Microbiology Chapter #10 - Transcription, Translation, and Translocation
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Bacterial Protein Coding Gene
- Polynucleotide sequence in the DNA
- Promoter region tells RNA polymerase where to start
- Reading Frame are genes that need to be replicated

Transcription: Initiation
- RNA polymerase and Sigma Factor bind to promoter region
- DNA unwinds and denatures "transcription bubble"
- RNA polymerase begins to synthesize complementary nucleotides 5 to 3
- Sigma Factor dissociates
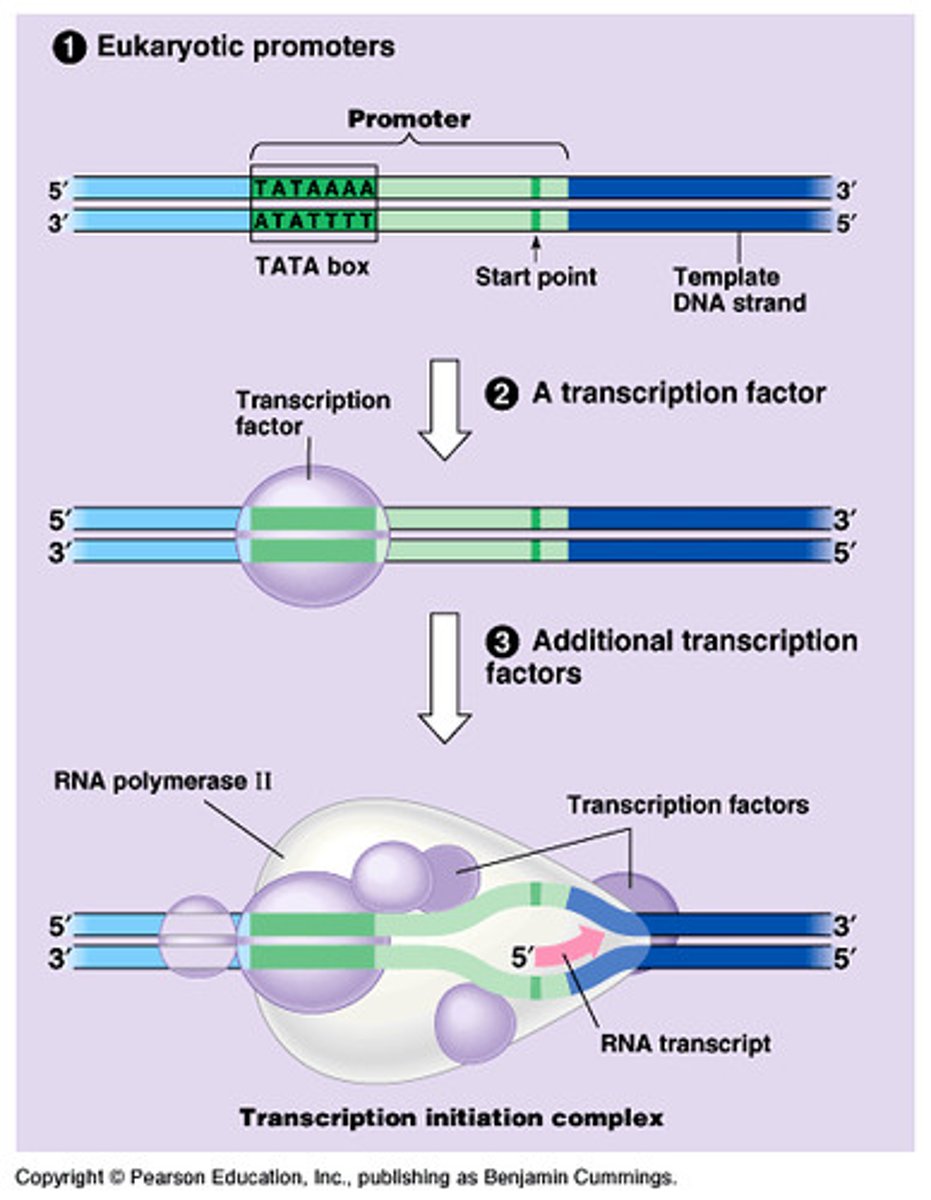
Transcription: Elongation
- RNA polymerase moves along, adding nucleotides
- Previous stretch of DNA reannealed
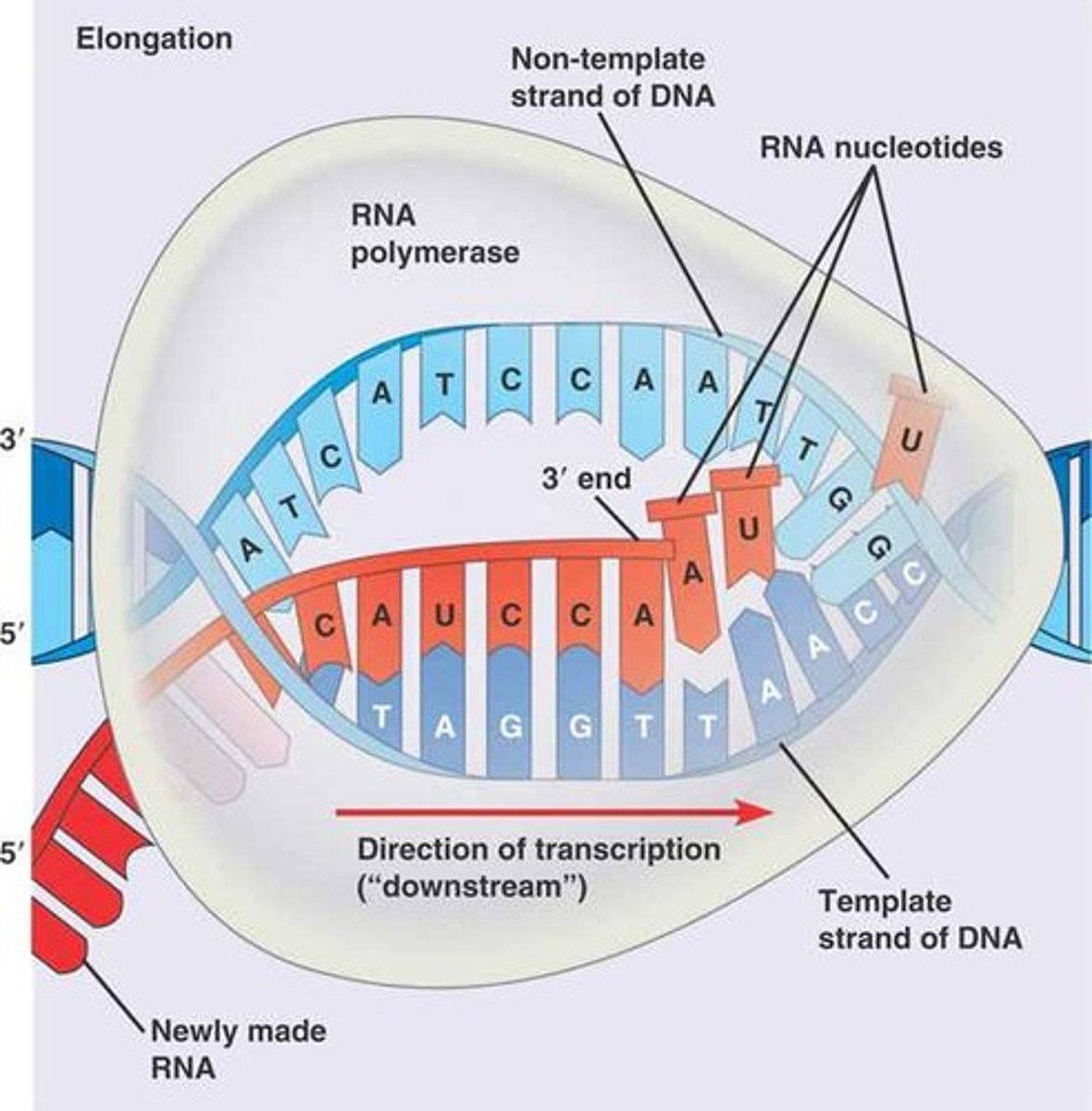
Transcription: Termination
- RNA polymerase recognizes signal and stops, releasing the pre-mRNA transcript
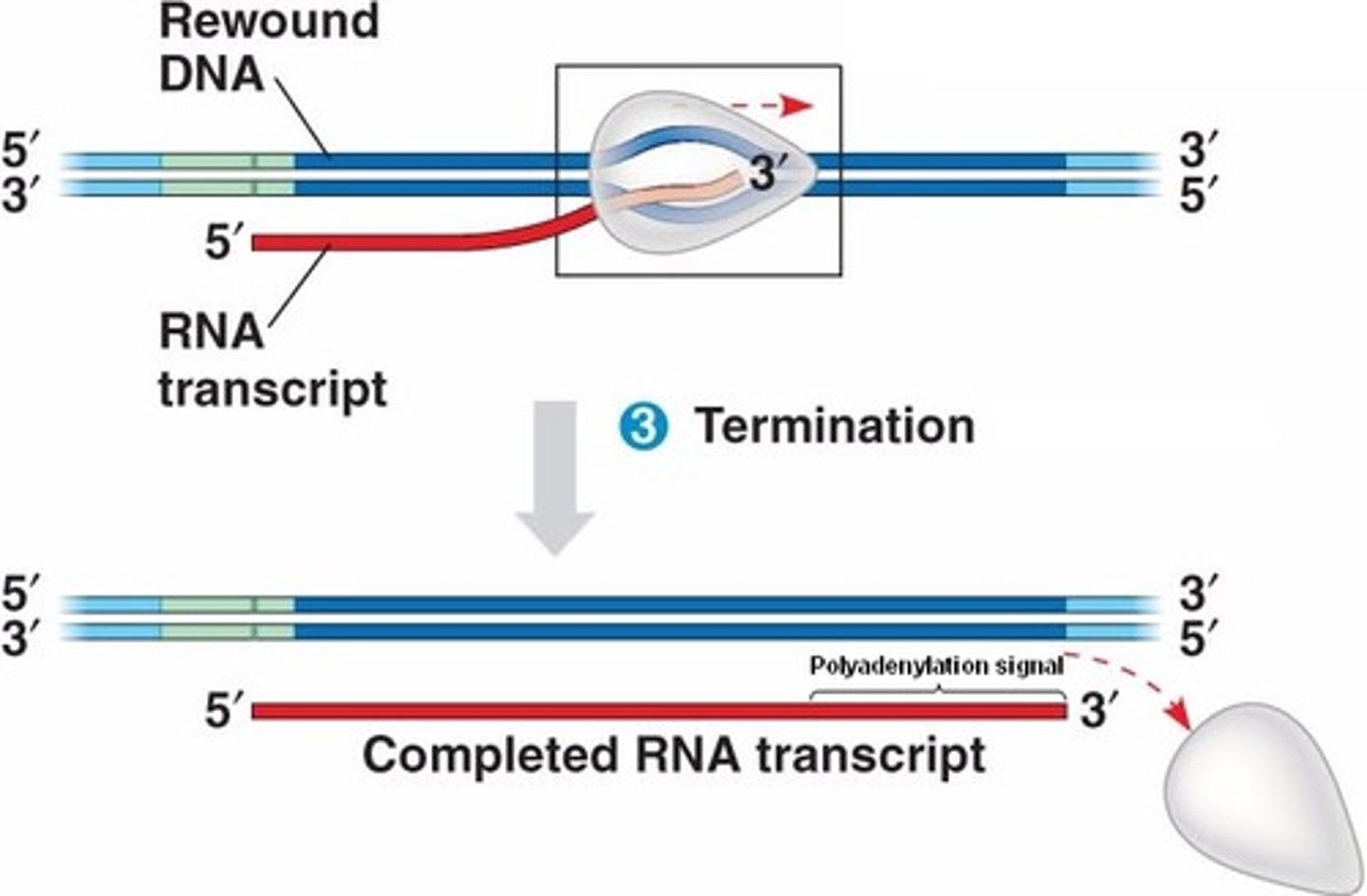
Bacterial Promoters
- show RNA polymerase where to bind and begin
Sigma Factors
- Recognize and bind to promoter sequence, signaling RNA polymerase to bind as well

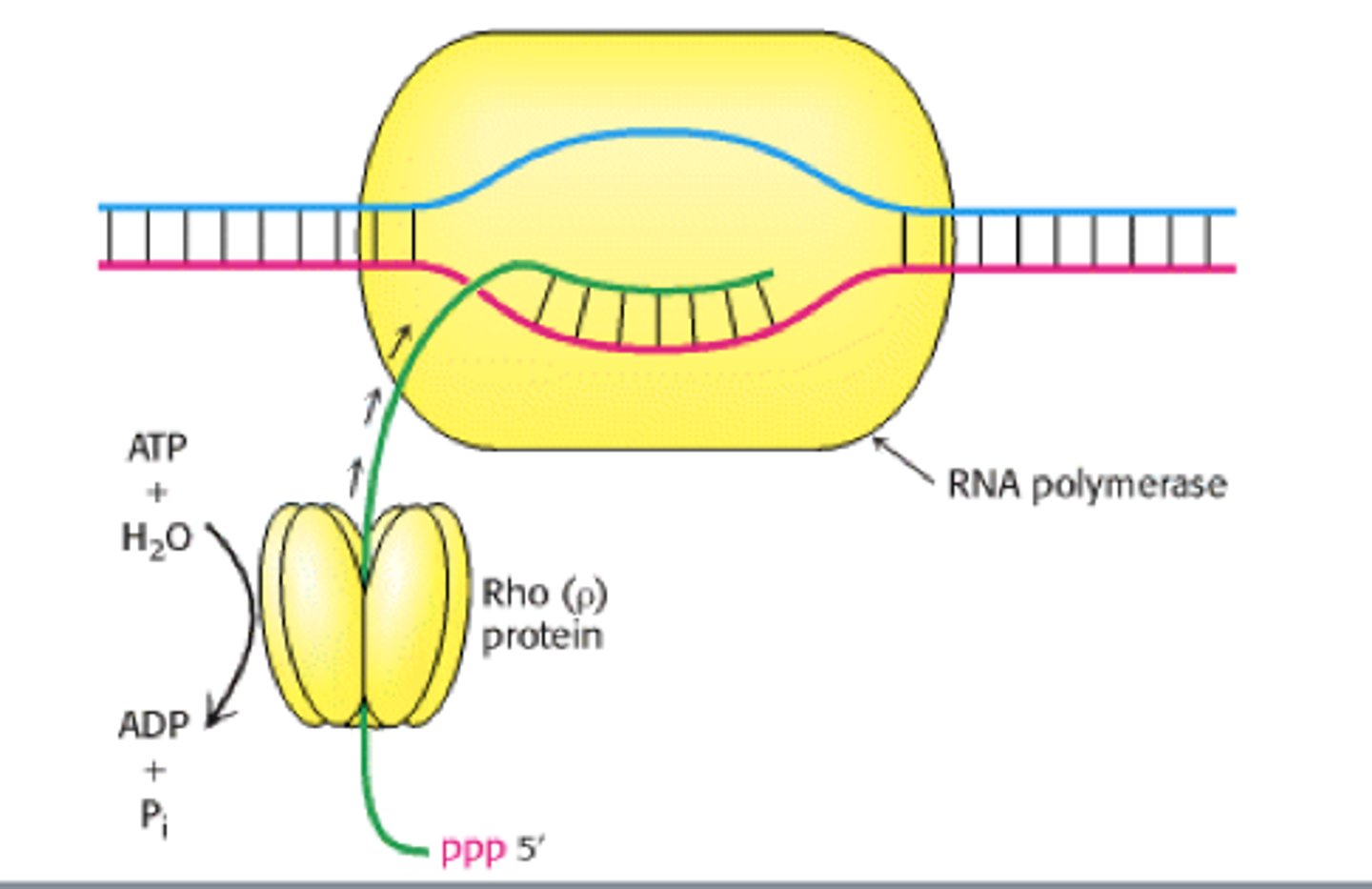
Factor-Dependent Termination
- The Rho Factor binds to a site on mRNA called "rut" and follows RNA polymerase along strand
- RNA polymerase pauses at rho-dependent pause site, and rho catches up and forces it off of the DNA
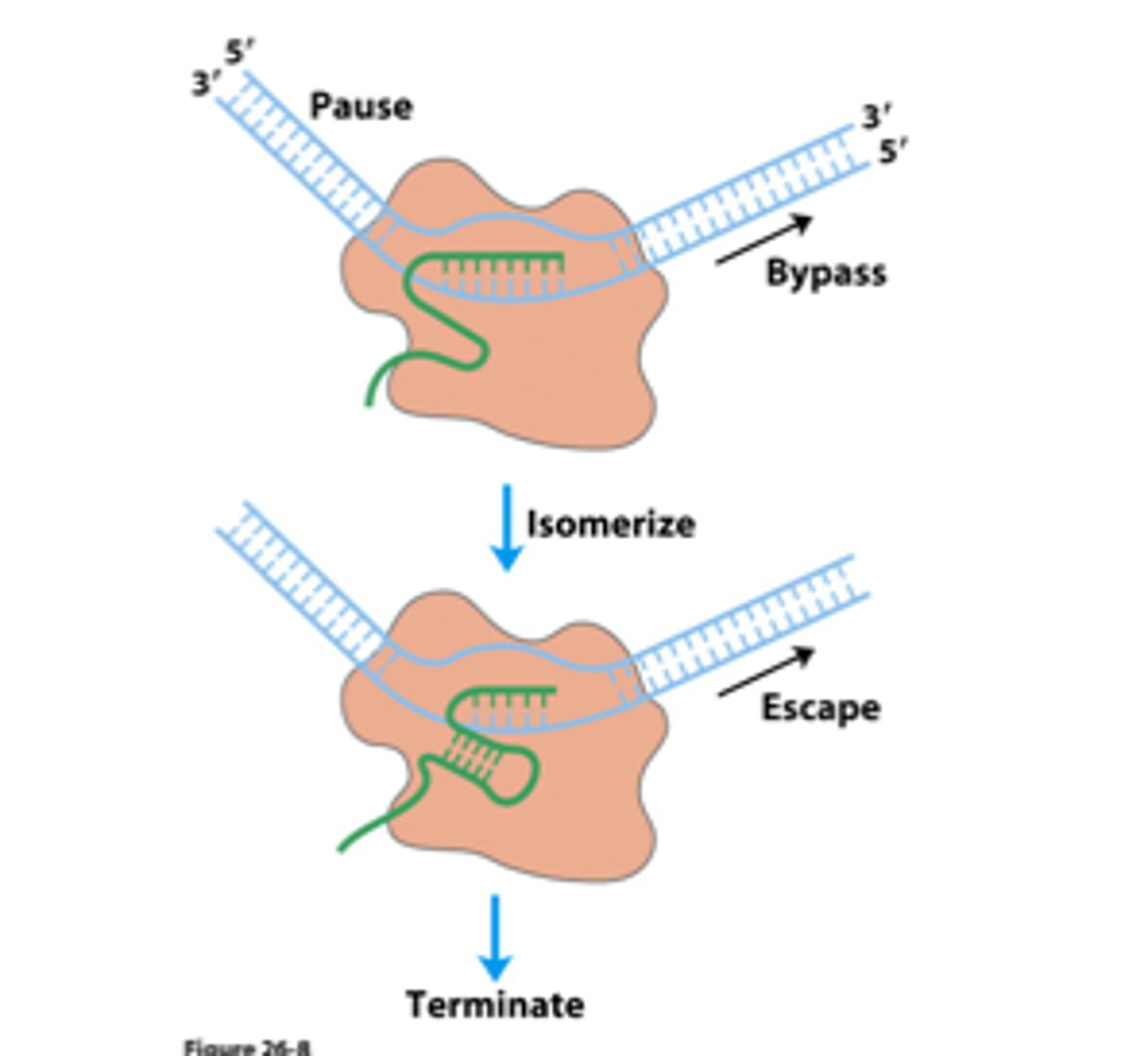
Factor-Independent Termination
- RNA polymerase transcribes inverted repeat but slows down at the A-rich sequence
- The inverted repeated folds back on itself in a hairpin strucutre, and RNA polymerase falls off
Universal Genetic Code
- Every living organism uses the same system to code for protein

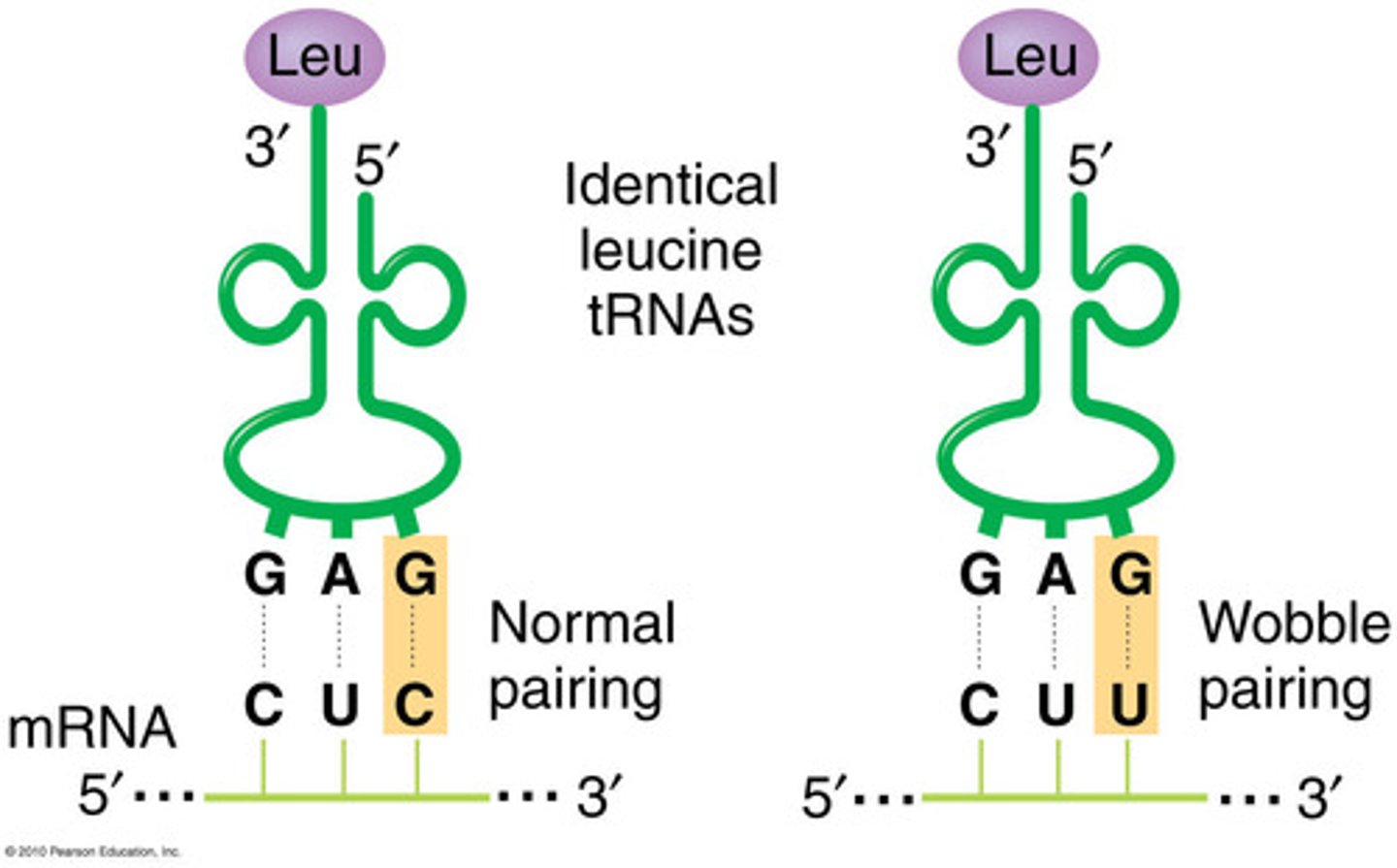
Wobble
- Reduces the amount of different tRNAs needed for translation
- Only the first two basepairs must be correct
tRNA
- Contain anticodons complementary to codons on mRNA
- Acceptor end where amino acid can attach
- Hairpin stucture

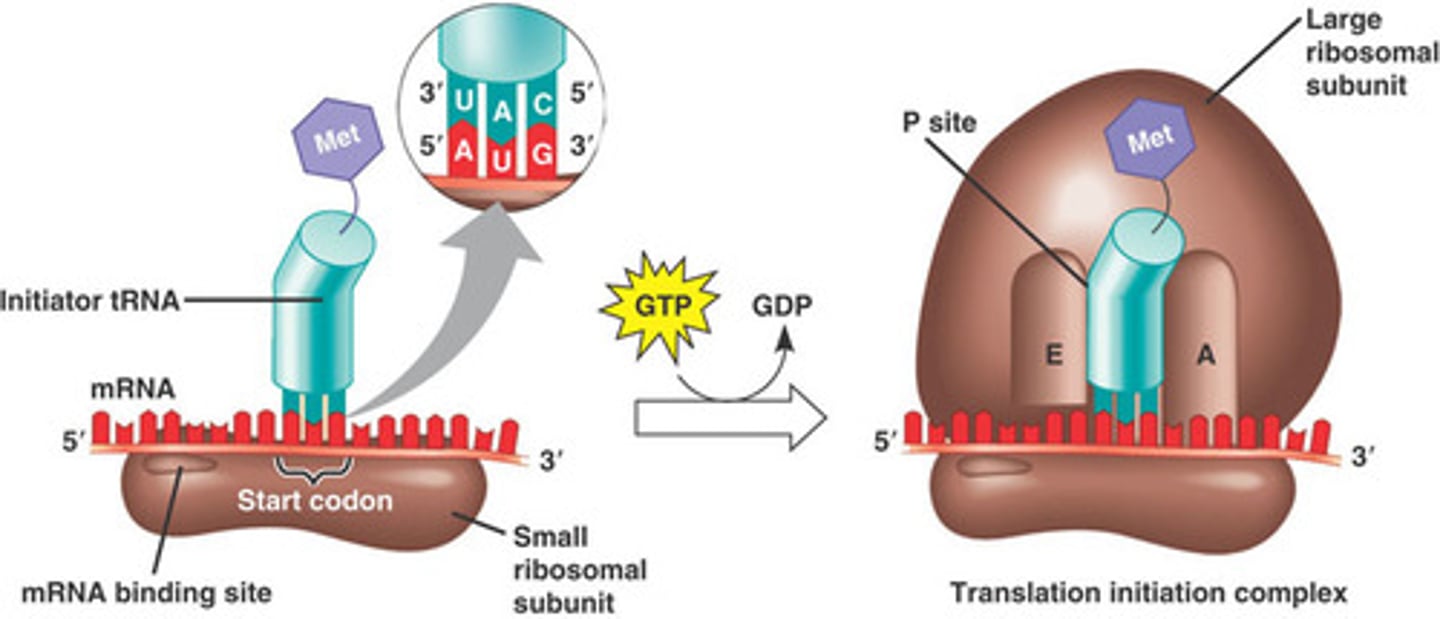
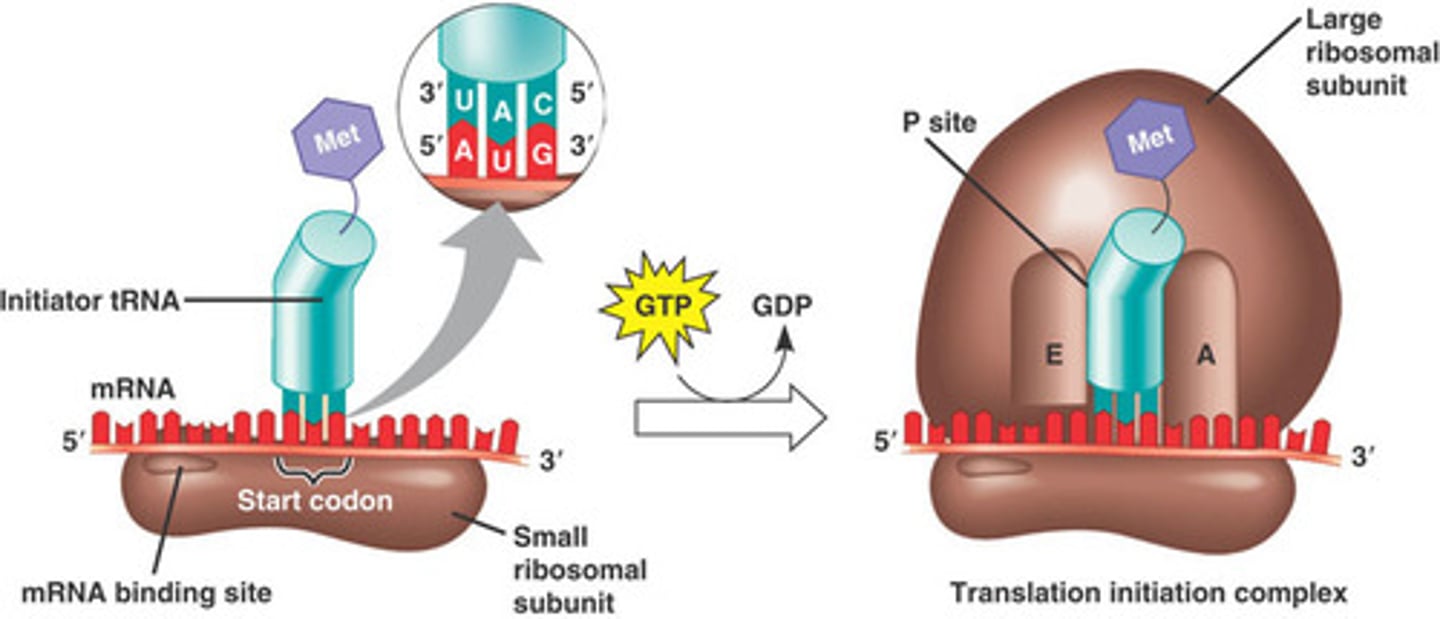
Translation Initiation Complex
- ATP group is added to an amino acid, then added to tRNA
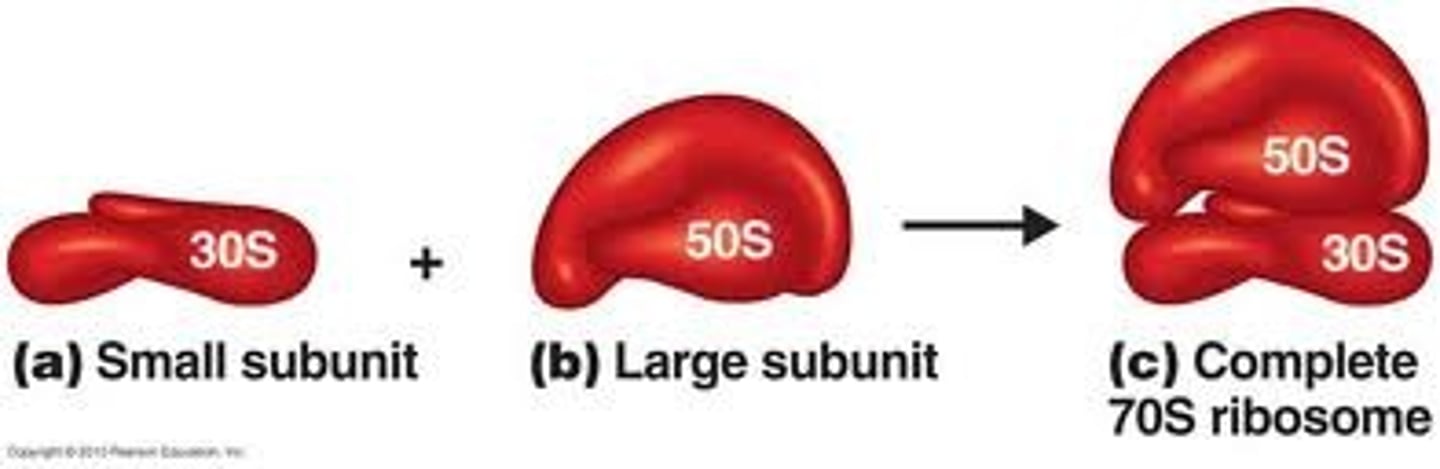
Bacterial Ribosomes
- Large 50S, Small 30S
- 70S Ribosome
- 3 sites for translation: A, P, and E
Initiator tRNA
- Carries N-formyl methionine
- Through GTP, large subunit of the ribosome is attached and the first tRNA attaches to the P site
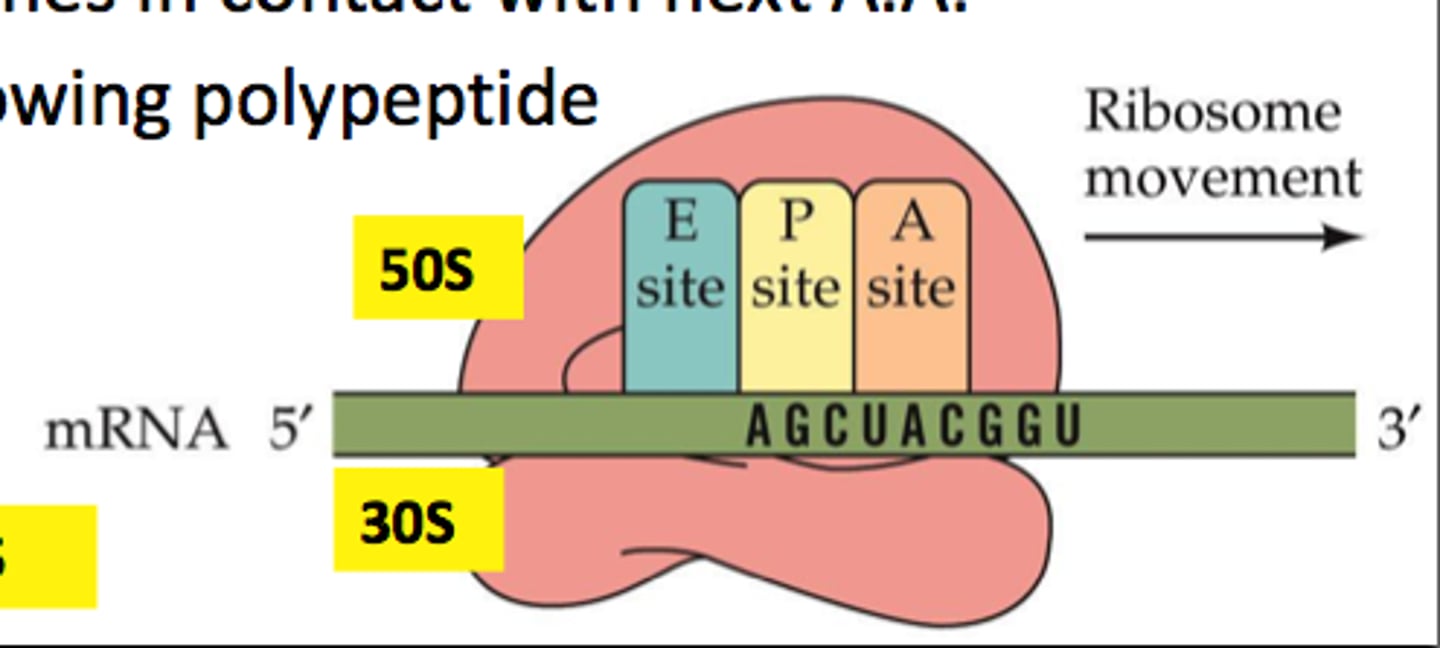
A, P, and E sites
- tRNA with the next amino acid enters the A site
- Peptide bond forms between the amino acids of the tRNAs in A and P site, creating chain
- Empty tRNA moves to E site and other tRNA moves to P
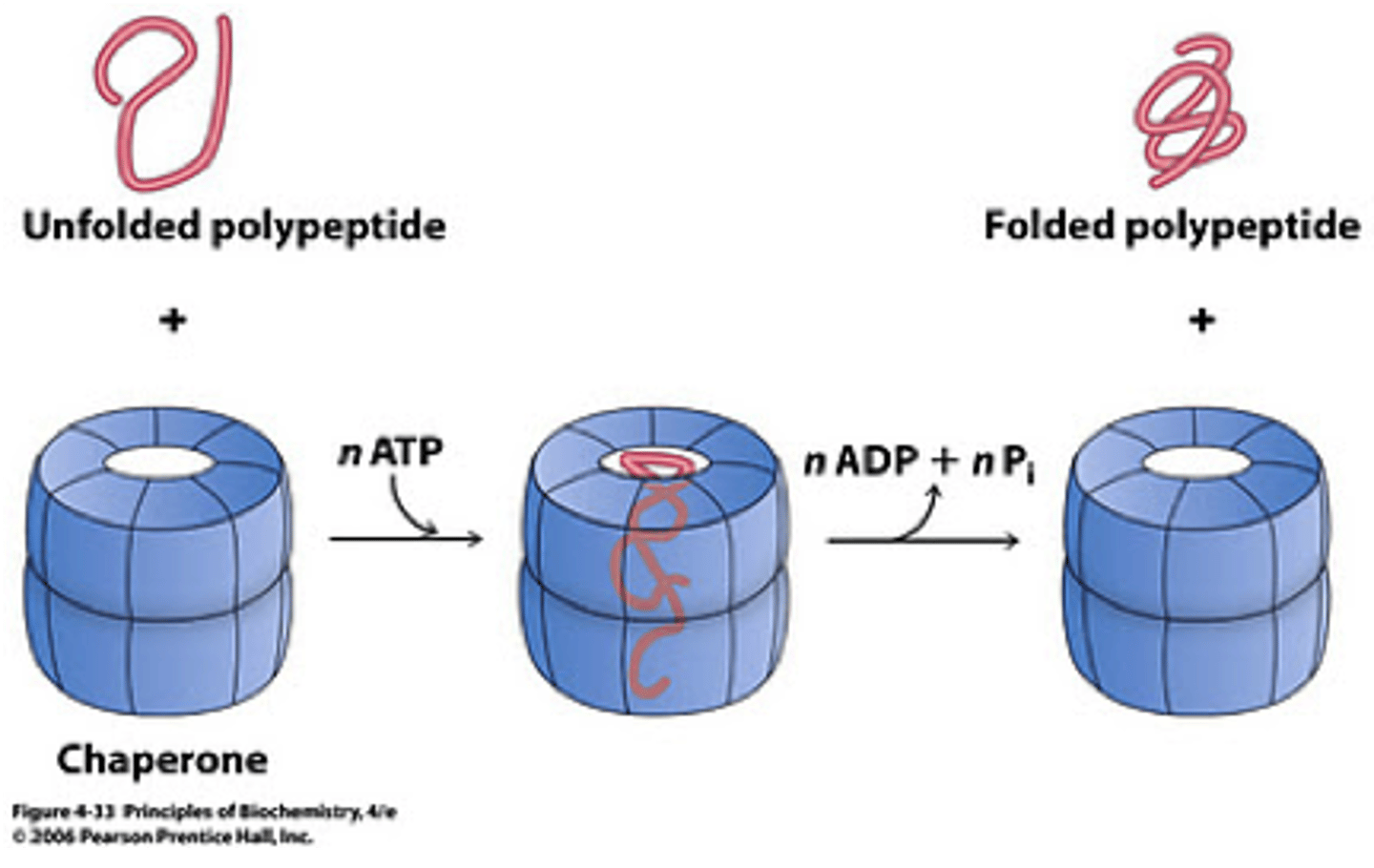
Molecular Chaperones
- Help proteins fold from secondary to tertiary
- Trigger Factor
Translocation
- Proteins are moved across the cytoplasm or to the plasma membrane
Secretion
- Proteins are moved from the cytoplasm to the external environment
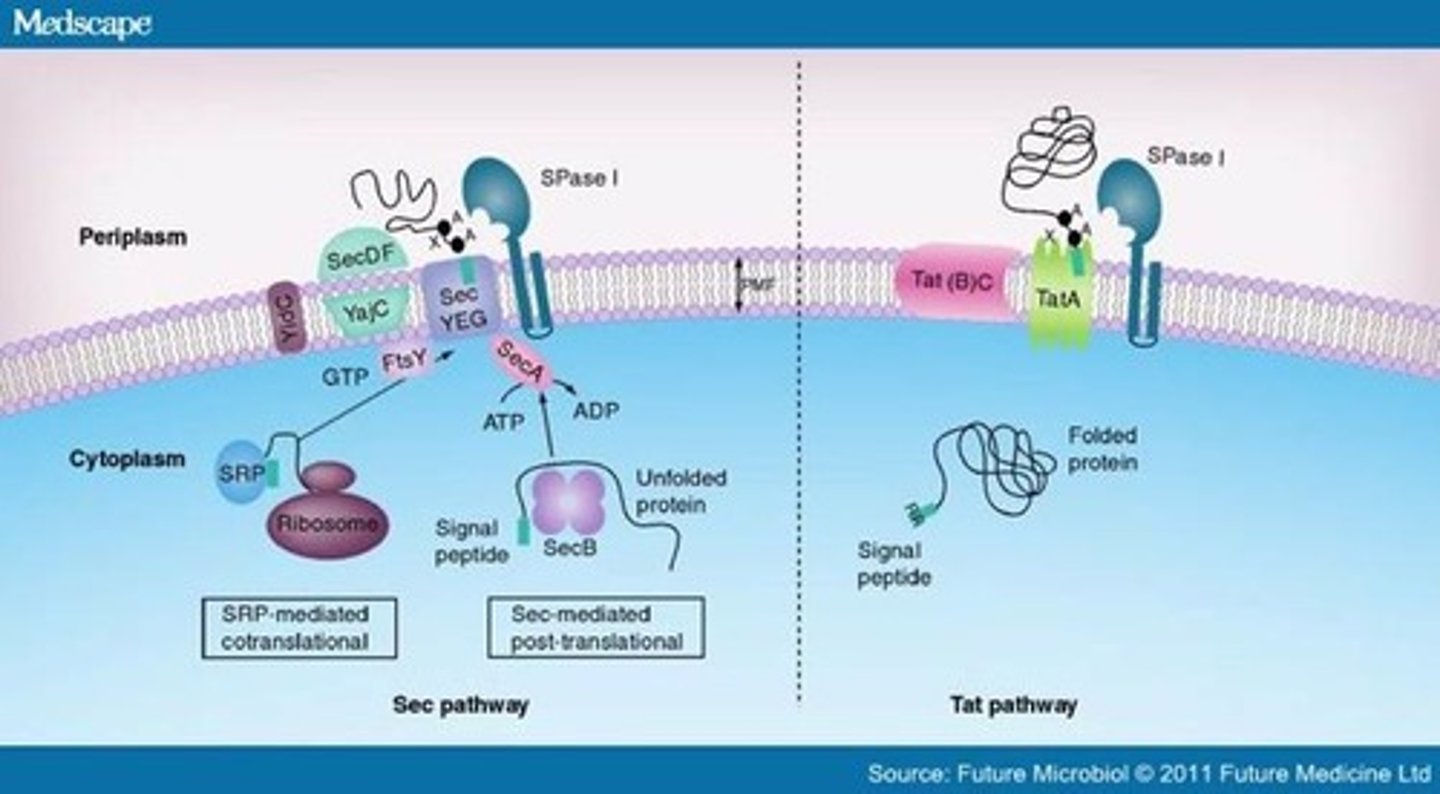
Translocation Systems
- Transports unfolded proteins across the membrane or into the membrane
- Sorted and targeted by signal peptide
- Signal Recognition Particle
Secretion (Sec) System
- Unfolded proteins to cytoplasmic membrane or periplasmic space
- SecA protein recognizes less hydrophobic signal peptides
- SecY, SecE, SecG form a channel in the membrane
- SecA threads peptide through channel, acts as a motor
- SecB keeps the protein unfolded
- SecDF uses the proton motive force to help

Twin Arginine Translocase (Tat) System
- Two consecutive arginines in a signal peptide
- Secretes only folded proteins
- Protein Docking Complex recognizes signal and escorts protein to pore complex with PMF
Maturation Steps
- Signal peptide removed by signal peptidase
Secretion of Protein in Gram Negatives: 2-step Processes
- Must pass through cytoplasmic membrane, periplasmic space, and outer membrane
- Step 1: Tat or Sec system
- Step 2: Type II (Proteobacteria anchored in both membranes, joined by pseudopilus), V (barrel structure in outer membrane), and IX (bacteriodetes)
Secretion of Protein in Gram Negatives: 1-step Processes
- Type I: ABC membrane fusion, barrel structure
- Type III: Injectosomes
- Type IV: DNA transfer
- Type VI: contractile weapons
- Type VII: Mycobacterium