Muscle HIstology/ Cytology
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
which is the longest cells in the body
nerve cells (neurons)
general characteristics of muscle
excitable
contractile
extensibility
elasticity
excitable
respond to stimulation
allows control
contractile
Can shorten forcefully - movement and load carrying
extensibility
they can be stretched passively
allows flexibility
increased by range of motion
elastcity
muscles recoil when stretched
prevents injury and provides force
general uses of muscle
tone and movement
tone
smooth muscle in arteries
maintains blood pressure
skeletal muscle - joint stability and posture
movement
smooth muscle in arteries -> movement in blood
digestive tract -> movement in food
skeletal muscle -> movement in body
muscle tissue is mostly made of
cells
intermixed with
connective tissue
myoblasts
what muscle cells start out as
releases the proteins that make up muscle
blasts = create
smooth muscle
non striated
spindle shaped cells
single nucleus (per cell)
Involuntary
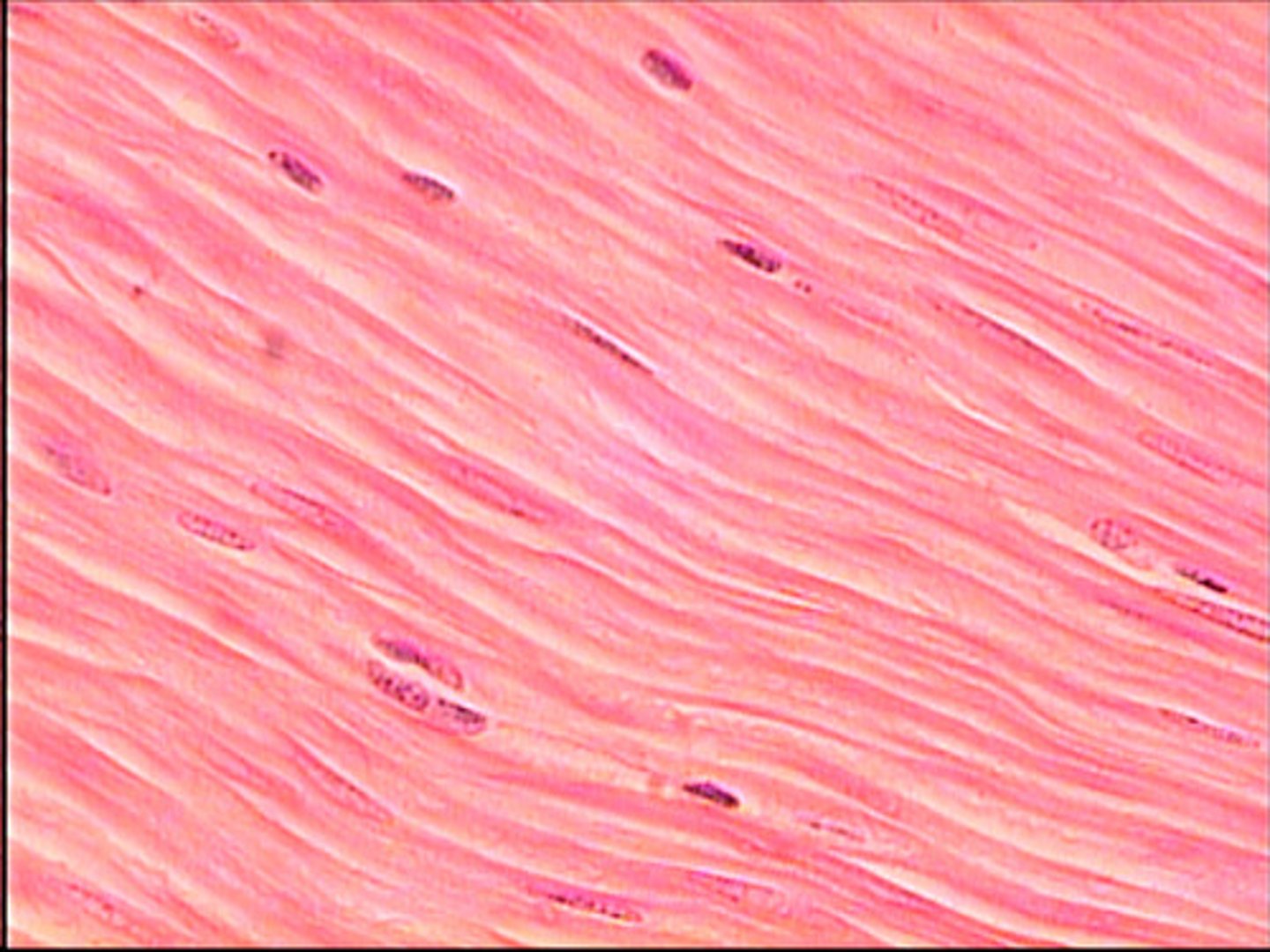
functions of smooth muscle
lines our blood vessels
lines gastrointestinal tract
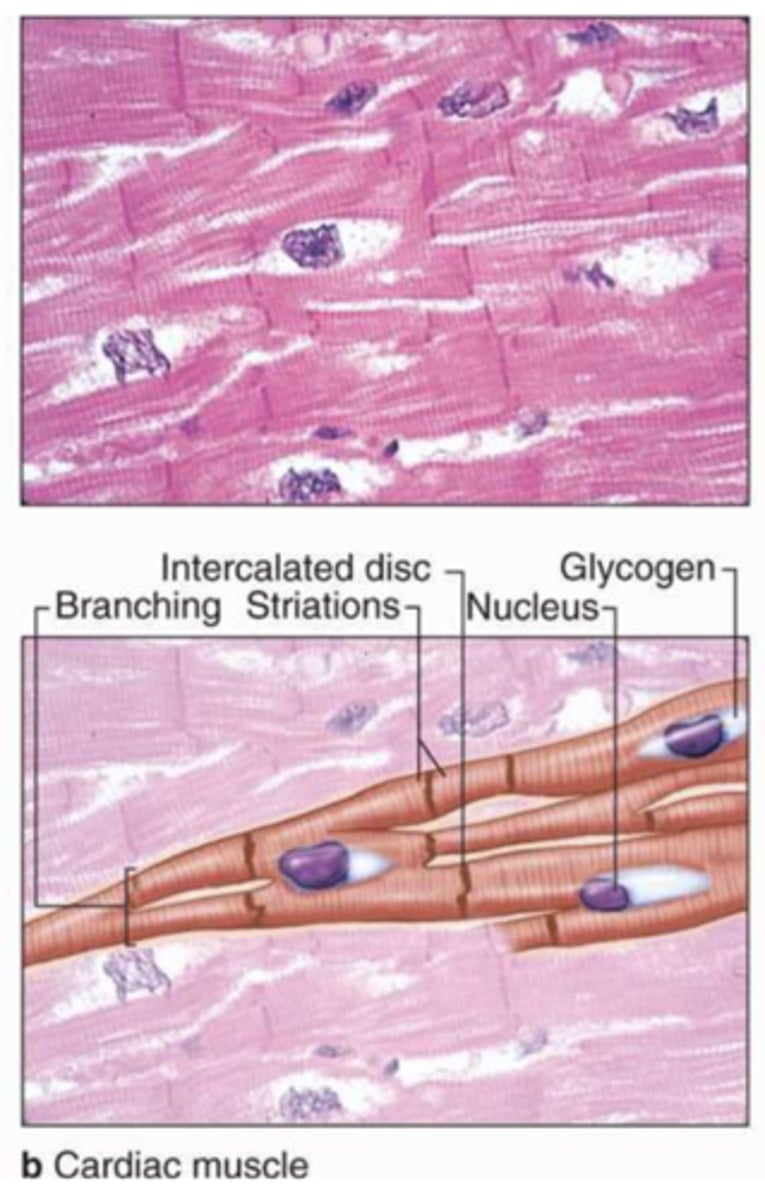
cardiac muscle
striated
cylindrical and branched
single nucleus
involuntary
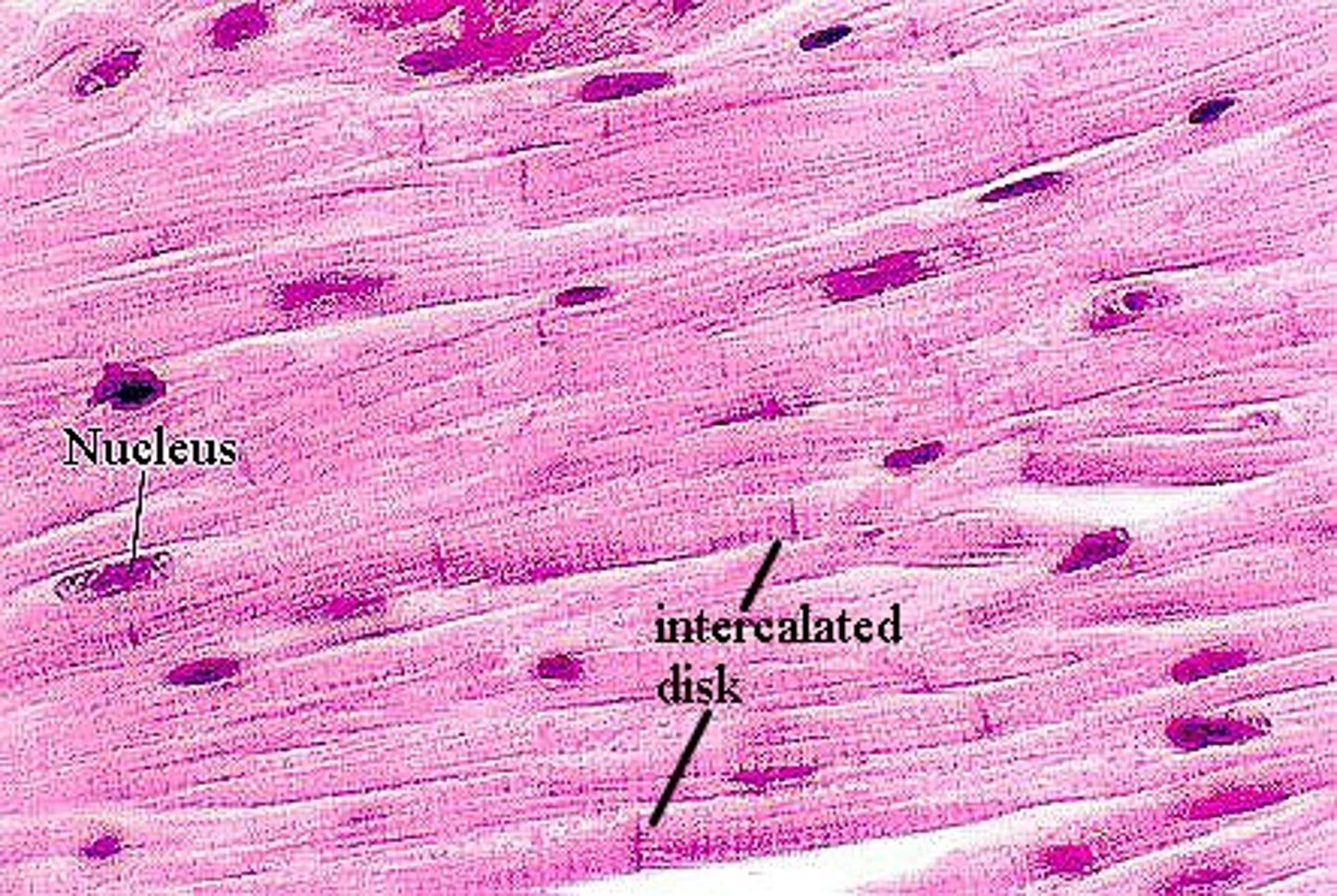
functions of cardiac muscle
pump blood
create blood pressure
skeletal muscle
striated
striped
long cylinders (for making proteins throughout the cell)
voluntary
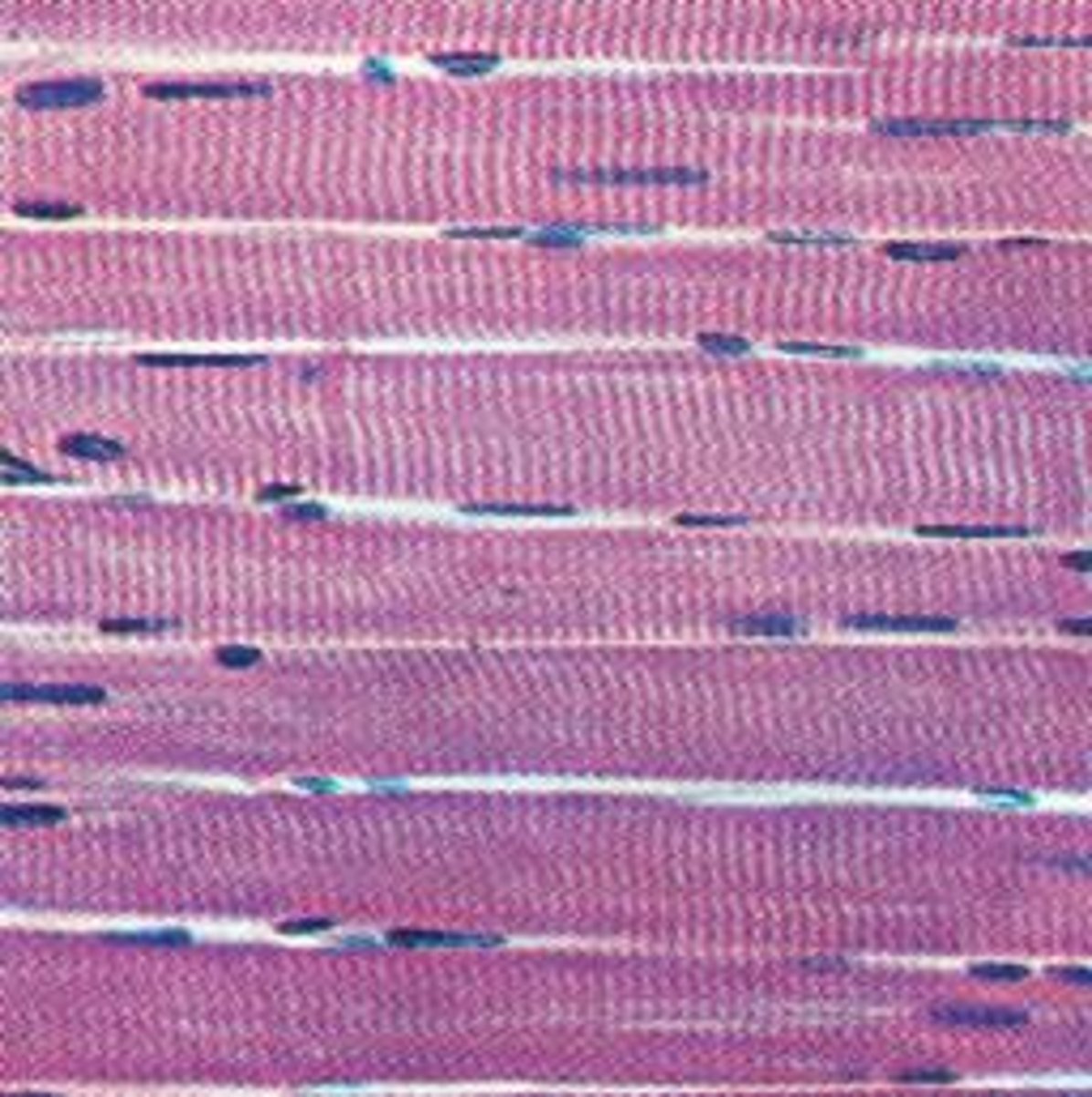
functions of skeletal muscle
body movement, maintenance of posture, protection and support, regulating elimination of materials, heat production
all energy breakdown from ATP is lost as heat
when you are exercising, you are using ATP to break down and release heart
ex: shivering
skeletal muscle cells are
surrounded by the endomysium
- areolar CT
thick cells
Skeletal Muscle Membrane (Sacrolemma)
Motor End Plate
Motor end plate
specialized region for communication with the nerves (neurons interact with the skeletal muscle
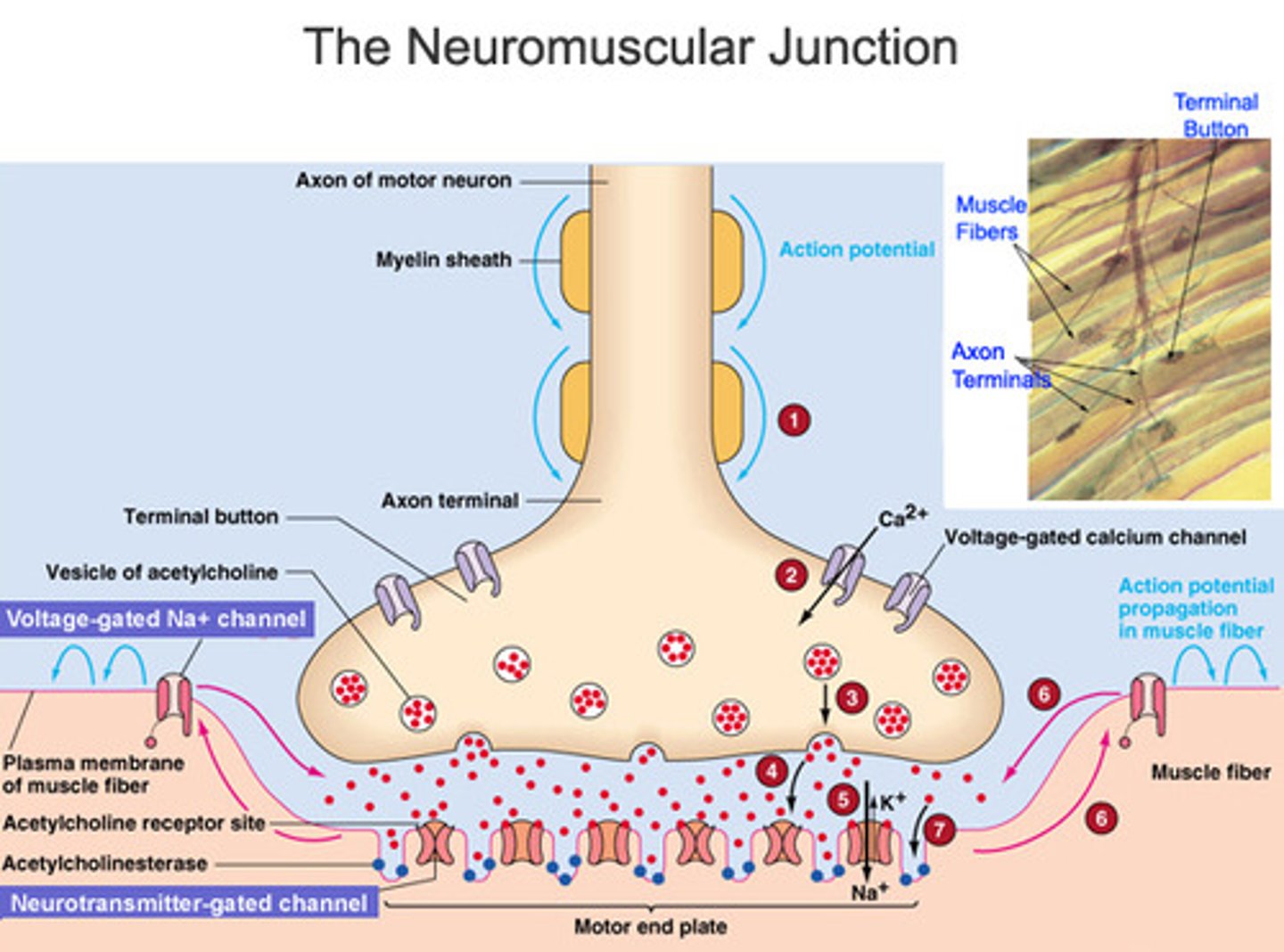
motor end plate has many
many acetylcholine (neurotransmitter) receptors
highly folded for more surface area
transverse tubules (T-Tibules)
part of the membrane
cylindrical indentations of sacolema
outer membrane "pokes in"
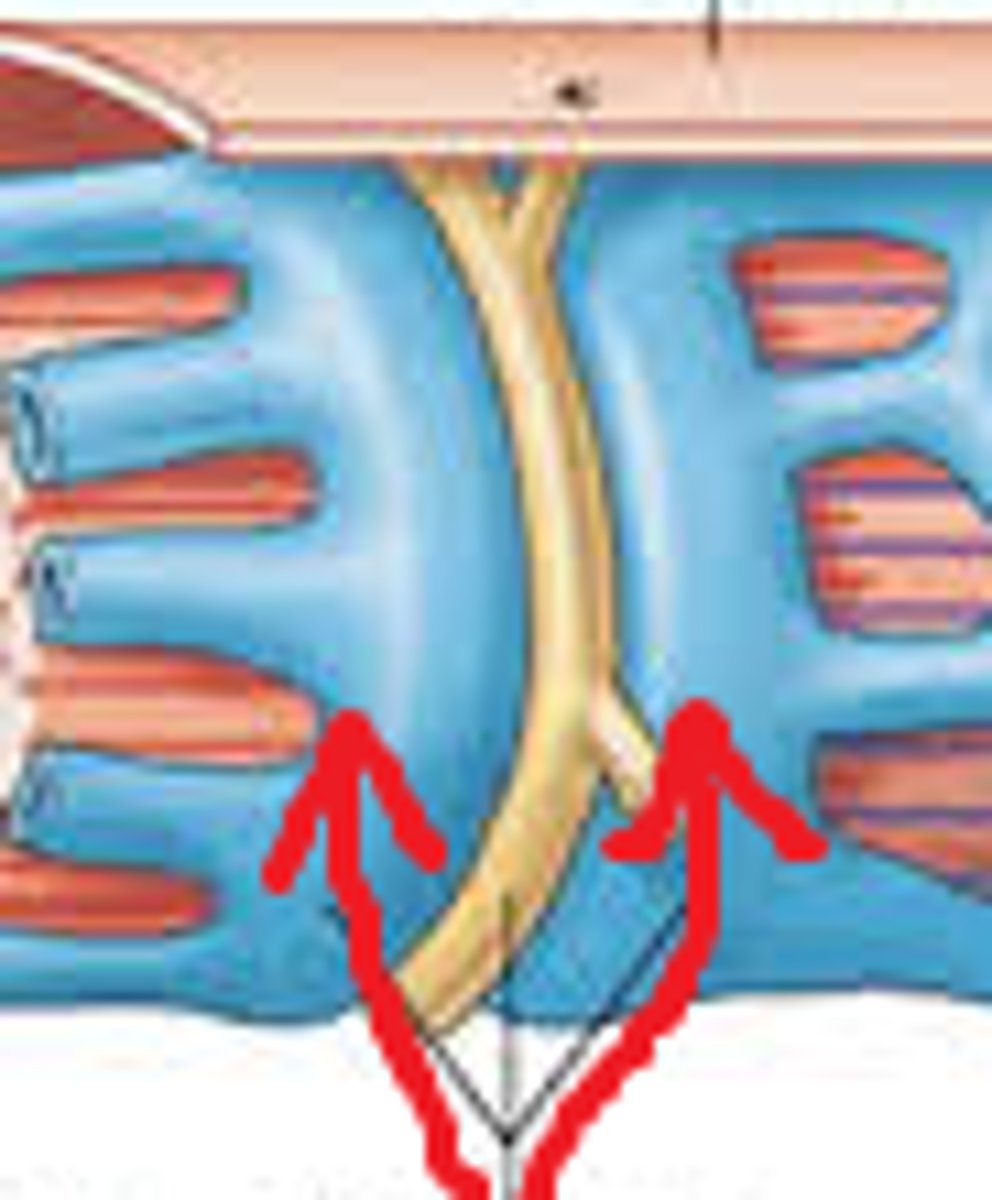
function of the t-tibules
allows action potential (stimulus from nerve) to spread deep into the thick cells
sarcoplasmic reticulum (non apart of membrane)
in muscle cells
sarcoplasmic reticulum function
calcium storage
important for muscle contraction
interacts with tubules to get stimulation from them
Multinucleate (multiple nuclei)
can produce proteins all throughout fiber
prevents cell proliferation (muscle cells don't divide much)
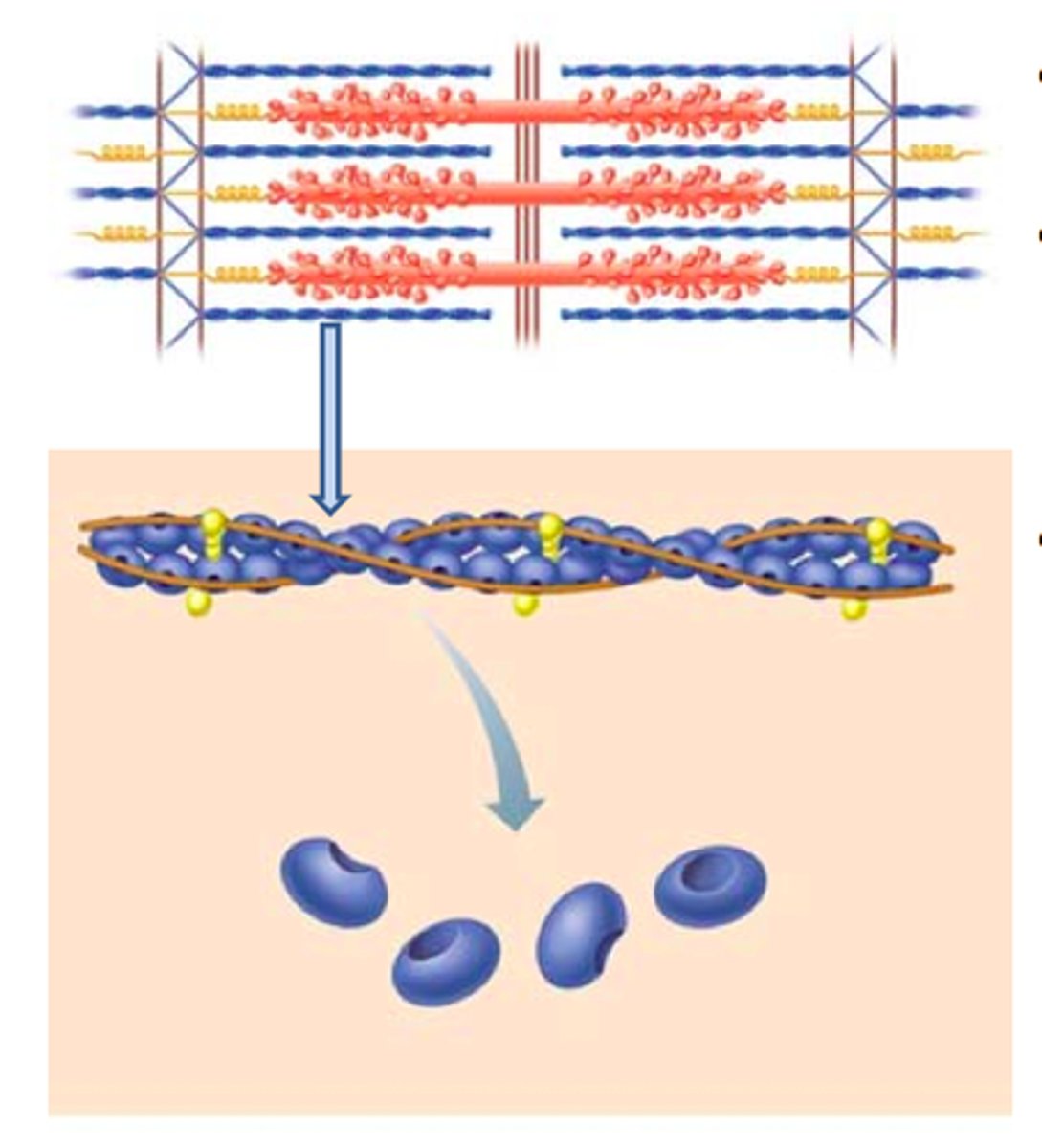
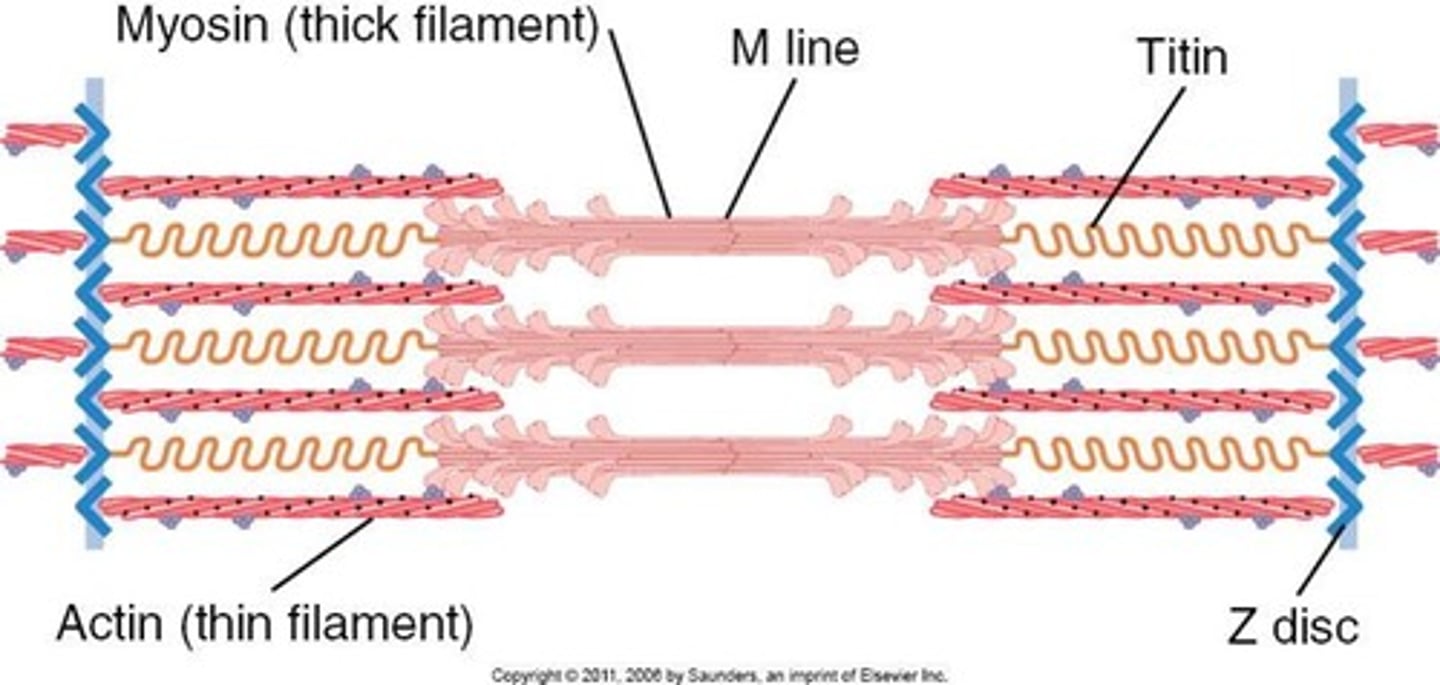
functional unit of muscle: Sarcromere
from one z-disk to the next
made up of myofilaments
z- line filaments together
different myofilaments
myosin
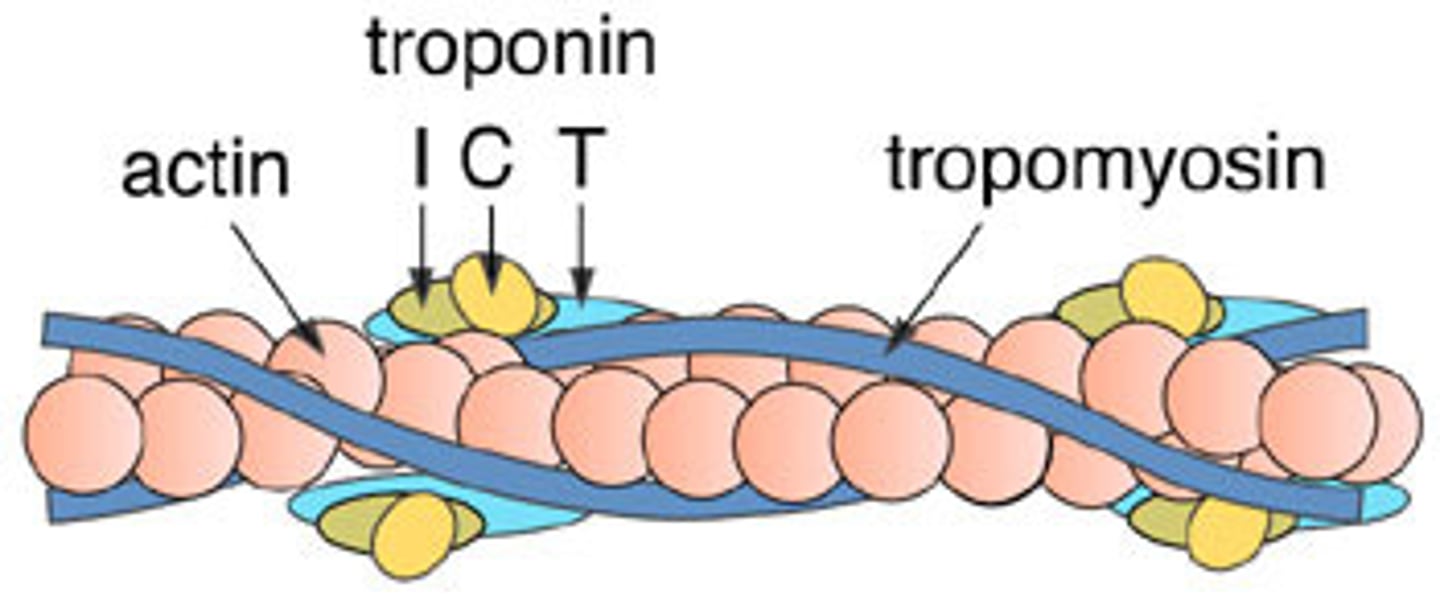
actin
troponin
tropomyosin
titin
myosin
thick filament
tail portion bundled into rope
head sticks out and crates sliding of filaments
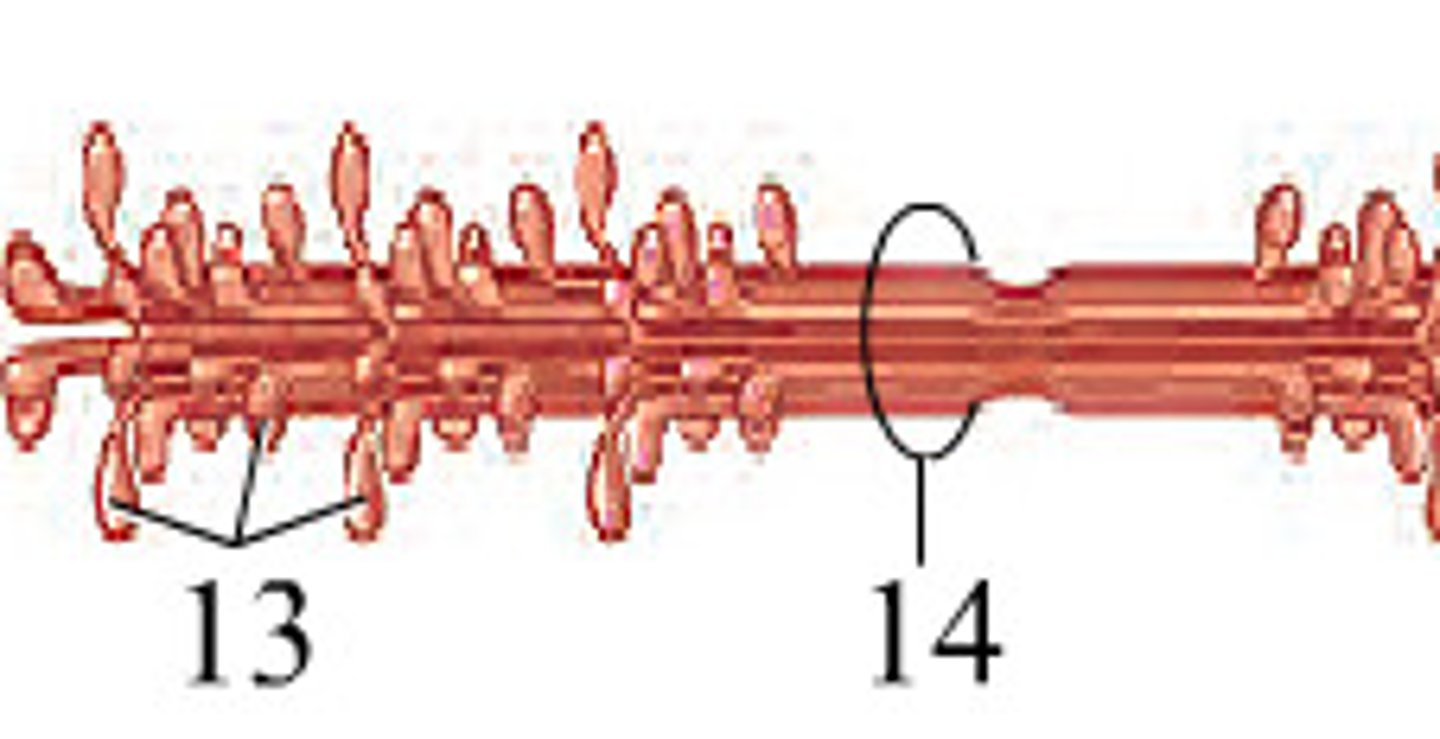
actin
thin filament
globular units string together
what does the sliding
troponin
calcium binding site
changes shape with calcium
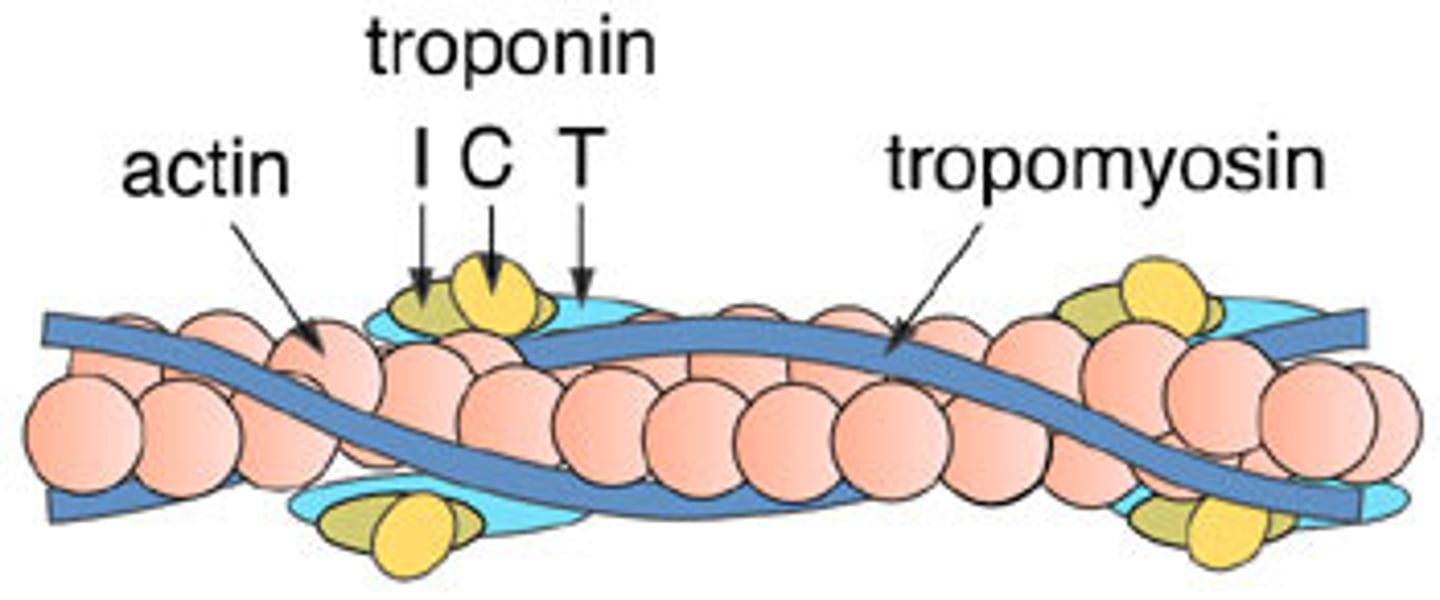
tropomyosin
wound around actin
strengthes actin, blocks myosiiin head from binding
titin
spring shaped
elastic component of muscle
what is the 3-d relationship with myosin
6 actins surround each mysoin
if there was to many it would overlap