Physics - electricity 2
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
How many electrons are in a coulomb?
6.25x10^18
What is conventional current?
The direction that a positive charge would take in a circuit
What produces DC current?
batteries
What produces AC current?
Generators
What does a high voltage mean
The electric charges are strongly pushed, which can result in a higher current if the circuit allows it
What is potential difference?
- a measure of how much energy each charge is carrying
- The driving force that pushes the charge around
What is ohms law
V = IR
What does a current/voltage graph look like for a filament lamp?
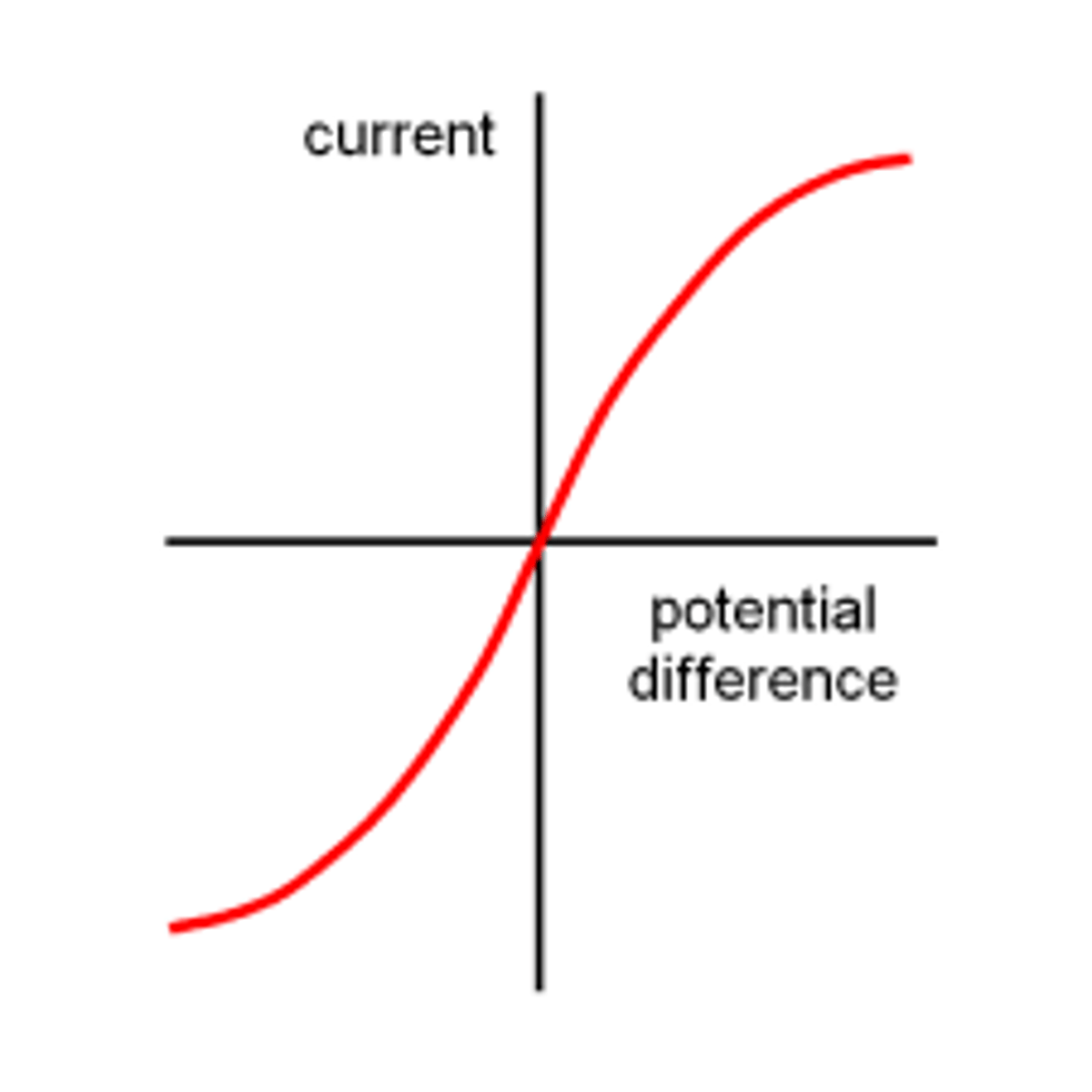
Why is a filament lamp graph S-shaped?
As the voltage increases, the filament heats up, which increases its resistance
What does a current/voltage graph look like for a diode?
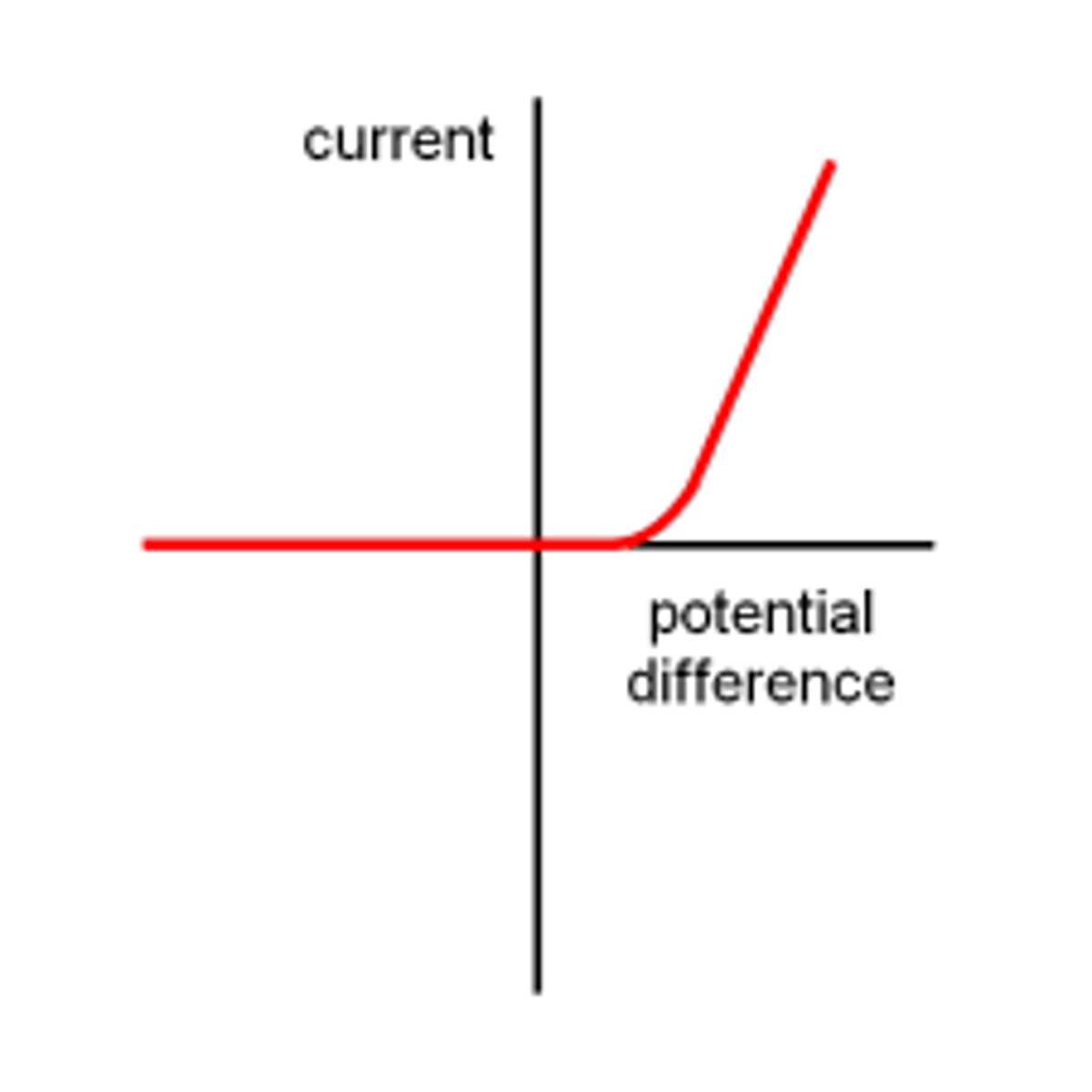
What does a current/voltage graph look like for a fixed resistor?
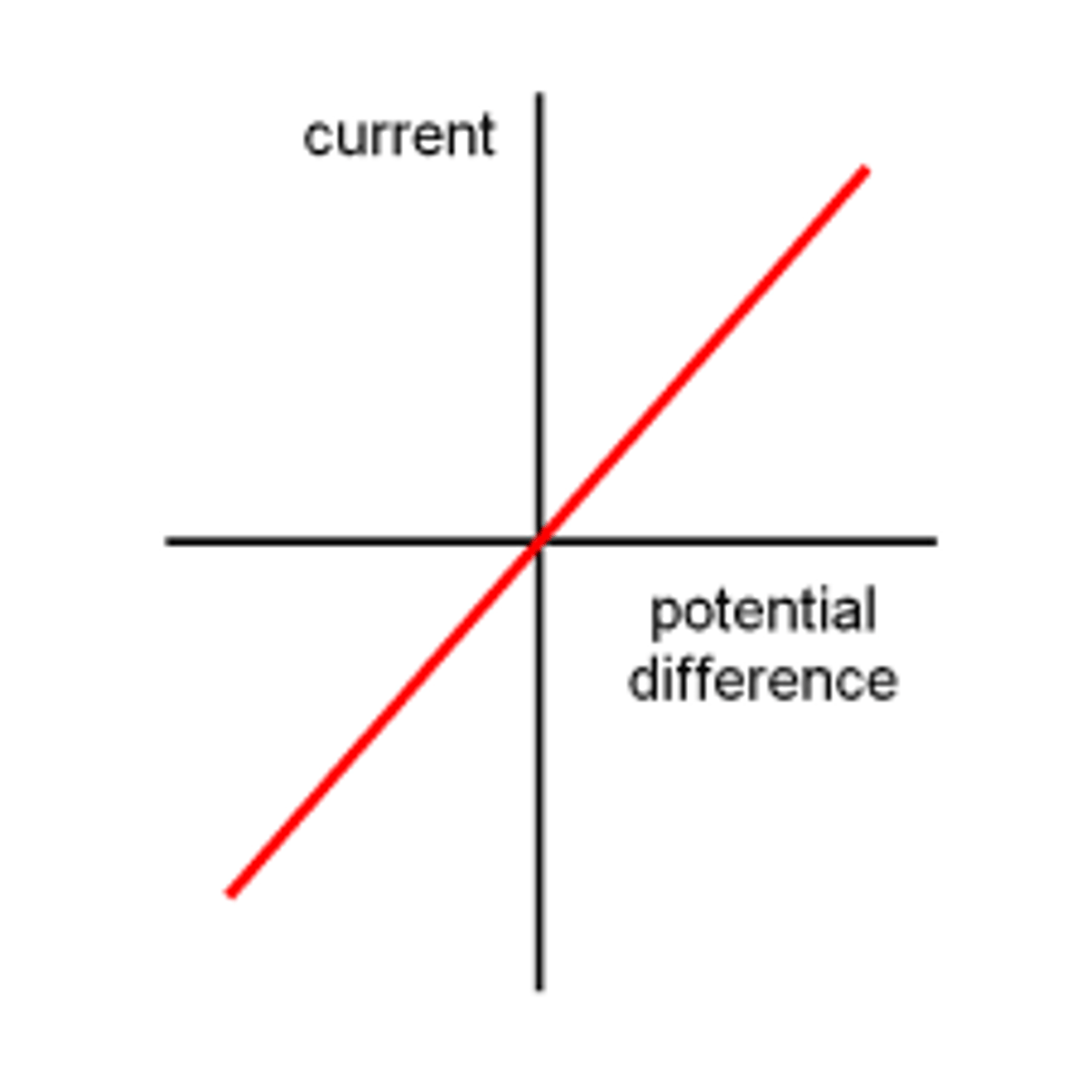
What does a steeper gradient mean in current/voltage graphs?
higher resistance
Why is a diode graph L-shaped
At positive voltages, the curve rises, indicating that current is free to flow through the device
Why is a fixed resistor graph straight?
because of Ohm's Law, which states that current is directly proportional to voltage when resistance is constant
How do you find the resistance of a current/voltage graphs?
For ohmic components, the resistance is constant and is equal to 1/gradient
What factors affect resistance?
- materials
- length of wire
- thickness
- temperature
How does the material of the wire affect resistance?
conductors (like copper) have a low resistance, whilst insulators (like rubber) have a low resistance
Why do conductors have a low resistance?
they have a high density of free electrons, which are weakly bound to atoms and can move easily throughout the material
Why do insulators have a high resistance?
their electrons are tightly bound to their atoms, making it very difficult for them to move and create an electric current
How does the length of the wire affect resistance?
The longer the wire, the greater the resistance
Why do longer wires have more resistance?
because the electros have a longer distance to travel
How does the thickness of the wire affect resistance?
A thinner wire has more resistance because there is less space for electrons to flow
How does the temperature of the wire affect resistance?
Higher temperatures increase the resistance because the atoms in the wire vibrate more when warm, making it harder for electrons to pass through
What is static electricity?
The buildup of electric charge on an object, usually caused by friction
Why does static electricity cause sparks?
the sudden, rapid movement of electrons to neutralize a large buildup of electric charge
How does static electricity work?
- When two insulating materials are rubbed together, electrons are transferred
- One material loses electrons and becomes positively charged, and the other gains electrons and becomes negatively charged.
- This static charge is a buildup of these imbalanced charges, which can then attract or repel other objects, or discharge in a spark.
How does lightning work?
occurs when oppositely charged particles within a storm cloud, between two clouds, or between a cloud and the ground become too strong for the air to insulate
What is static electricity used for?
photocopying, smoke precipitator, ink nozzle printer, spray paint
How can static build-up be prevented?
earthing. connecting objects to the ground with a wire allows excess charge to safely flow away
What are the dangers of static electricity?
- A build-up of charge can produce sparks, which may lead to explosions or fires if it happens near fuel which can be ignited.
- It's dangerous when you touch an object with a large electric charge, as it will discharge into you, causing an electric shock.
What are electric fields?
a region of space around a charged object where other charged particles will experience an electrostatic force
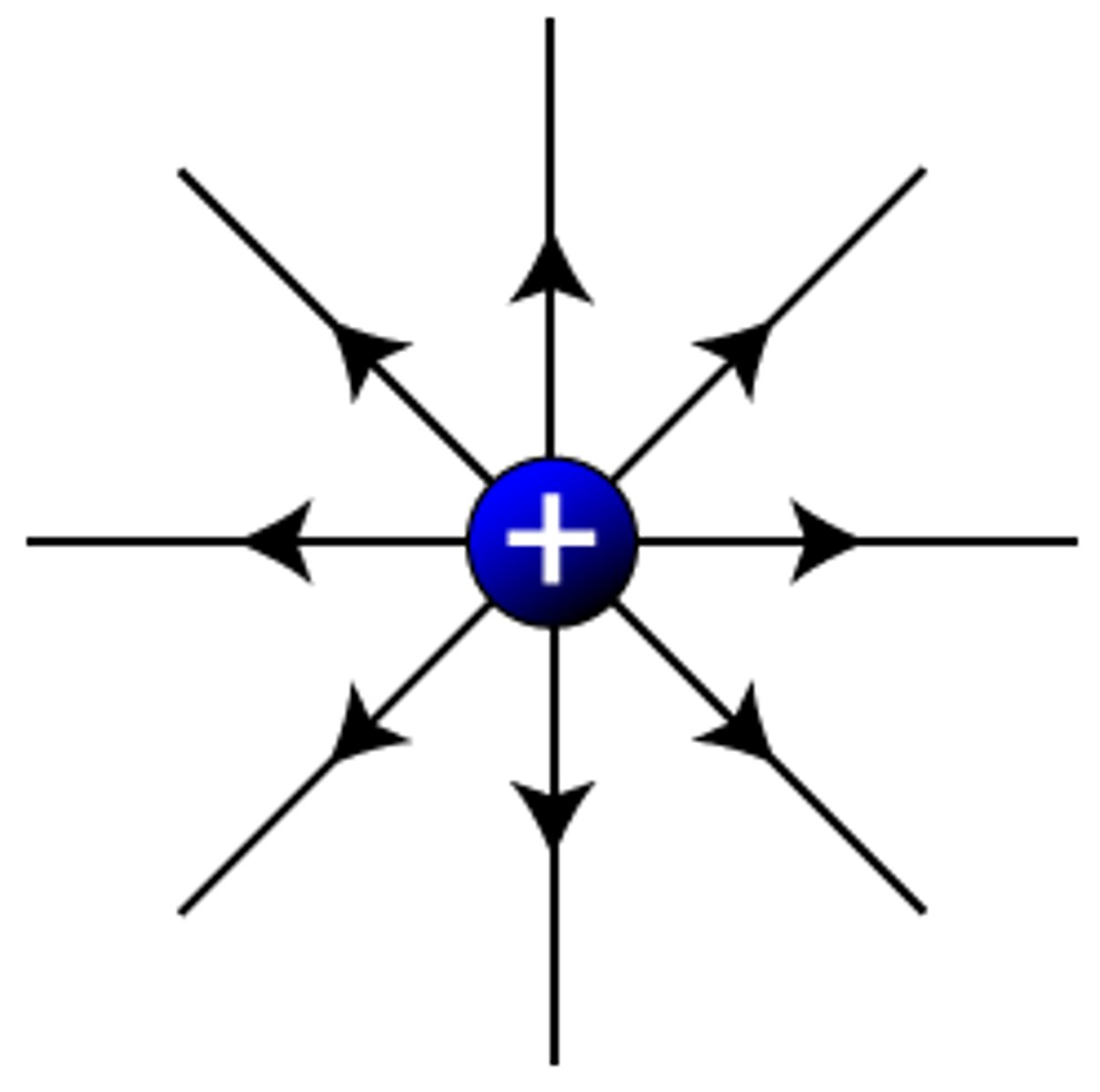
Positively charged electric field lines
Negatively charged electric field lines
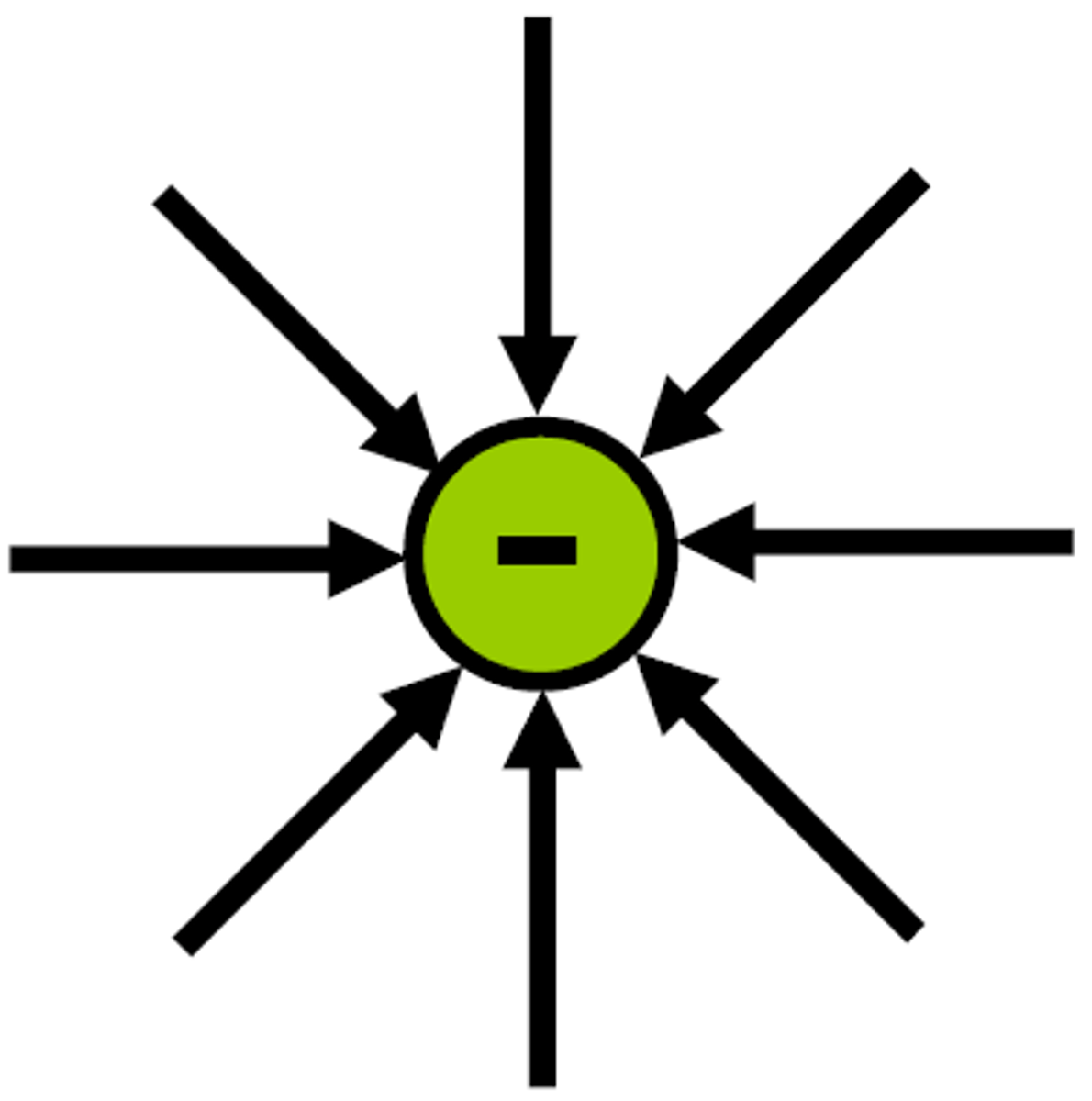
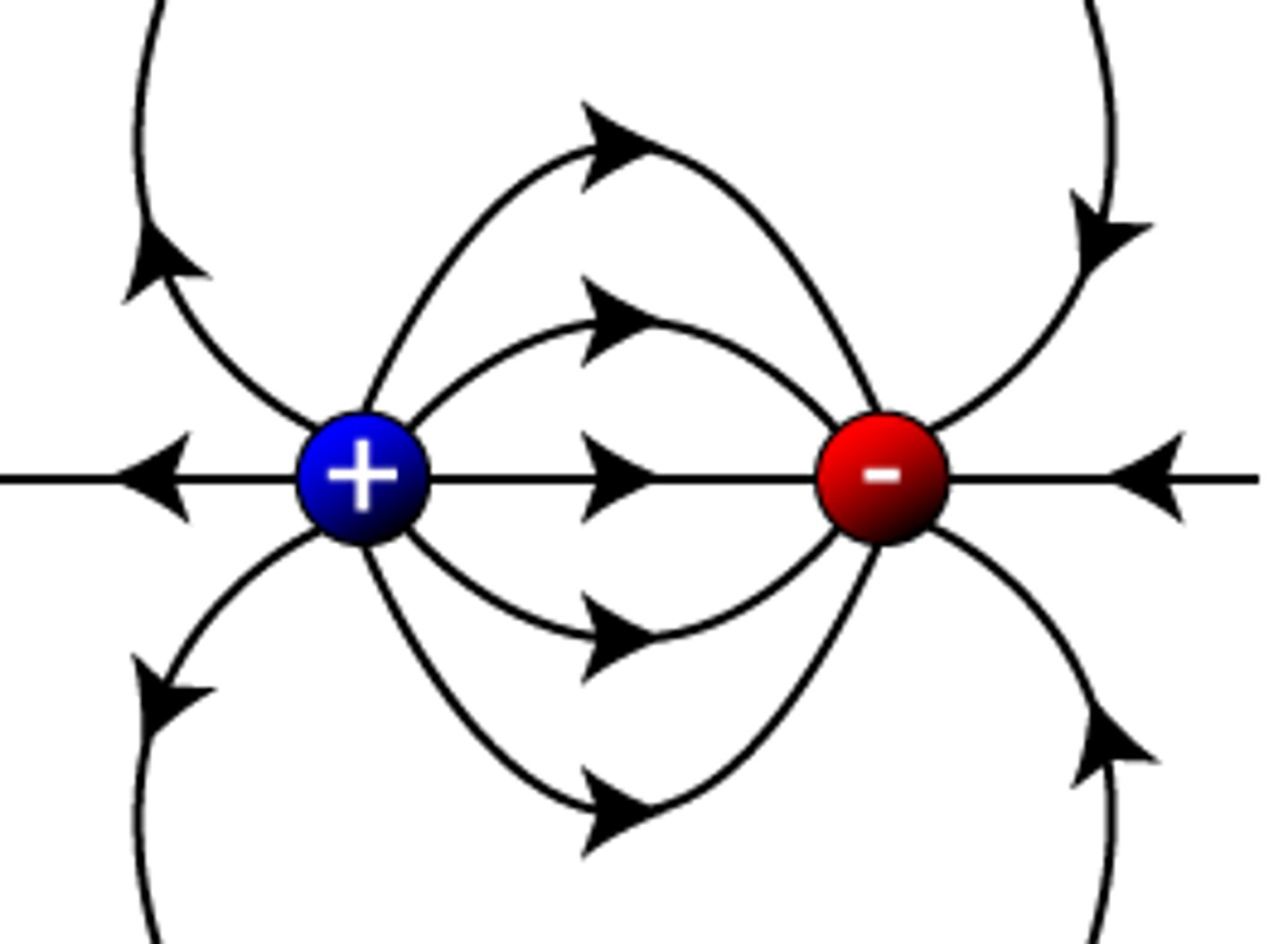
Oppositely charged electric field lines
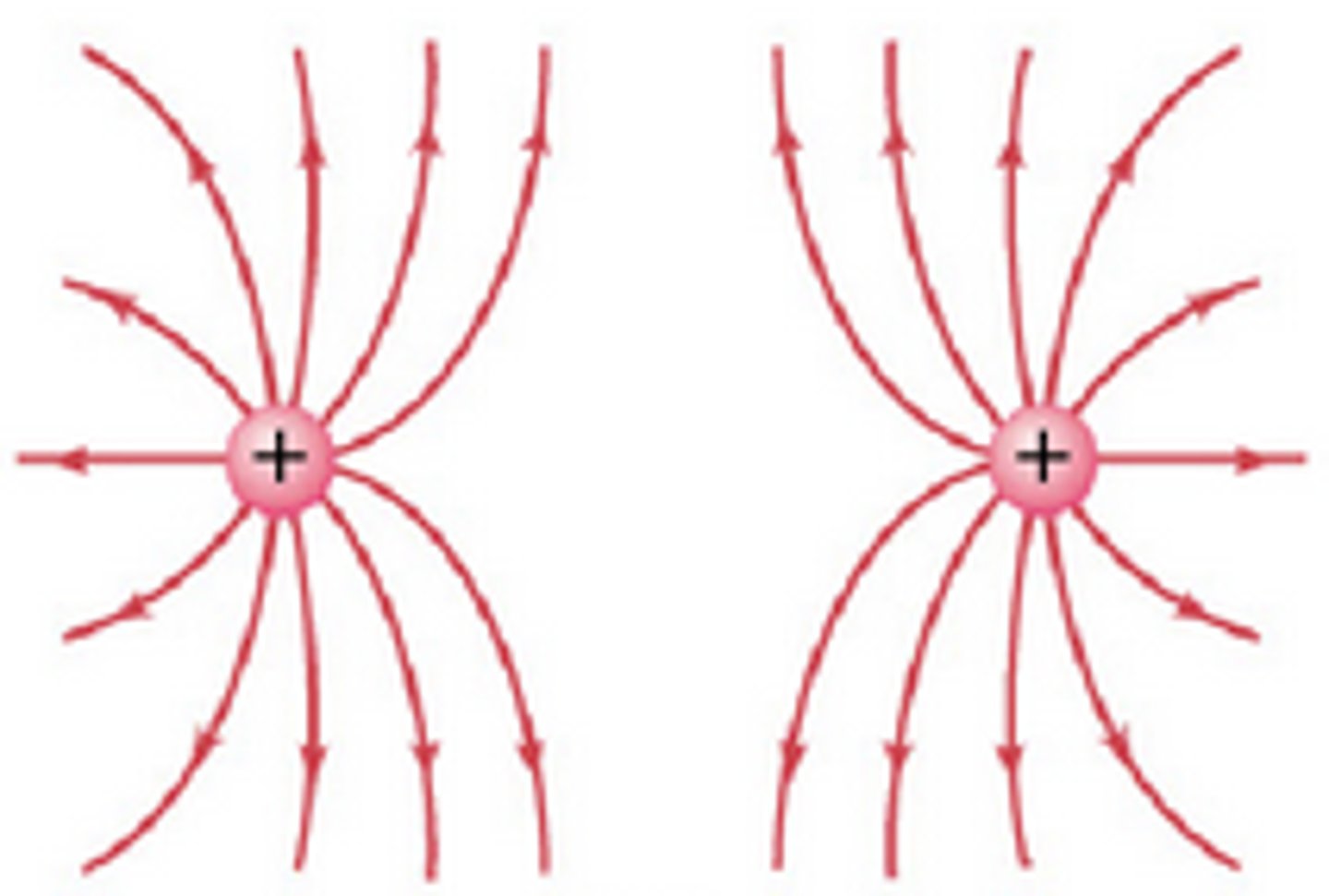
Similarly charged electric field lines
How do sparks in electric fields work?
If an electric field is strong enough, it can pull electrons from the air, creating sparks