Machine Learning basics
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
where do machine learning algorithms learn from
patterns from data
What is meant by examples and what is each one called
examples are training data, each one is called a sample
what is a sample characterised by
one or more features
what is a feature
an input variable given to a model
what is represented by columns
the features
what is supervised learning
trains model using labelled data “learning/ predicting using an answer key”
in supervised learning what do you give the machine
examples and correct answers
what is unsupervised learning
training with no labelled data
in unsupervised learning what do you give the model
only examples no correct answers or labels
give examples of supervised learning
Regression and classification
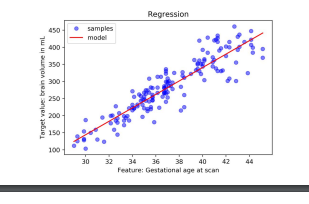
what is regression
where the known outputs are continuous, called target values. We are predicting a number
what is classification
categorical called labels, picking a label , we know the categories

give examples of unsupervised learning
Clustering and dimensionality reduction
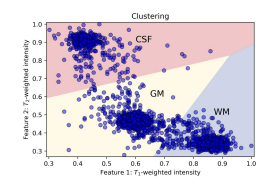
what is clustering
group samples with similar feature vectors into clusters, don’t know categories
what is dimensionality reduction
shrinking number of features while keeping important information

what is a sample
one data point (1 row in a dataset)
what is a feature vector
list of all features in 1 sample
ML task is to learn from a model f that returns?
predicted output y^
if we have N training samples then how many feature vectors do we have
N
what is underfitting
model not learning enough, doesn’t capture pattern in data
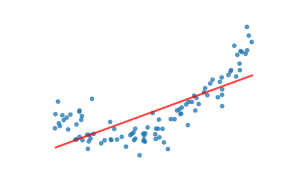
what are signs of underfitting
bad performance on training and test data , model is too basic (too few parameters)
what is overfitting
model learns too much , including noise and irrelevant details
what are signs of overfitting
good performance on training data, bad performance on test data, model too complex
what is just right
complex enough to capture real patterns , simple enough to ignore noise

what are signs of just right
good performance on training and test data , balanced model
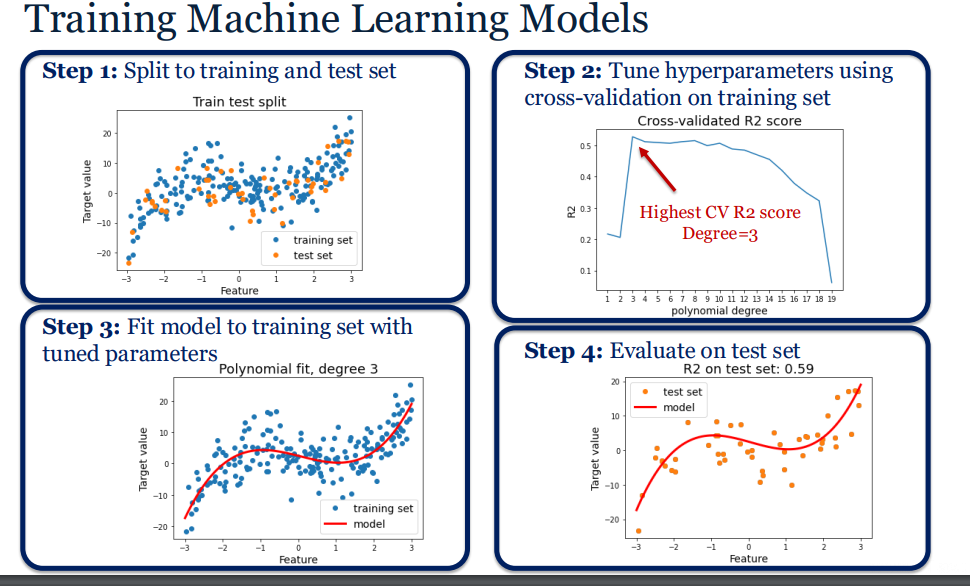
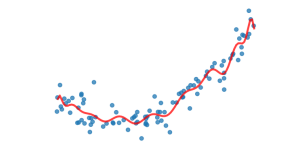
what is polynomial regression
linear regression but using a curve to fit to data
give the eq for polynomial regression
w is weights M is polynomial degree
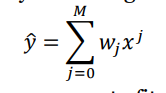
if M = 1 then and if M= 2 then and if M is 20 then
Straight line , underfitting , Curbed line , just right , crazy line , overfitting
what is a hyperparameter and give example
a setting chosen by me , i.e M and we choose it before training
what is Bias
error from being too simple , if its high it means systematic mistake
what is variance
error from being too sensitive , if its high it means its memorised noise
what is noise
randomness in data
what is training set
data the model learns from
what is R squared? and when is it perfect
measure of how well a regression model fits the data , its perfect when equal to 1
give eq for R squared
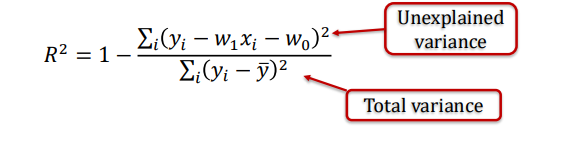
what happens to training R squared when we increase M and what does this mean
it increases, hence we cant detect overfitting as it using R squared alone
what is validation
data not used for training , used to choose best degree M
explain R squared on a validation set
highest when M is 2 , decreases after that
can identify optimal hyperparameters
explain test set
data not used during training and validation
used at the end to measure final performance
explain R squared on a test set
evaluates performance
when is cross validation used and what does it do
when dataset is small, splitting into training , validation and test wastes valuable data. it creates many validation sets
what are the steps for cross validation
set aside a test set
divide rest of data into k equal parts called folds
if k =5 we have 5 folds
perform 5 runs : in each run use 4 folds for training and 1 fold for validation
rotate which one is validation , so use a different fold for validation in each run
take the average of the 5 validation R squared scores
choose the hyperparameter with the best average score
combine all 5 folds into 1 training set and use it again with the best hyperparameter to create a strong model
evaluate on test set