Patho-Neurology
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Chronic, progressive failure of many cerebral functions including impairment of intellectual processes
loss of orientation, memory, language, judgement, decision making, behavior
not a disease, group of symptoms caused by brain damage
dementia-defined
neuron degeneration (no repair)
brain compression
atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels (plaque in brain)
brain trauma (athletes)
CNS infections & neuroinflammation (alcoholic)
dementia-pathophysiology
progressive neurological deterioration & continuing decline affecting memory, thinking skills, inability to carry out simplest tasks
most common type in older people
key factor=increase in age
LATE ONSET(non-hereditary) 60-80yrs & MOST COMMON
EARLY ONSET 30-50yrs/familial-autosomal dominant/ non-familial-down syndrome
alzheimer’s - defined
extracellular-deposition of beta-amyloid (plaque)
intracellular-accumulation of tau proteins(tangles)
degeneration of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons-loss of acetylcholine
alzheimer’s-pathophysiology
early symptoms-forgetfulness (short term memory), emotional upset
later symptoms-memory loss, disorientation, confusion, disorientation, lack of concentration, decline in problem solving
progressive:10-20yrs
alzheimer’s-signs & symptoms
no specific treatment
anticholinesterase drug-temporary (cholinesterase kills acetylcholine)
team approach needed to support patients & caregivers
treat symptoms, not cure
alzheimer’s-treatment
progressive, neurodegenerative disease of the basal ganglia with the loss of dopamine-providing neurons
hypokinetic movement
parkinson’s disease
intraneuronal Lewy Bodies inclusions composed of α-synuclein
Types: Primary: idiopathic-most common, 60-80yrs/ genetic association
Secondary: environmental-pesticides/herbicides
anti-psychotic meds
pseudo-parkinsonism (Muhammed Ali)
parkinson’s-pathogenesis
masked facies | stooped posture
rigidity | slow movement
poor balance | short shuffling steps
tremors
parkinson’s-signs & symptoms
levodopa-dopamine replacement therapy
anticholinergic drugs (blocks parasympathetic)- stops shakes
amantadine- decrease tremors
team approach-speech & language pathologist | physical & occupational therapy
monitoring & treatment of respiratory & UTIs
parkinson’s-treatment
progressive, debilitating neurodegenerative inherited disease
autosomal dominant Gg
doesn’t manifest until around 40yrs old
huntington’s
hyperkinetic disorder (artistic arm movement)
depletion of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)- inhibitor
levels of acetylcholine in the brain appear to be reduced
results in progressive atrophy of the brain
huntington’s-pathophysiology
mood swings | personality changes
restlessness
choreiform (purposeless) movements w/out conscious effort
emotional changes
huntington’s-signs & symptoms
DNA analysis because it’s inherited lol
huntington’s- diagnosis
no specific treatment | treat symptoms only
mortality: suicide | infection | heart disease
huntington’s- treatment
rapidly progressive & fatal neurodegenerative disease of the upper & lower motor neurons
AKA Lou Gehrig’s disease
no indication of inflammation around the nerves
cognition impaired
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS- defined
SOD I gene mutation - most common
military vets - Gulf War
risk-repeated trauma (athletes) - Lou Gehrig
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS- pathogenesis
spastic paralysis-loss of upper motor neurons
flaccid paralysis-loss of lower motor neurons
progressive muscle weakness & loss of fine motor skills (stumbling & falls common)
death from respiratory failure
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS- pathophysiology
limb cramping or weakness
similar to stroke- incoordination | slurring of speech | dysphagia-difficulty swallowing
single group paresis (muscle weakness) that spreads
hypotonia-muscle tone loss( ya insides)
survival: 3-5yrs from diagnosis
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS- clinical manifestations
maintain quality of life | involve family in treatment
not much you can do because ya fucked
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS- treatment
frequently occurring neurological disorders caused by pathologic processes in the blood vessels
cerebrovascular disease
ischemia (low blood flow)
hemorrhagic (balloon pop) - increased intracranial pressure
vascular malformation
cerebrovascular disease- pathogenesis
transient ischemic attacks (TIAS)
cerebral vascular accident (CVA {stroke}):
thrombotic-deep vein thrombosis
embolic- bone marrow goes to heart | amniotic fluid | O2 pocket
hemorrhagic- blood bleeds out
cerebrovascular disease- types
transient episode of neurologic dysfunction by focal brain, spinal cord, or retinal ischemia w/out acute infarction
acute- lasting less than an hour from ischemic event
reversible
transient ischemic attacks TIAS
atherosclerosis- most common
small embolus- blockage
vascular spasms- constriction
arteritis- artery inflammation
mass lesions- cancer
transient ischemic attacks TIAS- causes
difficult to diagnose after attack
directly located to location of ischemia
intermittent short episodes of impaired function
muscle weakness in arm of leg
visual disturbances
numbness & paresthesia (pins & needles)
transient aphasia (language disorder)
goes away & is a warning sign
transient ischemic attacks TIAS- signs & symptoms
rule out other causes
baseline bloodwork
MRI- preferred | CT scan
carotid doppler
angiography
transient ischemic attacks TIAS- diagnosis
risk stratification
start stroke prevention therapy
transient ischemic attacks TIAS- management
an infarction (tissue death by lack of blood flow) - hypoperfusion
leading cause of disability
african american-higher risk
cerebrovascular accidents CVAs- defined
ischemic- occlusion of blood vessel by a thrombus of embolus
hemorrhagic- rupture of cerebral vessel-hypertension
cerebrovascular accidents CVAs- classifications
hypertension- most common cause
bleeding→ compressed brain tissue→ ischemia, edema, ICP & necrosis
bleeding types: intracerebral | subarachnoid
cerebrovascular accidents CVAs- hemorrhagic stroke
non-modifiable factors
modifiable factors- hypertension, diabetes, smoking, sedentary lifestyle
cerebrovascular accidents CVAs- risk factors
lack of voluntary movement or sensation on the opposite side of body
initially flaccid paralysis → then becomes spastic later on
cerebrovascular accidents CVAs- signs & symptoms
focused on restoration of perfusion, countering ischemia, preventing necrosis
surgery: endarectomy- embolic & ischemic stroke | clot removal/clamp bleeding- hemorrhagic
aspirin | systemic anticoagulation | thrombolysis | anti-platelet therapy & statins | blood pressure control | glucocorticoids- minimizes brain swelling | underlying problems | immediate rehab
cerebrovascular accidents CVAs- treatments
aspirin- platelet antiaggregant
statins- cholesterol lowering drugs
control hypertension | control diabetes type II | stop smoking “cessation” | lifestyle changes
cerebrovascular accidents CVAs- prevention
inflammation & infection of the membrane covering the brain & spinal cord- dura mater, arachnoid mater, subarachnoid, pia mater
meningitis
bacteria-most severe (will fucking kill you) | N meningitidis gram- | S pneumonia gram +
viral (aseptic)- most common, not deadly (meds, autoimmune, cancer)
fungal- associated w/suppressed immune system (last of us)
meningitis- etiology
microorganisms reach the brain via: blood & nearby bordering tissue
infections spread rapidly through meninges
inflammatory response leads to increased intracranial pressure
exudate (pus) present in the cerebrospinal fluid
meningitis- pathophysiology
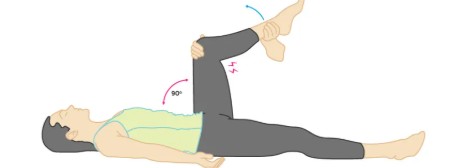
elicits pain or limited extension
hip & knee at 90°
Kernig sign
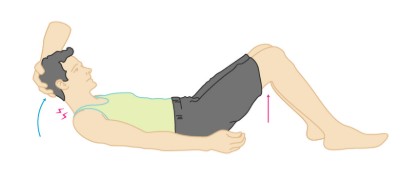
elicits hip & knee flexion
passive flexion of neck
Brudzinski sign
rapid diagnosis & treatments to prevent morbidity & mortality
identify organism that’s fucking you up
aggressive antimicrobial therapy
glucocorticoids- reduces swelling
vaccines available
meningitis- treatments
chronic progressive immune-mediated inflammatory disease w/ progressive demyelination of neurons in the CNS; brain, spinal cord, cranial nerves
targets oligodendrocytes
autoimmune
white people shit- mostly women
relapses/remission can happen- becomes irreversible over time
multiple sclerosis MS
Lhermitte sign
jolt in back- MS
paresthesia (pins & needles) | double vision
poor coordination | sensory deficits
loss of bowel & bladder control | memory loss
multiple sclerosis MS- clinical manifestations
full neurological exam | no specific marker
MRI- diagnosis & monitoring | CSF analysis
multiple sclerosis MS- diagnostics
no definitive treatment | corticosteroids
immunotherapy- transfusions | vitamin D
physical & occupational therapy
multiple sclerosis MS- treatment