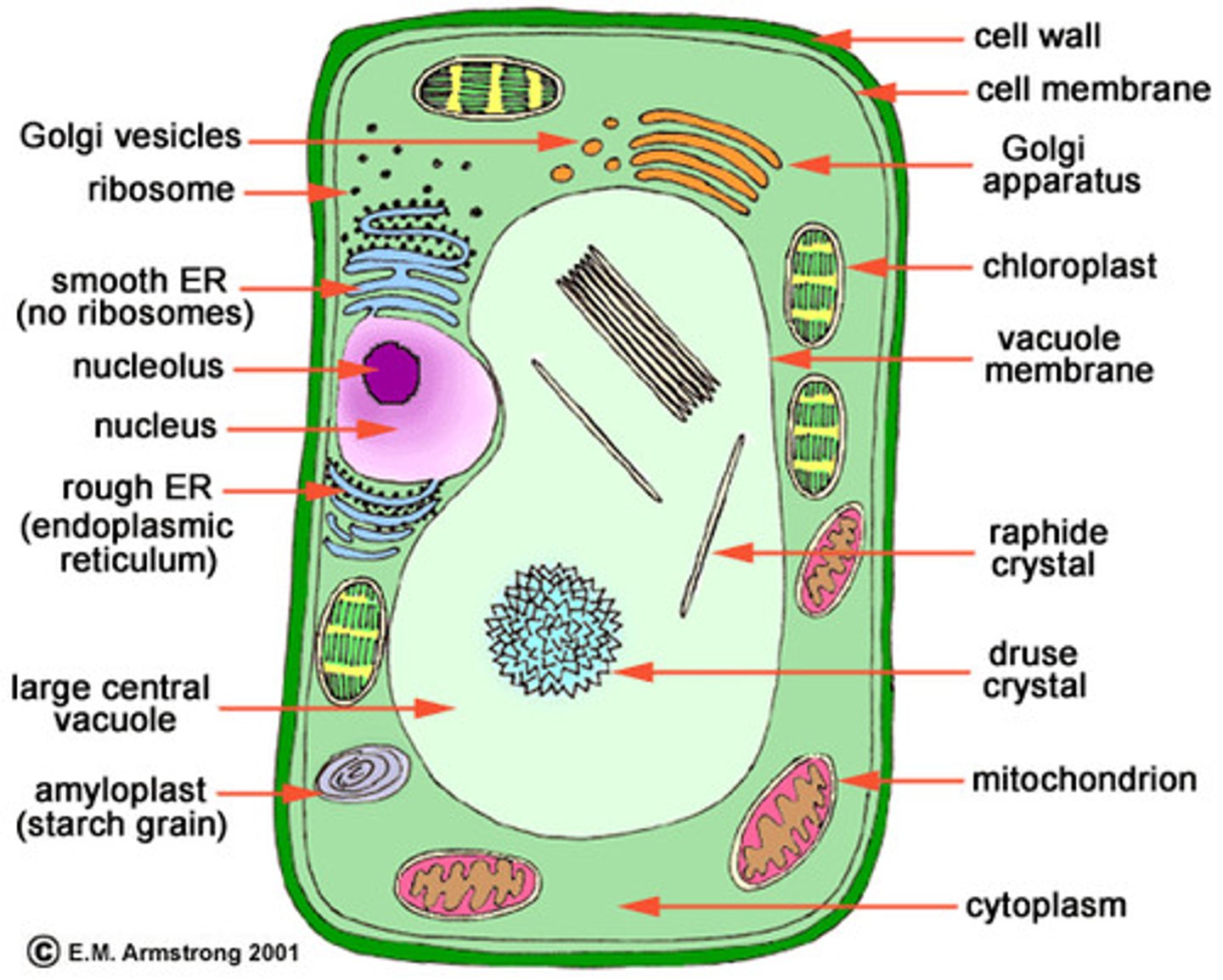
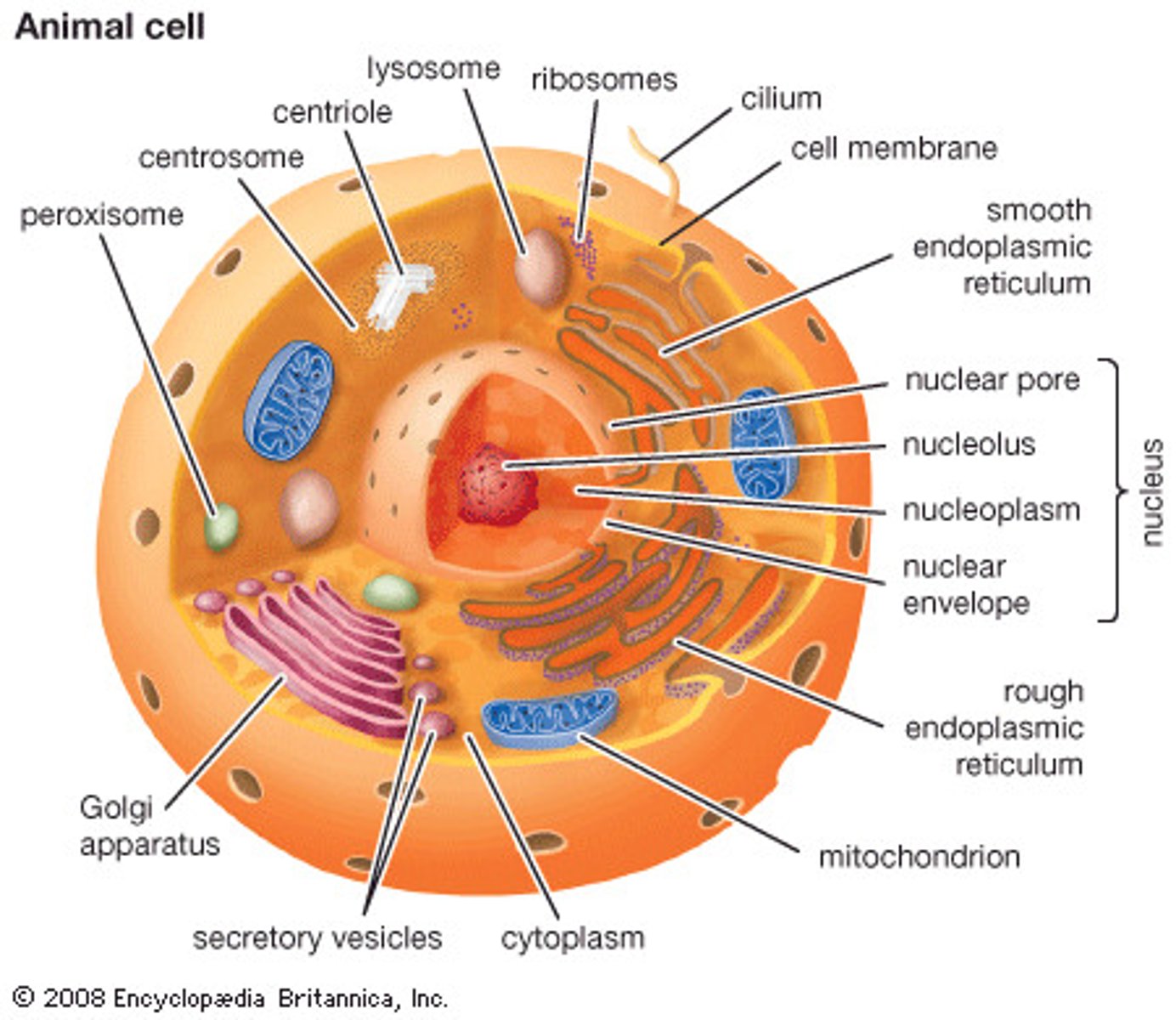
Animal Cells
Lack cell walls and chloroplasts, have small vacuoles.
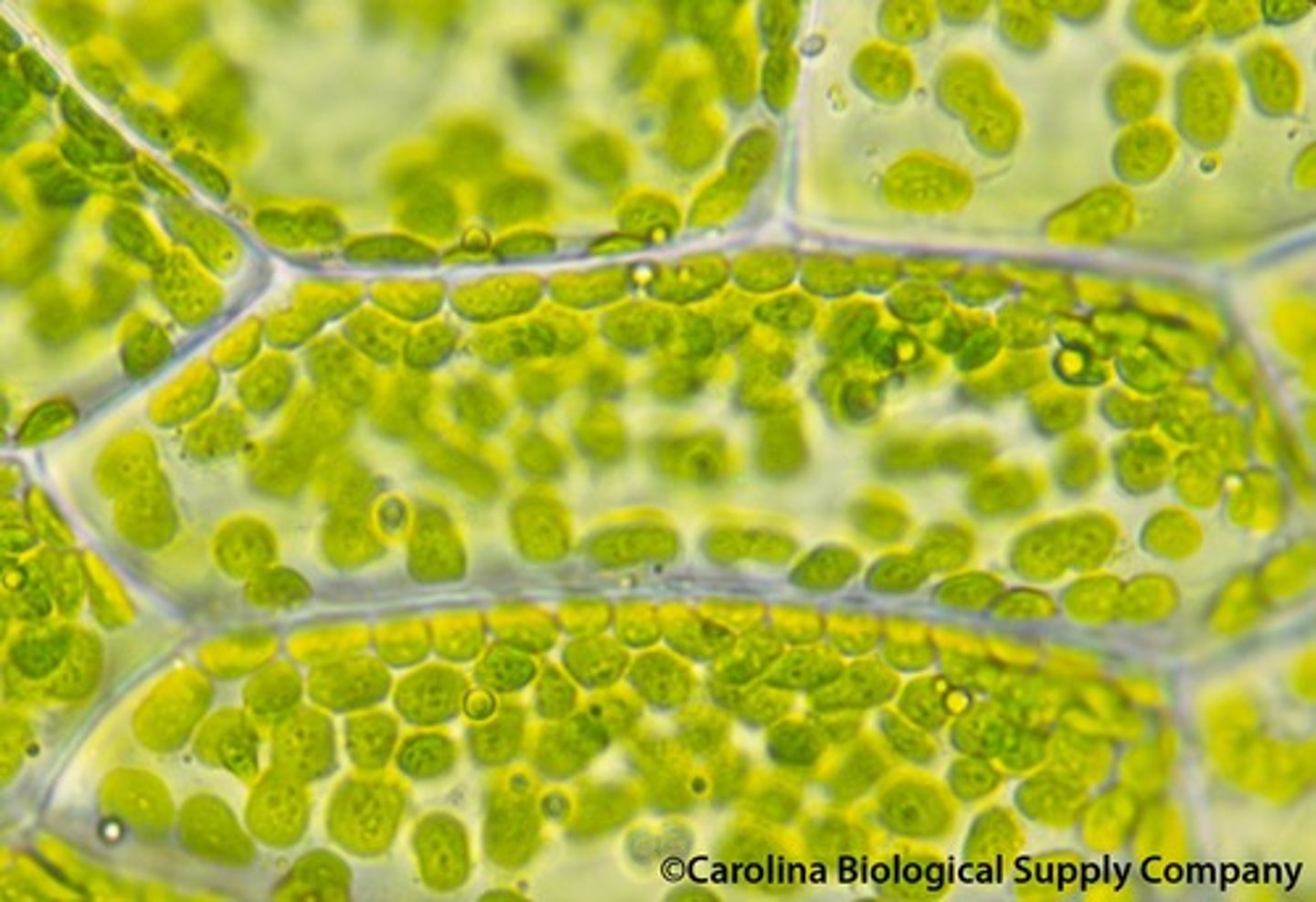
Chloroplasts
Contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
Amyloplasts
Store starch in plants.
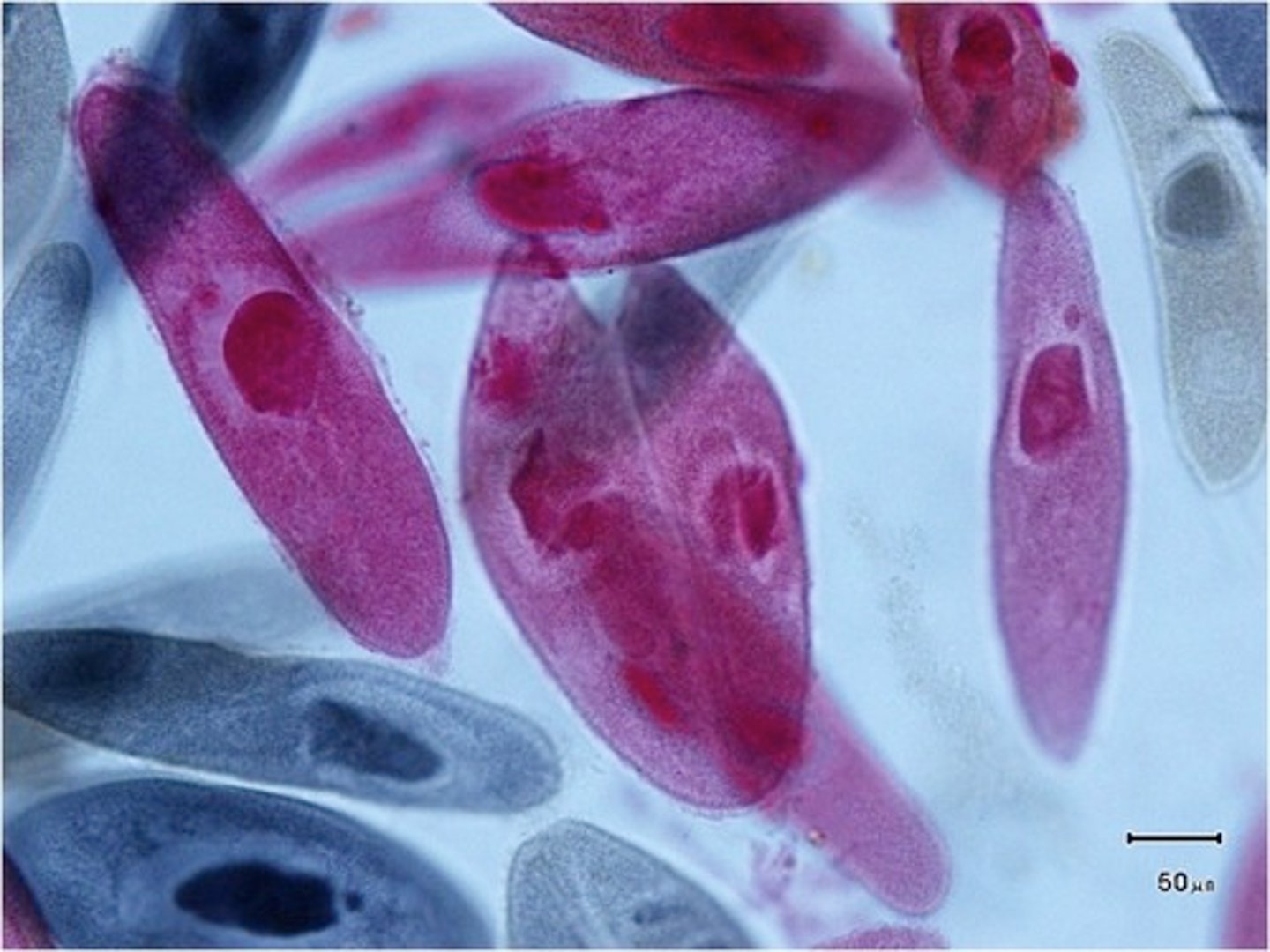
Paramecium
Single-celled organism with cilia for movement.
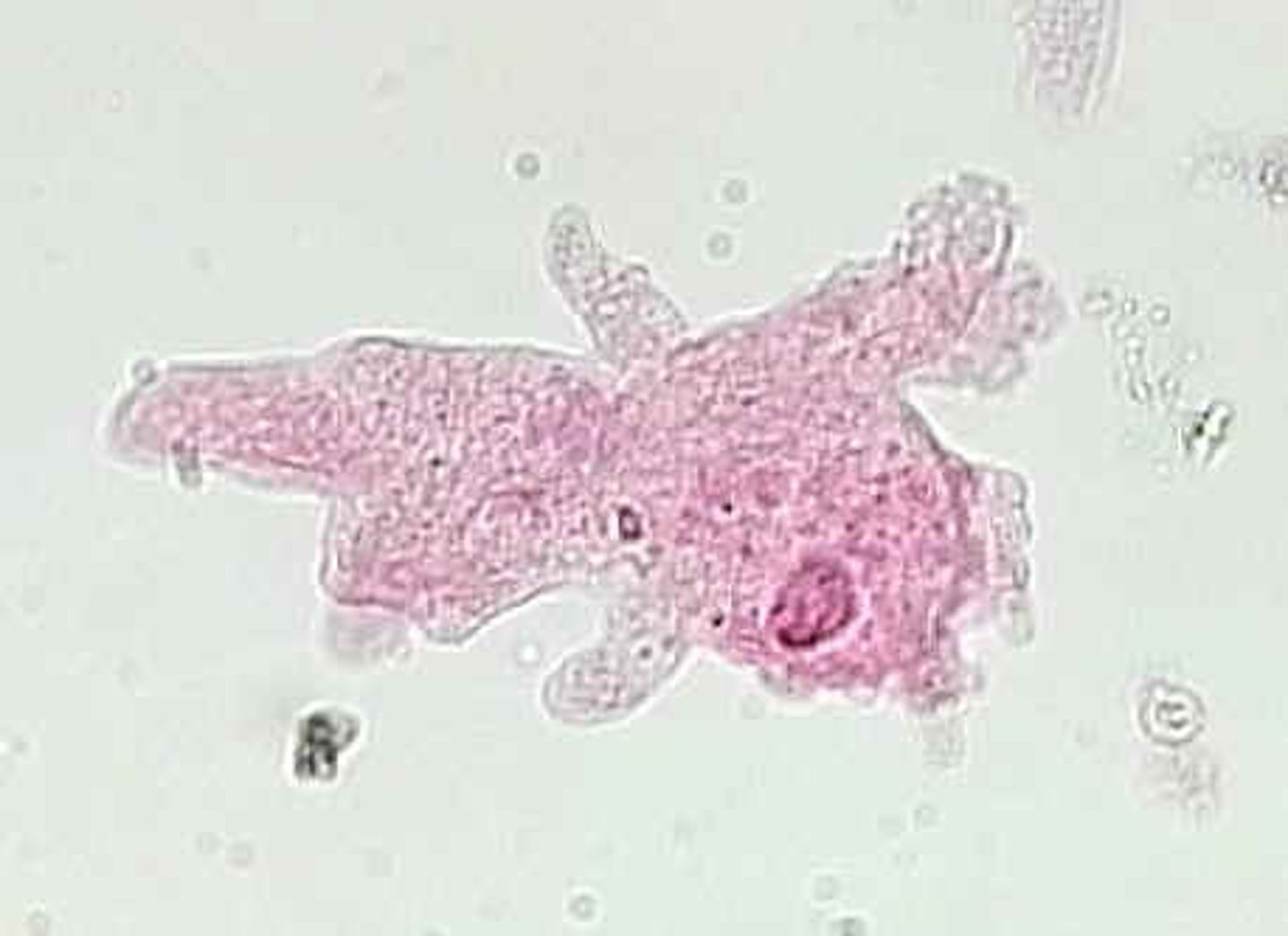
Amoeba
Single-celled organism with pseudopodia (false feet) for movement.
Brownian Movement
Random movement of particles due to thermal energy.
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane.
Hypertonic
Solution has a higher concentration of solutes than the cell (cell will lose water).
Hypotonic
Solution has a lower concentration of solutes than the cell (cell will gain water).
Isotonic
Solution has the same concentration of solutes as the cell (no net movement of water).
Solute
The substance being dissolved.
Solvent
The substance that does the dissolving (usually water).
Plasmolysis
Shrinking of plant cell membrane due to water loss in a hypertonic environment.
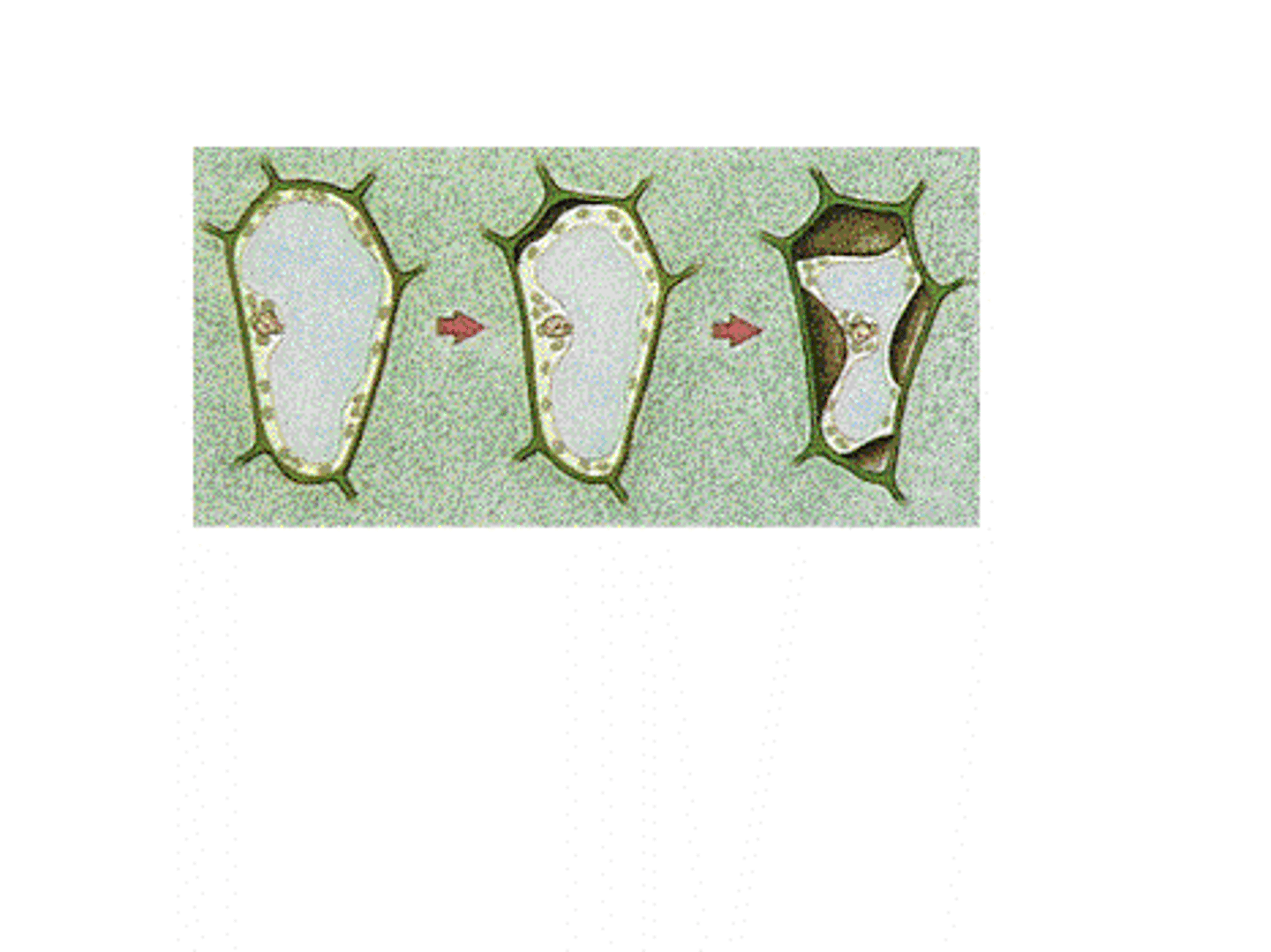
Turgor Pressure
Pressure exerted by the central vacuole in plant cells to maintain structure and prevent wilting.
Tonicity
Hypertonic-higher solutes
Isotonic-equal solutes
Hypotonic-lower solutes
Cytobaterica
has photosynthesis
smaller
______ molecules more faster
(final mass -initial mass)(divided by initial mass) x100
formula for percentage change
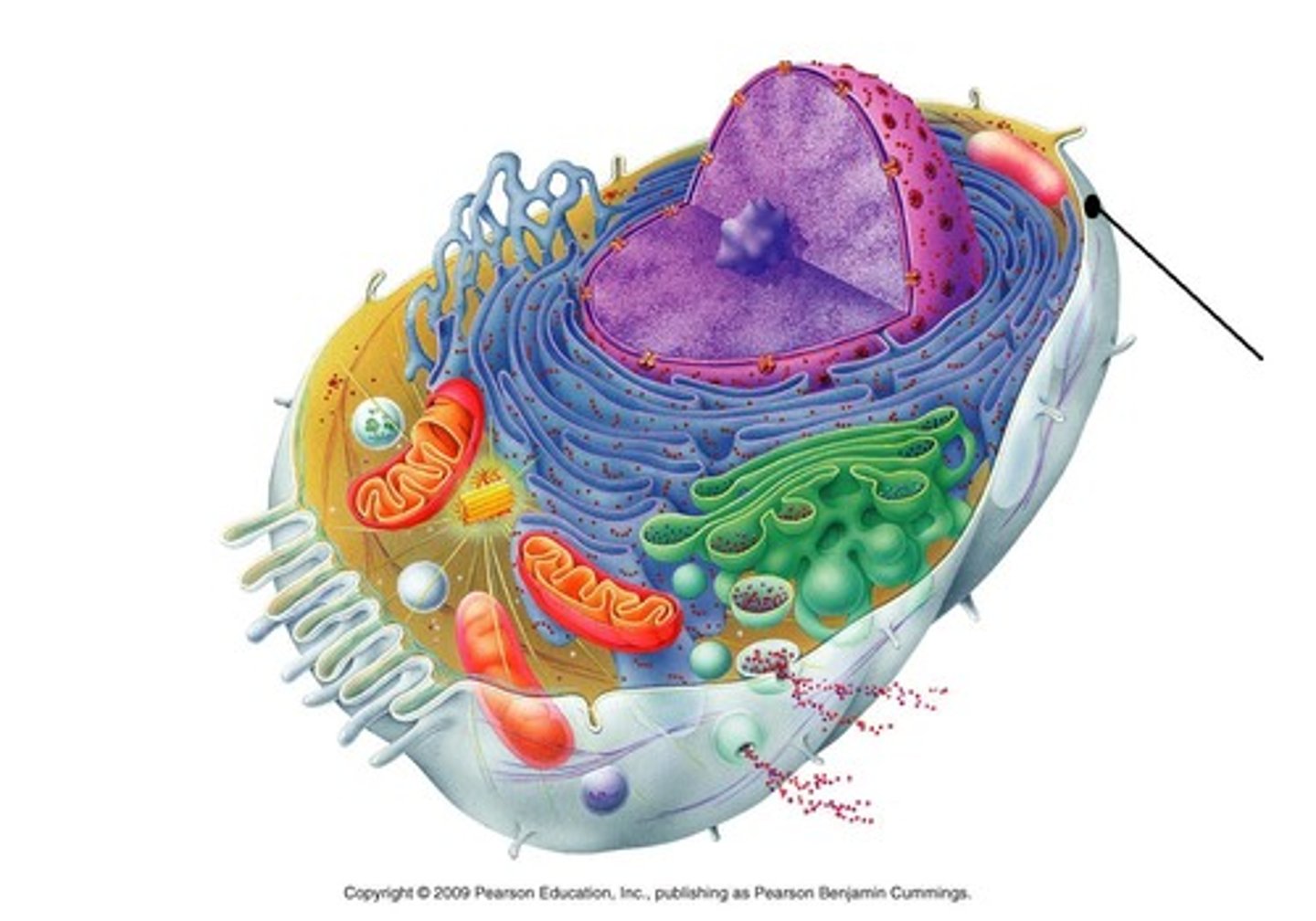
Nucleus
Membrane bound organelle where DNA is located in eukaryotes ; area where most of the genetic material is organized and expressed
Chromatin
A complex of protein and DNA found in the nucleus
Nucleolus
Site within the nucleus were ribosome subunit assembly occurs ; ribosomes are made here .
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum
Folded membranes embedded with ribosomes ; site of protein sorting and secretion .
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum
Folded membranes without ribosomes ; site of detoxification and lipid synthesis .
Golgi apparatus
Site of modification , sorting , and secretion of proteins and lipids ; the post office of the cell
Lysosomes
Site where macromolecules are degraded
Membrane - phospholipid bilayer
Membrane that controls movement of substances into and out of the cell ; site of cell signaling
Mitochondria
Site of ATP synthesis ,
Plastids - chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis in plants only
Plastids amyloplasts
Plastids that store starch in plants only
Plastids- chromoplasts
Plastids that store and synthesize pigments that give color to fruits , flowers , and vegetables ( plants only ) that provides cell never
Cell walls
plants , and fungi ; never present in animal cells Structure that provides cell support in bacteria ,
Storage vacuole
An organelle in plant cells that stores proteins , nutrients , and other compounds
Central vacuole
Site that provides storage and regulation of cell volume ; maintains turgor pressure