Autism Spectrum Disorder: DSM-5 Criteria, Symptoms, and Treatments
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What are the DSM-5 criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder?
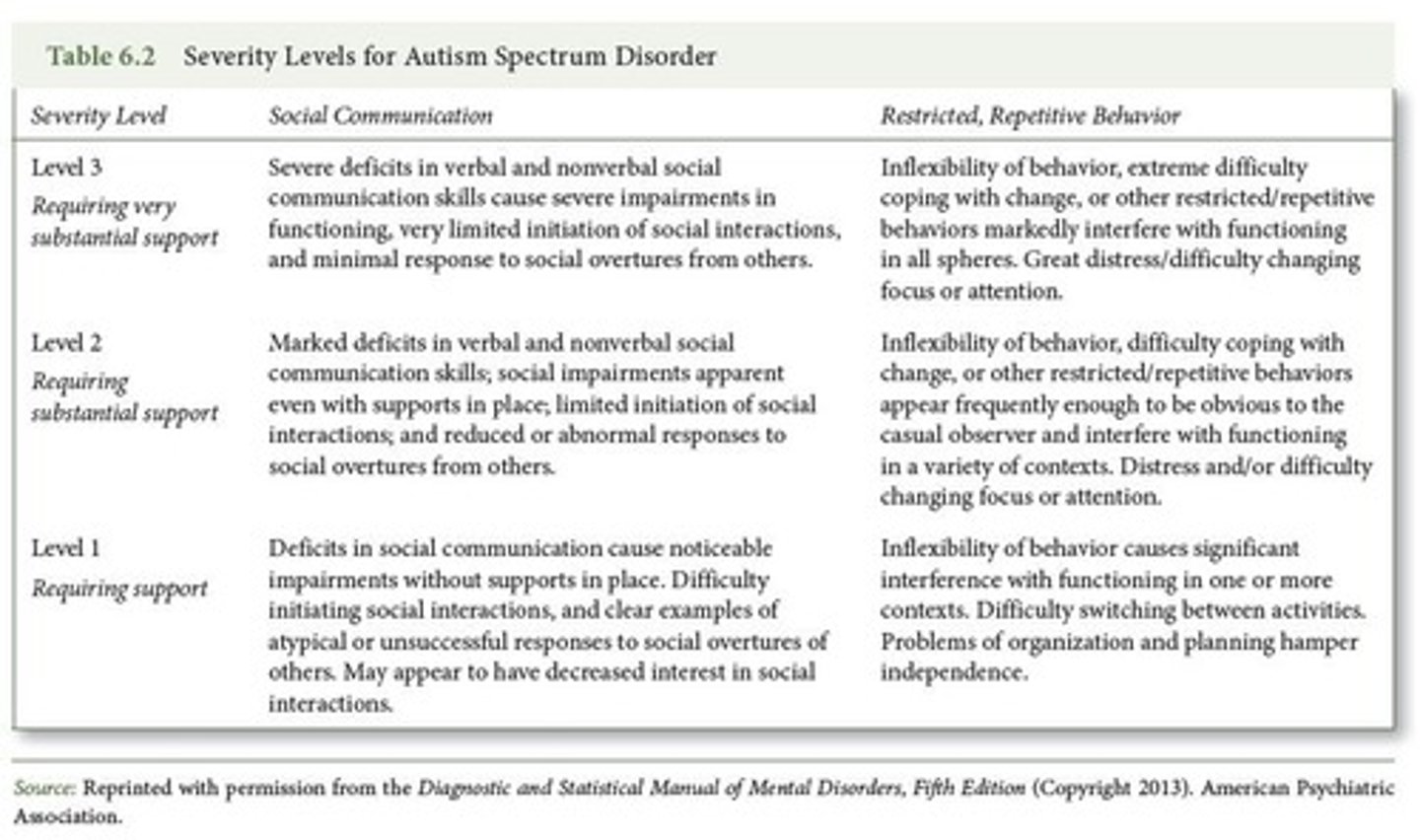
A. All 3 deficits in social communication/social interactions; B. 2 of 4 restrictive, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities; C. Must be present in early developmental period; D. Symptoms cause clinically significant impairment; E. Not better explained by Intellectual Disability or Global Developmental Delay.
What are the deficits in social communication/social interactions for Autism?
Deficits include: A. Reciprocity (failure of back and forth conversations, reduced sharing of interests/emotions, failure to initiate/respond to interactions); B. Nonverbal communication (poorly integrated verbal/nonverbal communication, abnormalities in eye contact/body language, total lack of facial expressions); C. Developing and maintaining relationships (difficulties adjusting behavior to social context, sharing imaginative play, absence of interest in peers).
What are the restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior in Autism?
Patterns include: A. Stereotyped movements or speech (motor stereotypies, lining up objects, echolalia); B. Insistence on sameness (extreme distress at small changes, rigid thinking); C. Highly restricted interests (strong attachment to unusual objects, perseverative interests); D. Hyper/hypo-reactive to sensory input (indifference to pain/temperature, adverse response to sounds/textures, excessive smelling/touching of objects).
What is the significance of the early developmental period in Autism diagnosis?
Symptoms must be present in the early developmental period to meet DSM-5 criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder.
What types of impairments must Autism symptoms cause?
Symptoms must cause clinically significant impairment in social, occupational, or other areas of current functioning.
What are the DSM-5 severity specifiers for Autism?
Severity specifiers include: A. With or without accompanying intellectual impairment; B. With or without accompanying language impairment; C. Associated with a known medical or genetic condition; D. Associated with another neurodevelopmental, mental, or behavioral disorder.
What percentage of individuals with Autism have an IQ below 70?
Approximately 33% of individuals with Autism have an IQ below 70, indicating Intellectual Disability.
What is echolalia in the context of Autism?
Echolalia refers to the repetition of phrases or sentences, often seen in individuals with Autism as a form of communication.
What challenges do individuals with Autism face in nonverbal communication?
Challenges include poorly integrated verbal and nonverbal communication, abnormalities in eye contact and body language, and a total lack of facial expressions.
What is meant by 'insistence on sameness' in Autism?
Insistence on sameness refers to extreme distress at small changes, difficulty with transitions, and rigid thinking patterns.
What are some examples of hyper-reactivity to sensory input in Autism?
Examples include adverse responses to specific sounds or textures, indicating heightened sensitivity to sensory experiences.
What are some examples of hypo-reactivity to sensory input in Autism?
Hypo-reactivity can manifest as appearing indifferent to pain or temperature, indicating reduced sensitivity to sensory experiences.
What difficulties might individuals with Autism experience in developing relationships?
Difficulties may include adjusting behavior to social contexts, sharing imaginative play, and a complete absence of interest in peers.
What is the role of the DSM-5 in diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder?
The DSM-5 provides standardized criteria for diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder, ensuring consistency in identification and treatment.
How does Autism affect social reciprocity?
Individuals with Autism may struggle with back-and-forth conversations, reduced sharing of interests or emotions, and may fail to initiate or respond to social interactions.
What is the significance of the developmental history in Autism diagnosis?
The developmental history helps confirm that symptoms were present early in life, which is crucial for an accurate diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder.
What is the prevalence of intellectual impairment in individuals with Autism?
Approximately 33% of individuals with Autism have an IQ below 70, while 42% have an IQ above 85, indicating a range of intellectual abilities.
What types of interests might be considered fixated in Autism?
Fixated interests may include strong attachments to unusual objects or excessively circumscribed or perseverative interests.
What are motor stereotypies in the context of Autism?
Motor stereotypies are repetitive movements, such as hand-flapping or rocking, commonly observed in individuals with Autism.
What is the impact of Autism on occupational functioning?
Symptoms of Autism can lead to significant challenges in occupational settings, affecting job performance and social interactions.
What percentage of boys are estimated to have ASD according to Maenner et al. (2020)?
32%
What are the DSM-5 specifiers for ASD?
With or without accompanying intellectual impairment; with or without accompanying language impairment; associated with a known medical or genetic condition or environmental factor; associated with another neurodevelopmental, mental, or behavioral disorder.
What are some known conditions associated with ASD?
Rett syndrome, Fragile X syndrome, Down syndrome, epilepsy, environmental exposure (e.g., valproate, fetal alcohol syndrome, very low birth weight).
What is the prevalence of ASD among US children as per Maenner et al. (2020)?
About 1.85%.
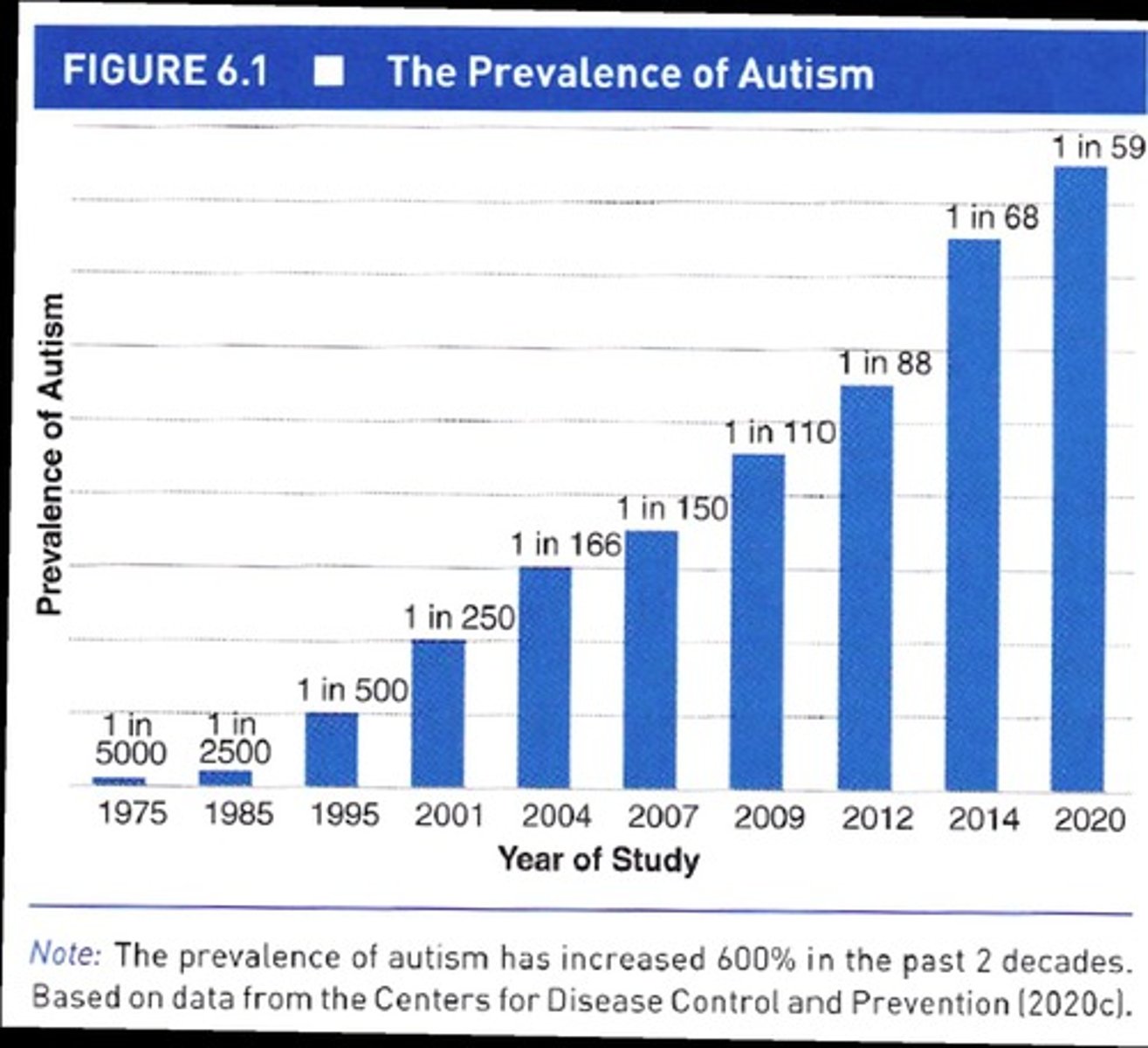
What is the male to female ratio for ASD prevalence?
Approximately 4:1 (boys:girls).
What are common comorbid disorders associated with ASD?
ADHD, behavioral and impulse-control disorders, anxiety, depression, bipolar disorders, tics and Tourette's, self-injury, feeding, elimination, or sleep disorders.
What percentage of individuals with ASD have at least one comorbid disorder?
70%.
What are communication challenges faced by individuals with ASD?
50% of those with ASD and Intellectual Disability are nonverbal; challenges include pronoun reversal, abnormal prosody, problems with pragmatics, and one-sided communication.
What significant changes were made in the DSM-5 regarding ASD?
ASD is now a single diagnosis; Asperger's Disorder and Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified (PDD-NOS) were collapsed into ASD; tightened criteria and added dimensional severity rating.
What is the Social Communication Disorder in relation to ASD?
It is similar to ASD but without restricted repetitive behaviors (RRBs) or disruptive behaviors, with problems in using verbal and nonverbal communication appropriately.
What factors may contribute to the increasing prevalence of ASD?
Real increases due to food allergies, metabolic disorders, neurological problems from toxins, advanced maternal age; changes in diagnostic practices, greater awareness, and broader definitions.
What did the multisite study by Lord et al. (2012) reveal about ASD diagnosis?
The site mattered more than other factors in diagnostic practices, suggesting variability in how distinctions among ASD, ASP, and PDD were interpreted.
What is the significance of the DSM-5's dimensional severity rating?
It allows for a more nuanced understanding of the severity of symptoms within the ASD diagnosis.
What are some reasons why ASD may be less noticeable in girls?
Girls may have stronger social and communication skills, which can mask ASD symptoms.
What is the impact of boys' hormones on the development of ASD?
Boys' hormones may play a role in the development of ASD, contributing to the higher prevalence in boys.
What is the significance of the term 'pronoun reversal' in ASD?
It refers to the use of 'you' or 's/he' instead of 'I', indicating a communication challenge.
What does abnormal prosody refer to in the context of ASD?
It refers to atypical tone and manner of speech, which can affect communication.
What does the term 'one-sided communication' mean for individuals with ASD?
It describes a tendency to talk to others rather than engaging in reciprocal conversation.
What is the typical age of onset for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Usually less than 2 years old.
What are some early signs of ASD?
Aloofness, avoidant behavior, lack of joint attention, and language delays.
What percentage of children with ASD show no signs until after age 2?
Approximately one-third.
What factors influence the prognosis of ASD?
IQ, linguistic ability, and social engagement.
Is there a cure for Autism Spectrum Disorder?
No, there is no cure for ASD.
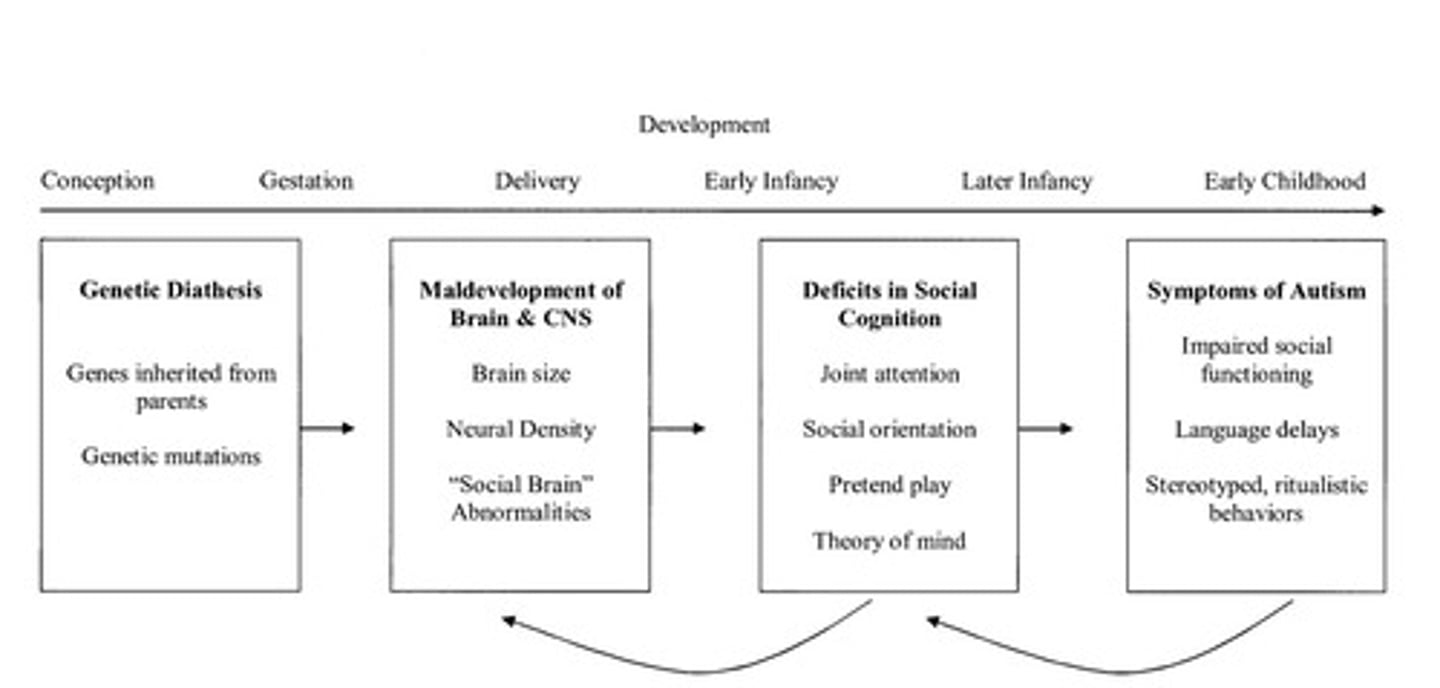
What are the main categories of factors contributing to ASD?
Genetic factors, early environment, brain structure and functioning, and social cognition deficits.
What is the concordance rate for ASD in monozygotic twins?
85-90%.
What is the concordance rate for ASD in dizygotic twins?
15-20%.
What environmental factors may contribute to ASD?
Prenatal toxins, viruses, maternal allergies, advanced parental age, and sex hormones from infertility treatments.
What is the growth dysregulation hypothesis related to ASD?
It suggests abnormal patterns of brain growth, including large head circumference and high synaptic density.
What brain region is associated with processing social information in ASD?
The amygdala, which is typically smaller in individuals with ASD.
How do individuals with ASD process facial information compared to neurotypical individuals?
ASD individuals process it in the inferior temporal gyri, while neurotypical individuals process it in the right fusiform gyrus.
What is joint attention?
Shared attention on an object or event, which includes responding to and initiating joint attention.
How does social orientation differ in children with ASD?
They focus more on objects than people and miss out on learning social communication skills.
What is symbolic play and how is it affected in ASD?
Symbolic play involves pretending one object is another; it is often delayed, more simple, and less creative in children with ASD.
What is theory of mind?
The understanding that others have mental states that motivate their behavior.
What role does social cognition play in ASD?
Deficits in social cognition lead to challenges in joint attention and social communication skills.
What is the impact of higher socio-economic status (SES) on ASD diagnosis?
ASD is more common among children with higher SES, possibly due to greater access to services.
What is the significance of linguistic ability in ASD prognosis?
Higher linguistic ability predicts better social outcomes later in life.
What percentage of the general population is affected by ASD?
1-2%.
What is the increased risk of ASD if a sibling has the disorder?
18-20% if one sibling has ASD, and approximately 33% if two siblings have ASD.
What genetic abnormalities are often linked to ASD?
About 30% of cases are linked to known genetic abnormalities or metabolic disorders.
What is the role of the prefrontal cortex in ASD?
It is involved in attention, organization, planning, and social cognition.
What is the False Belief Task?
A psychological test used to assess theory of mind, particularly in individuals with autism.
What are common treatment options for autism?
Medication, home-based treatments, school-based interventions, and emerging treatments for infants and toddlers.
What percentage of individuals with autism are on medication?
Approximately 50% are on at least one medication, and about 35% are on two or more medications.
What are atypical antipsychotics used for in autism treatment?
They are used to reduce behavioral issues like hyperactivity and emotional problems such as irritability.
What are some side effects of atypical antipsychotics?
Weight gain, sleepiness, and motor symptoms like tremors and rigidity.
What is the goal of Early Intensive Behavioral Intervention (EIBI)?
To increase areas of deficit in social communication and decrease excess behaviors like stereotypies.
What does Discrete Trial Training involve?
Teaching one behavior at a time using prompts and rewards in a structured environment.
What are the stages of Early Intensive Behavioral Intervention?
Stages include learning basic skills, receptive vocabulary, expressive vocabulary, communication improvement, peer interaction skills, and readiness for kindergarten.
What is Pivotal Response Training aimed at improving?
Motivation, self-regulation, and spontaneity in children with autism.
What is the TEACCH Program?
A school-based intervention that uses structured teaching and scaffolded learning to support children with autism.
What is the Picture Exchange Communication System?
A method used to help individuals with autism communicate using pictures.
What is the rationale behind academic inclusion for children with autism?
To allow children to learn from typically developing peers in a mainstream classroom setting.
What is Reciprocal Imitation Training (RIT)?
A treatment that focuses on teaching children to imitate the play of therapists in a naturalistic setting.
What does Joint Attention Symbolic Play Engagement and Regulation (JASPER) focus on?
Teaching joint attention and symbolic play through naturalistic interactions.
What are emerging treatments for infants and toddlers with autism focused on?
Addressing social deficits rather than just language and behavior.
What is a common challenge in academic inclusion for children with autism?
The need to train peers on how to interact effectively with children who have autism.
What is the significance of the 47% intervention group in EIBI?
This group achieved average or above-average IQ scores and was placed in typical classrooms, compared to only 3% in the control group.
What is a limitation of the Pivotal Response Training?
It has less empirical support compared to other methods, though many show improved communication skills.
What is a key feature of the TEACCH Program's teaching methods?
Using visual prompts and breaking tasks into simple steps to enhance learning.