Sex Determination & Gametogenesis in Mammals: Processes and Hormonal Regulation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is the mechanism for balancing gene dose in females?
X-chromosome inactivation, where one X chromosome is randomly inactivated early in development.
What is the role of long ncRNAs in X-chromosome inactivation?
They involve the recruitment of proteins to silence transcription of the inactive X chromosome.
What syndrome is associated with a mutation in the androgen receptor?
Androgen insensitivity syndrome, where XY individuals cannot respond to testosterone but can respond to estrogen.
What is the outcome of androgen insensitivity syndrome in XY individuals?
They have testes and testosterone but appear female and lack a uterus and oviducts.
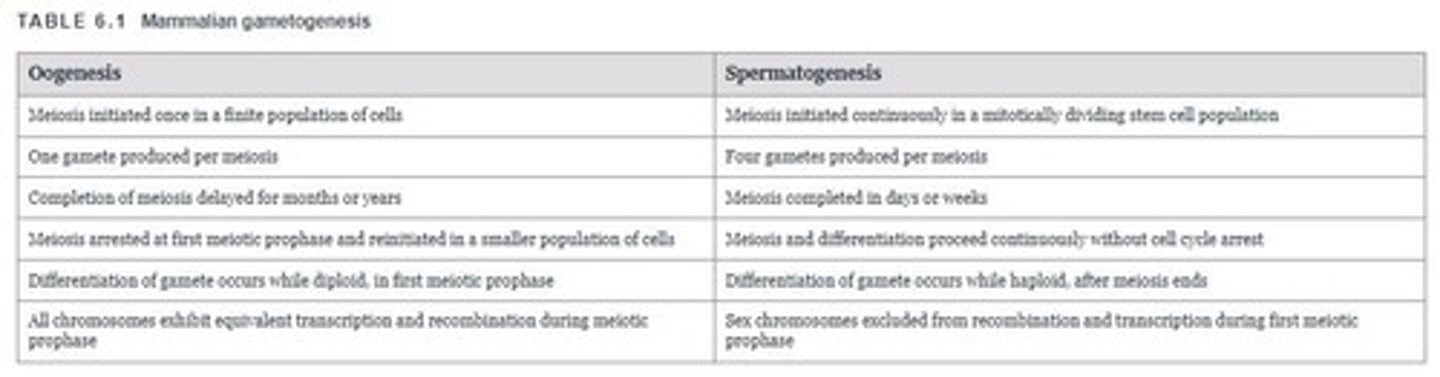
What is the significance of spermatogenesis in gametogenesis?
It is the process of sperm cell development in males.
What is the timing of oogenesis in gametogenesis?
It refers to the process of egg cell development in females, which occurs with specific timing during the reproductive cycle.
What are the key components of sex determination in mammals?
Chromosomal sex determination, gonadal sex determination, and hormonal regulation of the sexual phenotype.
What are PGCs in mammals?
Primordial germ cells that migrate from the genital ridge to the developing gonads.
What process intertwines with meiosis in the life cycle of animals?
Gametogenesis, which includes both spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
What is the primary focus of the lecture on sex determination and gametogenesis?
To describe how sex is determined and to diagram the processes of spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
What is the difference between primary and secondary sex determination?
Primary sex determination is based on chromosomal and gonadal factors, while secondary sex determination is influenced by hormonal regulation.
What is the mammalian pattern of sex determination?
It involves the presence of XX or XY chromosomes, leading to the development of female or male phenotypes, respectively.
What is the role of hormones in secondary sex determination?
Hormones such as AMH and steroids regulate the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
How does X-chromosome inactivation affect mRNA levels in males and females?
It ensures that females and males have similar mRNA levels from X chromosome genes despite females having two X chromosomes.