A&PII Exam 2
1/275
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
276 Terms
The lymphatic system
a series of vessels that directs lymphatic fluid one way, up to the heart, to put the fluid back into circulation
The lymphatic system takes
extra interstitial fluid (fluid between tissues) and brings it back to the heart to enter back into blood circulation
The lymphatic system also has
valves
The lymphatic system picks up
Lymph from the tissues
85% of fluid from capillaries goes back into
blood circulation
15% of fluid stays in
interstitial fluid which enters into lymphatic system
Roles of the lymphatic system
maintain fluid levels in the body, absorb fat from the digestive tract, protects the body from foreign invaders (bacteria, viruses, etc), transports and removes waste products and abnormal cells
Lymph (lymphatic fluid)
fluid in the lymphatic system, made of interstitial fluid plus other components
Lymphatic vessels
network of vessels that moves lymphatic fluid back towards heart
Collecting ducts
area where lymph is dumped to enter back into circulation
Primary lymphatic organs
bone marrow and thymus
Bone marrow
where WBCs, RBCs, and platelets are produced
Thymus
where T lymphocytes are trained and mature
Secondary lymphatic organs
Lymph nodes and spleen
Lymph nodes
monitor and filter lymph, contain many lymphocytes
Spleen
Largest lymphatic organ, filters blood, produces WBCs
Lymph nodes are connected by
lymph vessels
Other lymphoid tissue line
organs to create a layer of protection
Other lymphoid tissue
tonsils and adenoids, Peyer’s patches (line small intestine), and appendix
Lymphatic drainage
Right lymphatic duct
Thoracic duct
Right lymphatic duct empties into
right subclavian vein, uses skeletal and respiratory pump
Thoracic duct
empties into left subclavian vein
Palatine tonsil
Visible tonsil
Pharyngeal tonsil
adenoids when enlarged
Lymph nodes are
Natural Killer cells when mature
Spleen contains large number of
macrophages that eat worn out RBCs, stores platelets, produces of blood cells during fetal life
The immune system
the defense system of the body, against pathogens
Pathogens
Foreign substances or antigens
The immune system must be able to distinguish between
self and non-self proteins
Most body cells have surface proteins called
major histocompatibility complexes (MHC)
Innate immunity
“inborn” present from birth, non-specific, rapid response
Innate immunity includes the
skin, mucous membrane, natural killer cells, phagocytes (neutrophils and macrophages), mast cells, dendritic cells
Adaptive immunity
acquired or programmed immunity, specific immunity
Adaptive immunity contains
B cells, T cells, memory cells, Dendritic cells, macrophages, and NK cells
Innate immune system deals with
inflammation, fever, and antimicrobial proteins
Adaptive immune system deals with
antibody production, antibody/antigen interaction, antibody mediated immunity- B cells, and cell-mediated immunity- T cells
First line of defense in innate immunity
Skin and Mucous membranes
Skin
Keratinocytes, a natural physical barrier
Skin is continuously
remaking and sloughing off
Sweat glands
produce sweat, provides skin surface with acidic pH to prevent bacterial growth
Dendritic cells (Langerhans cells)
First line of defense if something breaches the cell
Mucous membranes are in the
respiratory tract, nasal passages, and gastrointestinal tract
Mucous can trap
particles
Tiny hairs “cilia”
pushes mucous to different areas
Urine is
acidic
Urine keeps
bacterial growth low
Stomach
acidic gastric juices
Eyes
tears
Mouth
Saliva
Second line of defense
internal defense (NKCs)
Natural Killer Cells are found in
spleen, lymph nodes, and red bone marrow
Natural killer cells can attack
body cells that display abnormal or unusual plasma membrane proteins and release toxic granules
Monocytes can differentiate into
macrophages or dendritic cells
Monocytes are concentrated in
lymphoid organs and in body regions in direct contact with the environment
Phagocytes
ingest things (neutrophils and macrophages)
Phagocytes can be
wandering or fixed
Chemotaxis
chemical attraction of phagocytes to a site of damage
Adherence
Attachment of phagocytes to the microbe or other foreign material
Ingestion
Engulfing of the microbe
Digestion
joins with lysosome and forms phagolysosome
Phagocytosis steps
Chemotaxis, Adherence, Ingestion, Digestion, and Killing
Inflammation
innate response to tissue damage
Four characteristics of inflammation
redness, heat, swelling, and pain
Inflammation is an
attempt to dispose of foreign material from entering the body
Inflammation steps
Vasodilation and increased permeability of local blood vessels (WBCs and platelets release histamine)
Emigration of phagocytes
Chemotaxis and microbial attack
Histamine increase
blood vessel permeability “leaky”
Prostaglandins released to
intensify effects of histamines and stimulates more emigration of phagocytes
Leukotriens released to increase
capillary permeability and attracts more phagocytes
Fever
elevation of temperature either locally or systemically (elevated temp, elevates metabolism, elevated efficiency of cells, specifically immune cells) and inhibits growth of microbes
Antimicrobial proteins
Discourage microbial growth
Antimicrobial proteins are found in
various fluids of the body
interferons are produced by
cells of the body that have been infected with virus to interfere with the viral replication in healthy cells
Intereferons are found in the
blood plasma
Interferons are
normally inactive but when activated, complement or enhance certain immune reactions
Adaptive immunity is specific because
response is aimed at a particular non-self antigen
Antigens
substances that are recognized as foreign and produces an immune response
Basic training
Recognize the difference between self and non-self antigens
Self tolerance
ability of the cells to learn to recognize self antigens and avoid attacking them
Autoimmune disease
caused by a loss of self tolerance
Cell mediated immunity
cytotoxic T cells attack cells displaying foreign antigens
Antibody-mediated immunity
B cells recognize antigens, become activated into plasma cells and make antibodies
Memory cells
process takes a while but second response is much quicker
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
Bind self and non-self proteins and display on cell surface
MHC I
Display antigens that are internally produced endogenous antigens
MHC I are found on the surface of
all body cells except RBCs because they don’t have a nucleus
MHC II can display as
MHC I or MHC II
MHC II is found in
immune cells capable of phagocytosis
Antigen Presenting Cells
when cells are capable of phagocytosis, the proteins they bring in are exogenous (from outside the cell)
Cell-mediated immunity
starts with a cell with MHC I displaying non-self protein
Cytotoxic T cells recognizes the non-self proteins an attaches to the cell
Cytotoxic T cells is now activated and divides to produce clones (divides into T cells and memory cytotoxic T cells)
Activated cytotoxic T cells attach MHC I cells which causes cells to undergo apoptosis (cell death)
Antibody mediated immunity is either activated by
free floating antigen or T helper cell
Antibody mediated immunity activated by free floating antigen
B cell has B cell receptors that contacts free floating antigen binds and activates B cell
B cell goes through clonal expansion (makes memory B cells and activated B cells)
Activated B cells start pumping out antibodies which is the exact same as the receptor
Binds and stops antigens or flags other cells to kill antigen
MHC II activates
T cells
Activated T helper cell goes to
bind a B cell to activate it or cytotoxic T cell
Antigens provoke
an immune response through stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies (viruses, bacteria)
Antibodies
proteins that can help immune cells destroy antigens
Antibodies are
immunoglobins
Antibodies are composed of
heavy and light chains
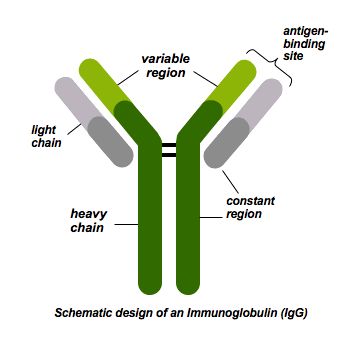
Constant region of antibodies
The majority, the same in all antibodies, part that is interested into the cell
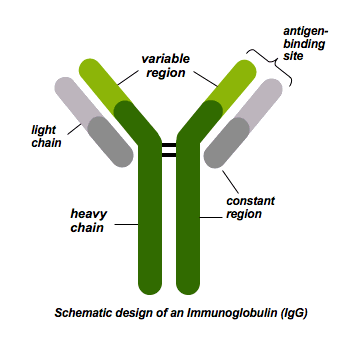
Variable region of antibodies
Varies, antigen binding area
Antigen/Antibody interaction
stops the antigen from infecting other cells