AP Microeconomics-Unit 2:Teacher MCQ-5
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
The table below lists the monthly individual demand schedules for text messages for the only three buyers in the market: Allison, Bill, and Chang. Which of the following combinations of price and quantity lies on the market demand curve?
(A)Price Quantity
4¢ 1,000
(B)Price Quantity
8¢ 350
(C)Price Quantity
12¢ 200
(D)Price Quantity
16¢ 270
(E)Price Quantity
20¢ 0
answer D
Toby's Toy Trains produces train sets in a monopolistically competitive market. If Toby increases the price of a train set by 5 percent, causing a 10 percent decrease in the quantity demanded of train sets, which of the following will occur?
(A) Toby's total revenue will increase.
(B) Toby's total revenue will decrease.
(C) Toby's total revenue will remain the same.
(D) The demand for Toby's train sets will increase.
(E) The demand for Toby's train sets will decrease.
answer B
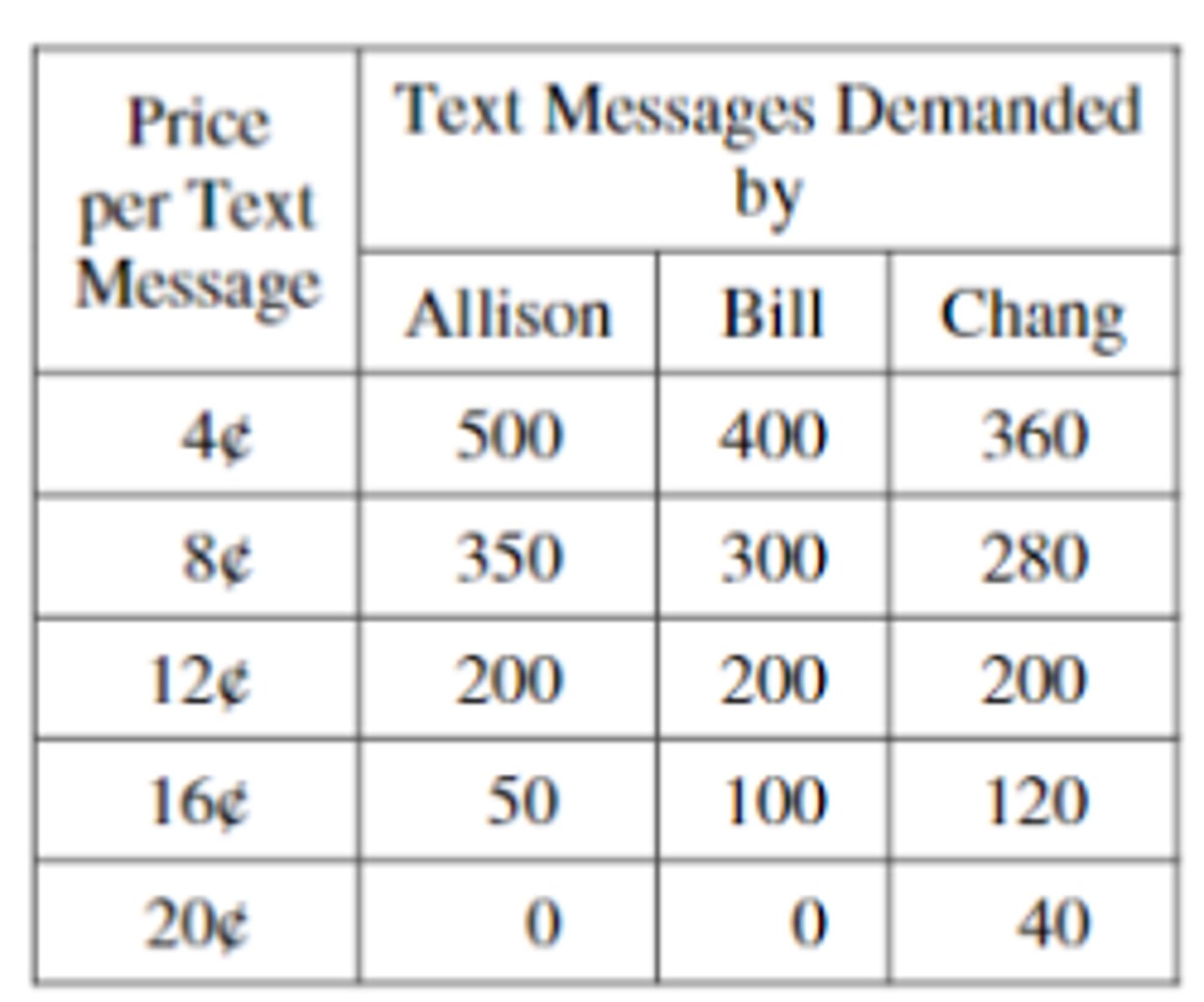
Apples are produced in a perfectly competitive market with no government intervention. Which of the following price changes will cause the total economic surplus to increase for the apple market depicted in the graph provided?
(A) A decrease in price from $8 to $6
(B) A decrease in price from $6 to $4
(C) A decrease in price from $6 to $0
(D) An increase in price from $6 to $8
(E) An increase in price from $8 to $12
answer A
If the price elasticity of supply for pickles is 2 and the price of pickles increases by 10 percent, then the quantity supplied of pickles will increase by
(A)0.2%
(B)5%
(C)8%
(D)12%
(E)20%
answer E
If a 10 percent increase in the price of good X results in a 20 percent decrease in the quantity of good Y demanded, which of the following is true?
(A) Good X and good Y are complementary goods, and the cross-price elasticity is -0.5.
(B) Good X and good Y are substitute goods, and the income elasticity is +2.
(C) Good X and good Y are complementary goods, and the cross-price elasticity is -2.
(D) Good X and good Y are normal goods, and the income elasticity is +2.
(E) Good X and good Y are substitute goods, and the cross-price elasticity is -2.
answer C
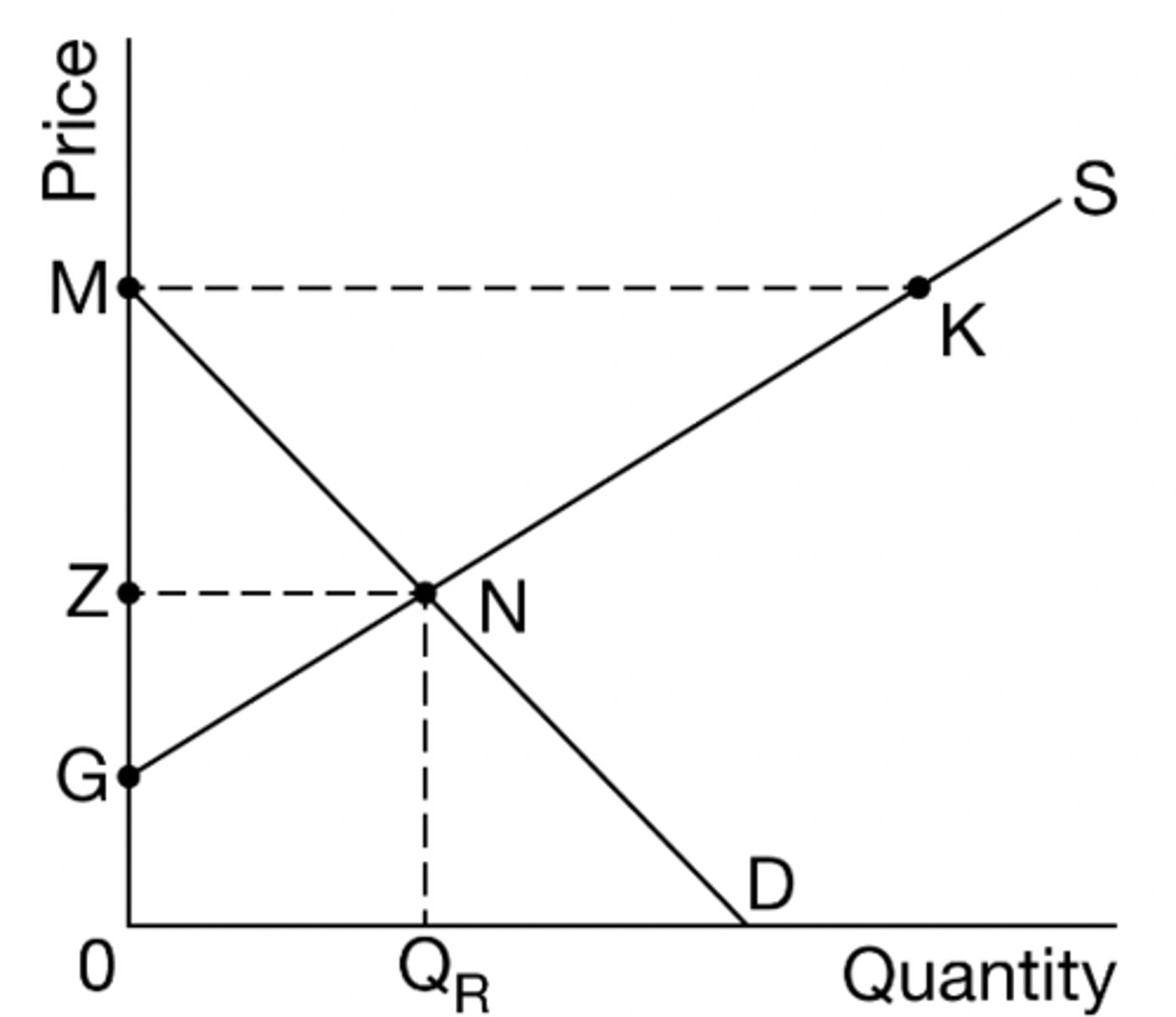
Based on the graph above, the consumer surplus at the market equilibrium price and quantity is shown by which area?
(A)GMK
(B)GMN
(C)GZN
(D)ZMN
(E)MNK
answer D
The economic concept of total consumer surplus refers to which of the following?
(A) The difference between the quantity of a good or service that people purchase and the amount that they actually consume
(B) The overproduction of goods and services relative to the socially optimal level of output
(C) The sum of the differences between the prices that consumers are willing to pay for a good or service and the price they actually pay
(D) The sum of the differences between the prices that consumers are willing to pay for a good or service and the minimum prices that sellers must receive to offer that quantity
(E) The difference between the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of a product at a given price
answer C
Consumer surplus exists because of the
(A) surplus of money that wealthy consumers hold
(B) surplus in marginal product that firms get when they hire an additional worker
(C) willingness of some consumers to pay a price higher than the market price for some units of a good
(D) additional utility that households obtain when the prices of substitutes fall
(E) increase in the availability of goods when income rises
answer C
Consumer surplus could be the shaded area in which of the following situations?
(A) A price floor set at P1 in the market
(B) A price floor set at P2 in the market
(C) A price ceiling set at P1 in the market
(D) A per-unit subsidy equal to P2-P1 granted to producers
(E) A per-unit tax equal to P2-P1 imposed on producers
answer C
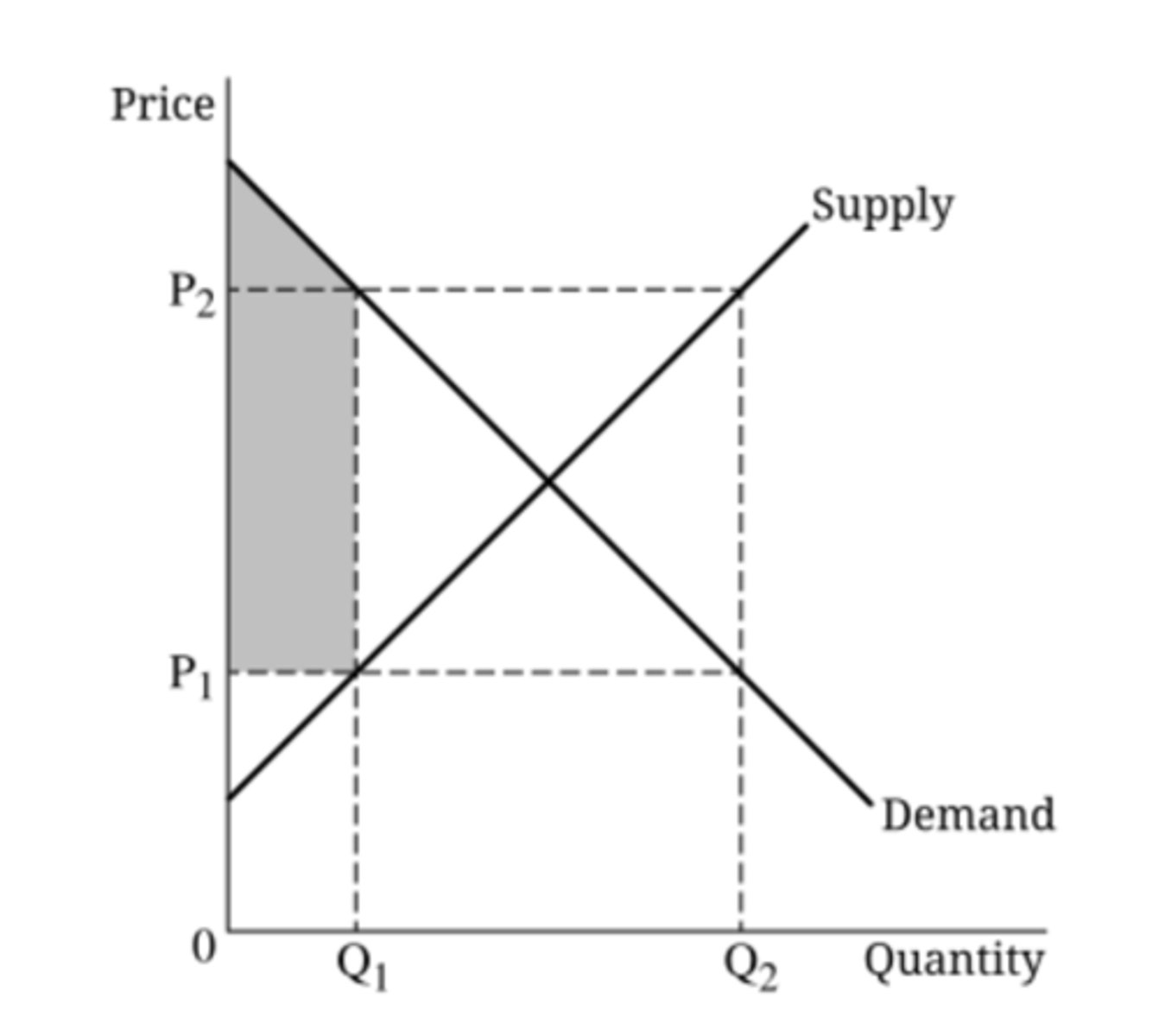
Consumer surplus in a market for a good exists because
(A) binding price floors encourage producers to increase the supply of the good
(B) some consumers would be willing to pay more than the equilibrium price of the good
(C) when the price of the good decreases, most consumers increase their demand for the good
(D) producers do not have market power to set their own price
(E) some producers charge different prices for the good in different markets
answer B
Consumer surplus is defined as
(A) opportunity cost minus total revenue
(B) total revenue minus opportunity cost
(C) the difference between the resource costs and the price that consumers pay
(D) the difference between the value that consumers place on a good and the price they pay
(E) the sum of external costs and benefits
answer D
The difference between the price a consumer would be willing to pay for a cone of ice cream and the actual market price that she pays gives a measure of her
(A) consumer surplus
(B) producer surplus
(C) marginal utility
(D) marginal cost
(E) ability to pay
answer A
The following questions refer to the graph below. The market is currently in equilibrium
In a competition equilibrium consumer surplus is the area of
(A) UVZ
(B) WYZ
(C) RVUT
(D) XVZY
(E) 0YZS
answer B
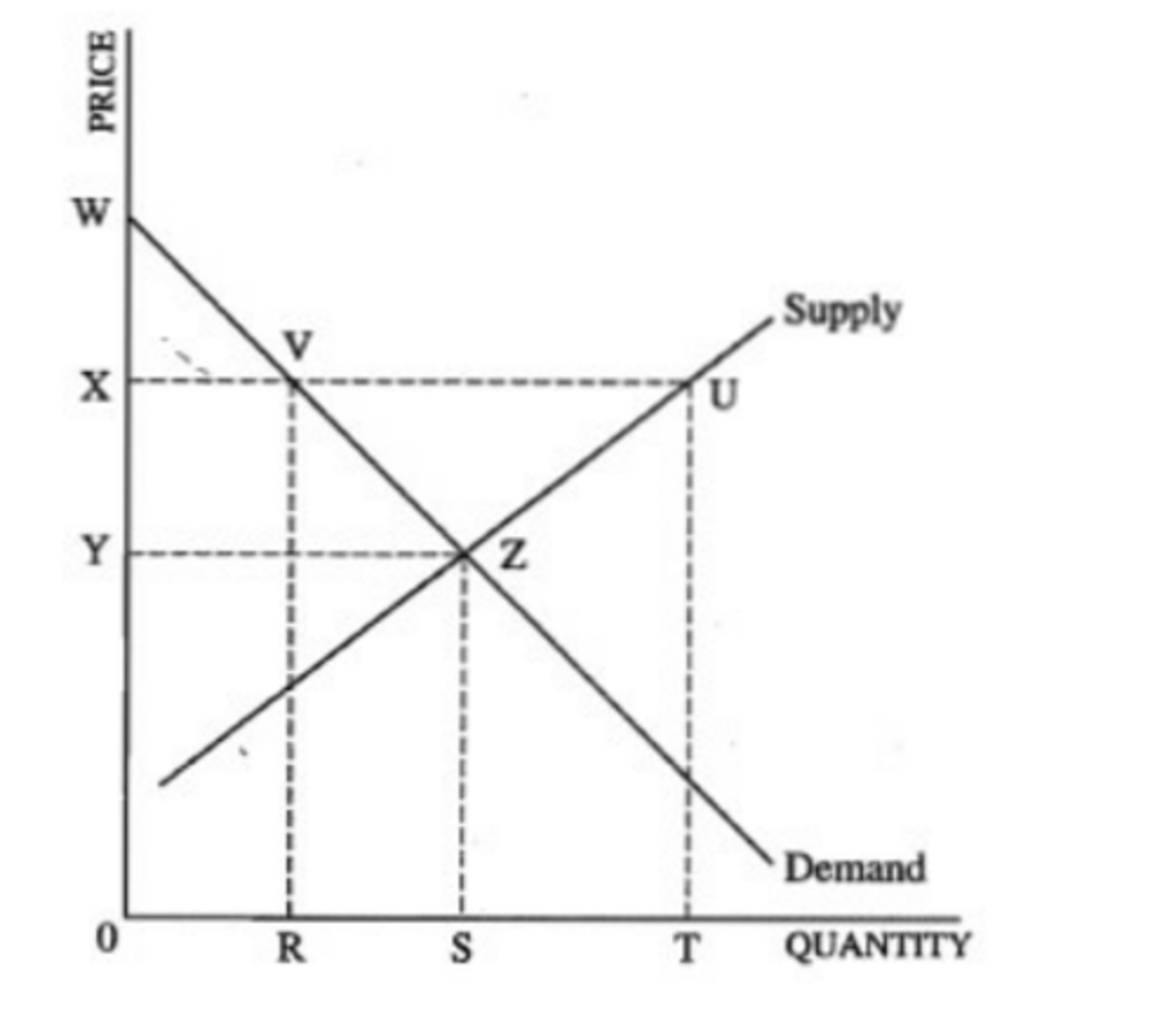
If a price floor is set at X, the quantity demanded will
(A) increase from 0R to 0S
(B) increase from 0R to 0T
(C) decrease from 0S to 0R
(D) decrease from 0T to 0R
(E) not change
answer C

The cross-price elasticity of demand between goods J and K is -3. A 20 percent decrease in the price of good K will result in a
(A) 3 percent decrease in the quantity demanded of good K
(B) 15 percent decrease in the quantity demanded of good K
(C) 6 percent increase in the quantity demanded of good J
(D) 12 percent increase in the quantity demanded of good J
(E) 60 percent increase in the quantity demanded of good J
answer E
Assume that a 2 percent increase in the price of bologna causes a 5 percent decrease in the demand for cheese. What
is the cross-price elasticity of demand between the two goods, and how are these goods related?
(A) Cross-price elasticity of demand equals -0.4, and these goods are complements.
(B) Cross-price elasticity of demand equals +0.4, and these goods are substitutes.
(C) Cross-price elasticity of demand equals -2.5, and these goods are complements.
(D) Cross-price elasticity of demand equals +2.5, and these goods are substitutes.
(E) Cross-price elasticity of demand equals -0.4, and these goods are substitutes.
answer C
The cross-price elasticity of demand for Goods X and Y is -2.8. Based on this information, what is true about Good X and Good Y?
(A) Good X is a normal good and Good Y is an inferior good.
(B) The goods are inferior.
(C) The goods are substitutes.
(D) The goods are complements.
(E) The goods have upward-sloping demand curves.
answer D
Which of the following is true of the cross-price elasticity of demand?
(A) It can indicate if a good is a necessity or a luxury.
(B) It is greater than zero for two goods that are substitutes.
(C) It is close to zero if the two goods are closely related.
(D) It is always negative because demand curves are downward sloping.
(E) It increases as income increases.
answer B
In relation to tacos, the cross-price elasticity of demand for Good X is negative. What would be the result if the price of tacos increases?
(A) There will be a movement up the demand curve for Good X because it is a complement to tacos.
(B) There will be a movement down the demand curve for Good X because it is a complement to tacos.
(C) The demand for Good X will increase because it is a substitute for tacos.
(D) The demand for Good X will decrease because it is a complement to tacos.
(E) The demand for Good X will increase because tacos and Good X are normal goods.
answer D
To determine whether two goods are complements, one would calculate the
(A) price elasticity of demand
(B) price elasticity of supply
(C) income elasticity of demand
(D) cross-price elasticity of demand
(E) input-price elasticity of supply
answer D
Zucchini is produced in a perfectly competitive market with a downward-sloping demand curve and an upwardsloping supply curve. Dawson Farm is a typical perfectly competitive farm that produces and sells zucchini at the equilibrium price of $1.75 per pound. Which of the following is true?
(A) No buyer in the market is willing to pay more than $1.75 per pound for zucchini.
(B) No buyer in the market is willing to pay more than $1.75 per pound for zucchini from Dawson Farm.
(C) Market demand for zucchini will increase if Dawson Farm lowers its price below $1.75 per pound.
(D) Dawson Farm would lose some but not all of its customers if it increases the price above$1.75 per pound for zucchini.
(E) Dawson Farm would likely be able to increase the demand for its zucchini by advertising.
answer B