Davidson Art 1010 Online Final Test Images
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
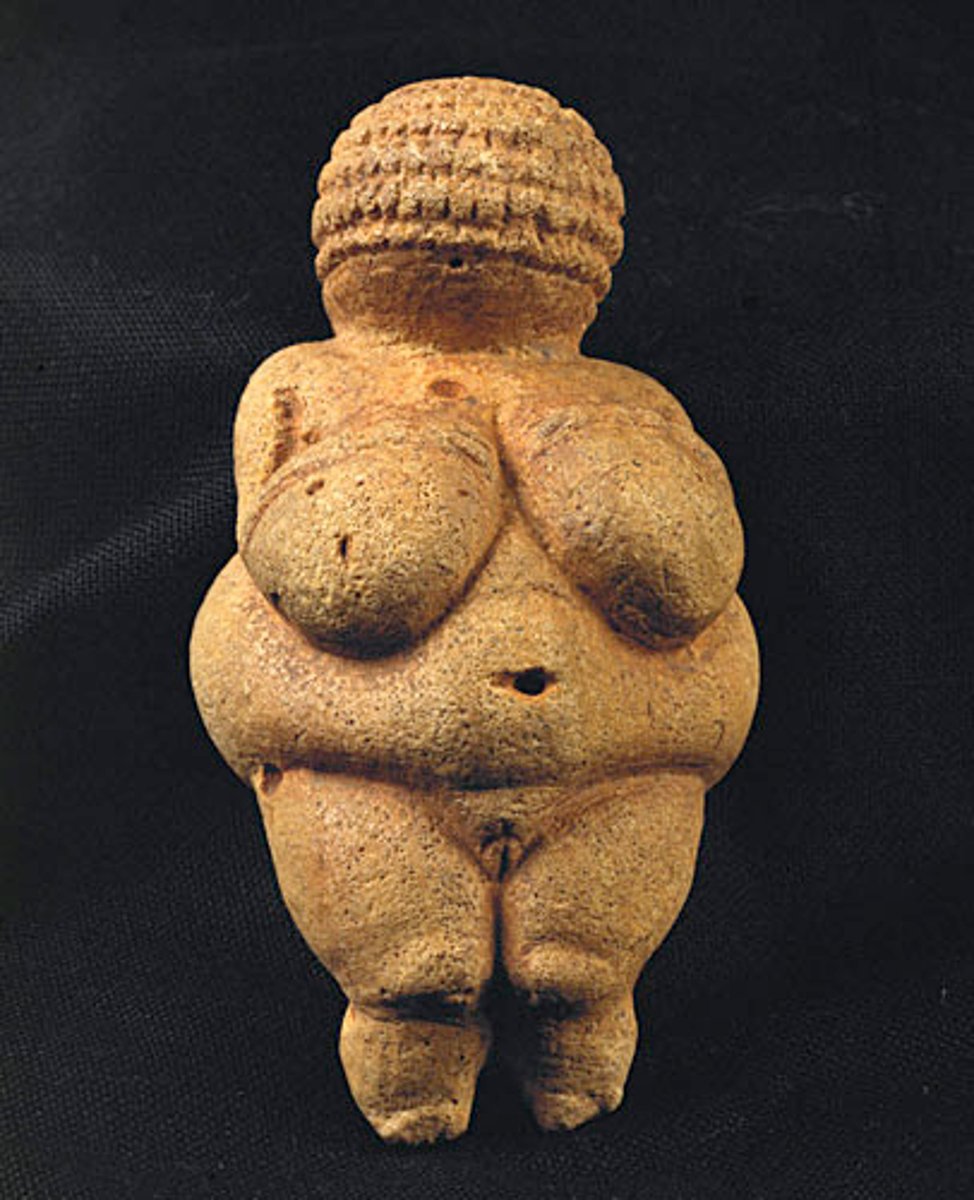
The Venus of Willendorf
(Paleolithic, Prehistoric)

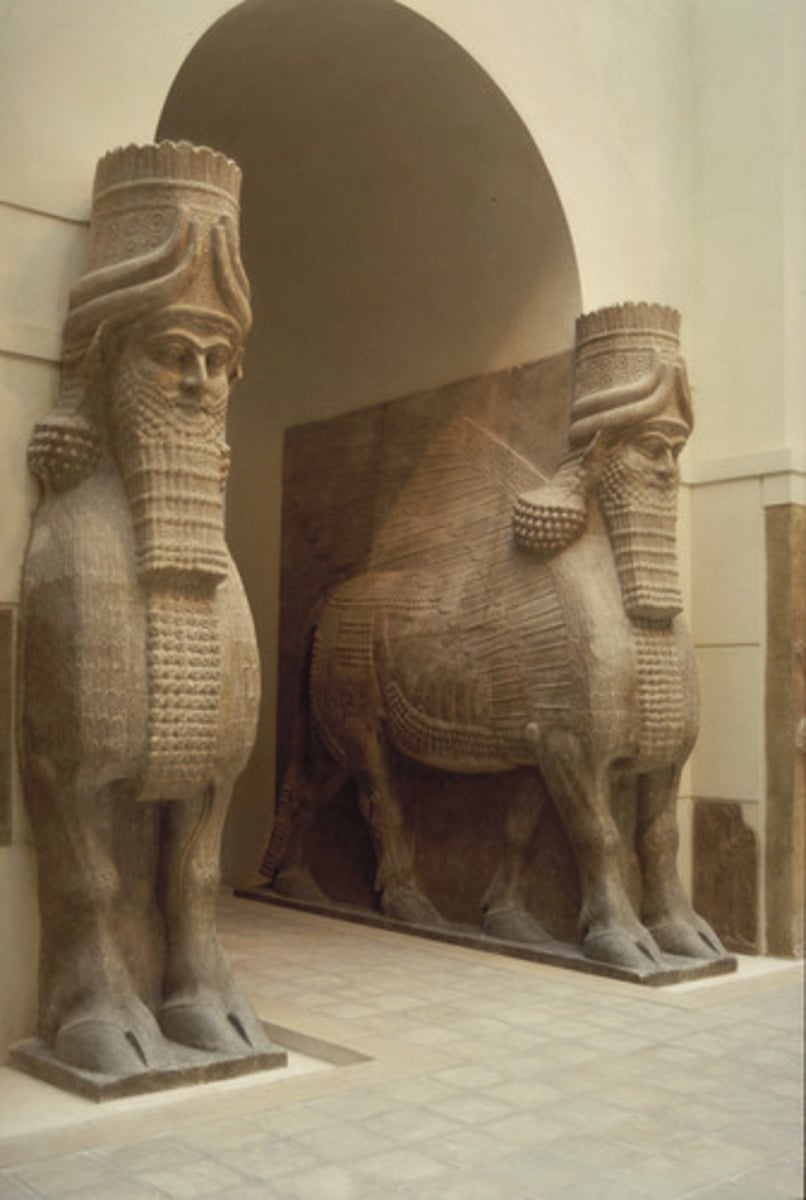
Lamassu (Assyrian)

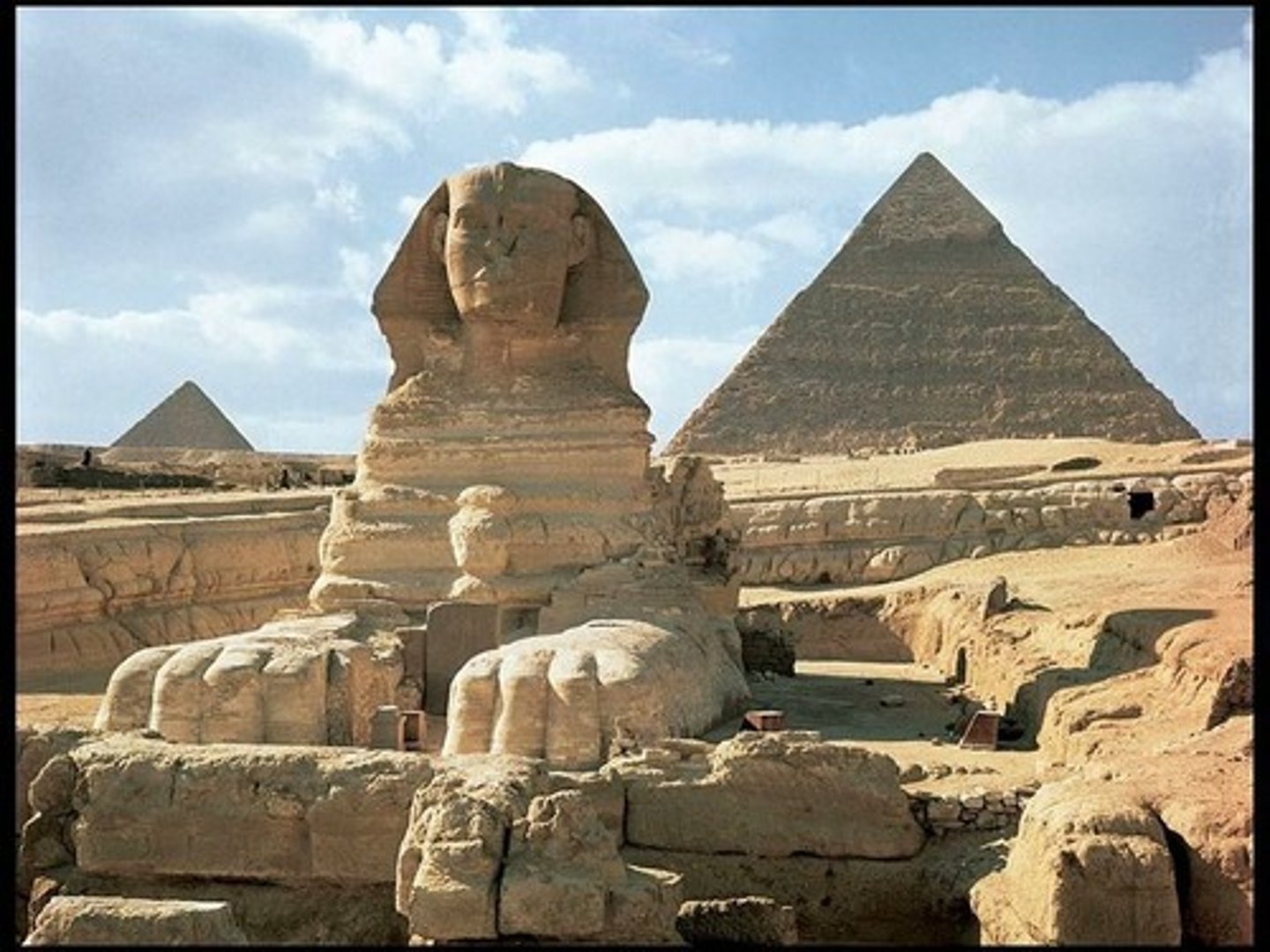
Great Pyramids of Giza and Sphinx
(Egyptian)

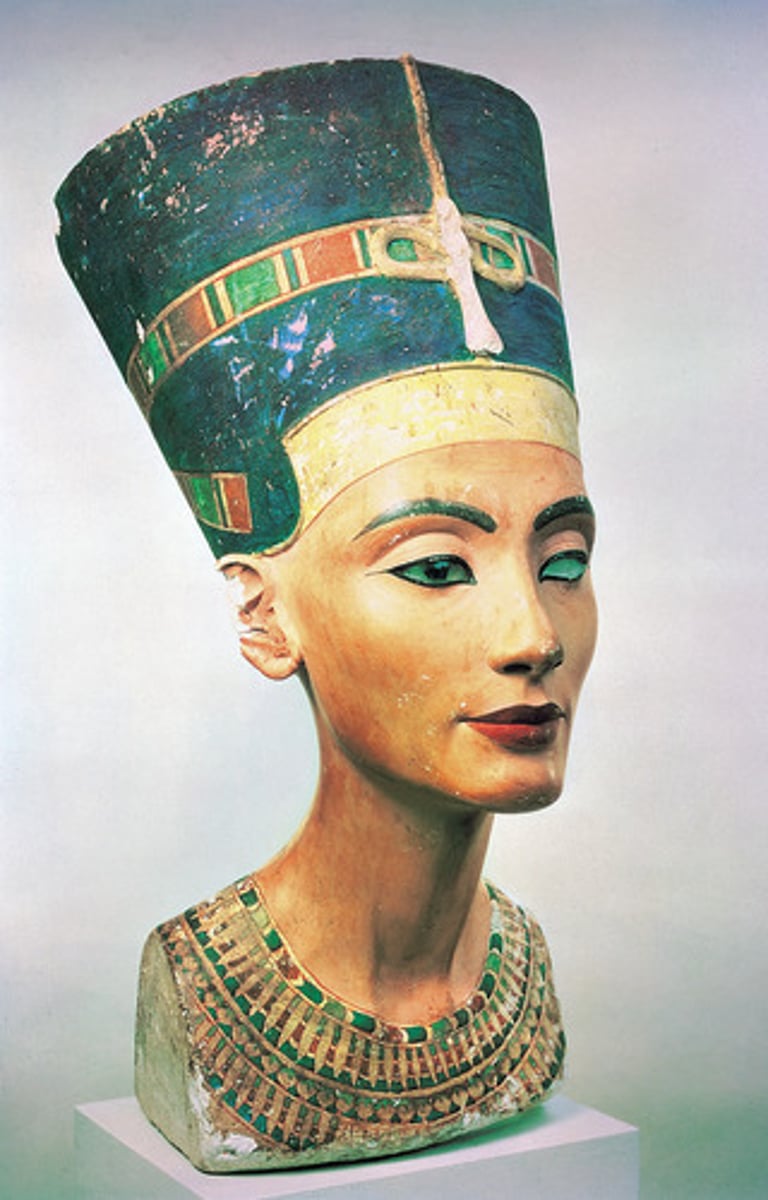
Queen Nefertiti
(Armana Period; Egyptian)

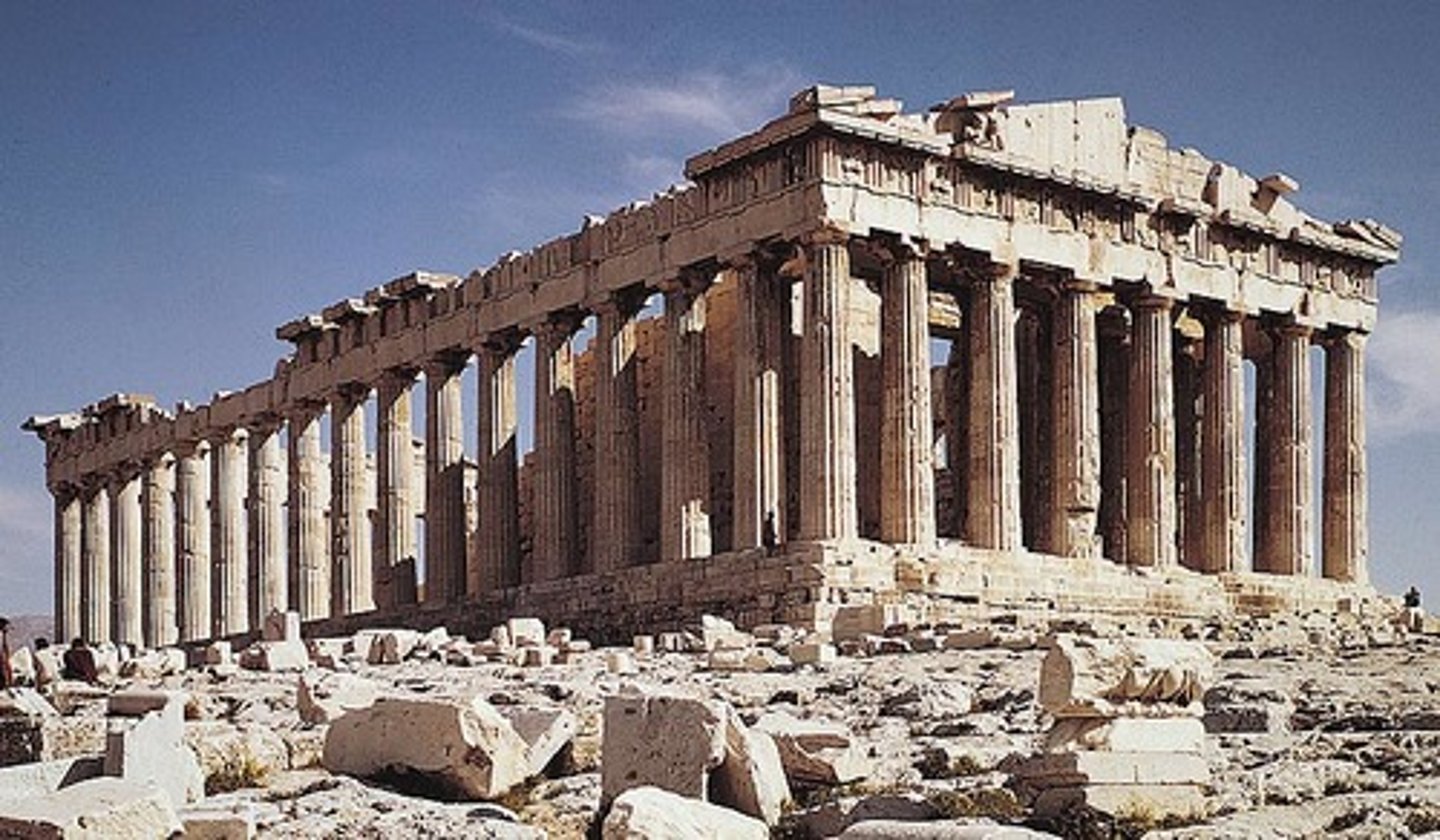
The Parthenon, Acropolis, Athens, Greece
By Iktinos and Kallikrates

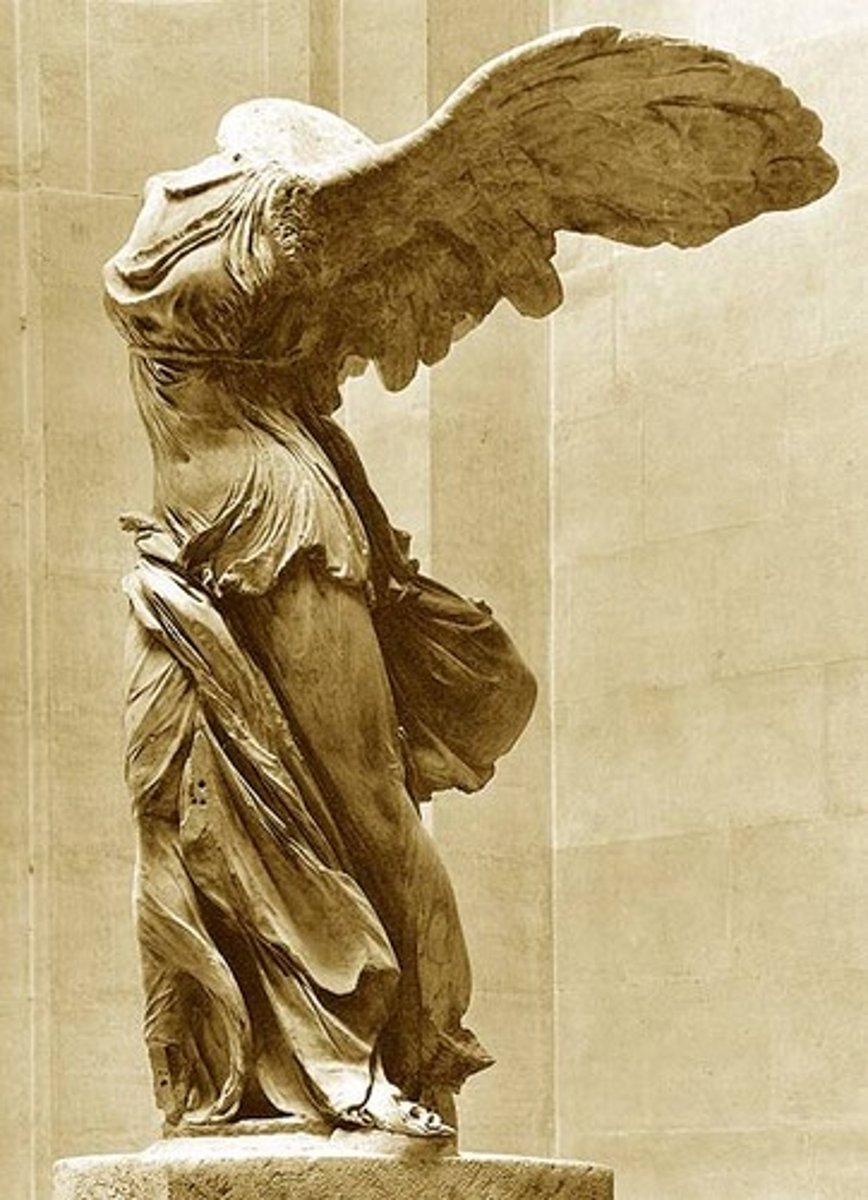
Nike of Samothrace
(Greek: Hellenistic period)

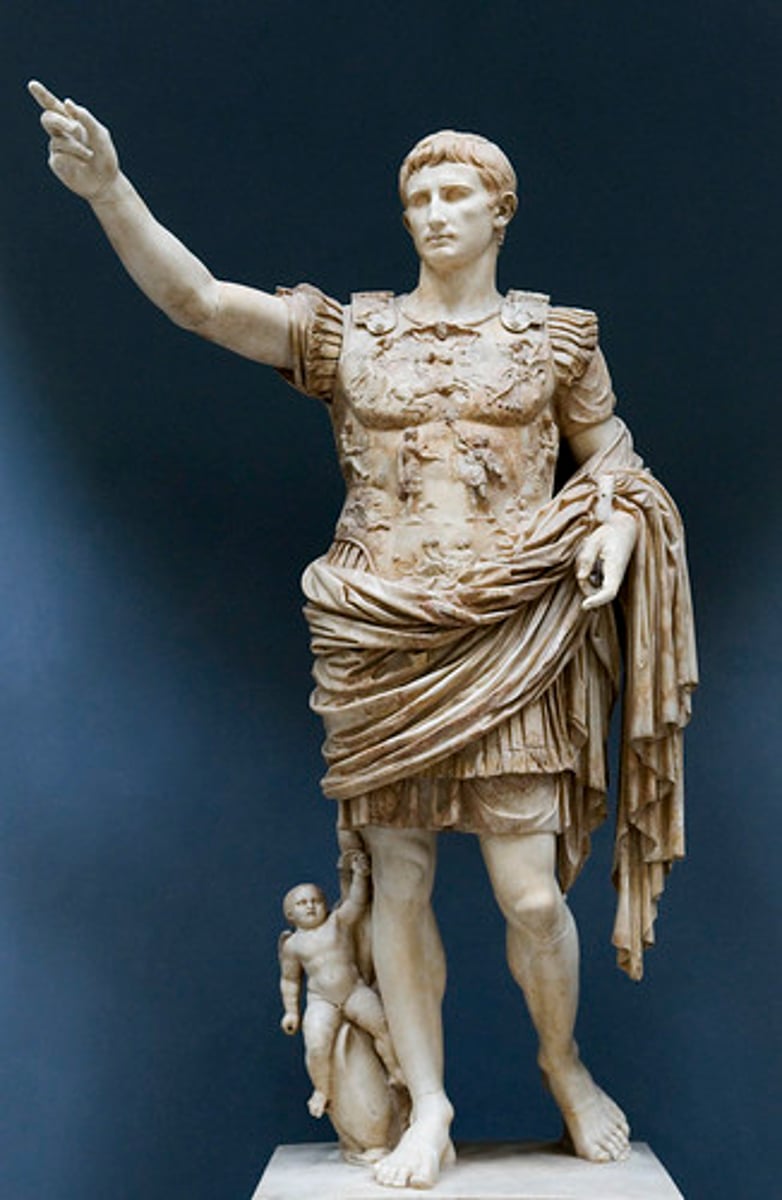
The Augustus of Primaporta
(Roman)

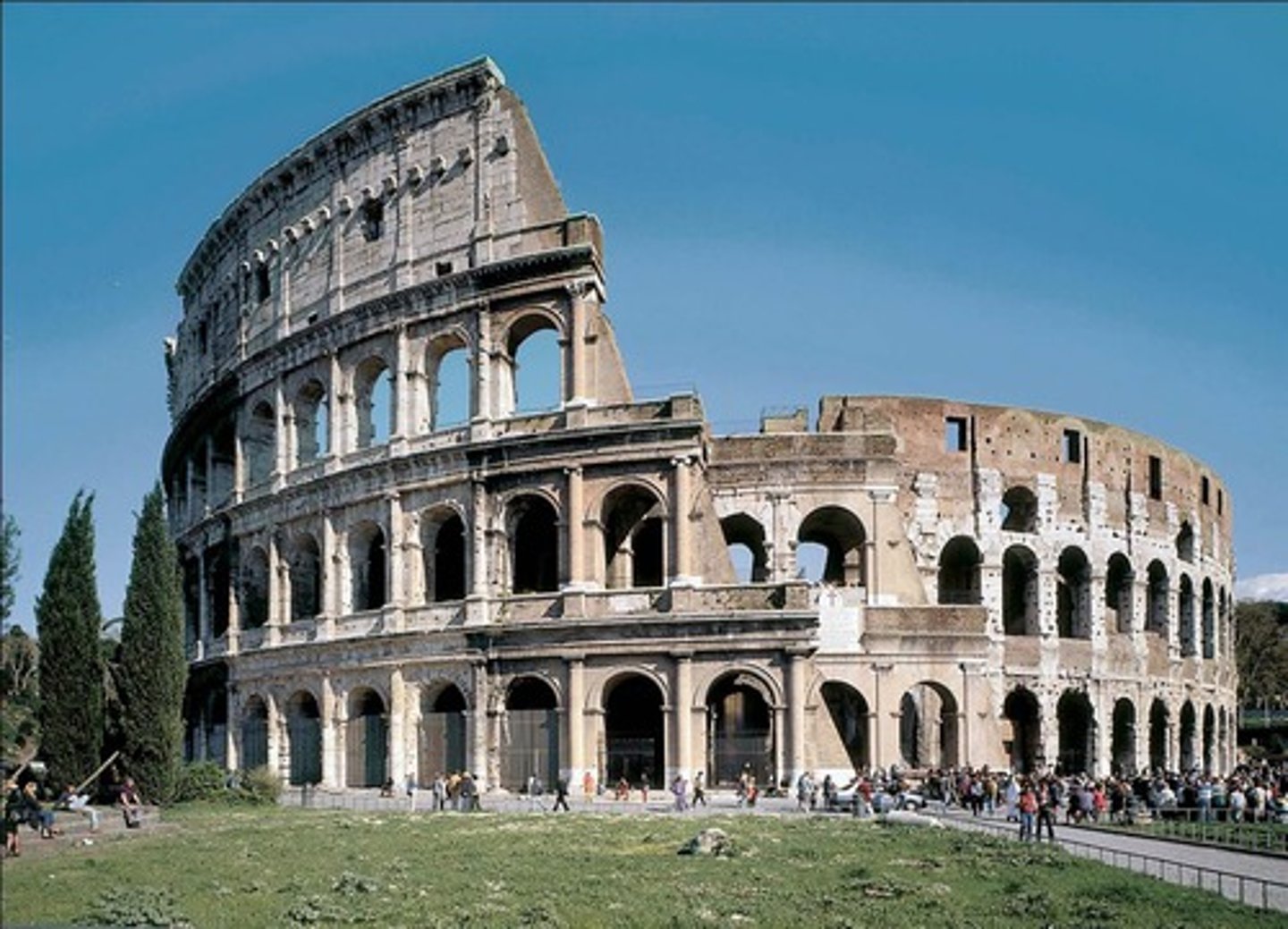
The Colosseum
(the Flavian Amphitheater), Rome

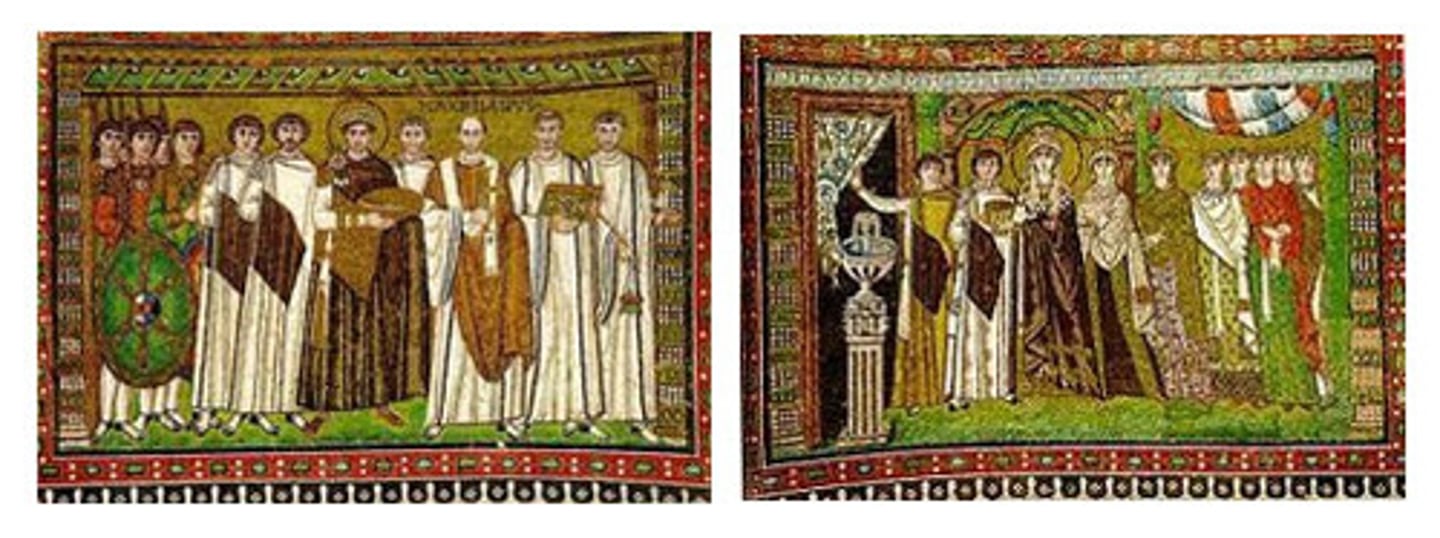
Justinian and His Attendants
Theodora and Her Attendants
(Byzantine)

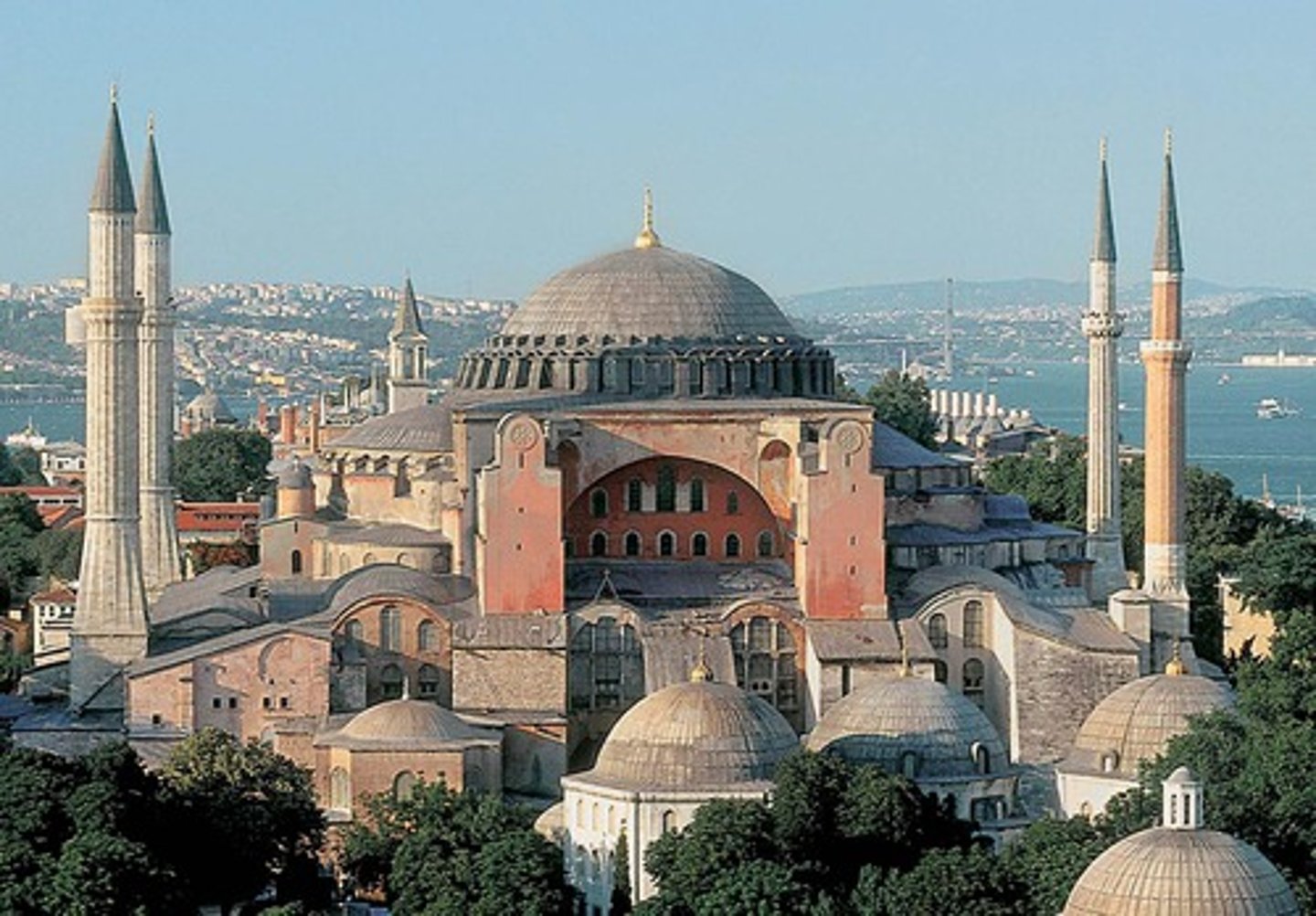
Hagia Sophia Constantinople (Istanbul, Turkey)
by Anthemus of Tralles & Isidorus of Miletus
(Byzantine)

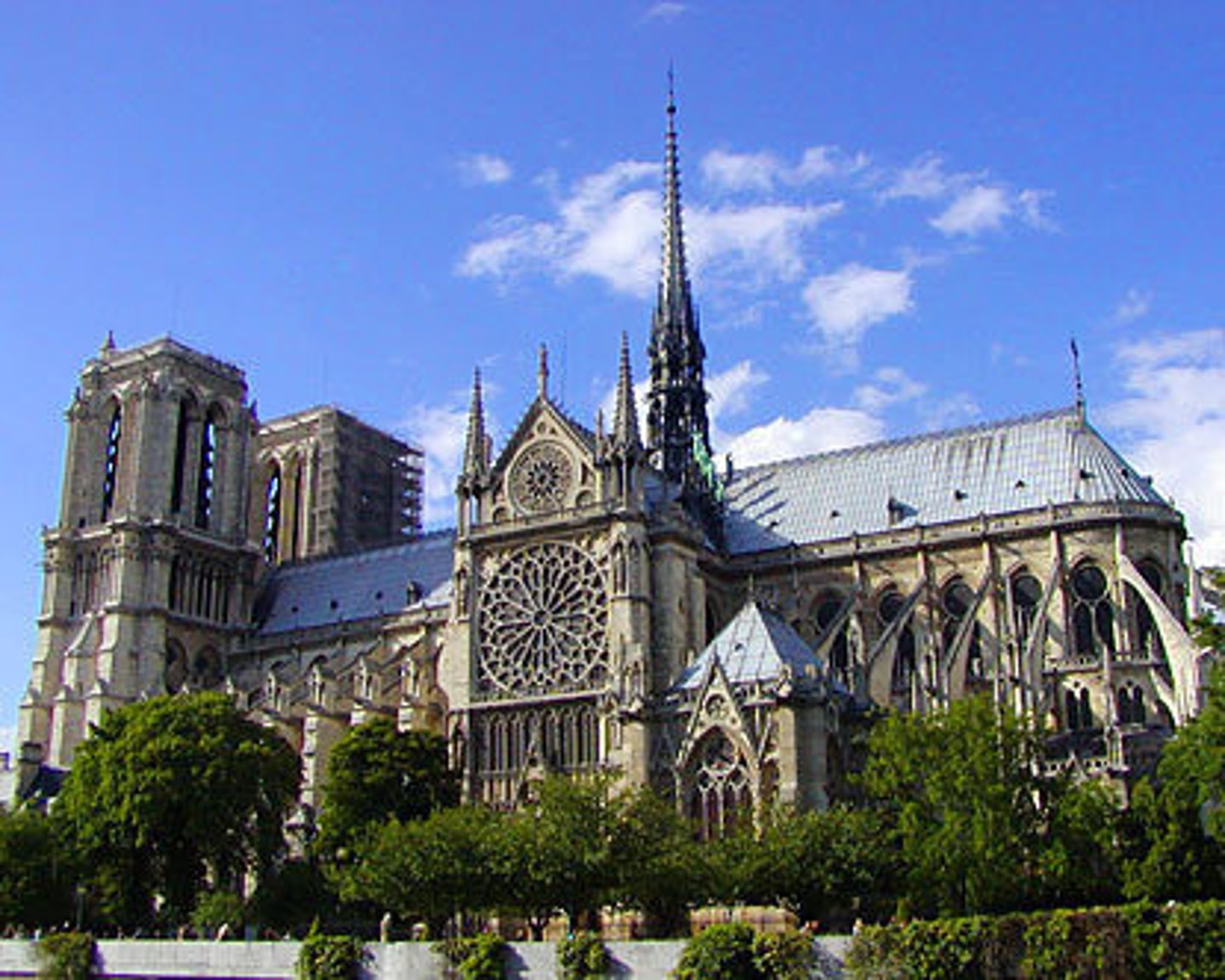
Notre Dame
Paris, France
(Gothic)

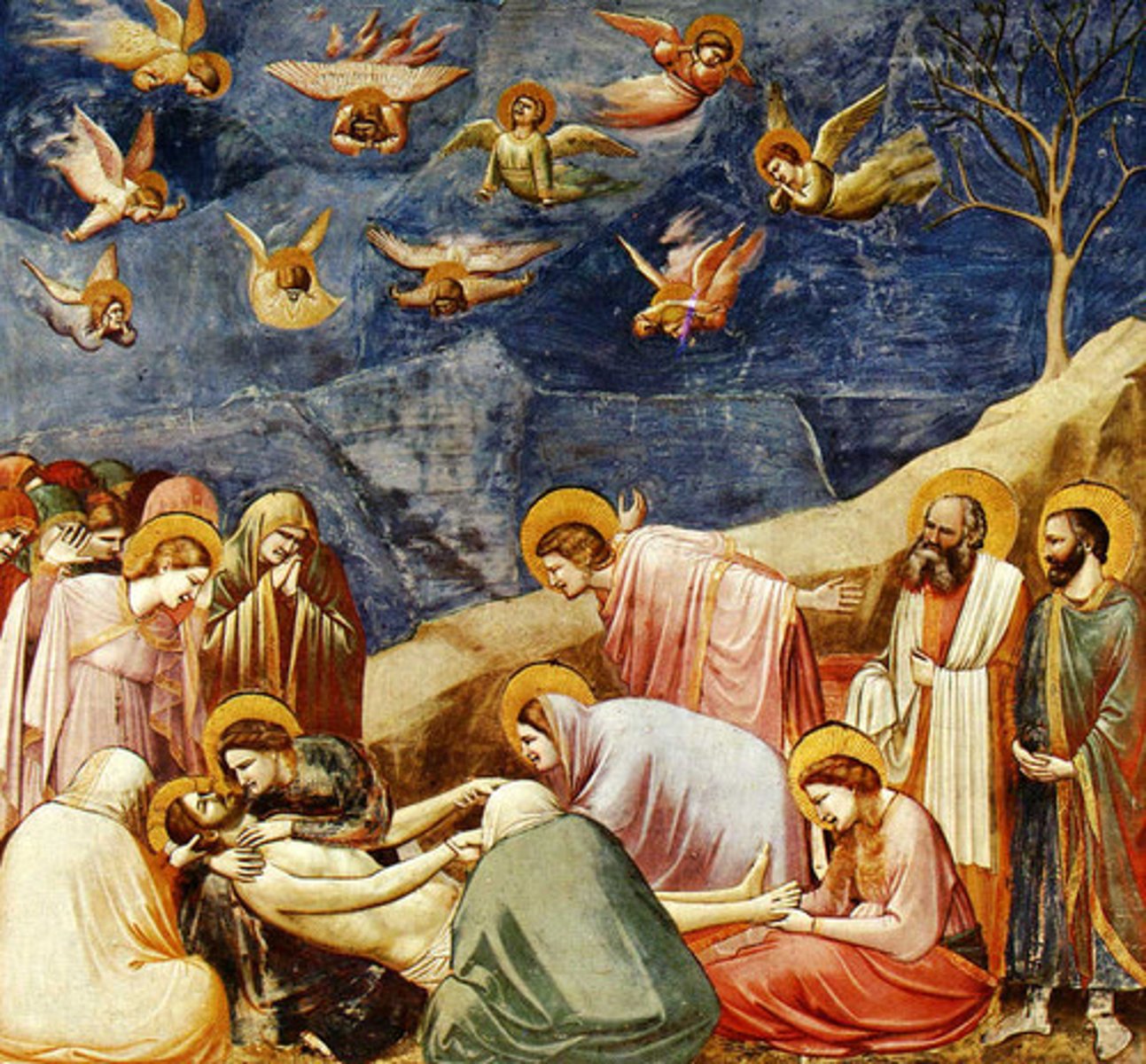
Lamentation by Giotto

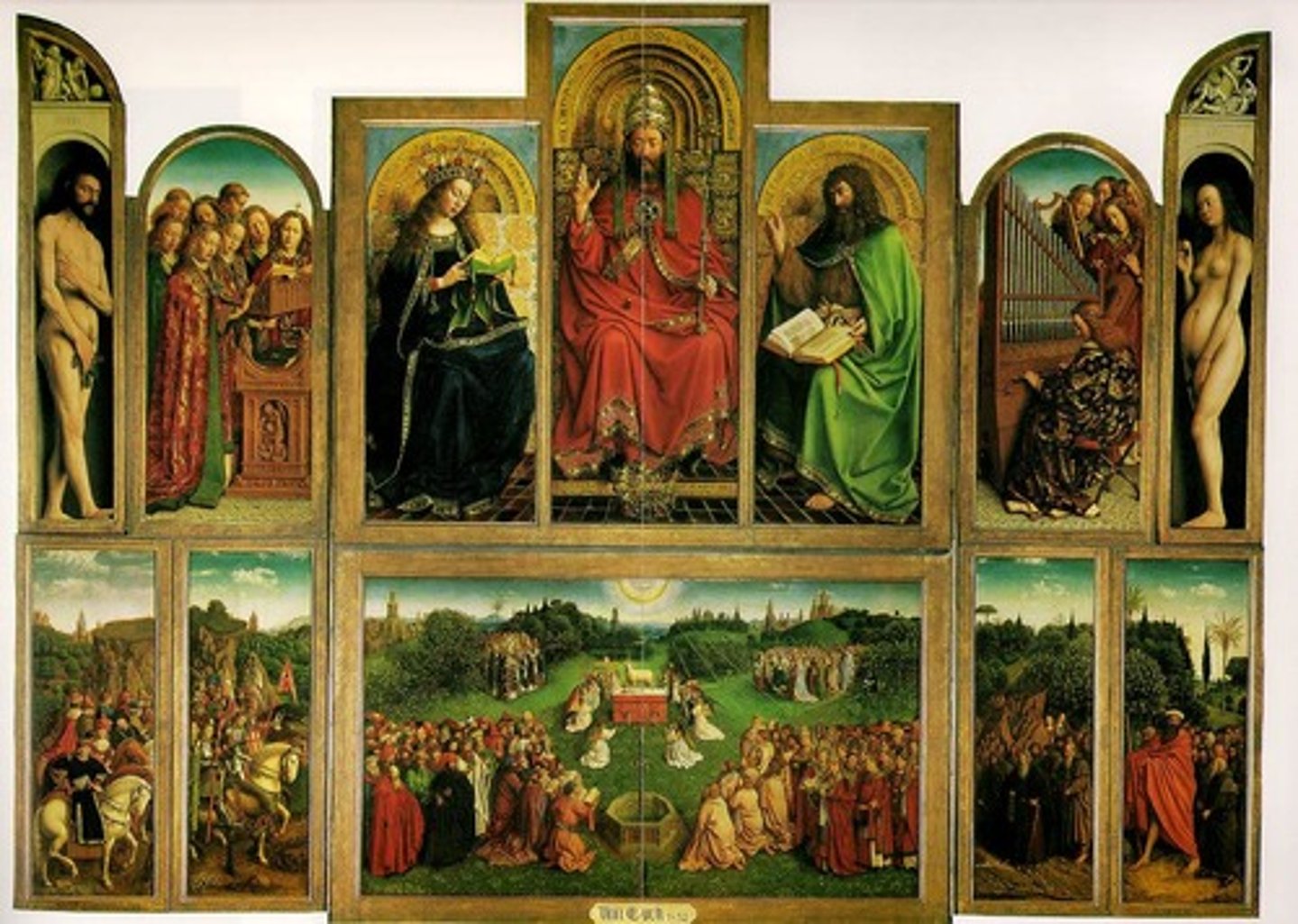
Ghent Altarpiece by Jan Van Eyck
(Northern Renaissance)

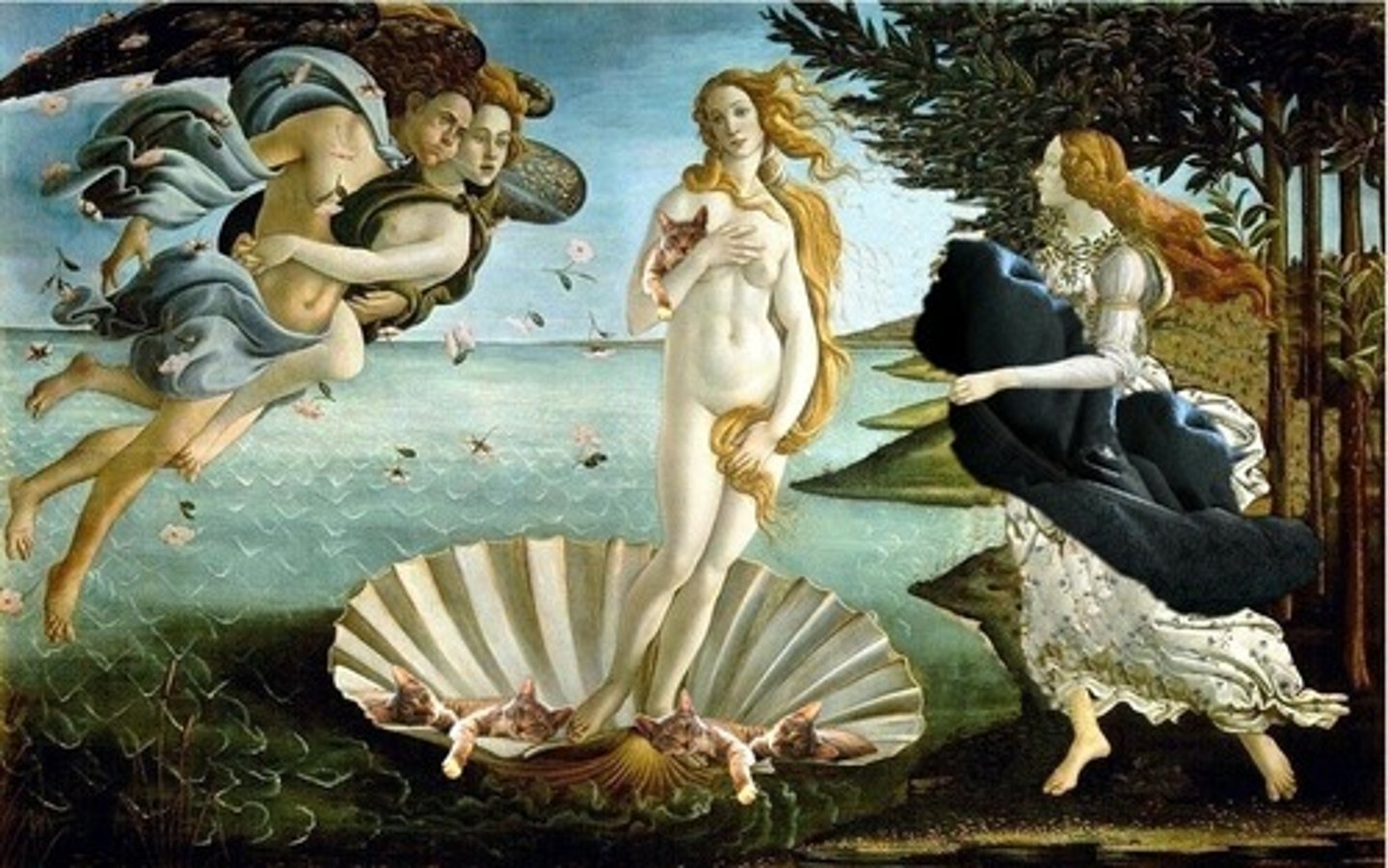
Birth of Venus by Sandro Botticelli
(Renaissance)

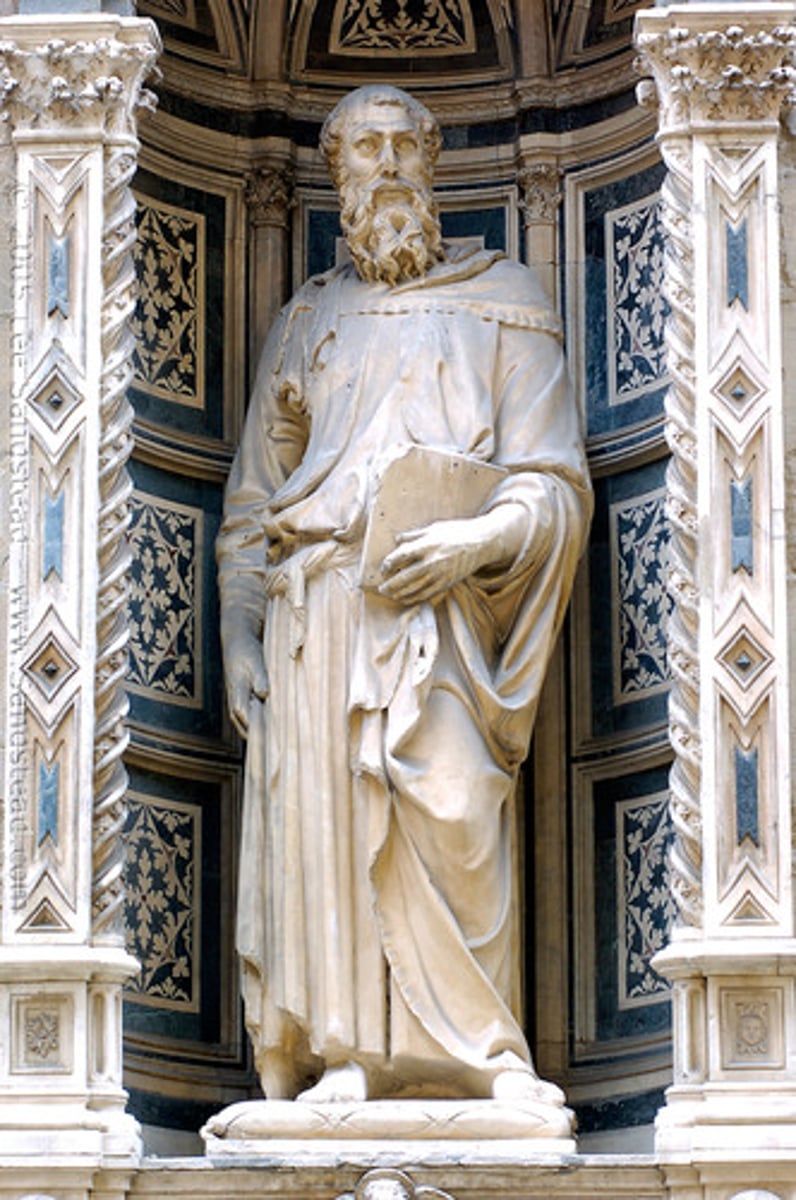
St. Mark by Donatello
Renaissance

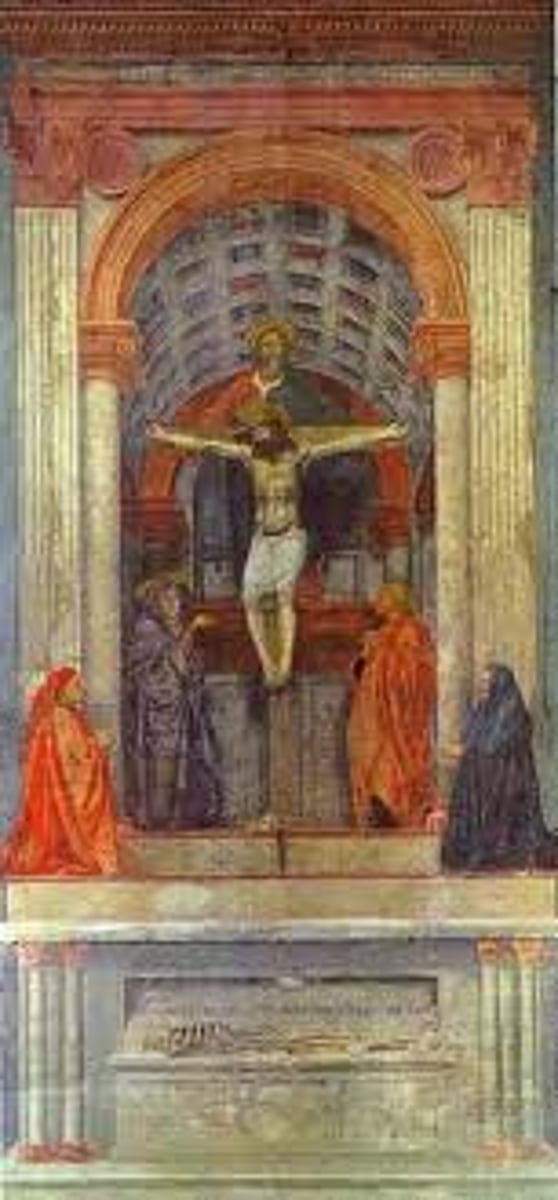
Holy Trinity by Masaccio
(Renaissance)

David by Michelangelo
(Renaissance)

Sistine Chapel ceiling
by Michelangelo
(Renaissance)

School of Athens
by Raphael
(Renaissance)

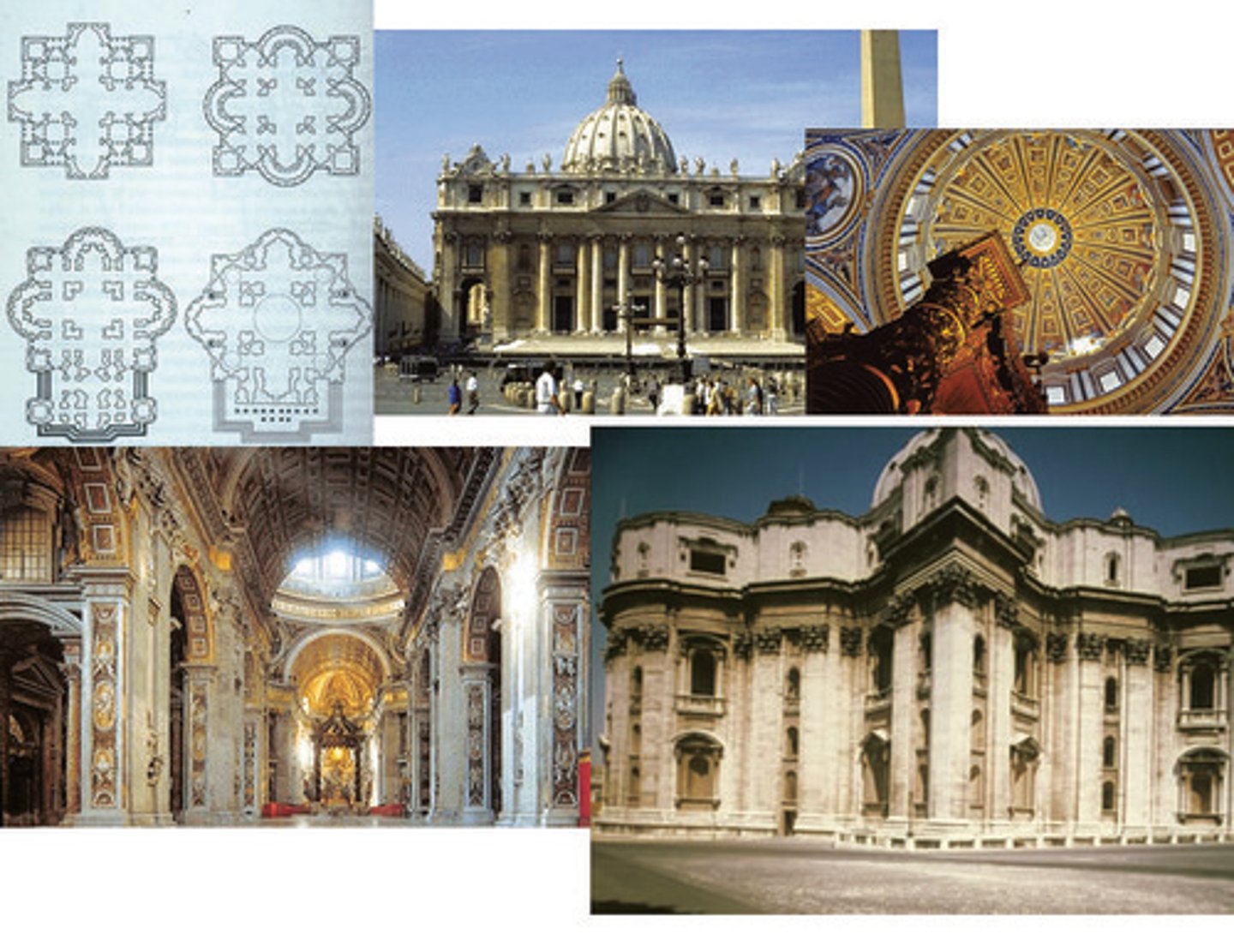
Plans for New St. Peter's
by Bramante, Michelangelo, Maderno
(Renaissance)
Last Judgment,
Sistine chapel
by Michelangelo

The Entombment
by Caravaggio
(Baroque)

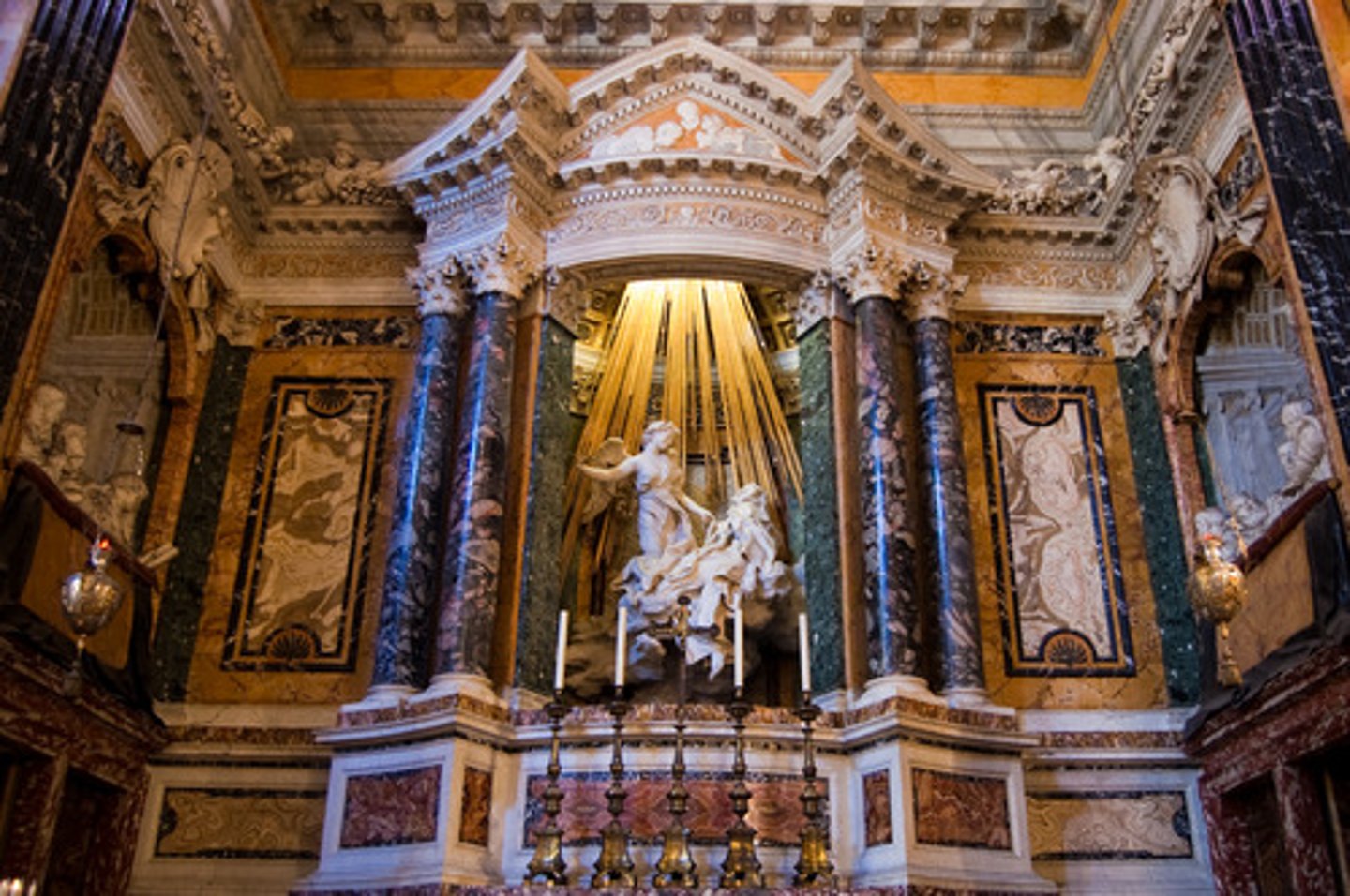
The Ecstasy of St. Theresa
by Bernini
(Baroque)

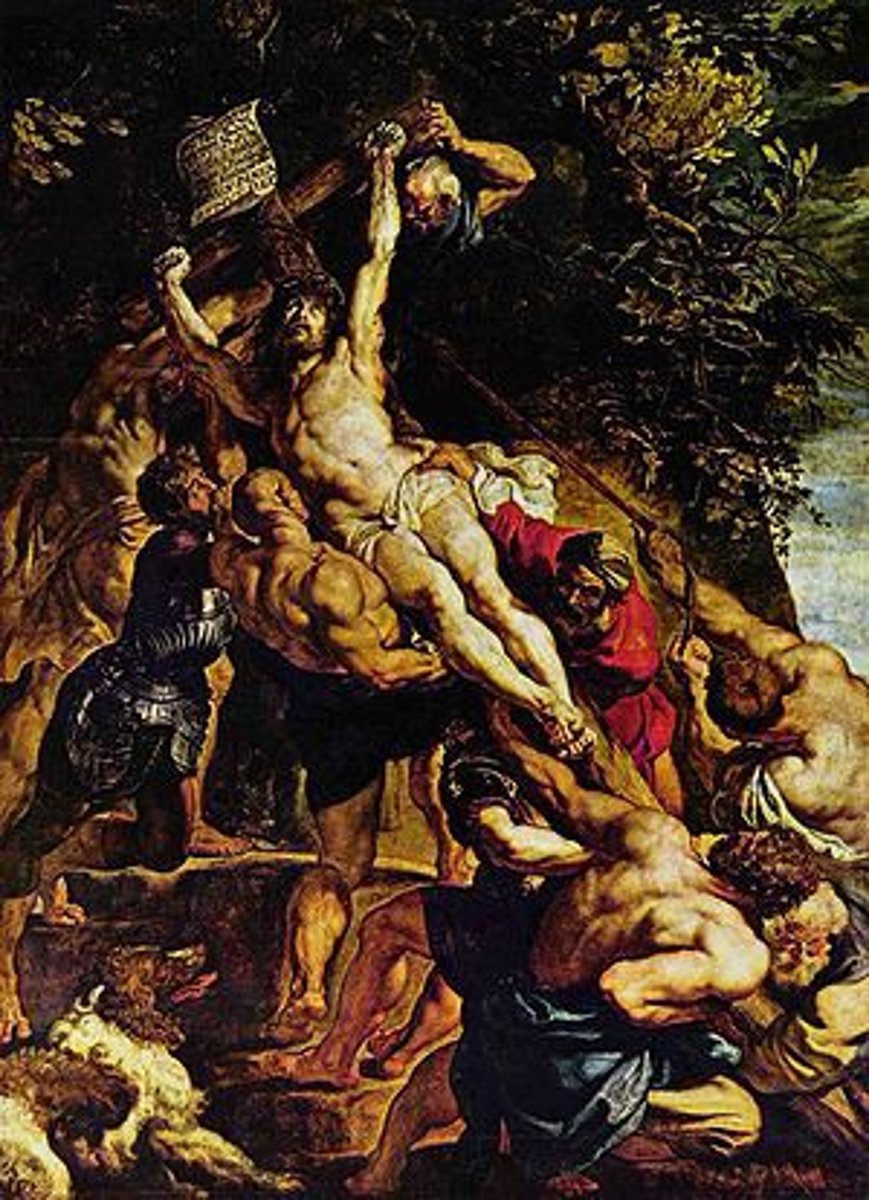
Raising of the Cross
by Rubens
(Baroque)

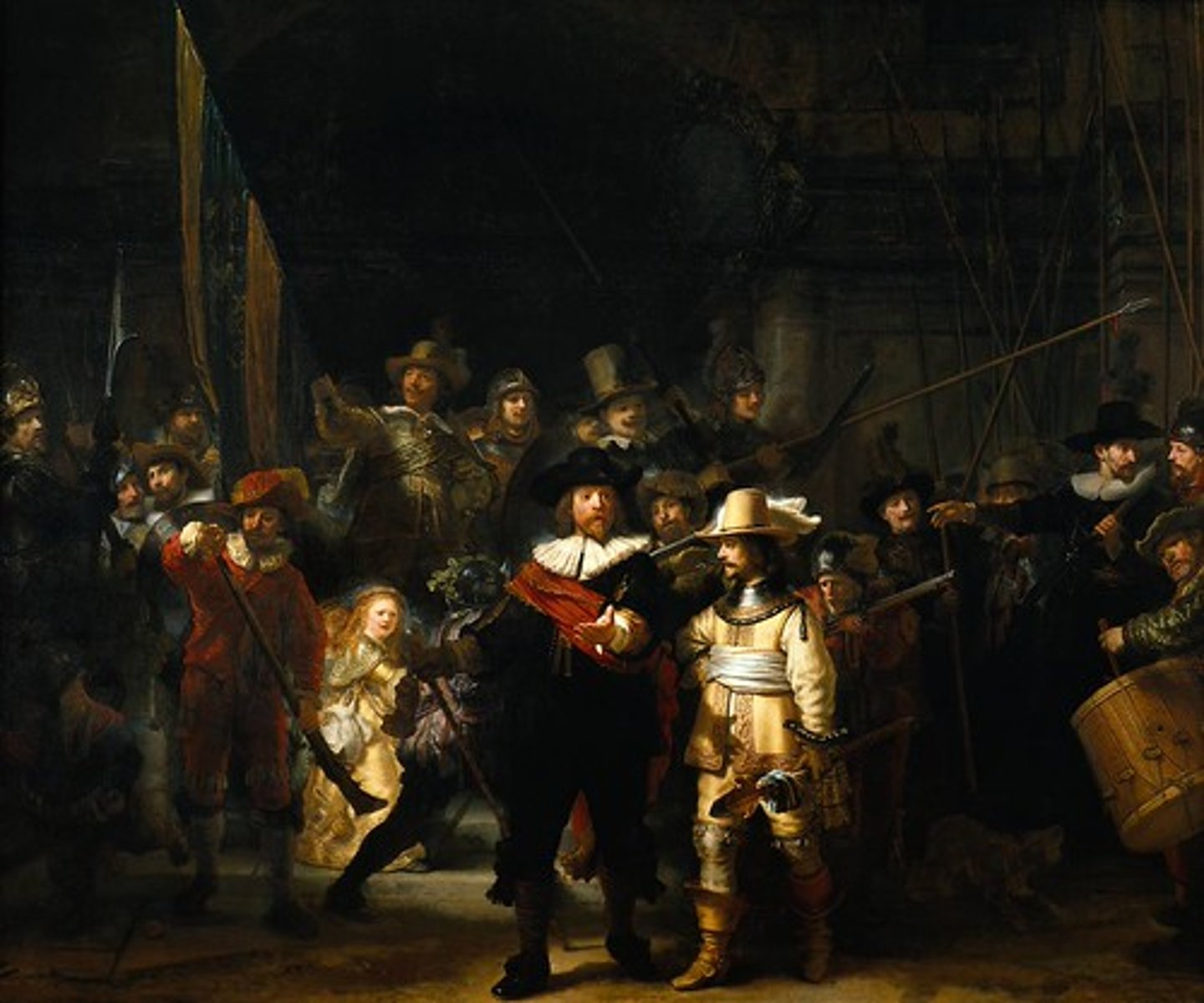
Night Watch by Rembrandt
(Baroque)

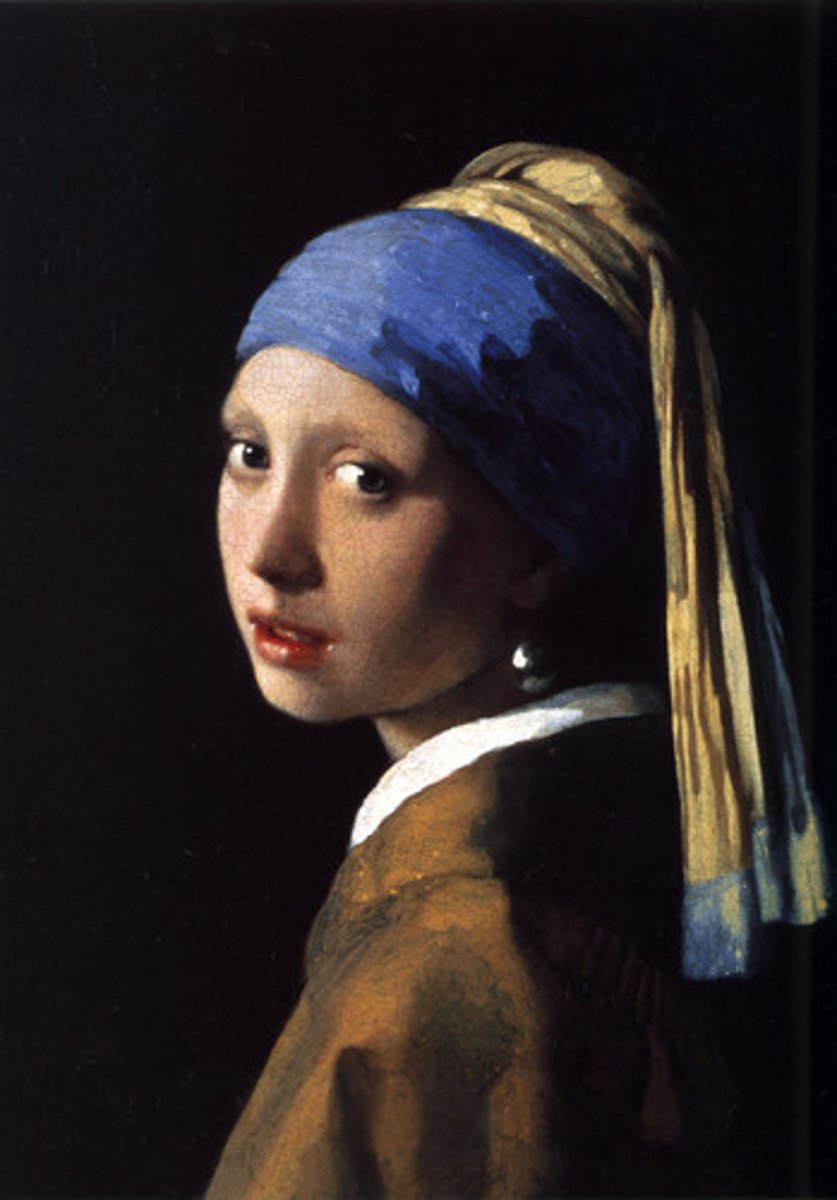
Girl with Pearl Earring
by Vermeer
(Baroque)

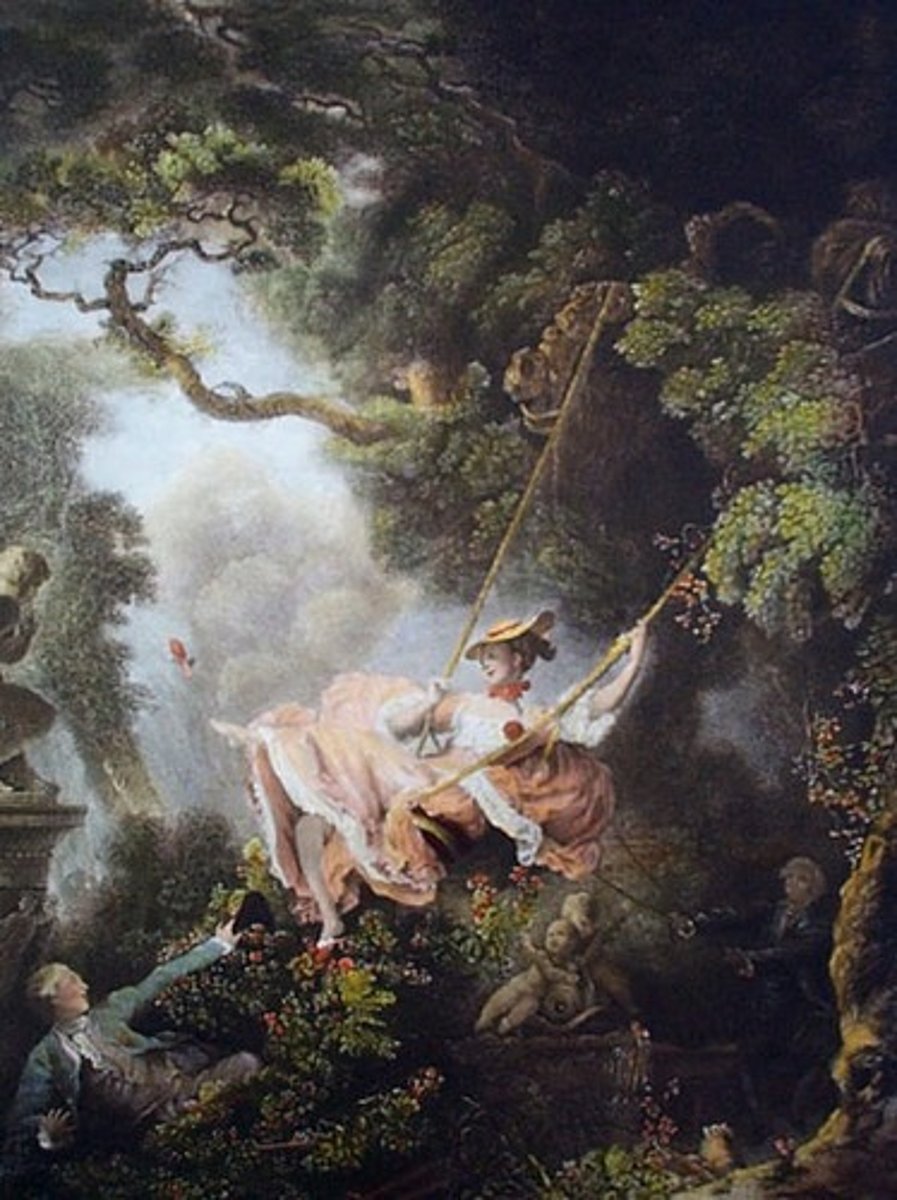
The Swing
by Jean-Honore Fragonard
(Rococo)

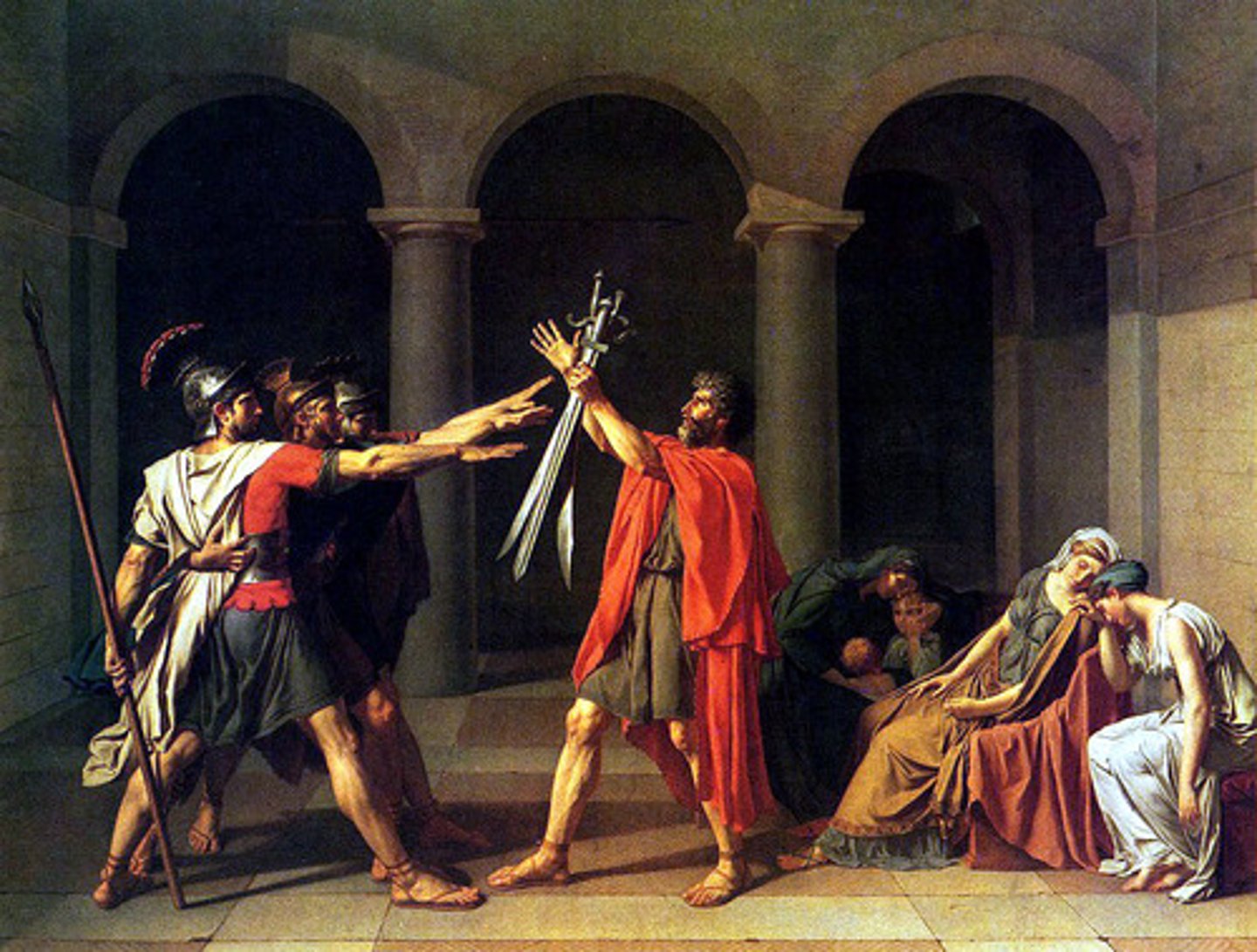
Oath of the Horatii
by Jacques-Louis David
(Neoclassicism)

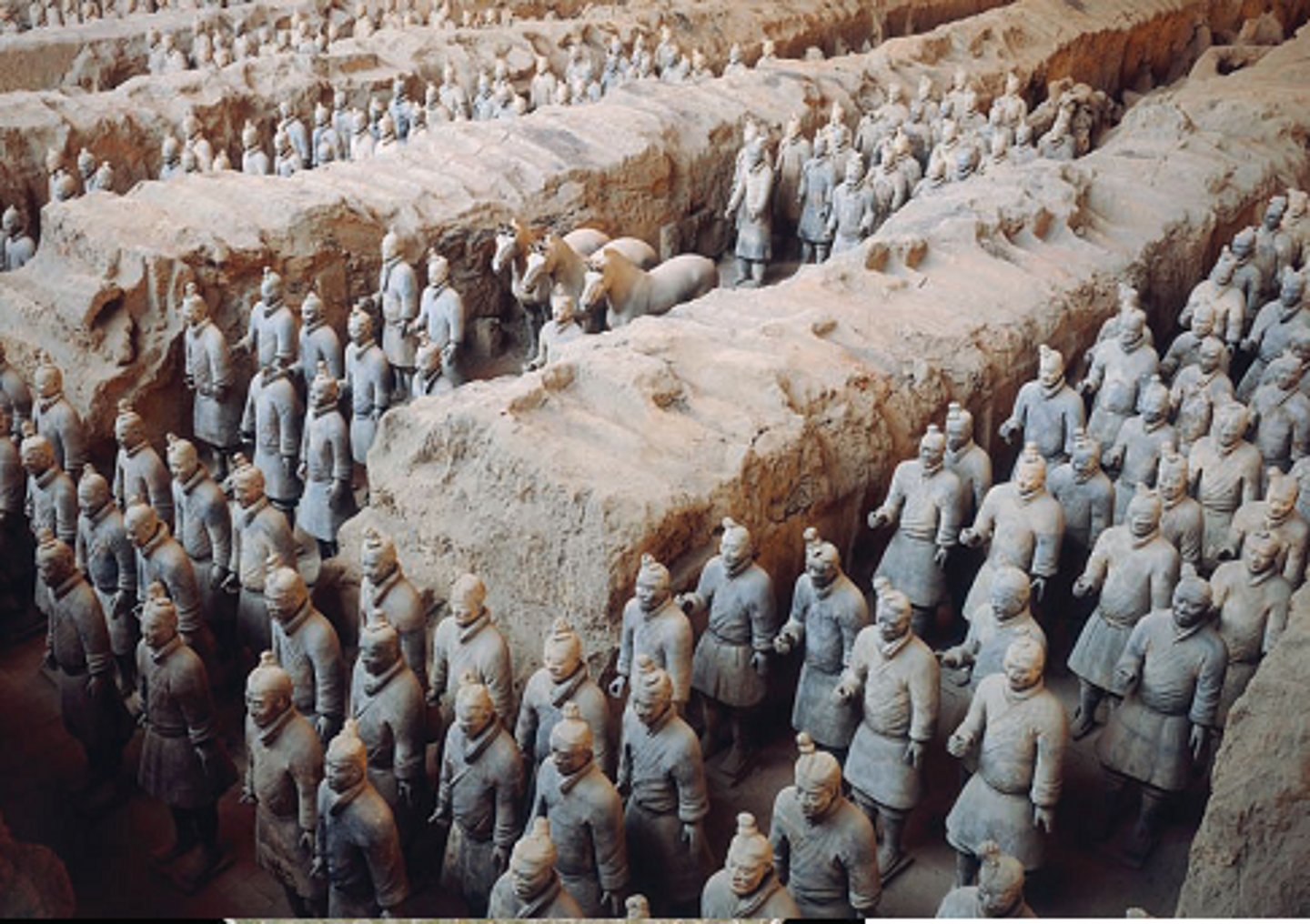
Terra cotta soldiers
depicting armies of Qin Shi Huang
(Chinese)

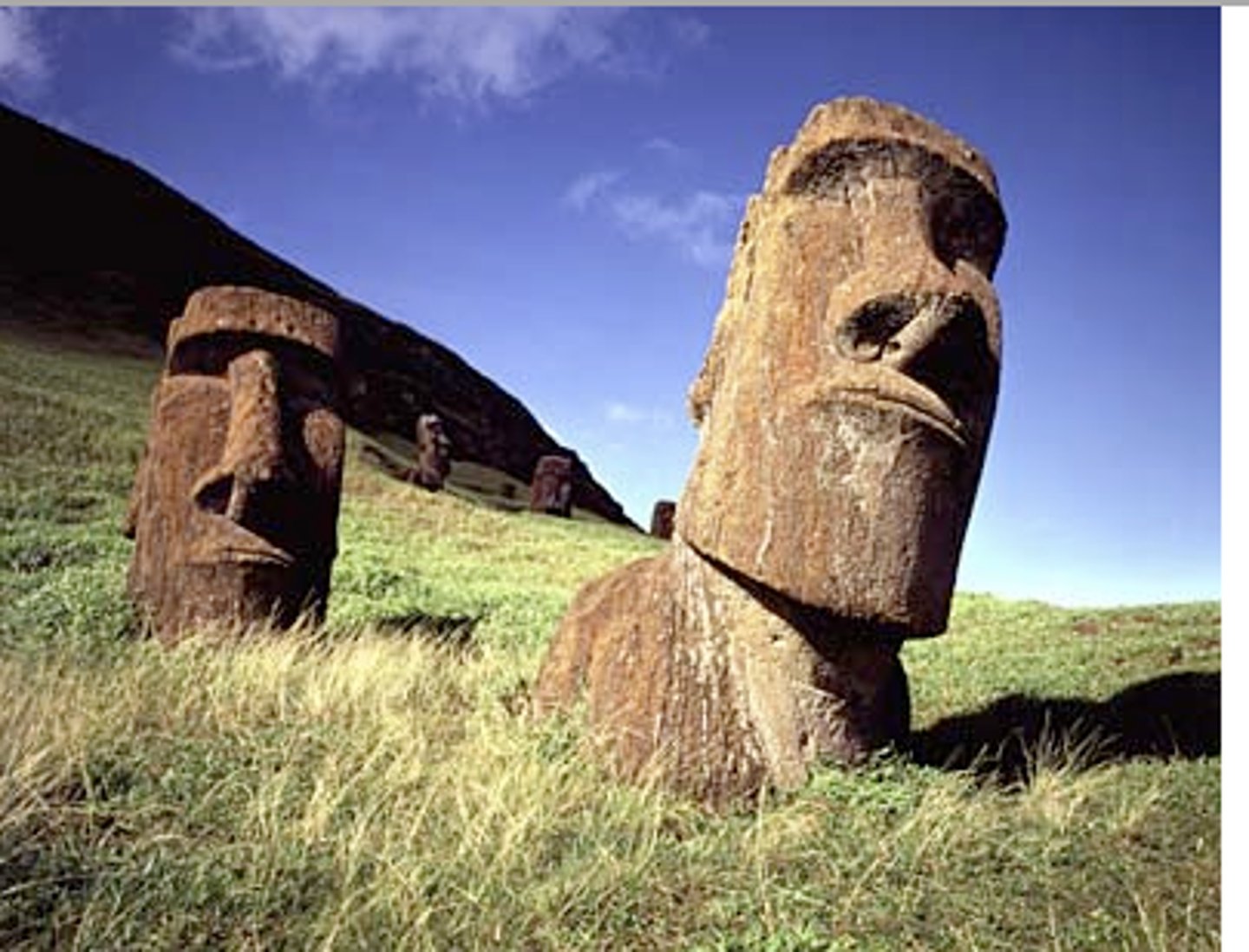
Easter Island Statue Heads,
Moai
(Eastern Polynesia)

Teotihuacan Pyramids
(Pre-Columbian, Mesoamerica)
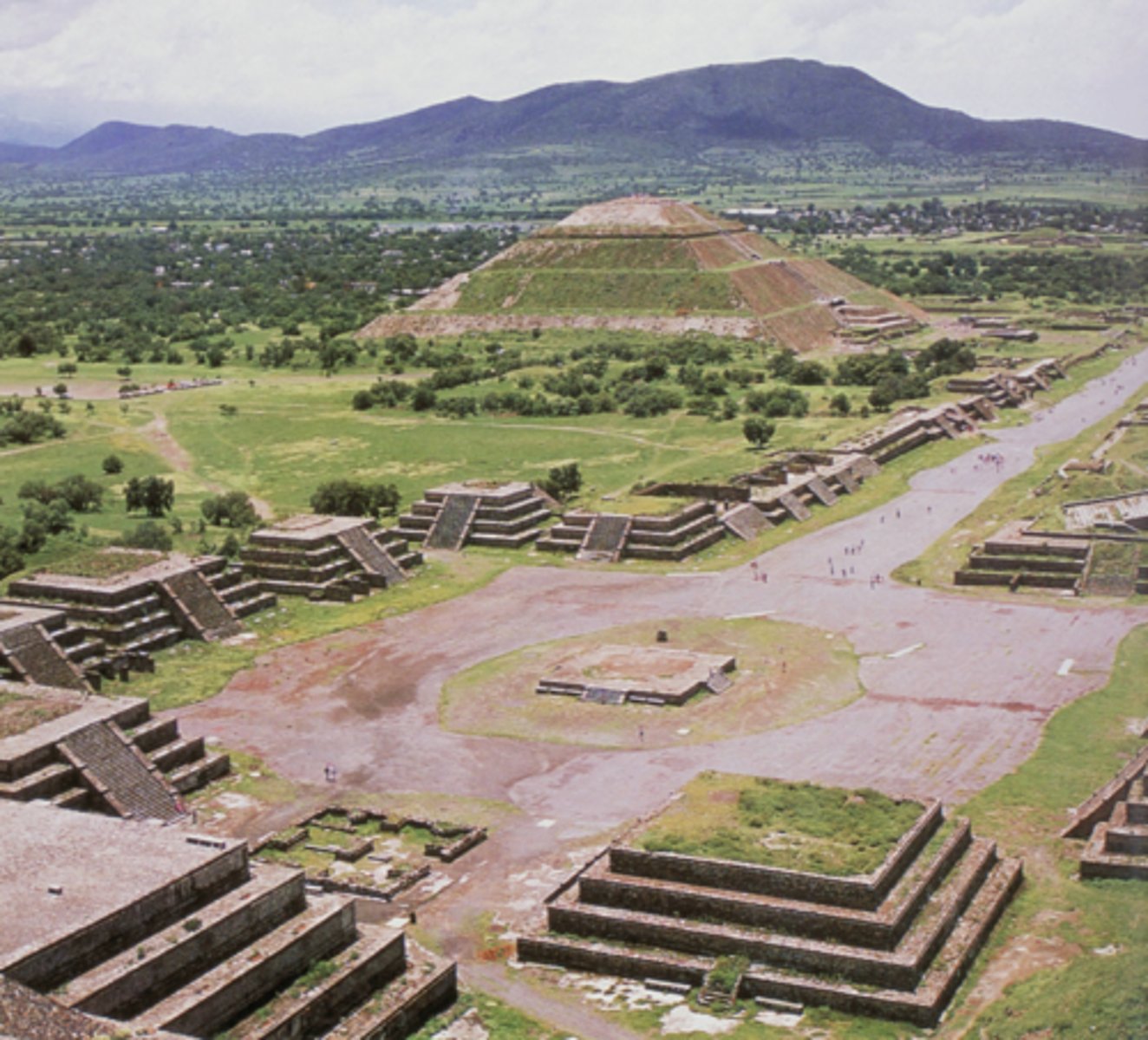

Gleaners by Millet
(Realism)
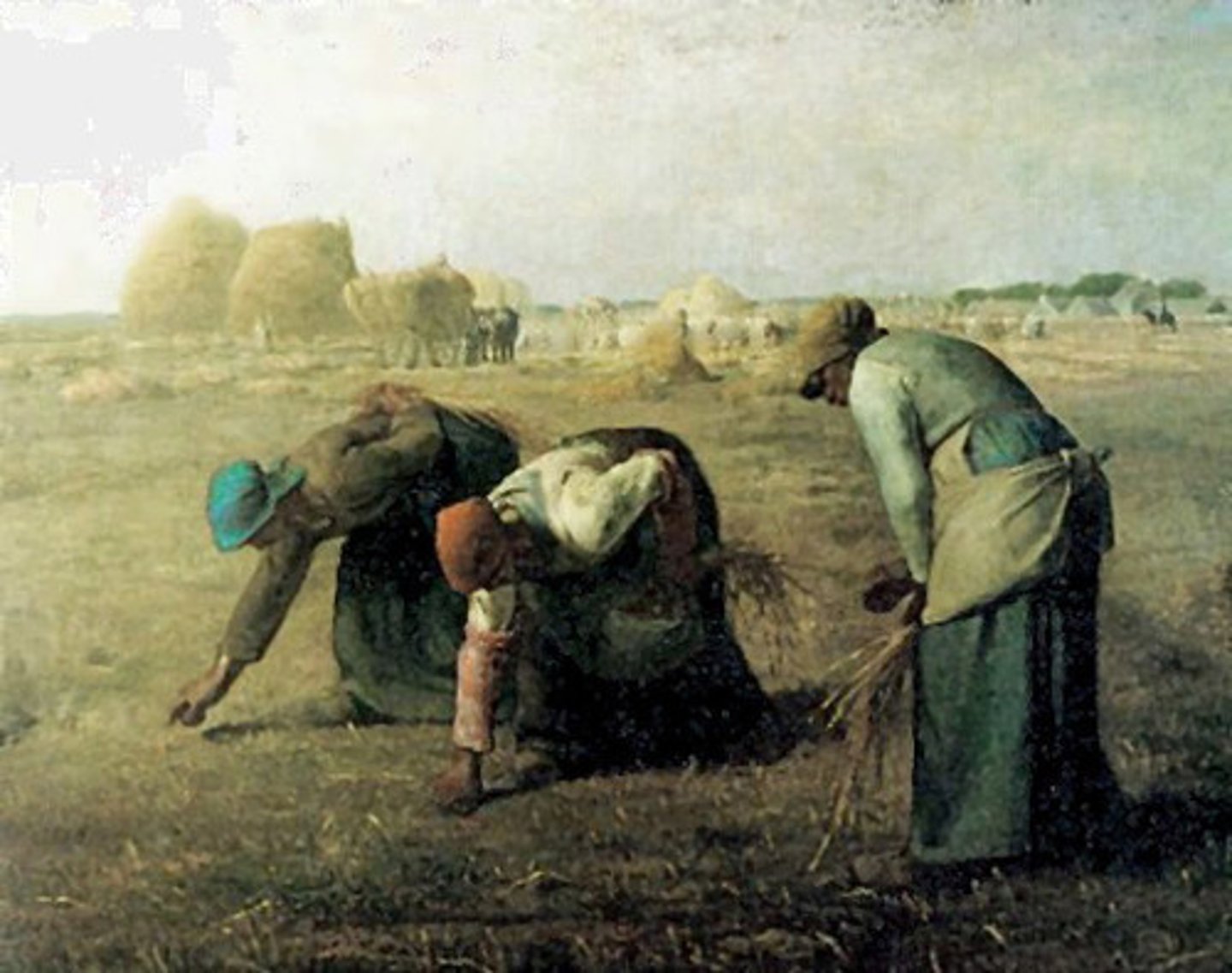

Luncheon on the Grass
by Edouard Manet
(Realism)
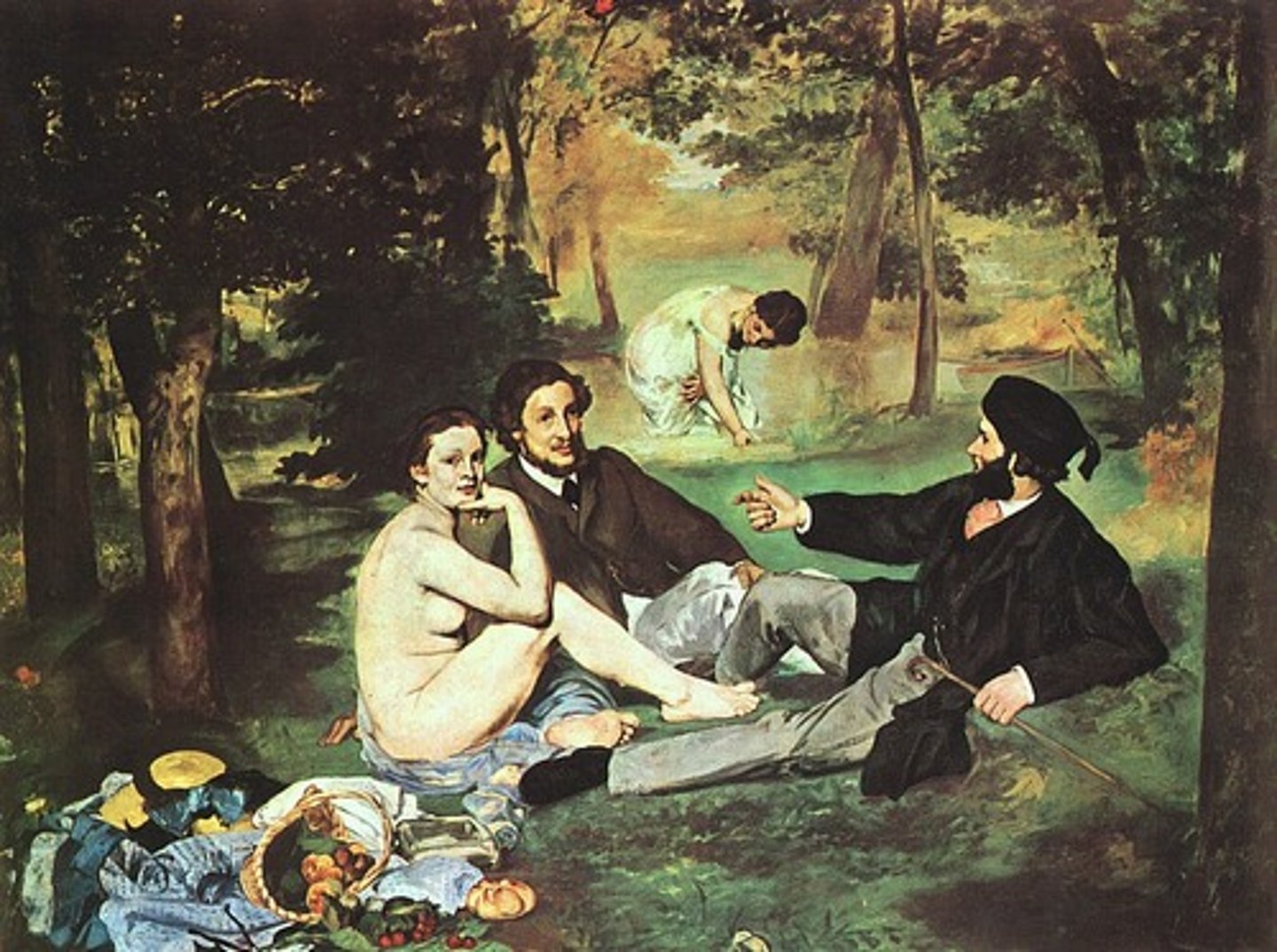

Japanese Bridge
by Claude Monet
(Impressionism)

The Scream by Munch
(Expressionism)

The Kiss by Gustav Klimt

Les Demoiselles d'Avignon
by Pablo Picasso
(Cubism)

Still Life Chair Caning
by Picasso
(Cubism)

Guernica
by Pablo Picasso
(Cubism)

The Persistence of Memory
by Salvador Dalí
(Surrealism)

Arch
In architecture, a curved structure, usually made of wedge-shaped stones, that serves to span an opening. This may be semicircular or rise to a point at the top.
Assemblages
Art that is made by assembling disparate elements - often everyday objects - scavenged by the artist or bought specially for the project
Avant-garde
A French military term for the vanguard or advanced guard, it was appropriated for artistic usage in early 19th-century France to describe art that was at the forefront of artistic development. The concept originated in socialist political theory and its first major artistic exponent was Gustave Courbet in his Realist paintings of the 1850s. Today avant-garde is almost synonymous with modern.
Capital
In architecture, the decorative sculpted block surmounting a column. In Classical architecture, the form of the capital is the most distinctive element of the various orders.
Catacombs
an underground cemetery consisting of a subterranean gallery with recesses for tombs, as constructed by the early Christians.
Centering
framing used to support an arch or dome while it is under construction
Chiaroscuro
An Italian word meaning light and dark that refers to the modulation of light and dark in order to produce an illusion of three-dimensional form.Also called modeling or shading.
Chi-rho monogram
is one of the earliest forms of christogram, formed by superimposing the first two (capital) letters—chi and rho (ΧΡ)
Classical
“of the highest standard” usually ascribed to idealism seen in ancient Greek and Roman thought.
Conceptual Art
Art created according to the belief that the essence of art resides in a motivating idea, and that any physical realization or recording of this idea is secondary. Conceptual art arose during the 1960s as artists tried to move away from producing objects that could be bought and sold. Conceptual works are often realized physically in materials that have little or no inherent value, such as a series of photographs or texts that document an activity. They are often ephemeral.
Contrapposto
The shift of weight of a standing figure onto one leg resulting in an asymmetrical realignment of the entire body. The ancient Greeks invented the position. As a result of contrapposto, this figure looks as though it can move, and it looks much more alive.
Counter-Reformation
The Church initially ignored Martin Luther, but Luther’s ideas (and variations of them, including Calvinism) quickly spread throughout Europe. He was asked to recant (to disavow) his writings at the Diet of Worms (an unfortunate name for a council held by the Holy Roman Emperor in the German city of Worms). When Luther refused, he was excommunicated (in other words, expelled from the church). The Church’s response to the threat from Luther and others during this period is called the Counter-Reformation (“counter” meaning against).
Cubism
A movement developed during the early 20th century by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque. In its most severe “analytical” phase, Cubism abstracted the forms of the visible world into fragments or facets drawn from multiple points of view, then constructed an image from them which had its own internal logic. A severely restricted palette of colors–often dominated by browns, grays, and ochres–was used to focus attention on structure rather than color.
Cuneiform
the earliest system of writing
Dada
An international art movement that emerged during World War I (1914–18). Believing that society itself had gone mad, Dada refused to make sense or to provide any sort of aesthetic refuge or comfort. Instead, it created “anti-art” that emphasized absurdity, irrationality, chance, whimsy, irony, and childishness. Deliberately shocking or provocative works, actions, and events were aimed at disrupting public complacency.
Dome
In architecture, a convex, evenly curved roof; technically, an arch rotated 360 degrees on its vertical axis. Like an arch, this may be hemispherical or pointed.
Edict of Milan
A.D. 313- agreement to treat Christians benevolently within the Roman Empire, associated with Constantine
Fauvism
A short-lived but influential art movement in France in the early 20th century that emphasized bold, arbitrary, expressive color.
Flying Buttress
consists of a strut or arch segment running from a freestanding pier to an outer wall
Gothic
Style of art and architecture that flourished in Europe, especially northern Europe, from the mid–12th to the 16th century. Gothic architecture found its finest expression in cathedrals, which are characterized by soaring interiors and large stained glass windows, features made possible by the use of the pointed arch and the flying buttress.
Hellenistic
Literally “Greek-like” or “based in Greek culture.” Descriptive of the art produced in Greece and in regions under Greek rule or cultural influence from 323 B.C.E. until the rise of the Roman Empire in the final decades of the 1st century B.C.E. Hellenistic art followed three broad trends: a continuing classicism; a new style characterized by dramatic emotion and turbulence; and a closely observed realism.
Humanism
celebrated humanity’s spiritual, intellectual, and physical capabilities.
Icons/Iconoclasm
In Byzantine and later Orthodox Christian art, a portrait of a sacred person or an image of a sacred event. Iconoclasm is the destruction of images or icons.
Keystone
The wedge-shaped, central stone in an arch. Inserted last, the keystone locks the other stones in place.
Lamassu
an Assyrian protective deity, often depicted as having a human's head, a body of an ox or a lion, and bird's wings.
Medici Family
A powerful Florentine family. Originally merchant bankers, the Medici rose in wealth, power, and prestige until figures such as Cosimo (1389-1464) and Lorenzo de’ Medici (the Magnificent) (1449-1492) assumed control of Florence. The Medici family would eventually produce two popes (Leo X, 1513-1521 and Clement VII, 1523- 1534) and marry into the most powerful monarchic dynasties in Europe. Their patronage of the arts is legendary.
Minimalism
A broad tendency during the 1960s and 1970s toward simple, primary forms. Minimalist artists often favored industrial materials (sheet metal, bricks, plywood, fluorescent lights), and their sculptures (which they preferred to call objects) tended to be set on the floor or attached to the wall rather than placed on a pedestal.
Neoclassical
Literally “new classicism,” a Western movement in painting, sculpture, and architecture of the late 18th and early 19th centuries that looked to the civilizations of ancient Greece and Rome for inspiration. These artists worked in a variety of individual styles, but in general, like any art labeled classical, this art emphasized order, clarity, and restraint.
Oculus
A circular opening in a wall or at the top of a dome
Pilgrimage
religious journey or expedition, popular in the Romanesque and Gothic era
Pointed Arch
an arch with a pointed apex
Pop Art
An art style of the 1960s, deriving its imagery from popular, mass-produced culture. Deliberately mundane, Pop art focused on the over familiar objects of daily life to give them new meanings as visual emblems.
Post-and-Lintel
In architecture, a structural system based on two or more uprights (posts) supporting a horizontal crosspiece (lintel or beam).
Radiating Chapels
Small, semi-circular chapels arranged around the apse of a large church.
Relics
A holy object that is supposedly from a saint
Reliquaries
A container or receptacle, such as a coffer or shrine, used to keep or display sacred relics.
Renaissance
literally means “re-birth”; characterized by a renewed interest in Classical art, architecture, literature, and philosophy. This era began in Italy and gradually spread to the rest of Europe.
Rib Vault
A variation on groin vaults, a ribbed barrel vault
Rococo
A style of art popular in Europe in the first three quarters of the 18th century. This architecture and furnishings emphasized ornate but small- scale decoration, curvilinear forms, and pastel colors.
Romanesque
A style of architecture and art dominant in Europe from the 10th to the 12th century. Romanesque architecture, based on ancient Roman precedents, emphasizes the round arch and the barrel vault.
Romanticism
A movement in Western art of the late 18th and early 19th century, generally assumed to be in opposition to Neoclassicism. Romantic works are marked by intense colors, turbulent emotions, complex composition, soft outlines, and sometimes heroic or exotic subject matter.
Stained Glass
The technique of creating images or decorations from precisely cut pieces of colored glass held together with strips of lead.
Surrealism
A movement of the early 20th century that emphasized imagery from dreams and fantasies.
The Protestant Reformation
1517- a major 16th century European movement aimed initially at reforming the beliefs and practices of the Roman Catholic Church.
The Salon
an annual exhibition of works of art by living artists, originally held at the Salon d'Apollon: it became, during the 19th century, the focal point of artistic controversy and was identified with academicism and official hostility to progress in art.
Ziggurats
In ancient Mesopotamian architecture, a monumental stepped structure symbolically understood as a mountain and serving as a platform for one or more temples.